2024 United States presidential election in South Carolina
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 76.76% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in South Carolina |
|---|
 |
The 2024 United States presidential election in South Carolina took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia will participate. South Carolina voters will choose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of South Carolina has nine electoral votes in the Electoral College.[1]
A Southern state in the heart of the Bible Belt, no Democrat has won South Carolina's electoral votes since Jimmy Carter of neighboring Georgia, in 1976, nor has it been contested at the presidential level since 2008, when Barack Obama lost the state by 9 points.
Incumbent Democratic President Joe Biden initially ran for re-election and became the party's presumptive nominee.[2] However, following what was widely viewed as a poor performance in the June 2024 presidential debate and amid increasing age and health concerns from within his party, he withdrew from the race on July 21 and endorsed Vice President Kamala Harris, who launched her presidential campaign the same day. Biden's withdrawal from the race makes him the first eligible president not to stand for re-election since Lyndon B. Johnson in 1968.
Former President and Republican nominee Donald Trump ran for re-election to a second non-consecutive term after losing in 2020.[3] Independent candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. gathered the required signatures to be on the ballot. Despite that, he dropped out of the race and endorsed Trump.[4]
South Carolina voted for Trump by a comfortable margin in the election, with him winning the state by 17.9%.[5] Trump received more than 1.48 million votes which was a record for votes cast for any candidate in the history of South Carolina. This was the largest Republican win in the state since 1988.
Trump was able to increase his support and gain ground in every county. Trump flipped Jasper County into the Republican column for the first time in a presidential race since Richard Nixon in 1972.
Primary elections
[edit]Democratic primary
[edit]On February 4, 2023, the Democratic National Committee approved a new 2024 primary calendar, moving South Carolina to hold its race first on February 3, 2024.[6] Due to protests to the change, the New Hampshire primary was scheduled for January 23, maintaining its traditional "first-in-the-nation" status. However, the primary was deemed non-binding, so the South Carolina primary was the first contest in which candidates could earn delegates.[7] President Biden won the primary in a landslide, winning all 55 of the state's unbound delegates.[8] The Democratic primary recorded low voter turnout among registered voters, with only 4% participating.[9]
The South Carolina Democratic primary was held on February 3, 2024.

- >90%
| Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Actual delegate count | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pledged | Unpledged | Total | |||
| Joe Biden (incumbent) | 126,493 | 96.2% | 55 | TBD | 55 |
| Marianne Williamson | 2,732 | 2.1% | 0 | TBD | 0 |
| Dean Phillips | 2,247 | 1.7% | 0 | 0 | |
| Total: | 131,472 | 100% | 55 | 10 | 65 |
Republican primary
[edit]The South Carolina Republican primary was held on February 24, 2024, the fifth contest in the nationwide Republican primaries. Nikki Haley, who served as the governor of South Carolina from 2011 to 2017, lost her home state to former president Donald Trump by 20 points. Trump won six congressional districts, earning a total of 47 delegates. Haley won the 1st district, earning three delegates. The Republican primary recorded a voter turnout of 23% among its registered voters, passing its 2016 turnout record.[11]
- 50–60%
- 60–70%
- 70–80%
- 80–90%
- 50–60%
- 60–70%
| Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Actual delegate count | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bound | Unbound | Total | |||
| Donald Trump | 452,496 | 59.79% | 47 | 47 | |
| Nikki Haley | 299,084 | 39.52% | 3 | 3 | |
| Ron DeSantis (withdrawn) | 2,953 | 0.39% | |||
| Vivek Ramaswamy (withdrawn) | 726 | 0.10% | |||
| Chris Christie (withdrawn) | 658 | 0.09% | |||
| Ryan Binkley | 528 | 0.07% | |||
| David Stuckenberg | 361 | 0.05% | |||
| Total: | 756,806 | 100.00% | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| Source: [13] | |||||
General election
[edit]Predictions
[edit]| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| Cook Political Report[14] | Solid R | December 19, 2023 |
| Inside Elections[15] | Solid R | April 26, 2023 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[16] | Safe R | June 29, 2023 |
| Decision Desk HQ/The Hill[17] | Safe R | December 14, 2023 |
| CNalysis[18] | Solid R | December 30, 2023 |
| CNN[19] | Solid R | January 14, 2024 |
| The Economist[20] | Safe R | October 16, 2024 |
| 538[21] | Solid R | October 21, 2024 |
| RCP[22] | Likely R | June 26, 2024 |
| NBC News[23] | Safe R | October 6, 2024 |
Polling
[edit]Donald Trump vs. Kamala Harris
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Donald Trump Republican |
Kamala Harris Democratic |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ActiVote[24] | October 5–29, 2024 | 400 (LV) | ± 4.9% | 58.5% | 41.5% | – |
| ActiVote[25] | September 9 – October 17, 2024 | 400 (LV) | ± 4.9% | 58% | 42% | – |
| Winthrop University[26] | September 21–29, 2024 | 1,068 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 52% | 42% | 6%[b] |
Donald Trump vs. Kamala Harris vs. Cornel West vs. Jill Stein vs. Chase Oliver
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Donald Trump Republican |
Kamala Harris Democratic |
Cornel West Independent |
Jill Stein Green |
Chase Oliver Libertarian |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Citadel[27] | October 17–25, 2024 | 1,241 (RV) | ± 3.6% | 53% | 41% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 6% |
| 1,136 (LV) | 54% | 42% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 4% | |||
| East Carolina University[28] | October 18–22, 2024 | 950 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 55% | 42% | – | – | 1% | 2% |
Donald Trump vs. Joe Biden
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Donald Trump Republican |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Zogby Strategies[29][A] | April 13–21, 2024 | 501 (LV) | – | 52% | 40% | 8% |
| Emerson College[30] | February 14–16, 2024 | 1,197 (RV) | ± 3.0% | 51% | 37% | 12% |
| The Citadel[31] | February 5–11, 2024 | 1,000 (RV) | ± 4.1% | 54% | 35% | 11% |
| Winthrop University[32] | February 2–10, 2024 | 1,717 (RV) | ± 2.4% | 50% | 35% | 15% |
| Mainstreet Research/Florida Atlantic University[33] | February 1–8, 2024 | 679 (RV) | ± 3.8% | 52% | 34% | 14% |
| 643 (LV) | 54% | 36% | 10% | |||
| Echelon Insights[34] | August 31 – September 7, 2022 | 600 (LV) | ± 5.1% | 51% | 39% | 10% |
| Blueprint Polling (D)[35] | August 24–25, 2022 | 721 (LV) | ± 3.7% | 46% | 34% | 20% |
Donald Trump vs. Joe Biden vs. Robert F. Kennedy Jr. vs. Jill Stein vs. Joe Manchin
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Donald Trump Republican |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. Independent |
Jill Stein Green |
Joe Manchin Independent |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Citadel[31] | February 5–11, 2024 | 1,000 (RV) | ± 4.1% | 49% | 32% | 9% | 3% | 4% | 3% |
Nikki Haley vs. Joe Biden
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Nikki Haley Republican |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Citadel[31] | February 5–11, 2024 | 1,000 (RV) | ± 4.1% | 50% | 28% | 22% |
| Winthrop University[32] | February 2–10, 2024 | 1,717 (RV) | ± 2.4% | 47% | 29% | 24% |
Nikki Haley vs. Joe Biden vs. Robert F. Kennedy Jr. vs. Jill Stein vs. Joe Manchin
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Nikki Haley Republican |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. Independent |
Jill Stein Green |
Joe Manchin Independent |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Citadel[31] | February 5–11, 2024 | 1,000 (RV) | ± 4.1% | 41% | 25% | 20% | 3% | 4% | 7% |
Donald Trump vs. Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Donald Trump Republican |
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. Independent |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Zogby Strategies[29][A] | April 13–21, 2024 | 501 (LV) | – | 47% | 40% | 13% |
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. vs. Joe Biden
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. Independent |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| John Zogby Strategies[29][A] | April 13–21, 2024 | 501 (LV) | – | 50% | 35% | 15% |
Ron DeSantis vs. Joe Biden
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Ron DeSantis Republican |
Joe Biden Democratic |
Other / Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echelon Insights[34] | August 31 – September 7, 2022 | 600 (LV) | ± 5.1% | 42% | 42% | 16% |
Ballot changes after the primaries
[edit]On July 21, 2024, Joe Biden announced his withdrawal from the Presidential race and endorsed Kamala Harris.[36][37] Harris and running mate Tim Walz replaced Biden on the South Carolina ballot.
On August 23, 2024, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., suspended his presidential campaign and endorsed Donald Trump.[38][39] The Alliance Party of South Carolina removed Kennedy's name from the ballot, fielding no presidential candidate on their ticket for the year.[40]
South Carolina political parties had until September 3 to make final changes and certify their presidential and vice presidential candidates for the state ballot.[41]
Results
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | 1,483,747 | 58.23% | +3.12% | ||
| Democratic | 1,028,452 | 40.36% | −3.07% | ||
| Libertarian | 12,669 | 0.50% | −0.61% | ||
| Green | 8,117 | 0.32% | +0.05% | ||
| Constitution | 5,352 | 0.21% | |||
| South Carolina Workers Party | 3,059 | 0.12% | |||
| United Citizens | 6,744 | 0.26% | |||
| Write-in | |||||
| Total votes | 2,548,140 | 100% | |||
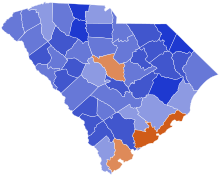
By county
[edit]| County | Donald Trump Republican |
Kamala Harris Democratic |
Various candidates Other parties |
Margin | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Abbeville | 8,509 | 70.63% | 3,399 | 28.21% | 140 | 1.16% | 5,110 | 42.42% | 12,048 |
| Aiken | 53,592 | 62.25% | 31,298 | 36.35% | 1,201 | 1.40% | 22,294 | 25.90% | 86,091 |
| Allendale | 813 | 26.89% | 2,165 | 71.62% | 45 | 1.49% | -1,352 | -44.73% | 3,023 |
| Anderson | 71,828 | 73.07% | 25,281 | 25.72% | 1,187 | 1.21% | 46,547 | 47.35% | 98,296 |
| Bamberg | 2,376 | 41.73% | 3,245 | 56.99% | 73 | 1.28% | -869 | -15.26% | 5,694 |
| Barnwell | 5,605 | 57.18% | 4,082 | 41.64% | 116 | 1.18% | 1,523 | 15.54% | 9,803 |
| Beaufort | 59,123 | 56.63% | 44,002 | 42.15% | 1,278 | 1.22% | 15,121 | 14.48% | 104,403 |
| Berkeley | 64,777 | 57.41% | 46,416 | 41.14% | 1,641 | 1.45% | 18,361 | 16.27% | 112,834 |
| Calhoun | 4,474 | 56.53% | 3,339 | 42.19% | 101 | 1.28% | 1,135 | 14.34% | 7,914 |
| Charleston | 99,265 | 46.27% | 111,427 | 51.94% | 3,829 | 1.79% | -12,162 | -5.67% | 214,521 |
| Cherokee | 18,697 | 75.27% | 5,939 | 23.91% | 203 | 0.82% | 12,758 | 51.36% | 24,839 |
| Chester | 9,030 | 58.05% | 6,353 | 40.84% | 173 | 1.11% | 2,677 | 17.21% | 15,556 |
| Chesterfield | 11,682 | 63.52% | 6,520 | 35.45% | 189 | 1.03% | 5,162 | 28.07% | 18,391 |
| Clarendon | 9,065 | 55.55% | 7,064 | 43.28% | 191 | 1.17% | 2,001 | 12.27% | 16,320 |
| Colleton | 10,696 | 58.52% | 7,376 | 40.36% | 204 | 1.12% | 3,320 | 18.16% | 18,276 |
| Darlington | 17,017 | 56.10% | 12,977 | 42.78% | 337 | 1.12% | 4,040 | 13.32% | 30,331 |
| Dillon | 6,526 | 55.02% | 5,241 | 44.19% | 94 | 0.79% | 1,285 | 10.83% | 11,861 |
| Dorchester | 43,839 | 56.37% | 32,489 | 41.78% | 1,436 | 1.85% | 11,350 | 14.59% | 77,764 |
| Edgefield | 9,092 | 65.32% | 4,659 | 33.47% | 168 | 1.21% | 4,433 | 31.85% | 13,919 |
| Fairfield | 4,792 | 42.73% | 6,277 | 55.97% | 146 | 1.30% | -1,485 | -13.24% | 11,215 |
| Florence | 32,615 | 53.34% | 27,706 | 45.32% | 819 | 1.34% | 4,909 | 8.02% | 61,140 |
| Georgetown | 22,326 | 59.14% | 14,965 | 39.64% | 463 | 1.22% | 7,361 | 19.50% | 37,754 |
| Greenville | 158,451 | 60.21% | 100,074 | 38.01% | 4,791 | 1.78% | 58,377 | 22.20% | 263,316 |
| Greenwood | 19,715 | 63.83% | 10,766 | 34.85% | 407 | 1.32% | 8,949 | 28.98% | 30,888 |
| Hampton | 3,801 | 46.17% | 4,328 | 52.57% | 104 | 1.26% | -527 | -6.40% | 8,233 |
| Horry | 141,719 | 68.81% | 62,325 | 30.26% | 1,910 | 0.93% | 79,394 | 38.55% | 205,954 |
| Jasper | 9,900 | 54.32% | 8,144 | 44.68% | 183 | 1.00% | 1,756 | 9.64% | 18,227 |
| Kershaw | 21,289 | 63.49% | 11,826 | 35.27% | 418 | 1.24% | 9,463 | 28.22% | 33,533 |
| Lancaster | 33,623 | 61.78% | 20,146 | 37.01% | 658 | 1.21% | 13,477 | 24.77% | 54,427 |
| Laurens | 21,110 | 69.87% | 8,769 | 29.02% | 334 | 1.11% | 12,341 | 40.85% | 30,213 |
| Lee | 3,078 | 38.11% | 4,505 | 55.78% | 493 | 6.11% | -1,427 | -17.67% | 8,076 |
| Lexington | 96,965 | 66.01% | 47,815 | 32.55% | 2,123 | 1.44% | 49,150 | 33.46% | 146,903 |
| Marion | 5,906 | 44.11% | 7,316 | 54.65% | 166 | 1.24% | -1,410 | -10.54% | 13,388 |
| Marlboro | 4,896 | 48.23% | 5,137 | 50.60% | 119 | 1.17% | -241 | -2.37% | 10,152 |
| McCormick | 3,565 | 57.94% | 2,513 | 40.84% | 75 | 1.22% | 1,052 | 17.10% | 6,153 |
| Newberry | 12,067 | 66.56% | 5,841 | 32.22% | 221 | 1.22% | 6,226 | 34.34% | 18,129 |
| Oconee | 31,772 | 75.18% | 9,987 | 23.63% | 505 | 1.19% | 21,785 | 51.55% | 42,264 |
| Orangeburg | 13,750 | 37.19% | 22,832 | 61.76% | 388 | 1.05% | -9,082 | -24.57% | 36,970 |
| Pickens | 45,728 | 75.64% | 13,891 | 22.98% | 832 | 1.38% | 31,837 | 52.66% | 60,451 |
| Richland | 58,019 | 31.81% | 121,110 | 66.39% | 3,282 | 1.51% | -63,091 | -38.31% | 182,411 |
| Saluda | 6,452 | 71.58% | 2,454 | 27.22% | 108 | 1.20% | 3,998 | 44.36% | 9,014 |
| Spartanburg | 103,032 | 66.22% | 50,710 | 32.59% | 1,855 | 1.19% | 52,232 | 33.63% | 155,597 |
| Sumter | 21,215 | 46.97% | 23,425 | 51.86% | 530 | 1.17% | -2,210 | -4.89% | 45,170 |
| Union | 8,102 | 65.93% | 4,084 | 33.23% | 103 | 0.84% | 4,018 | 32.70% | 12,289 |
| Williamsburg | 5,524 | 38.55% | 8,634 | 60.25% | 172 | 1.20% | -3,110 | -21.70% | 14,330 |
| York | 88,239 | 58.80% | 59,600 | 39.72% | 2,220 | 1.48% | 28,639 | 19.08% | 150,059 |
| Totals | 1,483,747 | 58.23% | 1,028,452 | 40.36% | 35,941 | 1.41% | 455,295 | 17.87% | 2,548,140 |
Counties that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]Jasper (largest municipality: Hardeeville)
By congressional district
[edit]Trump won 6 of 7 congressional districts.[43]
| District | Trump | Biden | Representative |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 56% | 43% | Nancy Mace |
| 2nd | 56% | 42% | Joe Wilson |
| 3rd | 71% | 28% | Jeff Duncan |
| 4th | 61% | 37% | William Timmons |
| 5th | 61% | 38% | Ralph Norman |
| 6th | 38% | 61% | Jim Clyburn |
| 7th | 63% | 36% | Tom Rice |
See also
[edit]- United States presidential elections in South Carolina
- 2024 United States presidential election
- 2024 Democratic Party presidential primaries
- 2024 Republican Party presidential primaries
- 2024 South Carolina elections
- 2024 United States elections
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c Poll conducted for Kennedy's campaign
References
[edit]- ^ Wang, Hansi; Jin, Connie; Levitt, Zach (April 26, 2021). "Here's How The 1st 2020 Census Results Changed Electoral College, House Seats". NPR. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ Kinery, Emma (April 25, 2023). "Biden launches 2024 reelection campaign, promising to fulfill economic policy vision". CNBC. Retrieved November 19, 2024.
- ^ Stracqualursi, Gabby Orr,Kristen Holmes,Veronica (November 16, 2022). "Former President Donald Trump announces a White House bid for 2024 | CNN Politics". CNN. Retrieved November 19, 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "RFK Ballot South Carolina".
- ^ "South Carolina Presidential Election Results". The New York Times. November 5, 2024. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 19, 2024.
- ^ Vakil, Caroline (February 4, 2023). "DNC approves adjusted early presidential primary schedule". The Hill. Retrieved March 13, 2023.
- ^ Kashinsky, Lisa (October 30, 2023). "Democrats launch write-in campaign for Biden in N.H." Politico. Retrieved October 30, 2023.
- ^ Nicholas, Peter (February 3, 2024). "Biden wins South Carolina primary, NBC News projects". NBC News. Retrieved February 5, 2024.
- ^ Hubbard, Kaia (February 4, 2024). "South Carolina Democratic primary turnout for 2024 and how it compares to previous years – CBS News". www.cbsnews.com. Retrieved February 7, 2024.
- ^ "South Carolina Democratic Primary Results". New York Times. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ "Here's what voter turnout looked like for South Carolina's primary elections". South Carolina Public Radio. February 27, 2024. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ "Rhode Island Presidential Primary". The AP. April 16, 2024. Retrieved April 18, 2024.
- ^ "10 Republicans will be on SC's presidential primary — but not Asa Hutchinson". The Post and Courier. Retrieved December 6, 2023.
- ^ "2024 CPR Electoral College Ratings". cookpolitical.com. Cook Political Report. December 19, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2024.
- ^ "Presidential Ratings". insideelections.com. Inside Elections. April 26, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2024.
- ^ "2024 Electoral College ratings". centerforpolitics.org. University of Virginia Center for Politics. June 29, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2024.
- ^ "2024 presidential predictions". elections2024.thehill.com/. The Hill. December 14, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2024.
- ^ "2024 Presidential Forecast". projects.cnalysis.com/. CNalysis. December 30, 2023. Retrieved January 11, 2024.
- ^ "Electoral College map 2024: Road to 270". CNN. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ "Trump v Biden: The Economist's presidential election prediction model". The Economist. Retrieved October 17, 2024.
- ^ Morris, G. Elliott (June 11, 2024). "2024 Election Forecast". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved October 24, 2024.
- ^ "2024 RCP Electoral College Map". RealClearPolitics. June 26, 2024. Retrieved June 26, 2024.
- ^ "Presidential Election Preview 2024". NBC News.
- ^ Allis, Victor (October 30, 2024). "Trump has large lead in South Carolina". ActiVote.
- ^ Allis, Victor (October 18, 2024). "Trump has large lead in South Carolina". ActiVote. Retrieved October 18, 2024.
- ^ "September 2024 Winthrop Poll". Winthrop University. Retrieved October 2, 2024.
- ^ "The Citadel Poll" (PDF). The Citadel. October 31, 2024.
- ^ Francia, Peter; Morris, Jonathan (October 27, 2024). "Trump Leads Harris by Thirteen Points in South Carolina". ECU Center for Survey Research.
- ^ a b c "Biden Is the Real Spoiler, Kennedy Only Candidate Who Can Beat Trump". Kennedy24. May 1, 2024.
- ^ Mumford, Camille (February 20, 2024). "South Carolina 2024 Poll: Trump with 23-Point Lead Over Haley Ahead of GOP Primary". Emerson Polling.
- ^ a b c d "Trump Leads Haley in South Carolina, but both candidates are finding advantages in the state". The Citadel. February 16, 2024. Archived from the original on March 1, 2024.
- ^ a b "February 2024 Winthrop Poll Results". Winthrop University. February 14, 2024.
- ^ "Mainstreet Research Survey – South Carolina" (PDF). FAU Polling. February 13, 2024.
- ^ a b Chavez, Krista (September 13, 2022). "New National Poll: 89% of Americans Say Congress Should Focus on Addressing Inflation, Not Breaking Up Tech". NetChoice.
- ^ "McMaster Leads by 11 in SC Gov. Race But Poll Shows Plenty of Upside for Cunningham". Blueprint Polling. August 30, 2022. Archived from the original on August 31, 2022.
- ^ "Biden drops out of 2024 race after disastrous debate inflamed age concerns. VP Harris gets his nod". AP News. July 21, 2024. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ Alvarez, Jeremy Herb, MJ Lee, Jeff Zeleny, Phil Mattingly, Arlette Saenz, Priscilla (July 21, 2024). "Inside Biden's unprecedented exit from the presidential race | CNN Politics". CNN. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "RFK Jr. suspends his presidential bid and backs Donald Trump before appearing with him at his rally". AP News. August 23, 2024. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ "Robert F Kennedy Jr suspends campaign and backs Trump". www.bbc.com. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ Kenmore, Abraham (August 27, 2024). "Alliance Party removes Robert F. Kennedy Jr. from SC's ballot". SC Daily Gazette. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ Kenmore, Abraham (September 3, 2024). "SC finalizing list of presidential candidates on November ballot, sample ballots available soon". SC Daily Gazette. Retrieved September 25, 2024.
- ^ "Candidate Listing". MySCVotes. Retrieved September 23, 2024.
- ^ https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1ZHx5E0-5vuXxcZShBgsAl_vwAntkkanGqYQp0owNjoQ/edit?gid=0#gid=0






