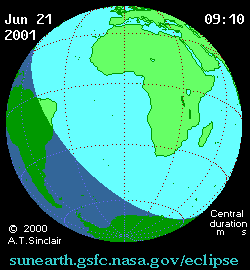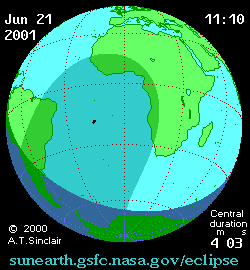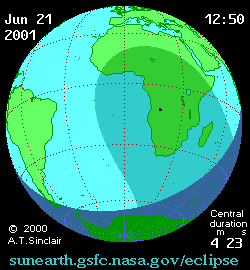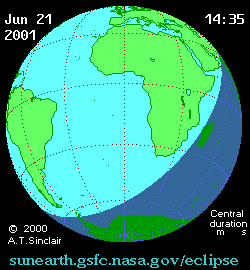
Solar eclipse of June 21, 2001
| Solar eclipse of June 21, 2001 | |
|---|---|
 Totality from Lusaka, Zambia by the Williams College eclipse expedition | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.5701 |
| Magnitude | 1.0495 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 297 s (4 min 57 s) |
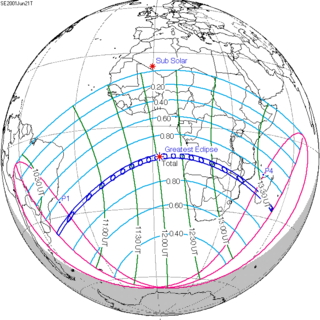
| Coordinates | 11°18′S 2°42′E / 11.3°S 2.7°E |
| Max. width of band | 200 km (120 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 9:33:04 |
| (U1) Total begin | 10:35:59 |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:04:46 |
| (U4) Total end | 13:31:37 |
| (P4) Partial end | 14:35:25 |
| References | |
| Saros | 127 (57 of 82) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9511 |
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, June 21, 2001,[1] with a magnitude of 1.0495. It was the first solar eclipse of the 21st century. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.25 days before perigee (on June 23, 2001, at 18:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2]
Many people traveled to Africa to watch the eclipse;[3][4][5] the Daily Telegraph reported that "while some tribesmen watch a celestial crocodile eating the sun, the modern African will be counting the cash brought in by thousands of visitors".[6]
Visibility
[edit]It was visible from a narrow corridor in the southern Atlantic Ocean and southern Africa, including Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, the southern tip of Malawi, and Madagascar. A partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including eastern South America and most of Africa.
Observations
[edit]Within the path of totality, Angola got the best conditions with the highest solar zenith angle, longest duration and largest chance of clear weather. Sumbe, capital of Cuanza Sul Province, where the path first touched land, was the best in Angola with 4 minutes and 34 seconds of totality. However, the Angolan Civil War[7] prevented many from traveling to the county, and only about 500 people observed the eclipse there. Besides tourists, there were also scientists from the United States, France, Brazil, South Africa, the Czech Republic, Portugal and Hungary.[8]
Zambia, though inferior to its neighbouring country Angola in the chance of clear weather, attracted many scientists and tourists due to its stable political situation and also the fact that its capital city Lusaka was also located within the path of totality.[7] The Zambian government made it a national holiday with one day off, and ZamPost also issues special postage stamps and first-day covers.[9] Scientists from the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, South Korea and China observed it in Zambia.[9] The Chinese Academy of Sciences sent a team of 6 people, carrying 3 gravimeters, 2 nuclear gyromagnetometers, 4 digital acquisition systems and recording systems to study the gravity anomalies recorded by Indian scientists during the total solar eclipse of October 24, 1995, and by Chinese scientists during the total solar eclipse of March 9, 1997, in Mohe County.[10][11] With continuous observation for more than 10 years after that, China obtained the first observational evidence that the gravity field propagates at the speed of light.[12]
Coincidence
[edit]Besides the eclipse, the day was also the June solstice (winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere where the path of totality passed) when the sun was at the northernmost limit. It was also the closest approach of Mars since 1988.[13]
Images
[edit]Eclipse details
[edit]Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[14]
| Event | Time (UTC) |
|---|---|
| First Penumbral External Contact | 2001 June 21 at 09:34:04.6 UTC |
| First Umbral External Contact | 2001 June 21 at 10:37:00.4 UTC |
| First Central Line | 2001 June 21 at 10:38:10.0 UTC |
| First Umbral Internal Contact | 2001 June 21 at 10:39:19.9 UTC |
| Ecliptic Conjunction | 2001 June 21 at 11:58:49.4 UTC |
| Equatorial Conjunction | 2001 June 21 at 11:58:54.2 UTC |
| Greatest Eclipse | 2001 June 21 at 12:04:46.3 UTC |
| Greatest Duration | 2001 June 21 at 12:07:11.5 UTC |
| Last Umbral Internal Contact | 2001 June 21 at 13:30:14.3 UTC |
| Last Central Line | 2001 June 21 at 13:31:26.2 UTC |
| Last Umbral External Contact | 2001 June 21 at 13:32:37.9 UTC |
| Last Penumbral External Contact | 2001 June 21 at 14:35:26.2 UTC |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Eclipse Magnitude | 1.04954 |
| Eclipse Obscuration | 1.10153 |
| Gamma | −0.57013 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 06h00m46.1s |
| Sun Declination | +23°26'18.2" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'44.3" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 06h01m00.5s |
| Moon Declination | +22°52'27.2" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 16'17.6" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 0°59'47.9" |
| ΔT | 64.2 s |
Eclipse season
[edit]This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| June 21 Ascending node (new moon) |
July 5 Descending node (full moon) |
|---|---|
 |

|
| Total solar eclipse Solar Saros 127 |
Partial lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 139 |
Related eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 2001
[edit]- A total lunar eclipse on January 9.
- A total solar eclipse on June 21.
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 5.
- An annular solar eclipse on December 14.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on December 30.
Metonic
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of September 2, 1997
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of April 8, 2005
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of May 10, 1994
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of August 1, 2008
Half-Saros
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of June 15, 1992
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 26, 2010
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 22, 1990
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 20, 2012
Solar Saros 127
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 11, 1983
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of July 2, 2019
Inex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 10, 1972
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 1, 2030
Triad
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 21, 1914
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of April 21, 2088
Solar eclipses of 2000–2003
[edit]This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[15]
The partial solar eclipses on February 5, 2000 and July 31, 2000 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2000 to 2003 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | July 1, 2000 Partial |
−1.28214 | 122 Partial projection in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
December 25, 2000 Partial |
1.13669 | |
127 Totality in Lusaka, Zambia |
June 21, 2001 Total |
−0.57013 | 132 Partial in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
December 14, 2001 Annular |
0.40885 | |
137 Partial in Los Angeles, CA, USA |
June 10, 2002 Annular |
0.19933 | 142 Totality in Woomera, South Australia |
December 4, 2002 Total |
−0.30204 | |
147 Annularity in Culloden, Scotland |
May 31, 2003 Annular |
0.99598 | 152
|
November 23, 2003 Total |
−0.96381 | |
Saros 127
[edit]This eclipse is a part of Saros series 127, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 82 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on October 10, 991 AD. It contains total eclipses from May 14, 1352 through August 15, 2091. There are no annular or hybrid eclipses in this set. The series ends at member 82 as a partial eclipse on March 21, 2452. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 31 at 5 minutes, 40 seconds on August 30, 1532. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[16]
| Series members 46–68 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
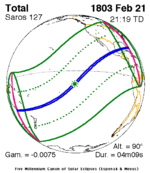 February 21, 1803 |
 March 4, 1821 |
 March 15, 1839 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
 March 25, 1857 |
 April 6, 1875 |
 April 16, 1893 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 April 28, 1911 |
 May 9, 1929 |
 May 20, 1947 |
| 55 | 56 | 57 |
 May 30, 1965 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 June 21, 2001 |
| 58 | 59 | 60 |
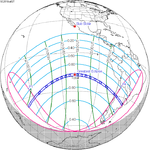 July 2, 2019 |
 July 13, 2037 |
 July 24, 2055 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 |
 August 3, 2073 |
 August 15, 2091 |
 August 26, 2109 |
| 64 | 65 | 66 |
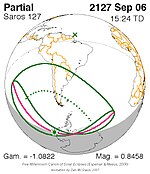 September 6, 2127 |
 September 16, 2145 |
 September 28, 2163 |
| 67 | 68 | |
 October 8, 2181 |
 October 19, 2199 | |
Metonic series
[edit]The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982 and June 21, 2058 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 21 | April 8–9 | January 26 | November 13–14 | September 1–2 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 21, 1982 |
 April 9, 1986 |
 January 26, 1990 |
 November 13, 1993 |
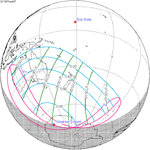 September 2, 1997 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 21, 2001 |
 April 8, 2005 |
 January 26, 2009 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 September 1, 2016 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
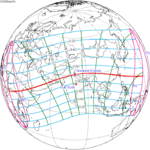 June 21, 2020 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 January 26, 2028 |
 November 14, 2031 |
 September 2, 2035 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 21, 2039 |
 April 9, 2043 |
 January 26, 2047 |
 November 14, 2050 |
 September 2, 2054 |
| 157 | ||||
 June 21, 2058 | ||||
Tritos series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 January 1, 1805 (Saros 109) |
 October 31, 1826 (Saros 111) |
 August 28, 1848 (Saros 113) | ||
 July 29, 1859 (Saros 114) |
 June 28, 1870 (Saros 115) |
 May 27, 1881 (Saros 116) |
 April 26, 1892 (Saros 117) |
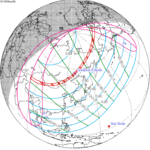 March 29, 1903 (Saros 118) |
 February 25, 1914 (Saros 119) |
 January 24, 1925 (Saros 120) |
 December 25, 1935 (Saros 121) |
 November 23, 1946 (Saros 122) |
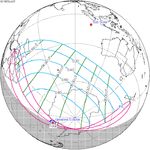 October 23, 1957 (Saros 123) |
 September 22, 1968 (Saros 124) |
 August 22, 1979 (Saros 125) |
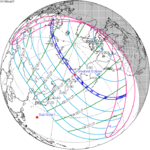 July 22, 1990 (Saros 126) |
 June 21, 2001 (Saros 127) |
 May 20, 2012 (Saros 128) |
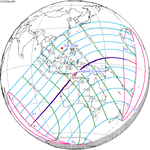 April 20, 2023 (Saros 129) |
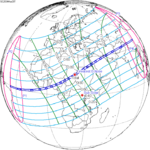 March 20, 2034 (Saros 130) |
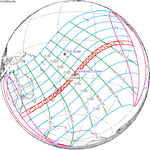 February 16, 2045 (Saros 131) |
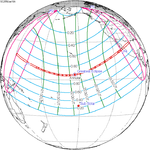 January 16, 2056 (Saros 132) |
 December 17, 2066 (Saros 133) |
 November 15, 2077 (Saros 134) |
 October 14, 2088 (Saros 135) |
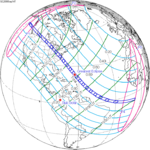 September 14, 2099 (Saros 136) |
 August 15, 2110 (Saros 137) |
 July 14, 2121 (Saros 138) |
 June 13, 2132 (Saros 139) |
 May 14, 2143 (Saros 140) |
 April 12, 2154 (Saros 141) |
 March 12, 2165 (Saros 142) |
 February 10, 2176 (Saros 143) |
 January 9, 2187 (Saros 144) |
 December 9, 2197 (Saros 145) | |||
Inex series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
 October 20, 1827 (Saros 121) |
 September 29, 1856 (Saros 122) |
 September 8, 1885 (Saros 123) |
 August 21, 1914 (Saros 124) |
 August 1, 1943 (Saros 125) |
 July 10, 1972 (Saros 126) |
 June 21, 2001 (Saros 127) |
 June 1, 2030 (Saros 128) |
 May 11, 2059 (Saros 129) |
 April 21, 2088 (Saros 130) |
 April 2, 2117 (Saros 131) |
 March 12, 2146 (Saros 132) |
 February 21, 2175 (Saros 133) |
||
Notes
[edit]- ^ "June 21, 2001 Total Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 11 August 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 11 August 2024.
- ^ "Thousands gather in Zambia for total solar eclipse". The News and Advance. 2001-06-21. p. 5. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Solar eclipse: Day declared national holiday as thousands come to Zambia". Hickory Daily Record. 2001-06-22. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "First total eclipse of new millennium sweeps across Africa". Arizona Daily Sun. 2001-06-22. p. 7. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Tradition and tourism flourish in solar eclipse". The Daily Telegraph. 2001-06-21. p. 17. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ a b "2001年6月21日非洲日全食" (in Chinese). Beijing Planetarium. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015.
- ^ "各国科学家和游客云集安哥拉观看日全食". Xinhua News Agency (in Chinese). Sohu News. 21 June 2001. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ a b Zeng Wei (21 June 2001). "日全食搅热赞比亚". Beijing Youth Daily (in Chinese). People.cn. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015.
- ^ "宇宙起源理论可能改写 6科学家赴非观测日全食". Beijing Youth Daily (in Chinese). Sohu News. 15 June 2001. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ Chai Shikuan, Xiong Sihao (25 June 2001). "中科院日全食观测队获得高质量观测数据" (in Chinese). Xinhua News Agency. Archived from the original on 2003-11-03.
- ^ Sun Zifa (26 December 2012). "中国科学家全球首获引力场以光速传播的观测证据" (in Chinese). China News Service. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015.
- ^ "Diamond Ring in the Sun". APOD. 21 June 2001.
- ^ "Total Solar Eclipse of 2001 Jun 21". EclipseWise.com. Retrieved 11 August 2024.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 127". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
[edit]- Fred Espenak and Jay Anderson. "Total Solar Eclipse of 2001 June 21". NASA, November 2004.
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Map Google
Photos:
- Spaceweather.com solar eclipse gallery
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Zambia
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Angola
- KryssTal - Eclipse in Zimbabwe - in a school by the Ruya River.
- Images from Zimbabwe by Crayford Manor House Astronomical Society Archived 2009-07-26 at the Wayback Machine
- Eclipse in African Skies, APOD 6/22/2001, totality from Lusaka, Zambia
- Bakasa Eclipse Sequence, APOD 7/6/2001, totality from Bakasa, Zimbabwe
- A Total Eclipse Over Africa, APOD 7/11/2001, totality from Malambanyama, Zambia
- Madagascar Totality, APOD 7/26/2001, from southern Madagascar
- Eclipse Over Acacia, APOD 12/3/2002, from Chisamba, Zambia
- Moon AND Sun, APOD 11/22/2003, totality from Chisamba, Zambia