2022 United States Senate election in New York
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
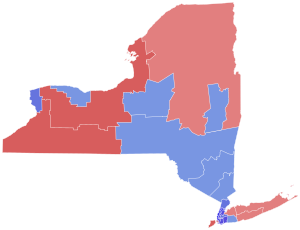
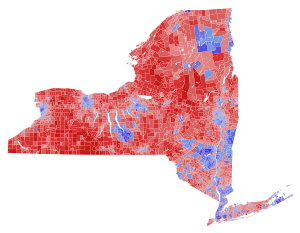
Schumer: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Pinion: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90% Tie: 40–50% 50% No votes | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in New York State |
|---|
 |
The 2022 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 8, 2022, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of New York.
Incumbent four-term Democratic Senator Chuck Schumer, who has served as Senate Majority Leader since 2021, was first elected in 1998, defeating Republican incumbent Al D'Amato. Schumer ran for a fifth term. Republican Joe Pinion is the first black Senate nominee of any major party in New York history. The filing deadline for the June primary was April 7, 2022.[1] Schumer became the longest-serving U.S. senator in the state's history once his fifth term began in the 118th Congress.[2]
Though Schumer was comfortably re-elected by a margin of 14.02%, he lost significant support on Long Island and Upstate New York compared to his last election in 2016. Pinion flipped the more conservative counties that Schumer had won in his previous runs, as well as some Democratic-leaning counties such as Nassau, Saratoga, Broome, Clinton, and Essex. However, Schumer's lead was large enough in New York City that it was called by most media outlets the moment the polls closed.[3]
Despite Democrats overperforming expectations on a national level during this cycle, this race was the most competitive in Schumer's Senate career since his first election in 1998, when he won by 10.5%, along with being the closest U.S. Senate election from New York since Hillary Clinton won by about 12.3 percentage points in 2000. This was due to a Democratic underperformance in New York state despite their overperformance nationally, and Schumer's performance was still the highest margin (aside from Thomas DiNapoli in the concurrent comptroller election) on the statewide ballot.
Democratic primary
[edit]Candidates
[edit]Nominee
[edit]- Chuck Schumer, incumbent U.S. Senator and Senate Majority Leader[4]
Disqualified
[edit]Declined
[edit]- Alessandra Biaggi, state senator from the 34th district (ran for U.S. House)[7][8]
- Jamaal Bowman, U.S. Representative for New York's 16th congressional district (ran for re-election)[9]
- Andrew Cuomo, former governor of New York, former attorney general of New York, and former U.S. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development[10]
- Mondaire Jones, U.S. Representative for New York's 17th congressional district (ran for re-election)[9]
- Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, U.S. Representative for New York's 14th congressional district (ran for re-election)[9][11][12][13]
- Jumaane Williams, New York City Public Advocate and former New York City Councilor for the 45th district (ran for governor)[14]
Endorsements
[edit]Polling
[edit]| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Chuck Schumer |
Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zogby Analytics | May 7–9, 2020 | 328 (LV) | ± 5.4% | 54% | 21% | 25% |
Republican primary
[edit]At the 2022 New York State Republican Convention, Joe Pinion was designated as the New York State Republican Party's preferred candidate for U.S. Senate. Pinion became the first Black individual to be backed by a major party in a U.S. Senate election in New York.[23]
Candidates
[edit]Nominee
[edit]- Joe Pinion, entrepreneur, TV host and candidate for New York State Assembly in 2018[24][25]
Disqualified
[edit]- Aleksander Mici, lawyer and candidate for New York City Council in 2021[24][25]
Declined
[edit]- Andrew Giuliani, former Trump administration official, son of Rudy Giuliani and Newsmax TV contributor (ran for governor)[26]
- John Katko, U.S. Representative for New York's 24th congressional district[27]
- Tom Reed, former U.S. Representative for New York's 23rd congressional district[28]
- Lee Zeldin, U.S. Representative for New York's 1st congressional district and former state senator from the 3rd district (ran for governor)[29]
Endorsements
[edit]- U.S. Representatives
- Elise Stefanik, U.S. Representative from New York's 21st congressional district (2015–present) and Chair of the House Republican Conference (2021–present)[30]
- Organizations
Conservative primary
[edit]Candidates
[edit]Nominee
[edit]- Joe Pinion, TV host and candidate for New York State Assembly in 2018[32]
Working Families primary
[edit]Candidates
[edit]Nominee
[edit]- Chuck Schumer, incumbent U.S. senator[33]
Other candidates
[edit]Diane Sare ran on an Independent ballot line labeled "LaRouche."[34][35]
General election
[edit]Predictions
[edit]| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| The Cook Political Report[36] | Solid D | November 19, 2021 |
| Inside Elections[37] | Solid D | January 7, 2022 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[38] | Safe D | November 3, 2021 |
| Politico[39] | Solid D | April 1, 2022 |
| RCP[40] | Likely D | October 18, 2022 |
| Fox News[41] | Solid D | May 12, 2022 |
| DDHQ[42] | Solid D | July 20, 2022 |
| 538[43] | Solid D | June 30, 2022 |
| The Economist[44] | Solid D | September 7, 2022 |
Endorsements
[edit]- Federal officials
- Joe Biden, President of the United States (2021–present)[45]
- Statewide officials
- Letitia James, Attorney General of New York (2019–present)[15]
- Individuals
- Lin-Manuel Miranda, actor and lyricist[46]
- Organizations
- American Israel PAC[47]
- Citizen Action of New York[47]
- Civil Service Employees Association[16]
- Feminist Majority PAC[17]
- Humane Society Legislative Fund[47]
- Jewish Dems[18]
- NARAL Pro-Choice America[47]
- National Association of Social Workers[47]
- National Education Association[47]
- Natural Resources Defense Council[19]
- New York AFL–CIO[47]
- New York State Nurses Association[47]
- New York State Public Employees Federation[47]
- New York State United Teachers[47]
- Newtown Action Alliance[47]
- Planned Parenthood[47]
- Population Connection Action Fund[20]
- Pro-Israel America[22]
- Public Employees Federation[21]
- Sierra Club[48]
- Stonewall Democrats[47]
- United Federation of Teachers[47]
- Newspapers
- U.S. Representatives
- Elise Stefanik, U.S. Representative from New York's 21st congressional district (2015–present) and Chair of the House Republican Conference (2021–present)[30]
- Organizations
- New York Federation of College Republicans[52]
- New York State Troopers Police Benevolent Association[53]
- New York Young Republican Club[31]
Polling
[edit]- Aggregate polls
| Source of poll aggregation |
Dates administered |
Dates updated |
Chuck Schumer (D) |
Joe Pinion (R) |
Undecided [b] |
Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Clear Politics | October 26–31, 2022 | November 8, 2022 | 54.7% | 39.3% | 6.0% | Schumer +15.4 |
| FiveThirtyEight | October 12 – November 8, 2022 | November 8, 2022 | 55.7% | 38.0% | 6.3% | Schumer +17.7 |
| 270towin | October 26 – November 7, 2022 | November 8, 2022 | 54.6% | 38.6% | 6.8% | Schumer +16.0 |
| Average | 55.0% | 38.6% | 6.4% | Schumer +16.4 | ||
- Graphical summary
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Chuck Schumer (D) |
Joe Pinion (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research Co. | November 4–6, 2022 | 450 (LV) | ± 4.6% | 55% | 37% | 2%[c] | 6% |
| ActiVote (D) | August 8 – November 6, 2022 | 279 (LV) | ± 6.0% | 60% | 40% | – | – |
| Emerson College | October 28–31, 2022 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 55% | 36% | 3%[d] | 6% |
| 57% | 39% | 4%[e] | – | ||||
| The Trafalgar Group (R) | October 27–31, 2022 | 1,198 (LV) | ± 2.9% | 51% | 40% | 5%[f] | 4% |
| KAConsulting (R)[A] | October 27–29, 2022 | 501 (LV) | ± 4.4% | 50% | 38% | – | 7% |
| Data for Progress (D) | October 26–28, 2022 | 818 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 56% | 39% | – | 5% |
| Long Island University | October 24–26, 2022 | 1,001 (A) | ± 3.0% | 54% | 27% | 9%[g] | 10% |
| Civiqs | October 22–25, 2022 | 593 (LV) | ± 5.0% | 56% | 41% | 1%[h] | 2% |
| Emerson College | October 20–24, 2022 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 51% | 36% | 6%[i] | 8% |
| 53% | 40% | 8%[j] | – | ||||
| SurveyUSA | October 14–18, 2022 | 702 (LV) | ± 5.4% | 52% | 38% | 4% | 6% |
| Quinnipiac University | October 12–16, 2022 | 1,617 (LV) | ± 2.4% | 54% | 42% | 1%[k] | 3% |
| Siena College | October 12–14, 2022 | 707 (LV) | ± 4.9% | 57% | 37% | 1%[l] | 5% |
| Marist College | October 3–6, 2022 | 900 (LV) | ± 4.4% | 52% | 39% | 1%[m] | 8% |
| 1,117 (RV) | ± 4.0% | 54% | 34% | 1%[n] | 11% | ||
| Siena College | September 16–25, 2022 | 655 (LV) | ± 3.9% | 55% | 36% | 1%[o] | 8% |
| Emerson College | September 4–6, 2022 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 55% | 31% | 5%[p] | 9% |
| McLaughlin & Associates (R) | August 7–9, 2022 | 600 (LV) | ± 4.0% | 51% | 36% | – | 13% |
| Emerson College | July 26–28, 2022 | 1,000 (LV) | ± 3.0% | 53% | 31% | 7% | 8% |
| Siena College | July 24–28, 2022 | 806 (LV) | ± 3.5% | 56% | 35% | 0% | 8% |
- Chuck Schumer vs. generic opponent
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size[a] |
Margin of error |
Chuck Schumer (D) |
Generic Opponent |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McLaughlin & Associates (R) | August 7–9, 2022 | 600 (LV) | ± 4.0% | 42% | 48% | 10% |
Results
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Chuck Schumer | 3,022,822 | 51.69% | −13.03% | |
| Working Families | Chuck Schumer | 297,739 | 5.09% | +1.82% | |
| Total | Chuck Schumer (incumbent) | 3,320,561 | 56.78% | −13.86% | |
| Republican | Joe Pinion | 2,204,499 | 37.69% | +14.37% | |
| Conservative | Joe Pinion | 296,652 | 5.07% | +1.45% | |
| Total | Joe Pinion | 2,501,151 | 42.76% | +15.58% | |
| LaRouche | Diane Sare | 26,844 | 0.46% | N/A | |
| Total votes | 5,848,556 | 100.0% | N/A | ||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Counties that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]- Broome (largest municipality: Binghamton)
- Cattaraugus (largest municipality: Olean)
- Cayuga (largest municipality: Auburn)
- Chautauqua (largest municipality: Jamestown)
- Chemung (largest municipality: Elmira)
- Chenango (largest municipality: Norwich)
- Clinton (largest municipality: Plattsburgh)
- Cortland (largest municipality: Cortland)
- Delaware (largest municipality: Sidney)
- Essex (largest municipality: Ticonderoga)
- Franklin (largest municipality: Malone)
- Fulton (largest municipality: Gloversville)
- Genesee (largest municipality: Batavia)
- Greene (largest municipality: Catskill)
- Herkimer (largest municipality: German Flatts)
- Jefferson (largest municipality: Le Ray)
- Lewis (largest municipality: Lowville)
- Livingston (largest municipality: Geneseo)
- Madison (largest municipality: Oneida)
- Montgomery (largest municipality: Amsterdam)
- Nassau (largest municipality: Hempstead)
- Niagara (largest municipality: Niagara Falls)
- Oneida (largest municipality: Utica)
- Ontario (largest municipality: Geneva)
- Orange (largest municipality: Kiryas Joel)
- Oswego (largest municipality: Oswego)
- Otsego (largest municipality: Oneonta)
- Putnam (largest municipality: Lake Carmel)
- Richmond (Staten Island, borough of New York City)
- St. Lawrence (largest municipality: Massena)
- Saratoga (largest municipality: Saratoga Springs)
- Schoharie (largest municipality: Cobleskill)
- Schuyler (largest municipality: Watkins Glen)
- Seneca (largest municipality: Seneca Falls)
- Suffolk (largest municipality: Brookhaven)
- Sullivan (largest municipality: Monticello)
- Tioga (largest municipality: Waverly)
- Warren (largest municipality: Glens Falls)
- Washington (largest municipality: Hudson Falls)
- Wayne (largest municipality: Newark)
- Yates (largest municipality: Penn Yan)
By congressional district
[edit]Schumer won 19 of 26 congressional districts, including four that elected Republicans.[55]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c Key:
A – all adults
RV – registered voters
LV – likely voters
V – unclear - ^ Calculated by taking the difference of 100% and all other candidates combined.
- ^ "Some other candidate" with 2%
- ^ Sare (I) with 1%; "Someone else" with 2%
- ^ Sare (I) with 1%; "Someone else" with 3%
- ^ Sare (I) with 5%
- ^ "Not planning to vote" with 6%; "Another candidate" with 3%
- ^ "Someone else" with 1%
- ^ "Someone else" with 4%; Sare (I) with 2%
- ^ "Someone else" with 6%; Sare (I) with 2%
- ^ "Someone else" with 1%
- ^ "Another candidate" with 1%; "Not going to vote" with 0%
- ^ "Another party's candidate" with 1%
- ^ "Another party's candidate" with 1%
- ^ "Another candidate" with 1%
- ^ "Someone else" with 5%
- Partisan clients
- ^ Poll conducted for Citizens United, a conservative non-profit organization.
References
[edit]- ^ Cillizza, Chris (April 20, 2020). "Does Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez have her eye on a Senate seat?". CNN Politics.
- ^ Matthews, Karen; Hajela, Deepti. "New York's Schumer keeps Senate seat, but majority role up for grabs". www.timesofisrael.com. Retrieved November 9, 2022.
- ^ McKinley, Jesse (November 9, 2022). "Tough N.Y. Election Holds Lessons for Republicans and Democrats Alike". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 12, 2022.
- ^ Glueck, Katie (February 17, 2022). "Hochul is the Star as Democrats Gather for a Cuomo-Free Convention". The New York Times.
- ^ "Moses Mugulusi". Ballotpedia. Archived from the original on September 11, 2021.
- ^ "New York Senate candidate encourages Americans to protest Hamas". The Jerusalem Post. June 5, 2021. Archived from the original on August 29, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ Murphy, Dan (February 7, 2022). "Reports: Biaggi to Announce Run for Congress in NY-3; Sound Shore Long Island & West". Yonkers Times. Retrieved February 7, 2022.
- ^ Eidler, Scott (February 7, 2022). "State Sen. Biaggi joins crowded race for Suozzi's seat in Congress". Newsday. Retrieved February 7, 2022.
- ^ a b c Otterbein, Holly (February 1, 2021). "Schumer quietly nails down the left amid AOC primary chatter". Politico. Retrieved February 1, 2021.
- ^ Axelrod, Tal (May 28, 2019). "Cuomo says he'll run for fourth term as NY governor". The Hill. Retrieved February 11, 2021.
- ^ Connolly, Griffin (January 4, 2021). "AOC won't say whether she'll mount primary challenge against Chuck Schumer". The Independent. Archived from the original on January 4, 2021.
- ^ Krieg, Gregory (August 8, 2021). "Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez does not rule out 2022 challenge to Chuck Schumer". CNN. Archived from the original on August 29, 2021. Retrieved August 30, 2021.
- ^ Ngo, Emily. "Schumer's path to reelection paved with campaign cash and statewide stops". www.ny1.com. Retrieved February 2, 2022.
Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez had been floated as a Schumer challenger, but her spokeswoman told NY1 she has filed for reelection and is ruling out seeking his seat.
- ^ Vakil, Caroline (October 27, 2021). "Jumaane Williams makes run for New York governor official". The Hill. Retrieved November 4, 2021.
- ^ a b Reisman, Nick (February 15, 2022). "Sen. Schumer and AG James endorse each other". Spectrum News.
- ^ a b Reisman, Nick (January 13, 2022). "CSEA endorse, DiNapoli and Schumer for re-election". Spectrum News. Retrieved February 14, 2022.
- ^ a b "2022 Feminist Majority PAC Endorsements". feministmajoritypac.org. Retrieved April 9, 2022.
- ^ a b "Jewish Dems Start 2022 Election Cycle With First Slate of Endorsements". www.jewishdems.org. November 30, 2021. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ a b Turrentine, Jeff (March 8, 2022). "NRDC Action Fund Endorses These Candidates in the 2022 Elections". Retrieved March 15, 2022.
- ^ a b "2022 House & Senate Endorsements". Population Connection Action Fund. Archived from the original on July 2, 2022. Retrieved April 21, 2022.
- ^ a b Reisman, Nick (December 13, 2021). "Schumer, DiNapoli receive early labor endorsement". spectrumlocalnews.com.
- ^ a b "Endorsed Candidates". proisraelamerica.org. Archived from the original on December 20, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ Gronewald, Anna; Mahoney, Bill (February 28, 2022). "New York Republicans talk inclusion with a diverse slate at convention". Politico. Retrieved March 1, 2022.
- ^ a b Whalen, Ryan (January 27, 2022). "GOP U.S. Senate candidate Pinion visits WNY". Spectrum News 1. Retrieved February 1, 2022.
- ^ a b Taddeo, Sarah (March 1, 2022). "Republican Joe Pinion secures GOP designation for historic bid against Schumer". Democrat and Chronicle.
- ^ Saric, Ivana (April 7, 2021). "Andrew Giuliani says he plans to run for New York governor". Axios. Retrieved April 7, 2021.
- ^ Zanona, Melanie (January 14, 2022). "Third House Republican who voted to impeach Trump calls it quits". CNN. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ "GOP Rep. Tom Reed apologizes, announces retirement amid misconduct claim". NBC News. Associated Press. March 22, 2021. Archived from the original on May 14, 2021. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
Reed said in his statement Sunday that he would not seek any elective office in 2022.
- ^ Shabad, Rebecca (April 8, 2021). "GOP Rep. Lee Zeldin announces run for governor of New York". NBC News. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ a b "Stefanik endorses Henry for AG, Pinion for Senate". spectrumlocalnews.com.
- ^ a b "Endorsement: Joe Pinion for United States Senate (New York)". nyyrc.com. New York Young Republican Club. June 7, 2022. Retrieved June 8, 2022.
- ^ Williams, Zach (February 26, 2022). "Political right highlights 2022 talking points at Conservative Party convention". City & State NY.
- ^ Reisman, Nick (February 22, 2022). "Working Families Party endorses Schumer's re-election". SpectrumLocalNews.com.
- ^ "NYSBOE: Public Reporting System : Who Filed".
- ^ "United States Senate election in New York, 2022".
- ^ "2022 Senate Race ratings". The Cook Political Report. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ "Senate ratings". Inside Elections. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- ^ "2022 Senate". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved January 28, 2021.
- ^ "New York Senate Race 2022". Politico. April 1, 2022.
- ^ "Battle for the Senate 2022". RCP. October 18, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". Fox News. May 12, 2022. Retrieved May 12, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". DDHQ. July 20, 2022. Retrieved July 20, 2022.
- ^ "2022 Election Forecast". FiveThirtyEight. June 30, 2022. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- ^ "Economist's 2022 Senate forecast". The Economist. September 7, 2022. Retrieved September 7, 2022.
- ^ Fandos, Nicholas (November 4, 2022). "Biden Will Campaign for Gov. Hochul in New York on Sunday". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 5, 2022. Retrieved November 5, 2022.
- ^ "Lin-Manuel Miranda cuts Broadway-focused ad for Schumer's reelection bid". October 17, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "Chuck Schumer's Ratings and Endorsements - Vote Smart". justfacts.votesmart.org. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ "Congressional Endorsements | Sierra Club Independent Action". www.sierraclubindependentaction.org.
- ^ "The Editorial Board: Schumer for U.S. Senate". October 28, 2022.
- ^ "Editorial endorsement: Reelect Charles Schumer to the U.S. Senate". October 23, 2022.
- ^ "Editorial: Schumer for U.S. Senate". Times Union. October 28, 2022. Archived from the original on November 1, 2022. Retrieved November 1, 2022.
- ^ "Endorsements". newyorkfcr.org. New York Federation of College Republicans. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ "🚨Key Endorsement Alert🚨 🚔 Honored to have the full support of The State Troopers. -> @nyspolice It's time to stand with law enforcement again.🗽 Together, we will fix New York. 🇺🇸 Together, we will save America #onward #backtheblue". Twitter. September 16, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ "2022 General Election Results — Certified December 15, 2022". New York State Board of Elections.
- ^ "New York 'Center of Gravity' in 2024 Campaign For House Control". Bloomberg Government. March 13, 2023. Retrieved March 16, 2023.
External links
[edit]- Official campaign websites
- Joe Pinion (R) for Senate
- Chuck Schumer (D) for Senate Archived February 11, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Diane Sare (LaRouche) for Senate