Dexoxadrol
Tools
Actions
General
Print/export
In other projects
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from C20H23NO2)
Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
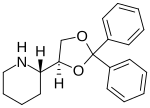
| Formula | C20H23NO2 |
| Molar mass | 309.409 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dexoxadrol (Dioxadrol) is a dissociative anaesthetic drug which has been found to be an NMDA antagonist and produces similar effects to PCP in animals. Dexoxadrol, along with another related drug etoxadrol, were developed as analgesics for use in humans, but development was discontinued after patients reported side effects such as nightmares and hallucinations.[1][2]
See also
[edit]- WMS-2539, a fluorinated derivative of dexoxadrol
References
[edit]- ^ Sax M, Wünsch B (2006). "Relationships between the structure of dexoxadrol and etoxadrol analogues and their NMDA receptor affinity". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (7): 723–32. doi:10.2174/156802606776894483. PMID 16719812.
- ^ Aepkers M, Wünsch B (December 2005). "Structure-affinity relationship studies of non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists derived from dexoxadrol and etoxadrol". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (24): 6836–49. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.07.030. PMID 16169732.
| AMPARTooltip α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
|
|---|---|
| KARTooltip Kainate receptor |
|
| NMDARTooltip N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
|
This hallucinogen-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
