Gold heptafluoride
Appearance
(Redirected from AuF7)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Difluorinegold(V) fluoride
| |||
| Other names
Gold heptafluoride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| AuF7 | |||
| Molar mass | 322.956 g/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Corrosive, toxic | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations
|
ReF7, IF7 | ||
Related compounds
|
AuF3, AuF5 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
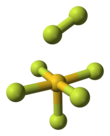
Gold heptafluoride is a gold(V) compound with the empirical formula AuF7. The synthesis of this compound from gold pentafluoride and a monatomic fluorine plasma was first reported in 1986.[1] However, current calculations suggest that the structure of the synthesized molecule was actually a difluorine ligand on a gold pentafluoride core, AuF5·F2. That would make it the first difluorine complex and the first compound containing a fluorine atom with an oxidation state of zero. The gold(V)–difluorine complex is calculated to be 205 kJ/mol more stable than "true" gold(VII) fluoride. The vibrational frequency at 734 cm−1 is the hallmark of the end-on coordinated difluorine molecule.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Timakov, A. A.; Prusakov, V. N.; Drobyshevskii, Y. V. (1986). "Gold heptafluoride" (PDF). Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR (in Russian). 291: 125–128. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 June 2022. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ Himmel, Daniel; Riedel, Sebastian (2007-05-31). "After 20 Years, Theoretical Evidence That "AuF7" Is Actually AuF5·F2". Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (13): 5338–5342. doi:10.1021/ic700431s. PMID 17511450.