Portal:Belarus
| Welcome to the Belarus Portal |
Сардэчна запрашаем да беларускага партала!
 |
 |

| |
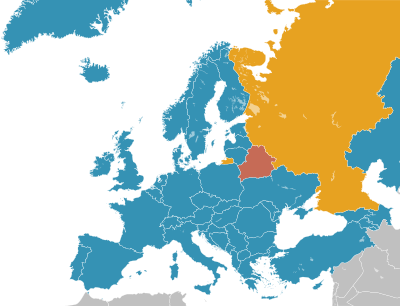
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) with a population of 9.1 million. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into six regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status.
Between the medieval period and the 20th century, different states at various times controlled the lands of modern-day Belarus, including Kievan Rus', the Principality of Polotsk, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and the Russian Empire. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution in 1917, different states arose competing for legitimacy amid the Civil War, ultimately ending in the rise of the Byelorussian SSR, which became a founding constituent republic of the Soviet Union in 1922. After the Polish-Soviet War (1918–1921), Belarus lost almost half of its territory to Poland. Much of the borders of Belarus took their modern shape in 1939, when some lands of the Second Polish Republic were reintegrated into it after the Soviet invasion of Poland, and were finalized after World War II. During World War II, military operations devastated Belarus, which lost about a quarter of its population and half of its economic resources. In 1945, the Byelorussian SSR became a founding member of the United Nations and the Soviet Union. The republic was home to a widespread and diverse anti-Nazi insurgent movement which dominated politics until well into the 1970s, overseeing Belarus' transformation from an agrarian to an industrial economy.
The parliament of the republic proclaimed the sovereignty of Belarus on 27 July 1990, and during the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Belarus gained independence on 25 August 1991. Following the adoption of a new constitution in 1994, Alexander Lukashenko was elected Belarus's first president in the country's first and only free election after independence, serving as president ever since. Lukashenko heads a highly centralized authoritarian government. Belarus ranks low in international measurements of freedom of the press and civil liberties. It has continued several Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership of large sections of the economy. Belarus is the only European country that continues to use capital punishment. In 2000, Belarus and Russia signed a treaty for greater cooperation, forming the Union State. (Full article...)
Selected article
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Belarus. At least one execution was carried out in the country in 2022.
Also known as an Exceptional Measure of Punishment (Russian: Исключительная Мера Наказания, ИМН), the death penalty has been a part of the country's legal system since gaining independence from the Soviet Union on August 25, 1991. The current national constitution prescribes this punishment for "grave crimes." Later laws have clarified the specific crimes for which capital punishment can be used. The death penalty can be imposed for crimes that occur against the state or against individuals. A few non-violent crimes can also be punishable by death. As of 2024[update], Belarus is the only country in Europe that continues to carry out the death penalty. Executions are carried out by a single shot to the back of the head. (Full article...)
Selected biography
Valery Vilyamovich Tsepkalo or Valery Vilyamavich Tsapkala (Russian: Валерий Вильямович Цепкало; Belarusian: Валерый Вільямавіч Цапкала; born 22 February 1965) is a Belarusian politician and entrepreneur. After graduating from the Moscow State Institute of International Relations with a doctoral degree in international law and serving in the embassy of the Soviet Union in Finland, Tsepkalo joined the staff of the Belarusian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. He later became an advisor on foreign political and economic relations to the Chairman of the Belarusian Parliament, Stanislav Shushkevich, and then a senior advisor to the Secretary General of the Commonwealth of Independent States.
He led Alexander Lukashenko's presidential campaign in the 1994 election and later took the post of First Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs. From 1997 to 2002, Tsepkalo was the Belarusian Ambassador to the United States and Mexico. In 2005–2006 he was Presidential Plenipotentiary Envoy in the Parliament. In 2005 he established the Belarus High Technologies Park (HTP), and led it until 2017. (Full article...)
General images
Selected picture
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that the Russian and Belarussian military exercise Zapad 2009 involved nuclear-capable ballistic missiles?
- ... that German national Rico Krieger was likely forced by the Belarusian KGB to lie in a state-televised plea titled "Confession of a German Terrorist"?
- ... that Obliskomzap People's Commissar for Public Charity V. L. Mukha resigned in protest over the dispersing of the First All-Belarusian Congress?
- ... that Rufina Bazlova has used traditional embroidery to depict protests in Belarus?
- ... that there are more than 9,000 swamps in Belarus?
- ... that Stsiapan Putsila faces criminal charges in Belarus—as does the Polish judge who refused to extradite him?
Featured articles
Related portals
Post Soviet states
Other countries
More Did you know
- ...there are large stands of primeval forest on the border between Poland and Belarus?
Topics
Subcategories
New article announcements
This page was created using Portal:Belarus/New article announcements. It is created for everyone interested in Belarus-related articles to notice everything new.
Urgent announcements
- NONE
This list was generated from these rules. Questions and feedback are always welcome! The search is being run daily with the most recent ~14 days of results. Note: Some articles may not be relevant to this project.
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-11-22 19:45 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Vladimir (name) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 85.249.23.7 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-22, score: 30
- Slivets (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Altenmann (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- Sheremetyevskaya railway station (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakoon (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 20
- Vyacheslav Bogdanovich (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KrivisKrivaitis (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 40
- Dnieper Flotilla (Ukraine) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by UeArtemis (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 30
- Vladyslav Vlasiuk (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Khonnit-mier (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 20
- Stipatosteus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SeismicShrimp (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- 2025 Aryna Sabalenka tennis season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ScottMarkz (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- Lutsk Border Detachment (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by M Waleed (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- On Black Slash-and-Burn Fields (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Altenmann (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 50
- Ukrainian energy crisis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Noble Attempt (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-11-18, score: 20
- Chaim Meir Chodosh (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DveykusBHashem (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 60
- Avangard (1939) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Soman (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- Chernihiv Border Detachment (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by M Waleed (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- Russia women's national futsal team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mishajang (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-15, score: 20
- Konstantin Pavlovich, Grand Duke of Russia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Artemis Andromeda (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-11-14, score: 30
- Testovskaya (Moskva-City) railway station (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 162 etc. (talk · contribs · new pages (40)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Battle of Vilnius (1812) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KeyMen12 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-08, score: 20
- Belarus-2 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 40
- Uładzimier Samojła (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SuuriMara (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 60
- Der Avangard (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Soman (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 40
- 25th Tank Division (Soviet Union) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Buckshot06 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 30
- Jazep (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- Bujnicki (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (60)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- Jewish refugees from Nazism (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Boxes12 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 30
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
- ^ Kopka, D. (2011). Welcome to Belarus: Passport to Eastern Europe & Russia. Passport Series. Milliken Publishing Company. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-7877-2770-3. Retrieved July 28, 2019.
- ^ Harshav, Benjamin. Marc Chagall and his times: a documentary narrative. Contraversions: Jews and Other Differences. Stanford University Press; 1 edition. August 2003. ISBN 0804742146.









































![Image 6The Fiddler, 1912–1913, by Marc Chagall, a Russian-French artist of Belarusian Jewish origin[2]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/4/4a/Image-Chagall_Fiddler.jpg/101px-Image-Chagall_Fiddler.jpg)
![Image 7White storks on their nest in Belarus, 2009. The Stork is the national symbol of Belarus.[1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/BY_stork1_2009.jpg/80px-BY_stork1_2009.jpg)































