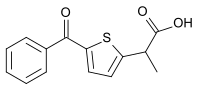
Tiaprofenic acid
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Surgam, Surgamyl, Tiaprofen, others |
| Other names | 5-Benzoyl-α-methyl-2-thiopheneacetic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Metabolism | 10% liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5-2.5h |
| Excretion | 50-80% urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.649 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H12O3S |
| Molar mass | 260.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tiaprofenic acid is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the arylpropionic acid (profen) class, used to treat pain, especially arthritic pain. The typical adult dose is 300 mg twice daily. It is not recommended for children.
Long-term use of tiaprofenic acid is associated with severe cystitis, roughly 100 times more commonly than other NSAIDs.[1] It is contraindicated in patients with cystitis and urinary tract infections. It is sparingly metabolised in the liver to two inactive metabolites. Most of the drug is eliminated unchanged in the urine. Renal disease impairs excretion, and should be used cautiously in renal disease.
It was patented in 1969 and approved for medical use in 1981.[2] It is available in generic formulations. A sustained-release preparation is available. It is an isomer of Suprofen.
References
[edit]- ^ Crawford ML, Waller PC, Wood SM (1997). "Severe cystitis associated with tiaprofenic acid". British Journal of Urology. 79 (4): 578–584. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410X.1997.00094.x. PMID 9126086.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 520. ISBN 9783527607495.
External links
[edit]- Manufacturer Data Sheet [1]
