South African Class 4A 4-8-2
| South African Class 4A & 4AR 4-8-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
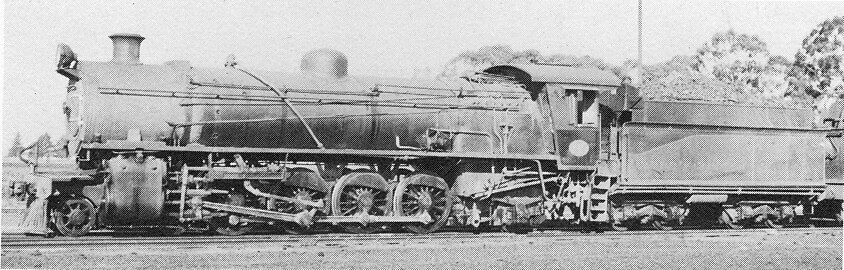
 No. 1559 at Hutchinson, Cape, 11 November 1916 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The leading coupled axle had flangeless wheels | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The South African Railways Class 4A 4-8-2 of 1913 was a steam locomotive.
In 1913 and 1914, ten Class 4A steam locomotives with a 4-8-2 Mountain type wheel arrangement were placed in service by the South African Railways.[1][2][3]
Manufacturer
[edit]
The Class 4 Mountain type locomotive was designed at the Salt River shops as a heavy mixed traffic locomotive by H.M. Beatty, the last Chief Locomotive Superintendent of the Cape Government Railways (CGR).[2][3]
Soon after the South African Railways (SAR) locomotive renumbering and classification scheme was carried out in 1912, an order was placed with North British Locomotive Company for a further ten locomotives of this type, built to an altered design. They were delivered late in 1913 and were designated Class 4A, numbered in the range from 1551 to 1560.[2][3][4]
Characteristics
[edit]The Class 4A locomotive was an improved version of the predecessor Class 4. It had a superheater added, which further resulted in the slide valves and Stephenson valve gear having to be replaced with piston valves and Walschaerts valve gear. The boilers were similar to those of the Class 4, except for the superheater and the length between tube-plates, which was 3 inches (76 millimetres) longer. The bar frames were identical to that of the Class 4, but the cylinders were of a 1 inch (25 millimetres) larger bore. The engines were erected at the Salt River shops in Cape Town during November 1913. Like their two forerunners, they were excellent steamers and, with the design alterations, gave a much better performance.[1][2][3]
The Class 4A were the only locomotives to be delivered with Type XM tenders, which had a coal capacity of 8 long tons (8.1 tonnes) and a water capacity of 4,000 imperial gallons (18,200 litres).[5][6]
The locomotive was the prototype for the Rhodesia Railways 10th Class, a scaled-down version that, like the Class 4A, gave long service.[7]
Watson Standard boilers
[edit]In the 1930s, many serving locomotives were reboilered with a standard boiler type designed by then Chief Mechanical Engineer A.G. Watson as part of his standardisation policy. Such Watson Standard reboilered locomotives were reclassified by adding an "R" suffix to their classification.[3][5][6]
All ten Class 4A locomotives were reboilered with Watson Standard no. 2 boilers during 1935 and reclassified to Class 4AR. No. 1554 was the first to be so modified and retained its original cab, which was cut back to accommodate the new boiler and wash-out plugs. It also initially retained its original cowcatcher. The other nine locomotives all had new Watson cabs fitted during reboilering, with their distinctive slanted fronts compared to the conventional vertical fronts of their original cabs.[2][3][8]
The new boiler's pitch was 6 inches (152 millimetres) higher than on the Class 4A. In the process the locomotives underwent some additional modifications. The trailing bissel truck remained unaltered, but the side control was redesigned and spring compensation was extended to include the bissel. This was one of the rare instances where reboilering actually appreciably reduced the total weight of the engine, from 85 long tons 8 hundredweight (86,770 kilograms) to 81 long tons 9 hundredweight (82,760 kilograms).[2][3][5][6]
An obvious visual difference between an original and a Watson Standard reboilered locomotive is usually a rectangular regulator cover, just to the rear of the chimney on the reboilered locomotive, but this was not always the case, as illustrated. A more obvious difference in the case of the Class 4AR is the top-fed feedwater supply to the boiler.[5][6]
Service
[edit]Their first ten years of service were spent working both passenger and goods trains on various sections of the Cape mainline. At first they worked out of Cape Town, but when more powerful locomotives became available, they were transferred to the Karoo, working between Touws River and Kimberley and also northward from Kimberley to Mafeking. They were then transferred to the Reef, from where they regularly served on the Zeerust, Breyten and Volksrust lines while also being employed in a variety of suburban and local train workings.[1][3]

During the Second World War, Class 4A no. 1554 was equipped with temporary protective armour to serve as the locomotive of an armoured train. The locomotive and train were stationed at Mapleton Camp of the Union Defence Force, where the SAR&H Brigade trained before going north to the Middle East.[9]
Armoured boiler cladding was added. The cab, front and sides of the smokebox were enclosed and some fittings on top of the boiler and firebox such as the safety valves and top feed were boxed in armour. Armour plating was also fitted to the sides of the running boards. The picture shows the locomotive and armoured train being inspected during 1942 by the Honourable F. C. Sturrock MP, South Africa's Minister of Transport at the time.[9]
The last Class 4AR locomotive was withdrawn from shunting operations on the West Rand in 1974 after more than 60 years in service. Some remained working in industrial service for several more years, with the last one being finally retired from Apex Colliery in 1983.[3][7][10]
Rhodesia Railways
[edit]A lighter version of the Class 4A was built by NBL for the Rhodesia Railways (RR). It was designated the RR 10th Class and was used on the long section south from Bulawayo in Southern Rhodesia through Bechuanaland Protectorate to Mafeking in the Cape Province.[7][10]
Like the SAR Class 4A, the RR 10th Class had combustion chambers, the only RR locomotive class with this feature.[10]
Preservation
[edit]Two of these engines survive.
| Number | Works nmr | THF / Private | Leaselend / Owner | Current Location | Outside South Africa | ? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1555 | NBL / 20229 | THF | MUSEUM | Bloemfontein Locomotive Depot | ||
| 1560 | NBL / 20233 | THF | Queenstown Locomotive Depot |
Illustration
[edit]The main picture shows no. 1559, as built, on the Cape Town-Johannesburg train, taking water at Hutchinson in the Karoo on 11 November 1916.[1]
In the pictures of reboilered Class 4AR locomotives, one locomotive has the rectangular regulator cover just to the rear of the chimney, while the other, no. 1554, has a bolted on cover plate instead, flush with the boiler cladding. Both have Watson cabs, while the pictures of Class 4A locomotives show their original cabs with conventional vertical fronts.[5][6]
-
Class 4A on a local between Langlaagte and Mayfair, c. 1930
-
Reboilered Class 4AR with the rectangular regulator cover and a Watson cab with its slanted front, c. 1970
-
Class 4A at Driehoek at Simmer & Jack's mine with a passenger train from Breyten, c. 1930
-
Class 4AR no. 1554 with its modified cab, a flush regulator cover, a modified buffer beam and standard cowcatcher, 8 April 1966
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Holland, D. F. (1972). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways. Vol. 2: 1910-1955 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, England: David & Charles. pp. 12–13, 22–23, 137. ISBN 978-0-7153-5427-8.
- ^ a b c d e f Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, July 1945. p. 513.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Paxton, Leith; Bourne, David (1985). Locomotives of the South African Railways (1st ed.). Cape Town: Struik. pp. 38–39. ISBN 0869772112.
- ^ North British Locomotive Company works list, compiled by Austrian locomotive historian Bernhard Schmeiser
- ^ a b c d e South African Railways & Harbours/Suid Afrikaanse Spoorweë en Hawens (15 Aug 1941). Locomotive Diagram Book/Lokomotiefdiagramboek, 3'6" Gauge/Spoorwydte. SAR/SAS Mechanical Department/Werktuigkundige Dept. Drawing Office/Tekenkantoor, Pretoria. p. 43.
- ^ a b c d e South African Railways & Harbours/Suid Afrikaanse Spoorweë en Hawens (15 Aug 1941). Locomotive Diagram Book/Lokomotiefdiagramboek, 2'0" & 3'6" Gauge/Spoorwydte, Steam Locomotives/Stoomlokomotiewe. SAR/SAS Mechanical Department/Werktuigkundige Dept. Drawing Office/Tekenkantoor, Pretoria. pp. 6a-7a, 41, 43.
- ^ a b c Soul of A Railway, System 7, Western Transvaal, based in Johannesburg, Part 24: Krugersdorp-Zeerust-Mafeking (Home Signal), Part 1 by Les Pivnic. Caption 35.[permanent dead link] (Accessed on 5 May 2017)
- ^ Soul of A Railway, System 7, Western Transvaal, based in Johannesburg, Part 3. Johannesburg Station in Transition by Les Pivnic. Caption 27.[permanent dead link] (Accessed on 27 March 2017)
- ^ a b Soul of A Railway, System 7, Western Transvaal, based in Johannesburg, Part 10. South-Eastwards as far as Volksrust (3rd part) by Les Pivnic. Caption 25.[permanent dead link] (Accessed on 11 April 2017)
- ^ a b c Durrant, AE (1989). Twilight of South African Steam (1st ed.). Newton Abbott: David & Charles. p. 13. ISBN 0715386387.