From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Ridazolol
Names
IUPAC name
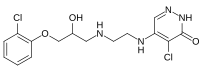
5-Chloro-4-[2-[[3-(2-chlorophenoxy)-2-hydroxypropyl]amino]ethylamino]-1H -pyridazin-6-one
Identifiers
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
UNII
InChI=1S/C15H18Cl2N4O3/c16-11-3-1-2-4-13(11)24-9-10(22)7-18-5-6-19-12-8-20-21-15(23)14(12)17/h1-4,8,10,18,22H,5-7,9H2,(H2,19,21,23)
Key: UUWABVCZFXKHSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C15H18Cl2N4O3/c16-11-3-1-2-4-13(11)24-9-10(22)7-18-5-6-19-12-8-20-21-15(23)14(12)17/h1-4,8,10,18,22H,5-7,9H2,(H2,19,21,23)
Key: UUWABVCZFXKHSU-UHFFFAOYAL
C1=CC=C(C(=C1)OCC(CNCCNC2=C(C(=O)NN=C2)Cl)O)Cl
Properties
C 15 H 18 Cl 2 N 4 O 3
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
Ridazolol is a pharmaceutical drug acting as a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist . It was investigated in the 1980 and 90s for its effects on coronary heart disease and essential hypertension (high blood pressure).[ 1] [ 2]
It is not known to be marketed anywhere in the world.[ 3]
^ Fach, WA; Starke, E; Becker, HJ (1992). "Duration of the effect and dose-response relationship of ridazolol in patients with coronary heart disease". Zeitschrift für Kardiologie . 81 (6): 320–5. PMID 1353933 . ^ Rommel, Th.; Demisch, L. (1994). "Influence of chronic ?-adrenoreceptor blocker treatment on melatonin secretion and sleep quality in patients with essential hypertension". Journal of Neural Transmission . 95 (1): 39–48. doi :10.1007/BF01283029 . PMID 7857585 . S2CID 31936176 . ^ "Ridazolol search results" . Drugs.com. Retrieved 2021-03-31 .
α1
Agonists Antagonists
Abanoquil Ajmalicine Alfuzosin Anisodamine Anisodine Atiprosin Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., brexpiprazole , clozapine , olanzapine , quetiapine , risperidone )Benoxathian Beta blockers (e.g., adimolol , amosulalol , arotinolol , carvedilol , eugenodilol , labetalol )Buflomedil Bunazosin Corynanthine Dapiprazole Domesticine Doxazosin Ergolines (e.g., acetergamine , ergotamine , dihydroergotamine , lisuride , nicergoline , terguride )Etoperidone Fenspiride Hydroxyzine Indoramin Ketanserin L-765,314 mCPP Mepiprazole Metazosin Monatepil Moxisylyte Naftopidil Nantenine Neldazosin Niaprazine Niguldipine Pardoprunox Pelanserin Perlapine Phendioxan Phenoxybenzamine Phentolamine Phenylpiperazine antidepressants (e.g., hydroxynefazodone , nefazodone , trazodone , triazoledione )Piperoxan Prazosin Quinazosin Quinidine Silodosin Spegatrine Spiperone Talipexole Tamsulosin Terazosin Tiodazosin Tolazoline Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin )Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline , clomipramine , doxepin , imipramine , trimipramine )Trimazosin Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Urapidil WB-4101 Zolertine
α2
Agonists Antagonists
1-PP Adimolol Amesergide Aptazapine Atipamezole Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine , brexpiprazole , clozapine , lurasidone , olanzapine , paliperidone , quetiapine , risperidone , zotepine )Azapirones (e.g., buspirone , gepirone , ipsapirone , tandospirone )BRL-44408 Buflomedil Cirazoline Efaroxan Esmirtazapine Fenmetozole Fluparoxan Idazoxan Ketanserin Lisuride mCPP Mianserin Mirtazapine NAN-190 Pardoprunox Phentolamine Phenoxybenzamine Piperoxan Piribedil Rauwolscine Rotigotine Setiptiline Spegatrine Spiroxatrine Sunepitron Terguride Tolazoline Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , fluphenazine , loxapine , thioridazine )Yohimbine
β