Portal:Tropical cyclones
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Tropical Storm Rolf, also known as Tropical Storm 01M, was an unusual Mediterranean tropical storm that brought flooding to Italy, France, Spain, and Switzerland in November 2011. Rolf originated from an extratropical system near western France on 4 November. Despite the generally unfavorable conditions in the Mediterranean Sea, Rolf transitioned into a subtropical depression on 7 November, before becoming a tropical storm later that day. On 8 November, Rolf reached its peak intensity, with 1-minute sustained winds peaking at 85 km/h (53 mph) and a minimum central pressure of 991 mb (29.3 inHg). During the next day, the storm made landfall on the island of Île du Levant, in France, and soon afterward, near Hyères in southeastern France. Following its second landfall, Rolf quickly weakened and dissipated on 10 November. Rolf was the first tropical cyclone ever to be officially monitored by the NOAA in the Mediterranean Sea.
Rolf caused widespread flooding across southwestern Europe, especially in France and Italy, with the majority of the damage from the storm occurring in those two countries. The rainfall worsened a series of ongoing floods in Europe at the time. Torrential rainfall from Rolf caused multiple rivers to overflow their banks in France and Italy, flooding multiple cities and resulting in extensive property damage. The storm forced numerous schools and businesses to close temporarily, and also caused significant damage to 300 farms in France. Floodwaters from Rolf's rainfall also cut the power to over 8,000 customers and necessitated thousands of rescues, in addition to forcing thousands of evacuations. Rolf killed 12 people, and was at the time, the costliest Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone on record, causing at least $1.25 billion (2011 USD, €926 million) in damages. It was later surpassed by Storm Daniel in 2023. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The Okeechobee hurricane of 1928, also known as the San Felipe Segundo hurricane, was one of the deadliest hurricanes in the recorded history of the North Atlantic basin, and the fourth deadliest hurricane in the United States, only behind the 1900 Galveston hurricane, 1899 San Ciriaco hurricane, and Hurricane Maria. The hurricane killed an estimated 2,500 people in the United States; most of the fatalities occurred in the state of Florida, particularly in Lake Okeechobee. It was the fourth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, the only major hurricane of the 1928 Atlantic hurricane season, and remains the deadliest disaster in Florida’s history to date. It developed off the west coast of Africa on September 6 as a tropical depression, but it strengthened into a tropical storm later that day, shortly before passing south of the Cape Verde islands. Further intensification was slow and halted late on September 7. About 48 hours later, the storm strengthened and became a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Still moving westward, the system reached Category 4 intensity before striking Guadeloupe on September 12, where it brought great destruction and resulted in 1,200 deaths. The islands of Martinique, Montserrat, and Nevis also reported damage and fatalities, but not nearly as severe as in Guadeloupe.
Around midday on September 13, the storm strengthened into a Category 5 hurricane and peaked with sustained winds of 160 mph (260 km/h). About six hours later, the system made landfall in Puerto Rico; it remains the only tropical cyclone on record to strike the island at Category 5 intensity. Very strong winds resulted in severe damage in Puerto Rico; 24,728 homes were destroyed and 192,444 were damaged throughout the island, leaving over 500,000 people homeless. Heavy rainfall also led to extreme damage to vegetation and agriculture. On Puerto Rico alone, there were 312 deaths and about US$50 million ($887 million today) in damage. While crossing the island and emerging into the Atlantic, the storm weakened slightly, falling to Category 4 intensity. It began crossing through the Bahamas on September 16, where it resulted in 18 fatalities. (Full article...)
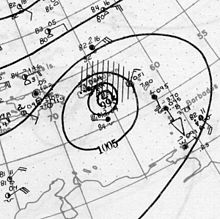
Selected image -

Selected season -

The 2016 Atlantic hurricane season was the first above-average hurricane season since 2012, producing 15 named storms, 7 hurricanes and 4 major hurricanes. The season officially started on June 1 and ended on November 30, though the first storm, Hurricane Alex which formed in the Northeastern Atlantic, developed on January 12, being the first hurricane to develop in January since 1938. The final storm, Otto, crossed into the Eastern Pacific on November 25, a few days before the official end. Following Alex, Tropical Storm Bonnie brought flooding to South Carolina and portions of North Carolina. Tropical Storm Colin in early June brought minor flooding and wind damage to parts of the Southeastern United States, especially Florida. Hurricane Earl left 94 fatalities in the Dominican Republic and Mexico, 81 of which occurred in the latter. In early September, Hurricane Hermine, the first hurricane to make landfall in Florida since Hurricane Wilma in 2005, brought extensive coastal flooding damage especially to the Forgotten and Nature coasts of Florida. Hermine was responsible for five fatalities and about $550 million (2016 USD) in damage.
The strongest, costliest, and deadliest storm of the season was Hurricane Matthew, the southernmost Category 5 Atlantic hurricane on record and the first to reach that intensity since Felix in 2007, ending the longest streak of seasons without a hurricane of such intensity in the Satellite Era. With at least 603 deaths attributed to it, Matthew was the deadliest Atlantic hurricane since Stan of 2005. Furthermore, damage from Matthew is estimated to be at least $16.5 billion, making it the ninth costliest Atlantic hurricane on record at the time. Hurricane Nicole became the first major hurricane to directly impact Bermuda since Hurricane Fabian in 2003, leaving widespread but relatively moderate damage on the island. The final tropical cyclone of the season – Hurricane Otto – brought severe flooding to Central America in November, particularly in Costa Rica and Nicaragua. Otto left 23 deaths and about $190 million in damage. On November 25, the storm emerged into the Eastern Pacific basin, the first such occurrence since Hurricane Cesar–Douglas in 1996. Most of the season's tropical cyclones impacted land, and nine of those storms caused loss of life. Collectively, the storms left at least 736 fatalities and $17.49 billion in damage, making the season the costliest since 2012. (Full article...)
Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones

Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2024)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2024)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2024)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2024–25)
- No active systems
Last updated: 09:03, 18 November 2024 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

November 17
- 1999 - Hurricane Lenny made landfall the island of Saint Croix at peak intensity causing extensive damage while maintaining an unprecedented west-east movement across the Caribbean Sea.
- 2020 - Hurricane Iota (pictured) makes landfall over Nicaragua, killing 61 people and causing damages of over US$1.4 billion.

November 18
- 1964 - Typhoon Louise moved through the Philippines, killing 576 people.
- 1991 - Cyclone Tia reaches its peak strength near Vanuatu, the first of six cyclones to affect the island during that cyclone season.
- 1994 - Hurricane Gordon (pictured) reached its peak intensity as a Category 1 hurricane to the east of North Carolina. Gordon had previously killed over 1,000 people in Haiti.

November 19
- 1970 - Typhoon Patsy makes landfall over the Philippine archipelago of Luzon as a strong typhoon. Patsy killed more than 260 people with damages losses of $80 million.
- 1979 - The 1977 Andhra Pradesh cyclone (pictured) made landfall on the coastline of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh with winds of about 210 km/h (130 mph), killing over 10,000 people and destroying 40% of India's food grain.
Did you know…




- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
- …that Cyclone Freddy (track pictured) in 2023 was the longest-lasting tropical cyclone worldwide?
- …that Cyclone Raquel (track pictured) travelled between the Australian and South Pacific basins between the 2014–15 and 2015–16 seasons, spanning both seasons in both basins?
- …that Hurricane Otis (pictured) in 2023 was the first Pacific hurricane to make landfall at Category 5 intensity and surpassed Hurricane Patricia as the strongest landfalling Pacific hurricane on record?
General images -

413 known tropical and subtropical cyclones have affected the U.S. state of North Carolina. Due to its location, many hurricanes have hit the state directly, and numerous hurricanes have passed near or through North Carolina in its history; the state is ranked fourth, after Florida, Texas, and Louisiana, in the number of cyclones that produced hurricane-force winds in a U.S. state. Hurricanes in North Carolina history are responsible for over $11 billion in damage (2008 USD) and almost 1,000 total fatalities. (Full article...)
Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus