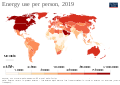
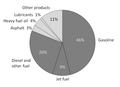
Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. The energy industry provides the energy required for human civilization to function, which it obtains from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, and renewable energy. (Full article...)
Selected article
Acceptance of peak oil is far from universal, and the only reliable way to identify its existence will be in retrospect. One alternative scenario is that global production will eventually follow an 'undulating plateau' for one or more decades before declining slowly.
Having accurately predicted the date of peak production in the US petroleum industry, which occurred in 1970, M. King Hubbert, who devised the theory, forecast that the world peak would occur in 1995 'if current trends continue'. Various subsequent predictions have been made as trends have fluctuated in the intervening years. Two milestones have passed, however. The peak of world oilfield discoveries occurred in 1965 and, due world population growth, production per capita peaked in 1979.
The effects of peak oil could be mitigated through conservation and switching to alternative fuels or unconventional oil sources. Such changes would bring their own challenges, ranging from the need to development alternative technologies to potential increases in greenhouse gas emissions.
Selected image

Photo credit: Luc Lviatour
Electricity ionizing the gas in a plasma lamp.
Did you know?

- The Power of Community: How Cuba Survived Peak Oil is a documentary film which details Cuba's efforts to recover from the 1990s economic crisis known as the Special Period?
- The Geysers (pictured), north of San Francisco, California, is the largest geothermal power development in the world?
- The International Energy Agency was founded in 1974 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis?
- Indian Railways has started to use Jatropha oil, blended with diesel fuel in various ratios, to power its Diesel locomotives?
- The South Wales Gas Pipeline is the largest high pressure gas pipeline in the United Kingdom?
- The Presbyterian Church (USA) was the first major religious denomination in the world to call on its followers to become carbon neutral?
- There was partial meltdown at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant in 1979?
- A hybrid electric vehicle achieves better fuel economy than a conventional vehicle without being hampered by the limited range of an electric vehicle?
Selected biography
In 1831, Faraday began his great series of experiments in which he discovered electromagnetic induction. He established that a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, a relation mathematically modelled by Faraday's law. Faraday later used the principle to construct the electric dynamo, the ancestor of modern power generators. He went on to investigate the fundamental nature of electricity, concluding in 1839 that, contrary to opinions at the time, only a single "electricity" exists, and the changing values of quantity and intensity (voltage and charge) would produce different groups of phenomena.
Some historians refer to Faraday as the best experimentalist in the history of science. Despite this his mathematical ability did not extend so far as trigonometry or any but the simplest algebra. He nevertheless possessed the ability to present his ideas in clear and simple language. During his lifetime, Faraday rejected a knighthood and twice refused to become President of the Royal Society.
In the news
- 20 November 2024 –
- Indian billionaire and Adani Group chairman Gautam Adani is indicted in the U.S. for his role in an alleged multi-billion dollar bribery and fraud scheme where he and seven others paid Indian government officials US$265 million to obtain contracts for Adani Green Energy. (AsiaOne) (Bloomberg)
- 18 November 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Ukrainian energy crisis, 17 November 2024 Russian strikes on Ukraine
- Ukraine re-implements nationwide rolling blackouts primarily due to yesterday's destruction of energy infrastructure by Russian airstrikes. (Reuters)
- 17 November 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russian strikes against Ukrainian infrastructure, Ukrainian energy crisis
- Russia launches its largest aerial attack on Ukraine in months. According to President of Ukraine Volodymyr Zelenskyy, around 120 missiles and 90 drones were launched, damaging energy infrastructure across the country, killing at least seven people, and causing widespread damage. (CNN) (BBC News)
General images
Quotations
- "We simply must balance our demand for energy with our rapidly shrinking resources. By acting now we can control our future instead of letting the future control us." – Jimmy Carter, 1977
- "It is sensible to improve energy efficiency and to develop alternative and sustainable sources of supply; it's sensible to replant the forests which we consume; it's sensible to re-examine industrial processes; it's sensible to tackle the problem of waste. I understand that the latest vogue is to call them 'no regrets' policies. Certainly we should have none in putting them into effect." – Margaret Thatcher, 1990
- "We have the opportunity and potential to create an oil-free future today, it is potentially right around the corner - and, more often than not, the technology is already here." – John Kerry, 2003
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus