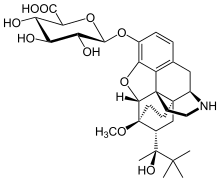
Norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.712 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H43NO10 |
| Molar mass | 589.682 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide (N3G) is a major active metabolite of the opioid modulator buprenorphine.[1] It has affinity for the κ-opioid receptor (Ki = 300 nM) and the nociceptin receptor (Ki = 18 μM), but not for the μ- or δ-opioid receptors.[1] Whether N3G acts as an agonist or antagonist of each of the former two respective sites has yet to be determined.[2] In animals, N3G has been found to produce sedation, decreased locomotion, and a small amount of antinociception, properties which are consistent with the effects of κ-opioid receptor agonists.[1] In addition, N3G has been found to reduce tidal volume but not respiratory rate.[1] Unlike norbuprenorphine, but similarly to buprenorphine and buprenorphine-3-glucuronide, N3G is not a substrate for P-glycoprotein.[2] However, due to its highly hydrophilic nature, N3G nonetheless passes the blood-brain-barrier in only very small amounts.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Brown SM, Holtzman M, Kim T, Kharasch ED (December 2011). "Buprenorphine metabolites, buprenorphine-3-glucuronide and norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide, are biologically active". Anesthesiology. 115 (6): 1251–60. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238fea0. PMC 3560935. PMID 22037640.
- ^ a b c Brown SM, Campbell SD, Crafford A, Regina KJ, Holtzman MJ, Kharasch ED (October 2012). "P-glycoprotein is a major determinant of norbuprenorphine brain exposure and antinociception". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 343 (1): 53–61. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.193433. PMC 3464040. PMID 22739506.
