Niravoline
Appearance
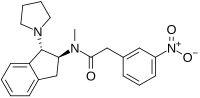
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Methyl-2-(3-nitrophenyl)-N-[(1S,2S)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H25N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 379.460 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Niravoline is a chemical compound with the formula C
22H
25N
3O
3.[1] It has diuretic and aquaretic effects and has been studied for its potential use for cerebral edema[2] and cirrhosis.[3]
It exerts its pharmacological effect as a kappa opioid receptor agonist.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ CID 9821174 from PubChem
- ^ Guéniau, C.; Oberlander, C. (1997). "The kappa opioid agonist niravoline decreases brain edema in the mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 282 (1): 1–6. PMID 9223533.
- ^ Gadano, A.; Moreau, R.; Pessione, F.; Trombino, C.; Giuily, N.; Sinnassamy, P.; Valla, D.; Lebrec, D. (2000). "Aquaretic effects of niravoline, a kappa-opioid agonist, in patients with cirrhosis". Journal of Hepatology. 32 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80187-7. PMID 10673065.
- ^ "Niravoline". NCI Thesaurus. National Cancer Institute.
