Northern Min
| Northern Min | |
|---|---|
| Min Bei | |
| Mâing-bă̤-ngṳ̌/閩北語 | |
| Native to | China |
| Region | Nanping (northwest Fujian) |
Native speakers | 2.5 million (2004)[1] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Kienning Colloquial Romanized (Jian'ou dialect) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | mnp |
| Glottolog | minb1236 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-ha |
 Northern Min | |
 Counties of Nanping prefecture, Fujian | |
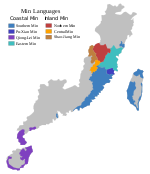
Northern Min (simplified Chinese: 闽北; traditional Chinese: 閩北; pinyin: Mǐnběi) is a group of mutually intelligible[citation needed] Min varieties spoken in Nanping prefecture of northwestern Fujian.
Classification and distribution
[edit]Early classifications of varieties of Chinese, such as those of Li Fang-Kuei in 1937 and Yuan Jiahua in 1960, divided Min into Northern and Southern subgroups.[5][6] However, in a 1963 report on a survey of Fujian, Pan Maoding and colleagues argued that the primary split was between inland and coastal groups.[6][7] In a reclassification that has been followed by most dialectologists since, they restricted the term Northern Min to inland dialects of Nanping prefecture, and classified the coastal dialects of Fuzhou and Ningde as Eastern Min.[8][9]
According to the Language Atlas of China, Northern Min varieties are spoken throughout the counties of Wuyishan (formerly Chong'an), Jianyang, Jian'ou, Zhenghe and Songxi, in the southern part of Pucheng County and the northeastern part of Shunchang County, and in Yanping District except for the Nanping dialect of the urban area of Nanping, which is an island of an isolated Mandarin dialect of uncertain affinity.[10][11] The Jianyang and Jian'ou dialects are often taken as representative.
Although coastal Min varieties can be derived from a proto-language with four series of stop or affricate initials at each point of articulation (e.g. /t/, /tʰ/, /d/ and /dʱ/), Northern Min varieties contain traces of two further series, one voiced and the other voiceless.[12][13][14] In Northern Min dialects, these initials have a different tonal development from other stops and affricates, though the details vary between varieties. Moreover, although in Jian'ou and Zhenghe these initials yield voiceless unaspirated initials (as in coastal varieties), they yield voiced sonorants or the zero initial in Jianyang and Wuyishan.[15] Because of these reflexes, Jerry Norman called these initials "softened" stops and affricates.[16]
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Zhang, Zhenxing, ed. (2012), Language Atlas of China (2nd ed.), City University of Hong Kong, p. 178, ISBN 978-7-10-007054-6.
- ^ Mei, Tsu-lin (1970), "Tones and prosody in Middle Chinese and the origin of the rising tone", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 30: 86–110, doi:10.2307/2718766, JSTOR 2718766
- ^ Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1984), Middle Chinese: A study in Historical Phonology, Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, p. 3, ISBN 978-0-7748-0192-8
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 - Min". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 2023-10-13. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ^ Kurpaska (2010), p. 49.
- ^ a b Norman (1988), p. 233.
- ^ Branner (2000), pp. 98–100.
- ^ Handel (2003), p. 48.
- ^ Kurpaska (2010), p. 52.
- ^ Wurm et al. (1987), Map B12.
- ^ Kurpaska (2010), p. 69.
- ^ Norman (1973), pp. 224–224, 228–229.
- ^ Norman (1988), pp. 228–230.
- ^ Branner (2000), pp. 100–104.
- ^ Handel (2003), p. 56.
- ^ Norman (1973), pp. 228–231.
- Branner, David Prager (2000), Problems in Comparative Chinese Dialectology — the Classification of Miin and Hakka, Trends in Linguistics series, vol. 123, Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, ISBN 978-3-11-015831-1.[permanent dead link]
- Handel, Zev (2003), "Northern Min tone values and the reconstruction of 'softened initials'" (PDF), Language and Linguistics, 4 (1): 47–84.
- Kurpaska, Maria (2010), Chinese Language(s): A Look Through the Prism of "The Great Dictionary of Modern Chinese Dialects", Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 978-3-11-021914-2.
- Norman, Jerry (1973), "Tonal development in Min", Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 1 (2): 222–238, JSTOR 23749795.
- —— (1988), Chinese, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-29653-3.
- Wurm, Stephen Adolphe; Li, Rong; Baumann, Theo; Lee, Mei W. (1987), Language Atlas of China, Longman, ISBN 978-962-359-085-3.
Further reading
[edit]- Akitani, Hiroyuki 秋谷裕幸. 2008. Minbeiqu sanxianshi fangyan yanjiu 閩北區三縣市方言研究. Taipei: Academia Sinica. ISBN 9789860157451 (Documents three Northern Min dialects in detail: Shibei 石陂 of Pucheng County; Zhenqian 镇前 of Zhenghe County; Dikou 迪口 of Jian'ou City)
- Fujian Normal University Research Institute 福建师范学院. n.d. Mindong, Bei fangyan diaocha ziliao huibian (part 1) 闽东、北方言调查资料汇编: 第1辑. Fujian Normal University Research Institute 福建师范学院, Dialectology group, Chinese language department 中文系语言教研组 方言调查小组.
- Huang Chin-wen 黄金文. 2001. 方言接觸與閩北方言演變 / Language contact and the phonological changes in North Min. Taipei: National Taiwan University.
- Ma Chongqi 馬重奇. 2014. 明清閩北方言韻書手抄本音系研究 / A phonological study of the manuscripts of Northern Fujian Dialect rhyme books in the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Beijing: Commercial Press. ISBN 978-7-100-07351-6
- Pan Weishui 潘渭水. 2007. Minbei fangyan yanjiu 闽北方言研究. Fuzhou: Fujian Educational Press 福建教育出版社.
- A Chinese-English dictionary of the Kien-Ning dialect. Foochow: Methodist Episcopal Anglo-Chinese Book Concern. 1901. OCLC 27038682.