List of sovereign states by date of formation
This article possibly contains original research. (July 2019) |
Below is a list of sovereign states with the dates of their formation (date of their independence or of their constitution), sorted by continent.
This list includes the 195 states which are currently member states of the United Nations or non-member observer states with the United Nations General Assembly. This does not include extinct states, but does include several states with limited recognition.[note 1]
For proposed states or various indigenous nations which consider themselves still under occupation, see list of active autonomist and secessionist movements.
Nation-building is a long evolutionary process, and in most cases the date of a country's "formation" cannot be objectively determined; e.g., the fact that England and France were sovereign kingdoms on equal footing in the medieval period does not prejudice the fact that England is not now a sovereign state (having passed sovereignty to Great Britain in 1707), while France is a Republic founded in 1870 (though the term France generally refers to the current French Fifth Republic government, formed in 1958).
Around 60 countries gained independence from the United Kingdom throughout its history, the most in the world, followed by around 40 countries that gained independence from France throughout its history.[2] Over 50% of the world's borders today were drawn as a result of British and French imperialism.[3][4][5]
An unambiguous measure is the date of national constitutions; but as constitutions are an almost entirely modern concept, all formation dates by that criterion are modern or early modern (the oldest extant constitution being that of San Marino, dating to 1600).
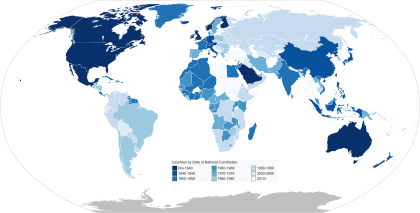
| Pre-1940 1940–1949 1950–1959 | 1960–1969 1970–1979 1980–1989 | 1990–1999 2000–2009 2010–present |
Independence dates for widely recognized states earlier than 1919 should be treated with caution, since prior to the founding of the League of Nations, there was no international body to recognize nationhood, and independence had no meaning beyond mutual recognition of de facto sovereigns (the role of the League of Nations was effectively taken over by the United Nations after the Second World War). See also: disputed territories.
Many countries have some remote (or fantastically remote) symbolic foundation date as part of their national mythology, sometimes artificially inflating a country's "age" for reasons of nationalism, sometimes merely gesturing at a long and gradual process of the formalizing national identity. Such dates do not reflect the formation of a state (an independent political entity).[citation needed]
The following list contains the formation dates of countries with a short description of formation events. For a more detailed description of a country's formation and history, please see the main article for that country.
Africa
[edit]| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 September 1958 | Provisional Government of the Algerian Republic proclaimed | 202 BC | Massinissa unifies Numidia which extended from the Moulouya river in the west to Cyrenaica in the east | 18 March 1845 | Lalla Maghnia treaty between French administration in Algeria and the Sherifian empire, the treaty confirms the Sherifian acquisitions in 1813, the Moulouya river is no longer the border between the two territories and is relocated to Oued Kiss. Algerian territory no longer comprises Oujda and Figuig | |
| 5 July 1962 | Algeria reclaims sovereignty over the entire Algerian territory upon independence from France | |||||
| 1975 | 11 November 1975 | Independence from Portugal | ||||
| 1 March 1960 | 1 August 1960 | Independence from France | 15 January 1894 | Borders of French Protectorate of Dahomey set at conclusion of Second Franco-Dahomean War | ||
| 30 September 1966 | 30 September 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 31 December 1999 | Sedudu ruled to belong to Botswana rather than Namibia by the International Court of Justice. | ||
| 30 September 2022 | Coup d'état | 5 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||
| 28 November 1966 | Monarchy replaced by republic | 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |||
| 5 July 1975 | 5 July 1975 | Independence from Portugal | ||||
| 20 May 1972 | 1 January 1960 | Independence from France | 1 October 1961 | Merger of part of British Cameroons with Cameroon | ||
| 21 September 1979 | Monarchy replaced by republic | 13 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||
| 10 October 2022 | National Transitional Council established | 11 August 1960 | Independence from France | 3 February 1997 | Aouzou Strip awarded to Chad | |
| 6 July 1975 | Independence from France declared | |||||
| 17 May 1997 | 30 June 1960 | Independence from Belgium | ||||
| 15 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 27 June 1977 | Independence from France | |||||
| 18 June 1953 | Egyptian revolution of 1952, Egyptian monarchy overthrown in a military coup, republic declared | 28 February 1922 | The UK ends its protectorate, granting independence to Egypt | 1925 | The eastern borders of Libya and British Egypt are changed to their present boundaries. | |
| 12 October 1968 | Independence from Spain | |||||
| 27 April 1993 | Independence from Ethiopia declared | 1 April 2002 | Badme ruled to be Eritrean by the Eritrea–Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC after the Eritrean–Ethiopian War). Contested by Ethiopia | |||
| 8 February 2006 | Constitution of Eswatini | 6 September 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||
| 21 August 1995 | 1995 Constitution of Ethiopia | 900 | Zagwe dynasty | 1 April 2002 | Badme ruled to be Eritrean by the Eritrea–Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC after the Eritrean–Ethiopian War). Contested by Ethiopia | |
| 17 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 18 February 1965 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 6 March 1957 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 13 December 1956 | Union of British Togoland with Gold Coast | |||
| 2 October 1958 | Independence from France | |||||
| 24 September 1973 | Independence from Portugal declared | |||||
| 10 September 1974 | Independence from Portugal recognized | |||||
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomous republic within French Community | |||||
| 7 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 12 December 1963 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 October 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 12 March 1868 | Area that is now Lesotho placed under British rule | |||
| 26 July 1847 | Independence from American Colonization Society | 6 January 1986 | Current constitution came into effect | |||
| 4 August 2014 | House of Representatives takes power.[note 2] | 24 December 1951 | Independence from UN Trusteeship (British and French administration after Italian governance ends in 1947) | 13 February 1984 | Aouzou Strip awarded to Chad. | |
| 14 October 1958 | The Malagasy Republic was created as autonomous state within French Community | |||||
| 26 June 1960 | France recognizes Madagascar's independence | |||||
| 6 July 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 25 November 1958 | French Sudan gains autonomy | 8 April 1960 | Senegal secedes from Mali Federation | |||
| 22 September 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 28 November 1960 | Independence from France | 11 August 1979 | Mauritania withdraws from Tiris al-Gharbiyya (part of Western Sahara) | |||
| 12 March 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 1965 | Separation of Chagos Archipelago | |||
| 18 November 1955 | Protectorate Abolished | 788 AD | Enthronement of Idris I in Volubilis | 6 November 1975 | Green March | |
| 27 October 1994 | Mozambique holds its first multiparty election since the Civil War | 25 June 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |||
| 21 March 1990 | Independence from South African rule | 1 March 1997 | Walvis Bay integrated into Namibia | |||
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomy within French Community | |||||
| 3 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 1 October 1960 | Independence from the United Kingdom | 15 January 1970 | Biafra re-integrated into Nigeria | |||
| 1 June 1961 | Northern Cameroons integrated in Nigeria | |||||
| 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |||||
| 12 July 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |||||
| 20 August 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 29 June 1976 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 April 1961 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 20 August 2012 | Federal Government of Somalia established.[note 3] | 1 July 1960 | Union of Trust Territory of Somalia (former Italian Somaliland) and State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland) | 18 May 1991 (disputed) | Somaliland declares independence, but is not recognized by any UN state. | |
| 31 May 1961 | Republic declared | 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster, which establishes a status of legislative equality between the self-governing dominion of the Union of South Africa and the UK | 21 March 1990 | De facto: South West Africa declares independence, forming Namibia | |
| 4 February 1997 | The post-Apartheid Constitution of South Africa comes into effect | 31 May 1910 | Creation of the autonomous Union of South Africa from the previously separate colonies of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal and Orange River | 27 April 1994 | De jure: Reincorporation of the nominally independent but unrecognised bantustans into post-apartheid South Africa | |
| 9 July 2011 | 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum | 9 July 2011 | Separation of Southern Sudan from Sudan | |||
| 15 April 2010 | First democratic election since the Second Sudanese Civil War | 1 January 1956 | Independence from Egyptian and British joint rule | 9 July 2011 | South Sudan secedes from Sudan | |
| 1 July 1991 | Amendment to Constitution of Tanzania ends status as one-party state | 9 December 1961 | Independence of Tanganyika from the United Kingdom | 26 April 1964 | Merger of Zanzibar with Tanganyika to form Tanzania | |
| 30 August 1958 | Autonomy within French Union | |||||
| 27 April 1960 | Independence from France | |||||
| 25 July 2022 | 2022 Constitution of Tunisia | 20 March 1956 | Independence from France | |||
| 1 March 1962 | Self-government granted | |||||
| 9 October 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 24 October 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 22 December 1987 | Robert Mugabe revises the Constitution of Zimbabwe to create an executive presidency.[note 4] | 11 November 1965 | Unilateral declaration of independence by Southern Rhodesia | 1901 | BSAC separates North-Eastern Rhodesia from Southern Rhodesia | |
| 18 April 1980 | Recognized independence from the United Kingdom as Zimbabwe |
Americas
[edit]| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 November 1981 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 10 December 1983 | The current Constitution of Argentina enters in force | 25 May 1810 | May Revolution installs first local government | 18 October 1884 | Conquest of the Desert | |
| 9 July 1816 | Argentine Declaration of Independence from Spain. | |||||
| 7 January 1964 | Internal self-governance granted | |||||
| 10 July 1973 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 30 November 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 1 January 1964 | Self-governing colony | 1859 | Treaty establishes border between British Honduras and Guatemala | |||
| 21 September 1981 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 25 January 2009 | Constitution of Bolivia | 6 August 1825 | Bolivian War of Independence from Spain. | 11 November 1903 | Treaty of Petrópolis with Brazil whereby Bolivia gained lands in Mato Grosso in exchange for the territory of Acre | |
| 21 July 1844 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 5 October 1988 | Constitution of Brazil established as the third Federative Republic | 7 September 1822 | Independence from the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves declared | 11 November 1903 | Signing of the Treaty of Petrópolis with Bolivia whereby Brazil was given the territory of Acre in exchange for lands in Mato Grosso | |
| 29 August 1825 | Independence recognized by Portugal | |||||
| 15 November 1889 | Proclamation of the Federal Republic | |||||
| 1 July 1867 | Granted nominal independence (Dominion status), establishing as a federation | 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster | 1 April 1999 | Nunavut Territory created as per native land claims act from two thirds of the area of Northwest Territories. | |
| 17 April 1982 | Constitution Act, 1982 established | |||||
| 17 August 1989 | Amendment to the Constitution of Chile ends the military dictatorship | 18 September 1810 | First Government Junta | 3 July 1929 | Chile awarded Arica district in Treaty of Lima | |
| 12 February 1818 | Chilean Declaration of Independence from Spain | |||||
| 25 April 1844 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 4 July 1991 | Colombian Constitution of 1991 established as a presidential republic. | 20 July 1810 | Colombia declares independence from Spain. | 4 July 1991 | The Sovereign territory was organized under the National Constituent Assembly. | |
| 17 December 1819 | Colombia merged with Venezuela, Panama, and Ecuador. | |||||
| 19 November 1831 | Gran Colombia dissolved creating a pact with Panama as the Republic of New Granada. | |||||
| 22 May 1858 | The Republic of New Granada was replaced to the Granadine Confederation under the 1858 constitution. | |||||
| 8 May 1863 | The Granadine Confederation was replaced to the United States of Colombia under the constitutional change of 1864. | |||||
| 30 January 1881 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 8 August 1886 | Establishment of the current sovereignty of Colombia as a republic. | |||||
| 7 November 1949 | Constitution of Costa Rica | 15 September 1821 | Costa Rica declared independence from Spain | 25 July 1824 | Partido de Nicoya | |
| 15 November 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 10 May 1850 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 1 January 1959 | Cuban Revolution | 10 October 1898 | Several wars were declared against Spain from 1868 to 1898, ending with the military support of USA to the Cuban Revolution. | |||
| 10 December 1898 | Spain loses the war against the United States and the military occupation of Cuba by the U.S. begins. | |||||
| 20 May 1902 | United States military occupation ends[6] | |||||
| 3 November 1978 | Constitution of Dominica | 27 February 1967 | Became an associated state of the United Kingdom | |||
| 3 November 1978 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 28 November 1966 | Civilian constitution of the Dominican Republic following the Dominican Civil War.[note 5] | 27 February 1844 | The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti | 9 May 1936 | Haiti and the Dominican Republic sign a treaty setting a definitive border. | |
| 14 October 1874 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 28 September 2008 | Constitution of Ecuador established. | 10 August 1809 | First declaration of Independence from Spain | 26 February 1946 | Rio Protocol ends border dispute with Peru | |
| 24 May 1822 | Second declaration of independence from Spain of Gran Colombia, of which Ecuador is a part of | |||||
| 13 May 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 16 February 1840 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 16 December 1983 | Constitution of El Salvador established as the third Unitary presidential republic | 15 September 1821 | El Salvador becomes independent from Spain, and 4 months later becomes province in First Mexican Empire | |||
| 1 July 1823 | El Salvador becomes a state of Federal Republic of Central America from the First Mexican Empire | |||||
| 2 February 1841 | Dissolution of the Federal Republic of Central America, El Salvador becomes independent nation | |||||
| 18 February 1841 | El Salvador was internationally recognized. | |||||
| 24 June 1865 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 30 September 1978 | Paul Scoon Takes power after the US Invasion Which Ousted the PRG | 27 February 1967 | Associated state of the United Kingdom | |||
| 7 February 1974 | Full independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 31 May 1985 | Constitution of Guatemala established | 15 September 1821 | Guatemala becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | |||
| 17 April 1839 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America declared | |||||
| 29 May 1863 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 26 May 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| March 1987 | Constitution of 1987 (superseded) | 1 January 1804 | The French colony Saint-Domingue gains independence as Haiti | 27 February 1844 | The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti | |
| 9 May 1936 | Haiti and the Dominican Republic sign a treaty setting a definitive border. | |||||
| 11 January 1982 | Constitution of Honduras. | 15 September 1821 | Honduras becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | 1 September 1972 | Swan Islands returned to Honduras from United States occupation | |
| 26 October 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 17 November 1894 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 6 August 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 7 February 1917 | Constitution of Mexico | 16 September 1810 | Independence from Spain declared | 30 December 1853 | Gadsden Purchase | |
| 27 September 1821 | Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire | |||||
| 28 December 1836 | Declaration of Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 9 January 1987 | Constitution of Nicaragua established | 15 September 1821 | Nicaragua becomes state in Federal Republic of Central America, which declared independence from Spain | |||
| 5 November 1838 | Independence from Federal Republic of Central America | |||||
| 24 July 1850 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 11 October 1972 | Constitution of Panama established | 3 November 1903 | Independence from Colombia | 31 December 1999 | Sovereignty of Panama Canal Zone transferred to Panama from the United States | |
| 10 May 1904 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 20 June 1992 | Democratic Constitution of Paraguay | 14 May 1811 | Independence from Spain declared | 1938 | Paraguay awarded a large portion of the Gran Chaco as a result of the Chaco War | |
| 10 September 1880 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 31 December 1993 | Constitution of Peru established | 28 July 1821 | Independence from Spain declared | 26 February 1942 | Rio Protocol ends border dispute with Ecuador | |
| 14 August 1879 | Independence from Spain recognized | |||||
| 27 February 1967 | Associated state of the United Kingdom | 19 December 1980 | Anguilla separated from Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla | |||
| 19 September 1983 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 February 1967 | Associated statehood | |||||
| 22 February 1979 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 27 October 1969 | Associated statehood | |||||
| 27 October 1979 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 15 December 1954 | Self-government granted | |||||
| 25 November 1975 | Independence from Netherlands | |||||
| 31 August 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 March 1789 | United States Constitution enters into force, replacing the previous Articles of Confederation and creating a new system of government | 4 July 1776 | Declaration of Independence from Great Britain is adopted by the United States Congress | 21 August 1959 | United States Territory: Territory of Hawaii joins the United States as the State of Hawaii | |
| 3 September 1783 | Independence from Great Britain recognized | 7 September 1981 | Insular area: The United States cedes Serrana Bank and Roncador Bank to the Republic of Colombia as a result of a treaty signed in 1972 | |||
| 8 December 1996 | 1996 Uruguayan constitutional referendum | 25 August 1825 | Independence from Empire of Brazil declared, joined in union with United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (current Argentina). | 1861 | Brazil-Uruguay border treaty | |
| 27 August 1828 | Treaty of Montevideo signed, recognizing Uruguay's independence by Brazil | |||||
| 19 July 1870 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 20 December 1999 | New Constitution of Venezuela establishes the Bolivarian Fifth Republic | 19 April 1810[7] | Independence from Spain declared | 3 October 1899 | Tribunal of Arbitration awards most of disputed territory to British Guyana. | |
| 13 January 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 30 March 1845 | Independence recognized by Spain |
Asia
[edit]| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 August 2021 | Fall of Kabul reestablished the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. | 1747 | Durrani Empire | 12 November 1893 | Durand Line Agreement | |
| 21 September 1991 | 2015 Armenian constitutional referendum creates a parliamentary republic | 189 BC | Kingdom of Armenia under Artaxiad dynasty[8] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Armenian SSR | |
| 880 | Evolving as a feudal kingdom in the ninth century, Armenia experienced a brief cultural, political and economic renewal under the Bagratuni dynasty. | |||||
| 21 September 1991 | Independence recognized by the Soviet Union | |||||
| 14 February 2002 | 2002 Constitution of Bahrain | 15 August 1971 | End of treaties with the United Kingdom | 1 July 1521 | Portuguese conquest of current territory | |
| 4 November 1972 | De jure: Constitution of Bangladesh | 26 March 1971 | Independence from Pakistan declared | 31 July 2015 | India and Bangladesh exchange enclaves | |
| February 27, 1991 | De facto: First general election since restoration of parliamentary democracy. | |||||
| 24 March 2008 | First elections to the National Assembly | 1885 | Ugyen Wangchuck ends period of civil war and unites Bhutan | 11 November 1865 | Treaty of Sinchula | |
| 29 September 1959 | De jure: Constitution of Brunei | 1 January 1984 | Brunei regains its independence after an agreement with the British on 4 January 1979 | 18 August 1841 | Kingdom of Sarawak founded | |
| 12 December 1962 | De facto: Martial law declared during the Brunei Revolt, suspending democratic elections indefinitely. | |||||
| 21 September 1993 | Constitution of Cambodia | 802 | Khmer Empire[9] | |||
| 9 November 1953 | France grants Cambodia independence | |||||
| 26 September 1989 | Becomes free from Vietnamese occupation; it gets back its name instead of the People's Republic of Kampuchea | |||||
| 1 January 1912 | A republic was formally established following the Xinhai Revolution, | August 15, 1945 | End of Japanese rule of Taiwan | 20 January 1955 | Loss of Yijiangshan Islands, resulting in the current free area of the Republic of China | |
| 25 December 1947 | The Republic of China adopted its constitution during the National Assembly on 25 December 1947, with further revisions and amendments since 1991 | April 28, 1952 | Treaty of San Francisco came into force | |||
| 1 October 1949 | Proclamation of the People's Republic of China in Beijing | 1600 BC | The Shang dynasty is the earliest dynasty of traditional | 6 October 2011 | Tajikistan ceded 1158 square kilometers of land to China | |
| 4 December 1982 | The People's Republic of China adopted its constitution during the 5th National People's Congress on 4 December 1982, with further revisions about every five years | |||||
| 26 January 1950 | De jure: Constitution of India | 15 August 1947 | Independence from the British Empire | 31 July 2015 | India and Bangladesh exchange exclaves | |
| 321 BC | Emperor Chandragupta Maurya with his mentor and teacher Chanakya unifies India | |||||
| 11 February 1979 | Iranian Revolution ended the monarchy and establishes the Islamic Republic on 11 February 1979 | 2600 BC | Founded by the Elamite | 10 February 1828 | Signing of the Treaty of Turkmenchay, whereby the territories that now constitute Armenia, Azerbaijan (the remaining part which hadn't been lost by the Treaty of Gulistan (1813)), and Iğdır are ceded to Russia | |
| 14 August 1971 | Bahrain's independence from Iran | |||||
| 30 November 1971 | Recapture of Abu Musa and the Greater and Lesser Tunbs | |||||
| 3 December 1979 | the new constitution was approved according to the results of the constitutional referendum of 2 and 3 December 1979 | |||||
| 15 October 2005 | Constitution of Iraq following the Iraq War[note 6] | 762 | The Abbasid Caliphate built the city of Baghdad along the Tigris in the 8th century as its capital, and the city became the leading metropolis of the Arab and Muslim world for five centuries | 28 February 1991 | Kuwait liberated.[note 6] | |
| 3 October 1932 | Kingdom of Iraq | |||||
| 14 May 1948 | Democratic state of Israel. Reading of the Declaration of Independence of Israel | 14 May 1948 | Democratic state of Israel. Reading of the Declaration of Independence of Israel | 14 December 1981 | The Golan Heights Law annexes the Golan Heights, conquered from Syria in the Six-day war to Israel proper; they were administered as a militarily-occupied territory until that point. | |
| 12 September 2005 | The Completion of Israel's unilateral disengagement from the Gaza Strip | |||||
| 22 December 1885 | On December 22, 1885, "Daijo-kan No. 69" were established, and the Cabinet system was established in place of the Daijo-kan system. | 11 February 660 BC | Traditional founding date of the imperial dynasty by Emperor Jimmu. | 15 May 1972 | Return of the Ryukyu Islands to Japan and abolition of the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands | |
| 1 January 1952 | Constitution of Jordan | 25 May 1946 | End of the British Mandate for Palestine | 26 October 1997 | Signing of the Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, whereby most of the disputed 400 square-kilometer area in the Arabah was handed back to Jordan | |
| 12 June 2011 | The Cabinet of Jordan is made an elected body[10] | |||||
| 9 September 1948 | Kim Il-sung declared Premier of North Korea, establishing the still-ruling Kim dynasty. Independence declared from the Soviet Union. | 25 July 918 | Foundation of the Goryeo Dynasty, the exonym Korea originated from the word Goryeo. | 12 October 1962 | Signing of the Sino–Korean Border Agreement with the People's Republic of China | |
| 25 December 1972 | The Constitution of North Korea replaced Communism with Juche as North Korea's governing philosophy.[note 7] | |||||
| 15 August 1948 | First Republic of Korea established, Independence declared from the United States | 27 July 1953 | Cease-fire in the Korean War creates the northern border along the Military Demarcation Line | |||
| 29 October 1987 | Current Sixth Republic of South Korea founded, ending military rule | |||||
| 11 November 1962 | Constitution of Kuwait | 1752 | Establishment of the Sheikhdom of Kuwait | 18 December 1969 | Formal division of Saudi-Kuwaiti neutral zone | |
| 10 June 2010 | Constitution of Kyrgyzstan introduces parliamentary system. | 31 August 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[11] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Kirghiz SSR | |
| 2 December 1975 | Lao PDR formed | 22 October 1953 | Independence from France | |||
| 23 May 1926 | Lebanese Republic formed | 26 November 1941 | Independence from France declared | 1 September 1920 | France establishes State of Greater Lebanon with current boundaries | |
| 22 November 1943 | Independence from France recognized | |||||
| 16 September 1963 | Formation of Malaysia[12][13] | 31 August 1957 | Malayan Independence[14] from the United Kingdom was declared in Dataran Merdeka (Independence Square) | 9 August 1965 | Singapore expelled from the Federation of Malaysia[15][16][17] | |
| 16 September 1963 | Malaysia was formed by the federation of North Borneo, Sarawak and Singapore with the existing States of the Federation of Malaya.[12][18] | |||||
| 11 November 1968 | Declaration of Republic | 26 July 1965 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||
| 12 February 1992 | Constitution of Mongolia declares the country a parliamentary democracy. | 1206 | Mongol Empire formed | |||
| 29 December 1911 | Proclamation of Mongolian independence from Manchu's Qing dynasty | |||||
| 1 February 2021 | The SAC with help from the Tatmadaw overthrows the elected government | 849 | Early Pagan Kingdom formed[19] | 4 January 1948 | Myanmar (Burma) declares independence from the British Empire | |
| 1956 | Signing of border treaty with the People's Republic of China | |||||
| 28 May 2008 | Formation of Republic | 25 September 1768 | Nepali unification | 2 December 1815 | Sugauli Treaty ends the Gurkha War | |
| 10 June 1749 | Beginning of the Al Said dynasty, current absolute monarchical line of Oman. | 26 January 1650 | Expulsion of the Portuguese | 8 December 1958 | Gwadar sold to Pakistan | |
| 1996 | Basic Law of Oman | |||||
| 14 August 1973 | Constitution of Pakistan | 14 August 1947 | Establishment from the Indian Empire after Independence from the British Empire and Partition of India | |||
| 4 May 1994 | Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area | 15 November 1988 | Palestinian Declaration of Independence | 15 June 2007 | Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip | |
| 2 February 1987 | The current form of government was established in 1987, as a compromise between different versions of the previous constitutions and patterned after the 1935 Commonwealth constitution | 12 June 1898 | The evolving revolutionary movement in the Philippines declares itself independent from the Spanish Empire.[20][21][22] Spain regarded this as an expression of continued rebellion.[note 8] This difference in viewpoints was not resolved. | 2012[23][24] | In 2012, the United Nations approved a 2009 claim by the Philippines to the Benham Rise.[24] | |
| 10 December 1898 | Spain, still sovereign,[note 9] cedes the Philippines to the United States via the Treaty of Paris (1898).[25] | |||||
| 4 July 1946 | The United States recognizes Philippine independence under the provisions of the Treaty of Manila (1946). The 1935 Constitution remained in effect until 1973, when the Marcos regime promulgated a newer one, in turn replaced by the present 1987 Constitution. | |||||
| 8 September 1971 | Influence from Britain concluded | 18 December 1878 | Independence from the Ottoman Empire | 4 November 2021 | Acquisition of the rest of Khor Al Adaid[26] | |
| 23 September 1932 | Regions of al-Hasa, Qatif, Nejd and Hejaz unified to become Saudi Arabia | 13 January 1902 | Establishment of the Third Saudi State | 4 November 2021 | Fixed border territory with Qatar | |
| 9 August 1965[15] | Singapore ceased to be a state of Malaysia | 3 June 1959 | Self-government under the United Kingdom | 9 August 1965 | Establishment of Singapore as an independent sovereign state[17] | |
| 9 August 1965 | separate from and independent of Malaysia[15][16] | |||||
| 22 May 1972 | Constitution of Sri Lanka | 4 February 1948 | Independence from United Kingdom | 14 February 1815 | De jure: The Kandyan Kingdom is annexed by British Ceylon | |
| 18 May 2009 | De facto: The Sri Lankan government regains control of the whole island following the end of the Sri Lankan Civil War. | |||||
| 27 February 2012 | Constitution of Syria[note 10] | 28 September 1961 | End of the United Arab Republic | 8 November 1941 | De jure: Lebanon declares independence from the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon[note 10] | |
| 10 June 1967 | De facto: Israel conquers the Golan Heights from Syria during the Six-day War | |||||
| 9 September 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[11] | 5 December 1929 | Establishment of the Tajik SSR | |||
| 6 April 2017 | Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand 2017 | 6 November 1767 | Salvage Independence by King Taksin the Great consist of expulsion of Burmese out of former capital (Through Taksin's reunification of Siam on October-6 November 1767) and Establish a New kingdom together with reunification of Thailand | 10 March 1909 | Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909 | |
| 20 May 2002 | Constitution of East Timor | 20 May 2002 | Independence was recognized by the international community following the UN-sponsored act of self-determination of 1999 | 1914 | The borders of Portuguese Timor are agreed.[27] | |
| 28 September 2008 | Constitution of Turkmenistan | 27 October 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union[11] | 7 August 1921 | Establishment of the Turkmen SSR | |
| 2 December 1971 | End of treaty relationship with the United Kingdom | 11 February 1972 | Ras al-Khaimah joins the UAE | |||
| 31 August 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union declared[11] | 24 October 1924 | Establishment of the Uzbek SSR | |||
| 31 December 1959 | North Vietnam declared a socialist republic | 2 September 1945 | Withdrawal of the Japanese after World War II | 2 July 1976 | Reunification of North Vietnam and South Vietnam as Socialist Republic of Vietnam | |
| 1 January 2014 | Current Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam | |||||
| 22 May 1990 | Unification of North Yemen and South Yemen | 1597 | Qasimid State/Zaidi Imamate[28] | |||
| 1 November 1918 | North Yemen independence from the Ottoman Empire | 21 September 2014 | Houthis seized control of the bulk of the former North Yemen territory and its capital Sana'a | |||
| 30 November 1967 | South Yemen independence from the United Kingdom | 26 April 2020 | Southern Transitional Council declares self-governance of Socotra and some areas controlled by the former PDR Yemen. |
- Table notes
- ^ Taiwan: For some clarification and more detail including the sovereignty status of the Republic of China, see the following articles: Cross-Strait relations, One-China policy and Political status of Taiwan.
- ^ Palestinian National Authority: For some clarification and more detail, see History of the State of Palestine.
- ^ Philippines: For some clarification and more detail, see Timeline of Philippine Sovereignty and Sovereignty of the Philippines.
Europe
[edit]| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 November 1989 | People's Republic of Bulgaria was replaced by the Republic of Bulgaria | 681 on territories of the Eastern Roman Empire | (Danubian) Bulgaria | 28 October 1944 | Under the 1944 Armistice with the Allies, Bulgaria renounces the 1941 annexation of Vardar Macedonia from Yugoslavia and Eastern Macedonia and Western Thrace from Greece. Formally confirmed on 10 February 1947 by Paris Peace Treaties. | |
| 1185 | Second Bulgarian Empire formed | |||||
| 13 July 1878 | Autonomy within Ottoman Empire recognized internationally by the Treaty of Berlin | |||||
| 22 September 1908 | Independence from Ottoman Empire | |||||
| 28 April 1993 | Current Constitution of Andorra entered force | 1278 | Independence from Aragon | 28 August 2001 | The Andorra–France border is adjusted to allow Andorra to construct the Envalira Tunnel access bridge | |
| 12 November 1918 | Declaration of the Republic of German-Austria | 17 September 1156 | Privilegium Minus: Sovereignty from Duchy of Bavaria as a Duchy of the Holy Roman Empire | 14 December 1921 | City of Sopron, and 8 other towns moved to Hungary after plebiscite | |
| 11 August 1804 | Proclamation of the Austrian Empire | |||||
| 27 April 1945 | Restoration of the Republic of Austria | |||||
| 28 November 1996 | Constitutional amendment abolishes the Supreme Soviet and establishes the National Assembly | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | |||
| 27 July 1990 | Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1945 | Western border with Poland: modification of the Curzon Line determined at the 1945 Yalta Conference | |||
| 25 August 1991 | Independence recognized by Soviet Union[11] | |||||
| 21 July 1831 | King Leopold I of Belgium swears allegiance to the constitution making the country a constitutional monarchy | 4 October 1830 | Independence was proclaimed by the provisonial government | 28 June 1919 | Belgian proper: Treaty of Versailles and annexation of the East Cantons | |
| 1 July 1962 | Belgian colonial empire: Ruanda-Urundi declares independence and split within two countries: Rwanda and Burundi. | |||||
| 3 March 1992 | 3 March 1992 | Independence declared from the SFR Yugoslavia[note 11] | 25 November 1943 | Establishment of SR Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia | ||
| 29 April 1991 | Socialist People's Republic of Albania was replaced by the Republic of Albania. | 1190 c. | Principality of Arbër was established by archon Progon. | 1945 | Occupied Kosovo, west Macedonia and border region of Montenegro returned to Yugoslavia | |
| 28 November 1912 | Declaration of independence from Ottoman Empire | |||||
| 28 November 1944 | Albanian state re-established after Italian/German occupation | |||||
| 8 October 1991 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia[note 11] | 879 | Duke Branimir was recognized as an independent ruler of the Duchy of Croatia by Pope John VIII.[29][30][31][32][33] | 10 February 1947 | Annexation of most of Istria to SR Croatia as a result of signing the 1947 Paris Peace Treaties | |
| 925 | Formation of Kingdom of Croatia by King Tomislav | |||||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, creating the Czech Republic and Slovakia | 870 | Formation of the Duchy of Bohemia | |||
| 5 June 1953 | Constitutional Act of Denmark | 965 | Harald Bluetooth unifies Denmark | 15 June 1920 | Denmark proper: Sønderjylland was recovered from Germany.[note 12] | |
| 24 February 1918 | Estonian Declaration of Independence, whereby a republic was declared[Europe 1] | 20 August 1991 | Independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 13] | 1 January 1945 | De facto: Eastern coast of Narva river and most of Petseri County were transferred to Russian SFSR | |
| 29 March 1809 | Diet of Porvoo, birth of Finland as an autonomous state entity within Russian Empire | 6 December 1917 | Independence from Russian Empire declared | 26 January 1956 | Porkkala returned from Soviet control | |
| 3 January 1918 | Independence from Russia recognized by the highest Soviet executive body, VTsIK | |||||
| 4 October 1958 | Establishment of the current semi-presidential system known as the Fifth Republic | 481 then 843 |
First creation with (Clovis), king of the Franks. Then creation of the Kingdom of France (West Francia), Treaty of Verdun | 10 February 1947 | Metropolitan France: Annexation of Tende, La Brigue and other villages formerly in Italy.[note 14][note 15] | |
| 22 September 1792 | French Republic founded. | 30 July 1980 | Overseas France: The New Hebrides Condominium declares independence and becomes Vanuatu. | |||
| 23 May 1949 | The Basic Law of Germany comes into effect. | 843 then
962 |
Creation of East Francia
East Francia becomes the Holy Roman Empire (with the Kingdom of Germany as a main part of the empire) |
3 October 1990 | Reunification of West Germany and East Germany | |
| 1815 | German Confederation founded | |||||
| 18 January 1871 | German Empire founded | |||||
| 1954 | German Democratic Republic (commonly referred to at the time as East Germany) declared fully sovereign | |||||
| 5 May 1955 | Federal Republic of Germany (commonly referred to at the time as West Germany) declared fully sovereign | |||||
| 15 May 1991 | Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany ends the Four Power occupation. | |||||
| 11 June 1975 | Third Hellenic Republic | 600 BC | Peloponnesian League / Spartan Alliance[35] | 10 February 1947 | Peace treaty with Italy awards the Dodecanese to Greece | |
| 478 BC | Delian League / Athenian Empire[36] | |||||
| 338 BC | League of Corinth / | |||||
| 3 February 1830 | Modern Greece Independence recognized by the London Protocol as Kingdom of Greece.[38] | |||||
| 23 October 1989 | People's Republic of Hungary was replaced by the Republic of Hungary. | 895 | Principality of Hungary formed | 10 February 1947 | With the Paris Peace Treaty, Hungary loses all territories that were regained with the First and Second Vienna Awards and during World War II, thus it returns to the 1937 borders (except for three villages in the northwest given to Czechoslovakia). | |
| 1 January 2012 | The Basic Law of Hungary comes into effect. | 1000 | Formation of the Kingdom of Hungary by Stephen I of Hungary. | |||
| 1 July 1845 | The Althingi resumes meeting after hiatus since 1799. | 1 December 1918 | Iceland becomes sovereign and independent from Denmark as the Kingdom of Iceland but retains a personal union with the King of Denmark. | 1 September 1972 | No territorial changes on land have taken place, however the expansion of the Exclusive Economic Zone was such an important change in territory for Iceland that it merits a special inclusion here. | |
| 17 June 1944 | Kingdom of Iceland becomes a Republic. | |||||
| 21 January 1919 | Elected Irish Parliament Dáil Éireann unilaterally declares Ireland's independence from the United Kingdom | 6 December 1922 | Irish Free State secedes from United Kingdom by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty but remains a dominion of the British Empire | 8 December 1922 | De facto: Northern Ireland secedes from the Irish Free State and rejoins the United Kingdom in accordance with the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922 | |
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster confers legislative independence from the United Kingdom | N/A | ||||
| 29 December 1937 | Constitution of Ireland establishes the roles of Taoiseach and President, and replaces the Irish Free State (or Saorstat Eireann in Irish language) with a new state named Ireland (or Éire in Irish language). | 18 April 1949 | Republic of Ireland Act 1948 terminates the functions of the British King in Ireland's diplomatic relations; domestic United Kingdom law purports that Ireland was one of the King's dominions until this date; Irish law does not accept this interpretation. | 2 December 1999 | De jure: Amendment to the Irish constitution removes irredentist claims to Northern Ireland.[note 16] | |
| 2 June 1946 | Italian Republic founded. | 1720 | Sovereignty of the Kingdom of Sardinia, existing since 1324 as part of the Spanish Empire first and subsequently of the Holy Roman Empire. | 1 January 1948 | The Peace treaty with Italy officially determines the boundaries of the Republic of Italy. The Italian Constitution of 1948 implements it at articles 10 and 117. | |
| 17 March 1861 | Italian unification | |||||
| 25 April 1945 | Disestablishment of the German-backed Italian Social Republic, whereby the unity and independence of the Italian state was restored | |||||
| 17 February 2008 | Kosovo Republic founded | 2008 | Kosovan-Serbian War | 2008 | Kosovo War | |
| 7 November 1922 | Constitution of Latvia enforced[Europe 1] | 4 May 1990 | Independence (from Soviet Union) reasserted[note 13] | 1944 | Abrene district ceded to Russian SFSR (modern Russia) | |
| 16 March 2003 | The 2003 Liechtenstein constitutional referendum increases the Prince's powers and makes the country an absolute monarchy[39] | 18 August 1866 | Dissolution of the German Confederation | 23 January 1719 | Purchase of Vaduz | |
| 11 March 1990 | Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 13][Europe 1] | 16 February 1918 | Independence declared from Germany and Russia | 27 October 1939 and 3 August 1940 |
Western part (approximately half) of Vilnius Region ceded to Lithuania | |
| 23 November 1890 | Separates from union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, becomes Grand Duchy in its own right | 1945 | End of German occupation during World War II | 19 April 1839 | Partition of Luxembourg under the Treaty of London | |
| 13 December 1974 | The State of Malta became a republic | 21 September 1964 | Independence from United Kingdom | 20 August 1801 | Gozo rejoined Malta | |
| 27 August 1997 | Constitution of Moldova (1997) | 27 August 1991 | Independence from Soviet Union[11] | 2 August 1940 | De jure: Moldavian SSR formed | |
| 2 September 1990 | De facto: Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic declares independence. The government is not recognized by any UN member, but has de facto control over the Transnistria region. | |||||
| 17 December 1962 | Amendment to Constitution of Monaco curtails the power of the prince and establishes the modern National Council | 1297 | François Grimaldi captures the fortress atop the Rock of Monaco. | 1848 | Secession of Menton and Roquebrune-Cap-Martin. | |
| 22 October 2007 | Constitution of Montenegro | 3 June 2006 | Declaration of independence from Serbia and Montenegro. | |||
| 24 August 1815 | Adoption of the constitution of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. | 26 July 1581 | Plakkaat van Verlatinghe signed, independence from Spain | 16 March 1839 | European Netherlands: The United Kingdom of the Netherlands divided under the Treaty of London (1839). | |
| 15 December 1954 | Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands signed | 5 May 1945 | Surrender of Nazi forces occupying the Netherlands | 25 November 1975 | Kingdom of the Netherlands: Suriname declares independence. | |
(until 2019 Republic of Macedonia) |
17 November 1991 | Constitution of North Macedonia | 8 September 1991 | After a referendum, the Socialist Republic of Macedonia declared independence from Yugoslavia[note 11] | 2 August 1944 | Establishment of SR Macedonia |
| 1814 | Constitution of Norway | 872 | King Harald I of Norway unifies the Petty kingdoms of Norway. | 27 February 1930 | Jan Mayen was made part of the Kingdom of Norway. | |
| 1814 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Denmark. | |||||
| 7 June 1905 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden. | |||||
| 8 May 1945 | German occupying forces surrender. | |||||
| 4 June 1989 | The first partially free Parliament's vote after 45-year-long Soviet domination | 966 | Adoption of Christianity by the first historically documented Polish ruler Mieszko I. | 15 February 1951 | Polish-Soviet border adjustment treaty | |
| 11 November 1918 | Poland regains its independence. | |||||
| 2 April 1976 | Constitution of Portugal | 5 October 1143 | Formation of Kingdom of Portugal by Treaty of Zamora signing. | 6 June 1801 | Continental Portugal: Spain occupies the present day border town of Olivença since the War of the Oranges. | |
| 20 December 1999 | Portuguese Overseas: De facto: Portuguese Macau transferred to the People's Republic of China | |||||
| 20 May 2002 | Portuguese Overseas: De jure: Portuguese Timor, occupied by Indonesia since 1975, officially dissolved to form the independent state of East Timor.[note 17] | |||||
| 22 December 1989 | Romanian Revolution of 1989 | 24 January 1859 | Autonomous Principality of Romania founded; becomes kingdom in 1866 and achieved independence 1878 Ottoman Empire | 10 February 1947 | Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina | |
| 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | |||||
| 1600 | Constitution of San Marino | 3 September 301 | Independence from Roman Empire | 1463 | Added Fiorentino, Montegiardino, Serravalle, and Faetano | |
| 27 April 1992 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia, forming the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[note 11] | 780 | 8th century-Creation of the Principality of Serbia in the Southeastern Europe. | 17 February 2008 (disputed)[40] | The region of Kosovo declared independence unilaterally on 17 February 2008, and is recognized by 97 UN states. Serbia recognizes the government of Kosovo but claims its territory as an Autonomous Province. | |
| 8 June 2006 | Republic of Serbia declared legal successor to Serbia and Montenegro, ending the process of the dissolution of Yugoslavia. | 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | |||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia | 820s | Principality of Nitra formed | |||
| 13 December 1991 | Constitution of Slovenia | 25 June 1991 | Declaration of independence from Yugoslavia[note 11] | 19 February 1945 | Formation of SR Slovenia | |
| 6 December 1978 | Spanish Constitution | 218 BC | The Roman Republic establishes the province of Hispania after the Second Punic War. Hispania is divided into two main provinces, Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior, marking the beginning of Romanization of the Iberian Peninsula. | 26 February 1976 | Spanish Sahara is lost following the Madrid Accords, resulting in the partition of the territory between Mauritania and Morocco. | |
| 568 | The Visigothic king Leovigild unifies the Iberian Peninsula under his rule, defeating the Suebi and establishing the Visigothic Kingdom as the dominant power in the region. This unification is considered the first consolidation of a Christian kingdom across the entire peninsula. | |||||
| 718 | The Battle of Covadonga takes place between the forces of the Umayyad Caliphate and a small group of Christian rebels led by Pelagius of Asturias. The Christian forces achieve victory, establishing the Kingdom of Asturias and initiating the resistance against Muslim rule in the Iberian Peninsula. | |||||
| 1479 | Dynastical unification of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon under the rule of the Catholic Monarchs. The governments, institutions, and legal traditions of each kingdom remained independent of each other; alien laws determined that the national of one kingdom was a foreigner in the other Crowns/States.[41] | |||||
| 1707~1716 | De jure unification of Spain under the Nueva Planta decrees, which abolished the separate laws and institutions of the Crown of Aragon, centralizing power under the Crown of Castile. | |||||
| 1831 | Formal dissolution of the historical crowns and kingdoms, resulting in the de jure creation of the unified Kingdom of Spain.
| |||||
| 1 January 1974 | Instrument of Government | 970 (Or prior) | Eric the Victorious, the first king of Sweden about whom anything definite is known, becomes king. | 29 March 1809 | Loss of Finland to Imperial Russia. | |
| 6 June 1523 | Gustav Vasa elected King of Sweden and marking a definite secession from the Kalmar Union. | |||||
| 12 November 1848 | Foundation of the federal state after Sonderbund war | 1291 | Traditional founding | 4 August 1815 | The canton of Valais joins the Swiss Confederation, following the cantons of Neuchâtel (19 May 1815) and Geneva (6 April 1815). | |
| 7 August 1815 | Restoration of the Ancien Régime (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte. | |||||
| 24 August 1991 | Independence of former Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic from Soviet Union declared.[11] | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | Annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts by Russia | |
| 22 January 1918 | Ukraine declares independence as the Ukrainian People's Republic. | |||||
| 8 December 1922 | The Irish Free State seceded from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922, however Northern Ireland opted to exclude itself from the Irish Free State two days later creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. | 927 | Kingdom of England | 1603 | The Kingdoms of Scotland, England and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots inherited the crowns of England and Ireland; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal and religious institutions.[42][43] | |
| 843 | Kingdom of Scotland
(Devolved Parliament since 1999) | |||||
| 1057[44] then 1165[45] |
Kingdom of Wales then Principality of Wales (Annexed by England in 1542) | |||||
| 1171 then 1542 |
Lordship of Ireland then Kingdom of Ireland | |||||
| 1 May 1707 | Kingdom of Great Britain
(United the parliaments of Scotland and England) |
|||||
| 1 January 1801 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland[46][47][48]
(United the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland) |
6 December 1922 then 8 December 1922 |
Irish Free State secedes from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922. | |||
| 12 April 1927 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
(Updated to current name) |
2 December 1999 | De jure: Removal of the Government of Ireland Act 1920 and implementation of the Northern Ireland Act 1998 removes irredentist claims to the Republic of Ireland | |||
| 1274 | Birth of current form of government the Papal conclave in 1274 | 7 June 1929 | Ratification of the Lateran Treaty, making the Vatican City a sovereign state | 11 February 1929 | Signing of the Lateran Treaty |
- Table notes
- ^ a b c The date of formation of the current states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania is subject to an international dispute. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania all maintain that they were illegally occupied by the Soviet Union, and that the current states are direct continuations of the pre-WWII states, which continued to exist through governments-in-exile. Russia maintains that the current three states are legally distinct entities newly created after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. All three states were admitted the UN as independent nations, not successor states of the USSR. For more information, see State continuity of the Baltic states.
Australia/Oceania
[edit]| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January 1901 | Commonwealth of Australia established as federation. | 1 January 1901 | Independence from United Kingdom. | 16 September 1975 | Papua New Guinea becomes formally independent of Australia | |
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster | |||||
| 3 March 1986 | Australia Act 1986 | |||||
| State in free association with New Zealand with a local prime minister | 4 August 1965 | 1962 autonomy of New Zealand | ||||
| 10 October 1970 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 12 July 1979 | Independence from United Kingdom | 1 October 1975 | Separation of the Gilbert Islands (later Kiribati) and the Ellice Islands (later Tuvalu) | |||
| 1 May 1979 | Constitution and local government established | 21 October 1986 | Compact of Free Association with the United States | |||
| 10 May 1979 | Constitution ratified | 3 November 1986 | Compact of Free Association with the United States | 10 May 1979 | Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae unite to form the Federated States of Micronesia | |
| 31 January 1968 | Independence from Australia and cessation of UN Trust Territory status | |||||
| 6 February 1840 | Treaty of Waitangi where the British Crown established a right to govern from indigenous Māori tribes[49] | 17 January 1853 | Self-Government | 1 June 1962 | Samoa becomes fully independent from New Zealand. It is also the first small-island country in the Pacific to become independent. | |
| 18 April 1856 | Responsible Government | |||||
| 26 September 1907 | Granted nominal independence (Dominion status). | |||||
| 25 October 1926 | Balfour Declaration of 1926 — Great Britain and the Dominions are "autonomous Communities within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs" | |||||
| 27 July 1938 | Governor-General ceases to represent the British Government and becomes the personal representative of the King. | |||||
| 25 November 1947 | Statute of Westminster adopted — Britain loses the power to legislate for New Zealand except by request | |||||
| 10 December 1947 | Full power to amend own constitution | |||||
| 1 December 1967 | Governor-General becomes a New Zealand appointment | |||||
| 1 January 1981 | Republic of Palau created upon adoption of constitution | 1 October 1994 | Emerged from United Nations trusteeship (administered by the United States). | |||
| 1 December 1973 | Self-governing territory | |||||
| 16 September 1975 | Independence from Australia | |||||
| 1 June 1962 | Independence from New Zealand | |||||
| 2 January 1976 | Self-government granted by United Kingdom | |||||
| 7 July 1978 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |||||
| 4 July 1970 | Independence from United Kingdom | 4 December 1845 | Unification of what is now the islands of Tonga by George Tupou I of Tonga | |||
| 1 October 1975 | Separation of Gilbert Islands (later Kiribati) and Ellice Islands (later Tuvalu) | 1 October 1978 | Independence from United Kingdom | 7 February 1979 | Treaty with United States recognizing Tuvaluan control over Funafuti, Nukufetau, Nukulaelae, and Niulakita atolls | |
| 30 July 1980 | Independence from joint British-French condominium[50] |
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification | Most recent significant territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 October 1991 | Declaration of independence from the Soviet Union | 28 May 1918 | Establishment of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic.[11] | 28 April 1920 | Establishment of the Azerbaijan SSR | |
| 4 August 1886 | Creation of the Republic of Colombia | 20 July 1810 | Independence declared from Spain | 3 November 1903 | Separation of Panama from Colombia | |
| 7 August 1819 | Independence recognized by Spain | |||||
| 1830 | Dissolution of Gran Colombia | |||||
| 16 August 1960 | Constitution of Cyprus establishes consocial government. Consociationalism de facto suspended in 1963.[51][52][53] | 16 August 1960 | Independence from United Kingdom | 23 July 1974 | Establishment of the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus | |
| 15 November 1983 (disputed) | Northern Cyprus declares independence. The government has de facto control of the northern part of the island, but is only recognized by Turkey | |||||
| 18 June 1953 | Egyptian revolution of 1952, Egyptian monarchy overthrown in a military coup, republic declared | 28 February 1922 | The UK ends its protectorate, granting independence to Egypt | 1925 | The eastern borders of Libya and British Egypt are changed to their present boundaries. | |
| 22 September 1792 | French Republic founded. | 481 then 843 |
First creation with (Clovis), king of the Franks. Then creation of the Kingdom of France (West Francia), Treaty of Verdun | 10 February 1947 | Metropolitan France: Annexation of Tende, La Brigue and other villages formerly in Italy.[note 18][note 19] | |
| 4 October 1958 | Establishment of the current semi-presidential system known as the Fifth Republic | 30 July 1980 | Overseas France: The New Hebrides Condominium declares independence and becomes Vanuatu. | |||
| 9 April 1991 | Independence from the Soviet Union declared | 1008 | Establishment of the Kingdom of Georgia | 23 July 1992 | Abkhazia unilaterally declared independence | |
| 26 May 1918 | Establishment of Democratic Republic of Georgia[11] | 28 November 1991 | South Ossetia unilaterally declared independence | |||
| 18 August 1945 | Ratification of the Constitution of Indonesia by the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence | 17 August 1945 | Indonesian Declaration of Independence from Netherlands | 20 May 2002 | Independence of East Timor, formerly administered as a province of Indonesia | |
| 27 December 1949 | Independence from the Netherlands recognized | |||||
| 30 August 1995 | Constitution of Kazakhstan | 16 December 1991 | Independence declared from the Soviet Union[11] | 5 December 1936 | Establishment of the Kazakh SSR | |
| 30 March 1993 (disputed) | Baikonur Cosmodrome and surrounding areas leased to Russia.[note 20] | |||||
| 3 November 1903 | Separation of Panama from Colombia, independence from Spain | 1 October 1979 | Panama Canal Zone | |||
| 25 December 1993 | 1993 Russian constitutional referendum replaces the Supreme Soviet with the Federal Assembly and increases presidential power. | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | Annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts by Russia | |
| 25 December 1991 | After the USSR ceased to exist, the Russian Federation became an independent state and was recognized by the international community as the successor state of the USSR. | |||||
| 6 December 1978 | Spanish Constitution | 1479 | Dinastical unification of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon by the Catholic Monarchs. The governments, institutions, and legal traditions of each kingdom remained independent of each other; alien laws (Leyes de extranjeria) determined that the national of one kingdom was a foreigner in the other Crowns/States.[41] | 26 February 1976 | Spanish Sahara is lost following the Madrid Accords. | |
| 1707~1716 | De jure by the Nueva Planta decrees | |||||
| 1831 | Dissolution of crowns and kingdoms and creation de jure, of the unified Kingdom of Spain. | |||||
| 24 June 2018 | 2017 Turkish constitutional referendum comes into effect; Turkey transitions from a parliamentary republic to a presidential republic. | 1299 | Formation of the Ottoman Empire | 29 June 1939 | Republic of Hatay joins Turkey after a public referandum. | |
| 29 October 1923 | The provincial government, formed in 1920, declares the foundation of the Republic of Turkey, as the legal successor state to the Ottoman Empire. |
Sortable list
[edit]In this list, "date of last subordination" refers to the last date of control by an external government. The list shows large groupings associated with the dates of independence from decolonization (e.g. 41 current states gained control of sovereignty from the United Kingdom and France between 1956 and 1966) or dissolution of a political union (e.g. 18 current states gained control of sovereignty from the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia between 1990 and 1992). In other cases, a sovereign state submitted to foreign military occupation or political subjugation for a period of time and later regained its independence (e.g. 6 current states gained control of sovereignty from Nazi Germany between 1944 and 1945).
Dates refer to de facto rule or occupation of the major territory, whether or not legitimized by international recognition.
In a union such as Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union, or the Kalmar Union, one of the constituents can be considered the dominant power – generally where the seat of government was located. The United Kingdom is a particularly complicated case. If England is viewed as the dominant member, then history can be traced from Roman conquest, Saxon invasions, 10th-century unification, and the 1066 Norman Conquest before the union of England and Scotland in 1707. However, if viewed from a Scottish perspective, an unbroken history of sovereignty can be traced from unification in 843 through the 1707 union with England (with a brief annexation by England from 1657 to 1660). Some Scots view the 1707 union as a ceding of sovereignty to England.[55]
There are cases where a state is completely extinguished or abolished without having any successor states. Cases like this occur when, for example, one state is annexed or conquered by another and ceases to exist even in nominal form (i.e. not even a "government in exile" is established). The most recent case in human history is the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), which was completely abolished after the German reunification. Modern Germany is a continuation of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany), it is not a successor state.
The Holy Roman Empire is not considered a state by modern historians, but a political entity bringing together several sovereign states in a confederation.
The concept of sovereign state should not be confused with that of nation (for example there are even stateless nations). This list has the date of creation of current sovereign states but not of nations. The historiography of some nations, such as the Bulgarians, even separates the different states founded by these nations (for example First, Second and Third Bulgarian State)
| Country | Continent | Date of latest territorial change | Acquisition of sovereignty |
Date of last subordination |
Previous governing power | Historical Notes | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | 12 November 1893 | July 1747 (Durrani Empire) | 1796 | 2021–present: 2004–2021: 2002–2004: 1996–2001: 1987–1992: |
Kabul | ||
| Europe | 1945 | 28 Nov 1912 | Nov 1944[56] | 1992–present: 1946–92: 1944–46: 1943–44: 1939–43: |
Tirana | ||
| Africa | 18 March 1845 | 3 July 1962[58] | 3 July 1962[59] | 1962–present: 1830–1962: Part of 1659–1830: De facto Independence of |
Algiers | ||
| Europe | 28 August 2001 | 7 Sep 1278[61][62] | Nov 1944[63] | 1278–present: Principality of Andorra (via Paréage of Andorra; occupied by France 1812–13, 1870, 1914, 1936, 1939, 1944) 987–1278: Part of France |
Andorra la Vella | ||
| Africa | 11 November 1975 | 11 Nov 1975[64] | 11 Nov 1975 | 1992–present: Republic of Angola 1975–1992: People's Republic of Angola (via the Alvor Agreement) 1972–1975: State of Angola (part of the Portuguese Empire) 1951–1972: Overseas Province of Angola (part of the Portuguese Empire) 1575–1951: State of West Africa (part of the Portuguese Empire) The territory of Angola has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Era, hosting a wide variety of ethnic groups, tribes and kingdoms (like the kingdoms of Kongo, Ndongo and Matamba). |
Luanda | ||
| The Americas | 1 November 1981 | 1 Nov 1981[65] | 1 Nov 1981 | 1981–present: 1632–1981: Part of the |
St. John's | ||
| The Americas | 18 October 1884 | 25 May 1810 | 9 July 1816[66] | 1861–present: 1831–1861: |
Buenos Aires | ||
| Asia/Europe | 5 December 1936 | 28 May 1918 | 23 Sep 1991[67] | 1991–present: 1920–1991: |
Yerevan | ||
| Australia | 16 September 1975 | 9 Oct 1942[note 21] | 9 Oct 1942 | 1942–present: 1901–1942: |
Canberra | ||
| Europe | 14 December 1921 | 1156 | 27 Apr 1945[note 22] | World War II Allies |
1955–present: Republic of Austria, a Federal state (via Austrian State Treaty) 1945–55: Allied-occupied Austria 1938–45: Annexed by Nazi Germany 1934–38: Federal State of Austria (client state of Italy) 1919–34: First Republic of Austria (via Treaty of Saint Germain) 1918–19: Republic of German-Austria (via Proclamation of Charles I) 1867–1918: Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, a dual monarchy with Hungary (via Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867) 1866: Austrian Empire 1815–1866: Austrian Empire (In union with other 38 states in the German Confederation) 1806–1815: Austrian Empire 1804–1806: Austrian Empire (State of the Holy Roman Empire) 1457–1804: Archduchy of Austria (State of the Holy Roman Empire) 1156–1457: Duchy of Austria (state of the Holy Roman Empire) |
Vienna | |
| Asia/Europe | 28 April 1920 | 28 May 1918 | 30 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: Republic of Azerbaijan (independence from Soviet Union declared 1991
1920–1991: Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, federated state of the 928–1043: Part of Ziyarid Kingdom |
Baku | ||
| The Americas | 7 January 1964 | 10 July 1973[69] | 10 July 1973 | 1973–present: Commonwealth of the Bahamas, a monarchy in personal union with the United Kingdom (Self-government gained from the United Kingdom in 1964; independence gained on 10 July 1973) 1718–1973: Part of the British Empire as its West Indies 1492–1718: Part of the Spanish Empire 500 to 800–1492: Inhabited by the Lucayans (a Taino people) |
Nassau | ||
| Asia | 1 July 1521 | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | 1971–present: Kingdom of Bahrain 1861–1971: Protectorate of the British Empire by way of the Perpetual Truce of Peace and Friendship |
Manama | ||
| Asia | 31 July 2015 | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | 1972–present: 1971–1972: |
Dhaka | ||
| The Americas | 30 November 1966 | 30 Nov 1966 | 30 Nov 1966 | 1966–present: Barbados 1625–1966: Part of the British Empire as its West Indies |
Bridgetown | ||
| Europe | 1945 | 25 Aug 1991[note 23] | 25 Aug 1991 | 1990–present: Republic of Belarus
1943–1990: Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, a federated state of the Soviet Union (USSR) |
Minsk | ||
| Europe | 1 July 1962 | 4 Oct 1830 | 1945 | 1830–present: Kingdom of Belgium (a Federal state, consisted of three regions and three communities) 1813–1830: Part of the Netherlands 1795–1813: Ruled by France 1713–1795: Austrian Netherlands (collective name of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, held by the Habsburg monarchy) 1581–1714: Spanish Netherlands (collective name of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, held in personal union by the Spanish Crown) |
Brussels | ||
| The Americas | 1859 | 21 Sep 1981[71] | 21 Sep 1981 | 1981–present: Belize Belizean-Guatemalan territorial dispute 1783-1981: 1506-1783: Early colonial period 20000 BC-1506: In the tenth century, Mayan society suffered a severe breakdown. Construction of public buildings ceased, the administrative centres lost power, and the population declined as social and economic systems lost their coherence. Some people continued to occupy, or perhaps reoccupied, sites such as Altun Ha, Xunantunich, and Lamanai, but these sites ceased being splendid ceremonial and civic centres. |
Belmopan | ||
| Africa | 15 January 1894 | 1 Aug 1960 | 1 Aug 1960 | 1990–present: Republic of Benin 1975–1990: People's Republic of Benin 1958–1975: Republic of Dahomey (French self-governing colony) |
Cotonou (De facto) and Porto-Novo (official) | ||
| Asia | 11 November 1865 | 1634 | 1634 | (none) | 1910–1947: protectorate of the Autonomous since at least the 10th century.[72] Unified 1634, after the Battle of Five Lamas. Early history is sketchy, but may have been part of Kamarupa kingdom, and may have been occupied by Tibetan-Mongol forces ca. 10th century.[73] |
Thimphu | |
| The Americas | 11 November 1903 | 6 Aug 1825 | 6 Aug 1825 | 2009–present: Plurinational State of Bolivia 1839–2009: Republic of Bolivia |
La Paz and Sucre | ||
| Europe | 25 November 1943 | 3 Mar 1992 | 3 Mar 1992 | 1997–present: Bosnia and Herzegovina (a Federal state)
1992–1997: Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina |
Sarajevo | ||
| Africa | 31 December 1999 | 30 Sep 1966[74] | 30 Sep 1966 | 1966–present : Republic of Botswana 1885–1966: Part of the British Empire as Bechuanaland Protectorate |
Gaborone | ||
| The Americas | 11 November 1903 | 7 Sep 1822[75] | 29 Aug 1825 (Treaty of Rio de Janeiro) | 1985–Present: 1964–1985: |
Brasília | ||
| Asia | 18 August 1841 | 1 Jan 1984 | 1 Jan 1984 | 1984–present: Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace
1945–1984: Part of the British Empire |
Bandar Seri Begawan | ||
| Europe | 28 October 1944 | 5 Oct 1908[76] | 5 Oct 1908 | 1990–present: 1946–1990: |
Sofia | ||
| Africa | 5 August 1960 | 5 Aug 1960[78] | 5 Aug 1960 | 1984–present: Burkina Faso 1960–1984:Republic of Upper Volta (independent) |
Ouagadougou | ||
| Africa | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | 1966–present: Republic of Burundi 1962–1966: Kingdom of Burundi (independent) |
Bujumbura (De facto) and Gitega (De jure) | ||
| Asia | 9 November 1953 | 9 Nov 1953 | 9 Nov 1953[79] | 1993–present: Kingdom of Cambodia
1992–1993: United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia |
Phnom Penh | ||
| Africa | 1 October 1961 | 1 Jan 1960 | 1 Oct 1961 | Republic of Cameroon
French Cameroons gained independence in 1960; added British Southern Cameroons in 1961. |
Iaundé | ||
| The Americas | 1 April 1999 | 11 Dec 1931[note 24] | 11 Dec 1931 |
1760–1783:
|
Ottawa | ||
| Africa | 5 July 1975 | 5 July 1975 | 5 July 1975[82] | Republic of Cabo Verde 1460–1975: Part of the Portuguese Empire In 1456, Alvise Cadamosto, Antoniotto Usodimare (Venetian and Genoese captains, respectively, in the service of Prince Henry the Navigator) and an unnamed Portuguese captain discovered some of the islands. During the next decade, Diogo Gomes and António de Noli (also captains in the service of Prince Henry) discovered the remaining islands of the archipelago.[citation needed] When they first landed in Cape Verde, the islands were barren of people but not of vegetation. |
Praia | ||
| Africa | 13 August 1960 | 13 Aug 1960 | 13 Aug 1960 | Central African Republic 1903–1960: Ubangi-Shari, part of the French Equatorial Africa, federation of colonial possessions of the French Empire |
Bangui | ||
| Africa | 3 February 1997 | 11 Aug 1960 | 11 Aug 1960 | 1960–present: Republic of Chad
1900–1960: French Chad, part of the French Equatorial Africa, federation of colonial possessions of the French Empire |
N'Djamena | ||
| The Americas | 3 July 1929 | 12 Feb 1818[note 25] | 12 Feb 1818 | 1990–Present: 1973–1990: |
Santiago | ||
| Asia | 6 October 2011[note 26] | 1600 BC c. (Shang dynasty)[note 27] | 2 September 1945 |
1949–present: The PRC government in Beijing considers itself the successor of the Republic of China (1912–1949) which legally inherited the whole of China from the Qing dynasty. The ROC government in Taipei denies the legitimacy of the PRC and considers itself the sole legitimate government of the whole of China. |
Beijing | ||
| The Americas | 4 July 1991 | 20 July 1810 | 7 Aug 1819 | 1886–present: 1863–1886: |
Bogotá | ||
| Africa | 6 July 1975 | 6 July 1975 | 6 July 1975 | 2001–present:Union of the Comores (a Federal state) 1975–2001: Federal and Islamic Republic of Comoros |
Moroni | ||
| Africa | 30 June 1960 | 30 June 1960 | 30 June 1960 |
1997–present: |
Kinshasa | ||
| Africa | 15 August 1960 | 15 Aug 1960 | 15 Aug 1960 |
1992–present: |
Brazzaville | ||
| Australia | 4 August 1965 | 1965 | 4 Aug 1965 | 1965–present: 1893-1965: 1858-1893: 1893-1901: Federation of Cook Islands 950-1865: part of the Tui'Tonga Empire 900-1200 500-1200: Polynesian culture |
Avarua | ||
| The Americas | 25 July 1824 | 14 Nov 1838 | 1838 | 1948–present: 1848–1948: |
San José | ||
| Europe | 10 February 1947 | 8 Oct 1991[29][30][31][32][33] | 8 Oct 1991 | 1991–present: 1945–1991: Federated state of the |
Zagreb | ||
| The Americas | 12 June 1901 | 20 May 1902 | 2 February 1909 | 1959–present: Republic of Cuba, sovereign communist state 1934–1959: Republic of Cuba, sovereign capitalist state |
Havana | ||
| Europe | 15 November 1983 (disputed) | 16 Aug 1960 | 16 Aug 1960 | 1960–present: 1878–1960: |
Nicosia | ||
| Europe | 1 January 1993 | 870 | 1 Jan 1993 | 1993–present: Czech Republic 1945–1993: Part of the Czechoslovakia (interrupted by Warsaw Pact armies in 1968) |
Prague | ||
| Europe | 15 June 1920 | 714[84] | 5 May 1945 | 2022: The sovereignty of Hans Island is partitioned between Denmark and Canada
2014: Denmark submits a claim for the North Pole to the UN |
Copenhagen | ||
| Africa | 27 June 1977 | 27 June 1977 | 27 June 1977 | 1977–present: Republic of Djibouti 1894–1977: Part of the French Colonial Empire as French Somaliland |
Djibouti | ||
| The Americas | 27 February 1967 | 3 Nov 1978 | 3 Nov 1978 | 1978–present: Commonwealth of Dominica 1763–1978: Part of the British Empire as its West Indies c.1690–1763: Part of the French Empire The island was originally inhabited by the Kalinago. |
Roseau | ||
| The Americas | 9 May 1936 | 27 Feb 1844[note 28] | 27 Feb 1844 | 1844–present: Dominican Republic 1822–1844: Part of the Republic of Haiti |
Santo Domingo | ||
| The Americas | 26 February 1946 | 13 May 1830 | 13 May 1830 | 1830–present: 1824–1830: |
Quito | ||
| Africa/Asia | 1925 | 28 Feb 1922[note 29] | 28 Feb 1922 | 1971–present: 1958–1971: Since 598,000 BC humans have been settled starting within a 30-metre (100 ft) terrace, with primitive Acheulean and Abbevillian (Chellean).[85] |
Cairo | ||
| The Americas | 2 February 1841 | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 |
1982–present: |
San Salvador | ||
| Africa | 12 October 1968 | 12 Oct 1968 | 12 Oct 1968 | 1968–present: Republic of Equatorial Guinea 1979: 1979 coup d'état 1778–1968: Part of the Spanish Empire 1640-1902: Aro Confederacy Equatorial Guinea was Spanish Guinea (Spanish Cameroons) |
Malabo | ||
| Africa | 1 April 2002 | 24 May 1993 | 24 May 1993 | 1993–present: State of Eritrea 1952–1993: Part of Ethiopia |
Asmara | ||
| Europe | 1 January 1945 | 24 Feb 1918[86] | 20 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: Republic of Estonia 1940–1991: Occupation by the Soviet Union (1940–1941), Germany (1941–1944) and again by the Soviet Union (1944–1991) |
Tallinn | ||
| Africa | 6 September 1968 | 6 Sep 1968 | 6 Sep 1968 | 2018–present: Kingdom of Eswatini 1968–2018: Kingdom of Swaziland
|
Lobamba (royal and legislative) and Mbabane (administrative) | ||
| Africa | 1 April 2002 | 900 c. (Zagwe Kingdom)[note 30] | 5 May 1941 | 1995–present: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (a Federal state, constituted by 10 regional states and 2 chartered cities) 1991–1995: Transitional Government of Ethiopia |
Addis Ababa | ||
| Australia | 10 October 1970 | 10 Oct 1970 | 10 Oct 1970 | 1987–present: Republic of Fiji 1970–1987: Dominion of Fiji 1874-1970: Colony of Fiji 1871–1874: Kingdom of Fiji The Kingdom of Fiji was the first unified Fijian state, and it covered all of modern Fiji, except the island of Rotuma. Cakobau was the Vunivalu (Warlord or Paramount Chief) of the island of Bau. His father, Tanoa Visawaqa, had conquered the Burebasaga Confederacy but never subdued western Fiji. Cakobau controlled most of the eastern parts of the Fijian Islands and declared himself King of Fiji (Self-proclaimed Tui Viti). This met with opposition from other chiefs, who regarded him as at best first among equals. However, in June 1871, John Bates Thurston, the British honorary consul, persuaded the Fijian chiefs to accept a constitutional monarchy with Cakobau as the King, but with real power in the hands of a cabinet and legislature dominated by Australian settlers. The Legislative Assembly met for the first time in Levuka in November 1871. 900 BC: Discovery of Fiji The majority of Fiji's islands were formed through volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Today, some geothermic activity still occurs on the islands of Vanua Levu and Taveuni. Fiji was settled first by the Lapita culture, around 1,500–1,000 years BC, followed by a large influx of people with predominantly Melanesian genetics about the time of the beginning of the Common Era. Europeans visited Fiji from the 17th century, and, after a brief period as an independent kingdom, the British established the Colony of Fiji in 1874. Fiji was a Crown colony until 1970, when it gained independence as the Dominion of Fiji. A republic was declared in 1987, following a series of coups d'état. |
Suva | ||
| Europe | 26 January 1956 | 6 Dec 1917 | 4 Jan 1918 | 1919–present: Republic of Finland 1918–1919: Kingdom of Finland 1809–1917: Grand Duchy of Finland, Governorate-General of the Russian Empire |
Helsinki | ||
| Europe | 30 July 1980 | 481 | 1944 | 1958—Present: 1946–1958: Note: The French Colonial Empire was founded by the order of Francis I of France. In 1534, Francis sent Jacques Cartier to explore the St. Lawrence River in Quebec. |
Paris | ||
| Africa | 17 August 1960 | 17 Aug 1960 | 17 Aug 1960 | 1960–present: Gabonese Republic 1910–1960: Part of the French Equatorial Africa, federation of colonial possessions of the French Empire |
Libreville | ||
| Africa | 18 February 1965 | 18 Feb 1965 | 18 Feb 1965 | 1970–present: Republic of The Gambia 1965–1970: Gambia (monarchy) |
Banjul | ||
| Asia/Europe | 23 July 1992 | 26 May 1918 | 9 Apr 1991 | 1991–Present: Republic of Georgia 1921–1991: Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, a federated state of the Soviet Union 1918–1921 : Democratic Republic of Georgia 1801–1918: Part of the Russian Empire 1490–1801 Fragmentized into three independent kingdoms – Kartli, Kakheti, and Imereti and five semi-independent principalities – Odishi, (Mingrelia), Guria, Abkhazia, Svaneti, and Samtskhe 1008–1490: Kingdom of Georgia |
Tbilisi | ||
| Europe | 3 October 1990 | 1 July 1867 (North German Confederation) | 15 Mar 1991 | 1990–Present: 1949–1990: Divided between |
Berlin | ||
| Europe | 10 February 1947 | 25 Mar 1822 | 1945 | 1974–Present: 1967–1974: |
Athens | ||
| Africa | 13 December 1956 | 6 May 1957 | 6 May 1957 | 1957–Present: Republic of Ghana 1867–1957: British Gold Coast |
Accra | ||
| The Americas | 27 February 1967 | 7 Feb 1974 | 7 Feb 1974 | 1974–present: Grenada 1783–1974: Part of the British Empire, as its West Indies |
St. George's | ||
| The Americas | 1859 | 17 Apr 1839 | 17 Apr 1839 | 1922–present: 1921–1922: |
Guatemala City | ||
| Africa | 2 October 1958 | 2 Oct 1958 | 2 Oct 1958 | 1958–present: Republic of Guinea
1894–1958: French Guinea, part of the French West Africa, part of the French Empire |
Conakry | ||
| Africa | 24 September 1973 | 24 Sep 1973 | 10 Sep 1974 | 1974–present: Republic of Guinea-Bissau
1474–1974: Portuguese Guinea Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and Algarves 1226-1474: Mali Empire |
Bissau | ||
| The Americas | 26 May 1966 | 26 May 1966 | 26 May 1966 | 1970–present: Co-operative Republic of Guyana
1966–1970: Guyana (monarchy) |
Georgetown | ||
| The Americas | 27 February 1844 | 1 Jan 1804 | 1 Jan 1804 | 1859–present: Republic of Haiti
1849–1859: Second Empire of Haiti |
Port-au-Prince | ||
| The Americas | 1 September 1972 | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 | 1922–present: 1921–1922: Federated state of the |
Tegucigalpa | ||
| Europe | 10 February 1947 | 895 | 1918 23 Oct 1989 |
1989–present: Third Hungarian Republic 1949–1989: Hungarian People's Republic |
Budapest | ||
| Europe | 1 December 1918 | 1 Dec 1918 | 1 Dec 1918 | 1945–present: Republic of Iceland
1944–1945: Republic of Iceland (occupied by the United States)
1918–1944: Kingdom of Iceland, with a personal union with Denmark (Occupied by the United Kingdom and Canada in 1940 and 1941 and by the United States in 1941–1944)
1814–1918: Part of the Kingdom of Denmark
1523–1814: Part of Denmark-Norway, a real union between the kingdoms of Norway and Denmark |
Reykjavík | ||
| Asia | 31 July 2015 | 15 Aug 1947 | 15 Aug 1947 | 1950–present: 1947–1950: Since 2.2 million BC, India has been settled starting with Hominins who were from Africa by the expansion of civilization with the Madrasian and Soanian cultures.[91]: 147 [92][93]: 167–170 |
New Delhi | ||
| Asia/Australia | 20 May 2002 | 17 Aug 1945 | 27 Dec 1949 | 1949–present: Republic of Indonesia
1945–1949: Indonesian Struggle for Independence |
Jakarta | ||
| Asia | 30 November 1971 | 1501 (Safavid Empire)[note 32] | 17 October 1941 | Anglo-Soviet withdrawal from Tehran |
1980–present: Islamic Republic of Iran
1979–1980: Under an Interim Government |
Tehran | |
| Asia | 28 February 1991 | 3 Oct 1932 | 1 May 2003 | 2003–present: 2003: American Invasion[94] |
Baghdad | ||
| Europe | 2 December 1999 | 11 Dec 1931[note 33] | 11 Dec 1931 | 1937–Present: 1931–1937: |
Dublin | ||
| Asia | 12 September 2005 | 14 May 1948 | 14 May 1948 | The 12 tribes conquer the holy land under the leadership of Joshua, then Israel goes through "The period of the judges" leading to the Kingdom of Israel unified under King Saul, c. 1020 BC, divided into separate kingdoms of Israel and Judea, which fall to Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires in 722 and 586 BC, respectively. In the 2nd century BC, Judea re-gains independence as Hasmonean kingdom after revolt against the Hellenist Seleucid Empire. Conquered by Pompey of the Roman Empire in 63 BC, and subsequently falls to Byzantine, Umayyad, Abbasid, Crusader, Mamluk, Ottoman Turkish, and British rule, before regaining independence as the State of Israel in 1948. | Jerusalem | ||
| Europe | 1 January 1948 | 1003 (County of Savoy) | 17 May 1861 | 1946–present: 1945–1946: |
Rome | ||
| Africa | 4 December 1958 | 7 Aug 1960 | 7 Aug 1960 | 1960–present 1886–1962: Part of the |
Abidjan (former capital; still hosts some government offices) and Yamoussoukro (de jure) | ||
| The Americas | 6 August 1962 | 6 Aug 1962 | 6 Aug 1962 | 1962–present: Jamaica 1707–1962: Part of the British Empire |
Kingston | ||
| Asia | 15 May 1972 | 539 c.[note 34]. | 28 Apr 1952 | 1952–present: 1945–1952: |
Tokyo | ||
| Asia | 26 October 1997 | 25 May 1946 | 2 Aug 1958 | 1958–present: Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
Feb–Aug 1958: Federated state of the Arab Federation, governed from Baghdad, Iraq. |
Amman | ||
| Asia/Europe | 30 March 1993 (disputed) | 16 Dec 1991 | 16 Dec 1991 | 1991–present: Republic of Kazakhstan 1936–1991:Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, federated state of the Soviet Union
|
Astana | ||
| Africa | 12 December 1963 | 12 Dec 1963 | 12 Dec 1963 | 1964–present: Republic of Kenya
1963–1964: Kenya (monarchy) |
Nairóbi | ||
| Australia | 1 October 1975 | 12 July 1979 | 12 July 1979 | 1979–present: Republic of Kiribati 1877-1976: British Western Pacific Territories 1892–1976: Gilbert and Ellice Islands, part of the British Empire 600 BC-1892: Pre-Colonial Kiribati The islands which now form the Republic of Kiribati have been inhabited for at least seven hundred years, and possibly much longer. The initial Austronesian peoples’ population, which remains the overwhelming majority today, was visited by Polynesian and Melanesian invaders before the first European sailors visited the islands in the 17th century. For much of the subsequent period, the main island chain, the Gilbert Islands, was ruled as part of the British Empire. The country gained its independence in 1979 and has since been known as Kiribati. |
Tarawa do Sul | ||
| Europe | 17 February 2008 | 17 Feb 2008 | 17 Feb 2008 | 2008–present: Kosovo
North Kosovo crisis (2011–2013) Clashes between the Republic of Kosovo and ethnic Serbs in northern Kosovo began on 25 July 2011. Second Republic of Kosovo 2008 Kosovo Declaration of Independence First Republic of Kosovo
1992-2006: Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija 1992-2006: Federal Republic of Yugoslavia 1945-1992: Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo
1928-1939: Kingdom of Albania
German Occupation of Albania Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia 1918-1941: Kingdom of Yugoslavia First Balcan War
1882-1918: Kingdom of Serbia 1455-1912: Ottoman Kosovo 1387-1478: Principality of Dukagjini 1402-1459: Serbian Despotate
1371-1402: Moravian Serbia 1371-1412: District of Brancovíc
1346-1371: Serbian Empire 1217-1346: Dardani Peoples 400 BC-28 BC: Kingdom of Dardania The Dardani were the most stable and conservative ethnic element among the peoples of the central Balkans, retaining an enduring presence in the region for several centuries. |
Pristina | ||
| Asia | 12 October 1962 | 9 Sep 1948 | 9 Sep 1948 | 1948–present: 1945–1948: Occupied by the |
Pyongyang | ||
| Asia | 27 July 1953 | 15 Aug 1948 | 15 Aug 1948 | 1987–present: 1981–1987: |
Seoul | ||
| Asia | 18 December 1969 | 1752 | Feb 1991 | 1991–present: State of Kuwait 1990–1991: Kuwait Governorate, governorate of Iraq |
Kuwait City | ||
| Asia | 5 December 1936 | 31 Aug 1991 | 31 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: Kyrgyz Republic (the name "Republic of Kyrgyzstan" was adopted in 1990, changed to current in 1993) 1936–1991: Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic, federated state of the Soviet Union |
Bishkek | ||
| Asia | 22 October 1953 | 22 Oct 1953 | 22 Oct 1953 | 1975–present: Lao People's Democratic Republic
1953–1975: Kingdom of Laos, independent state |
Vientiane | ||
| Europe | 1944 | 18 Nov 1918[101] | 4 May 1990 | 1991–present: Republic of Latvia 1940–1991: Occupation by Germany (1940–1944) and later by the Soviet Union (1944–1991) |
Riga | ||
| Asia | 1 September 1920 | 22 Nov 1943 | 31 Dec 1946 | 1920–1943: |
Beirut | ||
| Africa | 12 March 1868 | 4 Oct 1966 | 4 Oct 1966 | 1966–present: 1884–1966: |
Maseru | ||
| Africa | 6 January 1986 | 26 July 1847 | 26 July 1847 | American Colonization Society | 1847–present: Republic of Liberia 1980-1984: People's Redemption Council 1980 coup d'etat 1821–1847: Settled but not claimed by the United States[102] 1834-1857: Republic of Maryland 1822-1847: Colony of Liberia |
Monrovia | |
| Africa | 13 February 1984 | 24 Dec 1951[103] | 24 Dec 1951 | 2011–present: 1977–2011: |
Tripoli | ||
| Europe | 23 January 1719 | 18 August 1866 | 18 August 1866 | 1866–present: Liechtenstein
1866: Dissolution of the German Confederation |
Vaduz | ||
| Europe | 3 August 1940 | 16 Feb 1918 | 11 Mar 1990 | 1991–present: Republic of Lithuania 1940–1991: Occupation by Germany (1940–1944) and later by the Soviet Union (1944–1991) |
Vilnius | ||
| Europe | 19 April 1839 | 15 Mar 1815 | 1945 | 1890–present: Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, independent state with its own dynasty 1866–1890: Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, independent state in personal union with Netherlands |
Luxembourg | ||
| Africa | 14 October 1958 | 26 June 1960 | 26 June 1960 | 2014–present: Republic of Madagascar (Fourth Republic) 2009–2014: High Transitional Authority |
Antananarivo | ||
| Africa | 6 July 1964 | 6 July 1964 | 6 July 1964 | 1964–present: Republic of Malawi 1963–1964: Nyasaland, part of the British Empire |
Lilongwe | ||
| Asia | 9 August 1965 | 31 Aug 1957[14] | 31 Aug 1957 | The Federation of Malaya gained independence in 1957; in 1963 it added territories of Sabah, Sarawak and Singapore, and changed its name to Malaysia (a federal state).[52] Singapore became independent in 1965.
|
Kuala Lumpur (de jure, legislative and royal) and Putrajaya (administrative and judicial) | ||
| Asia | 26 July 1965 | 26 July 1965 | 26 July 1965 | Unified according to legend by King Koimala (1117–1141).
Independent sultanate until 1887, when it became a British protectorate. |
Malé | ||
| Africa | 8 April 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | 1960–present: Republic of Mali 1959–1960: part of Mali Federation, a territory with self-rule within the French Community, governed from Dakar, Senegal. |
Bamako | ||
| Europe | 20 August 1801 | 21 Sep 1964 | 21 Sep 1964 | 1974–present: Republic of Malta
1964–1974: State of Malta |
Valletta | ||
| Australia | 1 May 1979 | 21 Oct 1986 | 21 Oct 1986 |
1986–present: Republic of the Marshall Islands (independent state) |
Majuro | ||
| Africa | 11 August 1979 | 28 Nov 1960 | 28 Nov 1960 | 1960–present: Islamic Republic of Mauritania 1903–1960: Colony of Mauritania, part of the French West Africa (a federation of French colonial territories), part of the French Empire |
Nouakchott | ||
| Africa | 1965 | 12 Mar 1968 | 12 Mar 1968 | 1992–present: Republic of Mauritius 1968–1992: Mauritius, independent state (monarchy) |
Port Louis | ||
| The Americas | 30 December 1853 | 16 Sep 1810 | 1864 | 1867–Present: 1864–1867: |
Mexico City | ||
| Australia | 10 May 1979 | 3 Nov 1986 | 3 Nov 1986 | 1979–present: 1947–1979: 1919–1947: 1914–1919: 1899–1914: Part of 1574–1899: Part of the |
Palikir | ||
| Europe | 2 September 1990 | 27 Aug 1991 | 27 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: 1940-1991: 1941-1944: 1917-1918: 1346-1859: |
Chișinău | ||
| Europe | 1848 | 2 Feb 1861 | 1945 | 1911–present: Monaco
1911: Constitution of Monaco Sixth Coalition 1814: part of French Empire 1297-1814: House of Grimaldi (under the sovereignty of the Republic of Genoa) Grimaldi Man Grimaldi Manis the name formerly given to two human skeletons of the Upper Paleolithic discovered in Italy in 1901. The remains are now recognized as representing two individuals, and are dated to ca. 26,000 to 22,000 years ago (i.e. c. 24000–20000 BC) and classified as part of the wider Early European modern humans population of the late Aurignacian to early Gravettian. |
Monaco | ||
| Asia | 29 December 1911 | 29 Dec 1911 | 13 Mar 1921 | 1990-present: Mongolia
Modern Mongolia
Mongolian Revolution of 1990
1945: Inner Mongolian People's Republic was a state in Inner Mongolia founded shortly after the Second World War. It existed from 9 September 1945 until 6 November 1945 ᠪᠦᠭᠦᠳᠡ ᠨᠠᠶᠢᠷᠠᠮᠳᠠᠬᠤ ᠥᠪᠥᠷ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠠᠷᠠᠳ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ
1924-1992: Mongolian People's Republic Outer Mongolia gained independence from Qing China in 1911, and enjoyed brief autonomy before it was seized by the Republic of China in 1919. After a Soviet-backed revolution in 1921, the Mongolian People's Republic was established in 1924.
Mongolian Revolution of 1921
1919-1921: Chinese Mongolia ᠭᠠᠳᠠᠭᠠᠳᠤ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ 1911-1919: Bogd Khanate of Mongolia 1691-1911: Qing Dynasty 1634-1757: Dzungar Khanate 1399-1634: Oirat Confederation 1368-1635: Northern Yuan 1271-1368: Yuan Dynasty 1206-1368: Mongol Empire The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the more famous title of Genghis Khan (c. 1162 – 1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the East with the West, and the Pacific to the Mediterranean, in an enforced Pax Mongolica, allowing the exchange of trade, technologies, commodities, and ideologies across Eurasia. 1130-1206: Khamag Mongol 9th-12th century: Mongol khanates 907-1125: Liao Dynasty 744-840: Uyghur Khaganate 647-682: Protectorate General to Pacify the North 628-646: Xueyantuo 682-744: Second Turkic Khaganate (Celestial Turks were a Turkic people in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his sons, succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the main power in the region and established the First Turkic Khaganate, one of several nomadic dynasties that would shape the future geolocation, culture, and dominant beliefs of Turkic peoples) 330-555: Rouran Khaganate 93-234: Xianbei State 209 BC-93 AD: Xiongnu 600-300 BC: Pazyryk Culture 700-300 BC: Chandman Culture 1100-300 BC: Slab-grave Culture 1400-700 BC: Deer stones Culture 1450-1150 BC: Ulaanzuukh Culture 1500-1000 BC: Sagsai Culture 1800-1600 BC: Munkhkhairkhan culture 2750-1900 BC: Chemurchek Culture 330-2500 BC: Afanasievo Culture |
Ulaanbaatar | ||
| Europe | 3 June 2006 | 21 May 2006[note 35] | 21 May 2006 (independence referendum) June 3, 2006 |
2006–present: Montenegro 2003–2006: Part of the union of Serbia and Montenegro 1992–2003: Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (with Serbia) 1945–1991: Part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia 1943–1945: Occupied by Nazi Germany 1941–1943: Occupied by the Kingdom of Italy 1918–1941: Part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia (Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes) 1910–1918: Kingdom of Montenegro 1852–1910: Principality of Montenegro 1516–1852: Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro 1499–1516: Part of the Ottoman Empire 1356–1499: Principality of Zeta 1346–1356: Part of the Serbian Empire 1217–1346: Part of the Kingdom of Serbia 1186–1217: Part of the Grand Principality of Serbia 1077–1186: Kingdom of Duklja 843–1077: Principality of Duklja 625–843: Duklja (vassal state of the Byzantine Empire) |
Podgorica | ||
| Africa | 6 November 1975 | 788[104] | 7 Apr 1956 | 1955–present: 1912–1956: |
Rabat | ||
| Africa | 25 June 1975 | 25 June 1975 | 25 June 1975 | Portuguese colony from 1498 to 1975. | Maputo | ||
| Asia | 4 January 1948 | 4 Jan 1948 | 4 Jan 1948 | Pagan Kingdom founded 849. Occupied by Japan 1942–1945 | Naypyidaw | ||
| Africa | 1 March 1997 | 21 Mar 1990 | 21 Mar 1990 | German colony from 1884; governed by South Africa 1915–1990 | Windhoek | ||
| Australia | 31 January 1968 | 31 Jan 1968 | 31 Jan 1968 | Previously occupied by Germany 1888, Australia 1914, Japan 1942–45, | Yaren | ||
| Asia | 2 December 1815 | 1559 c. (Gorkha Kingdom) | 1768 (Unification of Nepal) | (none) | 1816–1923: protectorate of the Autonomous throughout its recorded history, and certainly since its 1768 unification.[105] The ancient Maurya Empire occupied southern Nepal, but not the core Kathmandu valley.[citation needed] |
Kathmandu | |
| Europe | 25 November 1975 | 26 July 1581 (de facto) 30 Jan 1648 (de jure) |
1945 |
1945–present: Note: The Dutch Empire was created in 1602, after the foundation of the Dutch East India Company, in the government of the stadtholder Maurice, Prince of Orange. |
Amsterdam | ||
| Australia | 1 June 1962 | 25 Nov 1947[note 36] | 25 Nov 1947 | 1947–present: Realm of New Zealand, a monarchy in a personal union with the United Kingdom.[107][108] New Zealand (a sovereign state) has one Antarctic territorial claim (the Ross Dependency), one dependent territory (Tokelau), and two associated states (the Cook Islands and Niue) 1907–1947: Dominion of New Zealand, a Dominion within the British Empire |
Wellington | ||
| The Americas | 1930[109] | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 | 1898–Present: 1896–1898: Federated state of the |
Managua | ||
| Africa | 4 December 1958 | 3 Aug 1960 | 3 Aug 1960 | Became part of 1804-1903: Sokoto Caliphate 1403-1901: Songhai Empire 1404-1500: Agadéz Sultanate 1235-1632: part of Mali Empire 700-1430: Gao Empire 700-1380: Kanem Empire |
Niamey | ||
| Africa | 15 January 1970 | 1 Oct 1960 | 1 Oct 1960 | Became part of the 1900-1914: 1502-1897: 1430-1591: Songhai Empire 1380-1893: 1500-1840: Kwararafa, a pre-colonial confederation in the north of what is now Nigeria |
Abuja | ||
| Europe | 2 August 1944 | 8 Sep 1991 | 8 Sep 1991 | 2019–present: 1991–2019: |
Skopje | ||
| Europe | 27 February 1930 | 872 | 8 May 1945 | 1940–present: Kingdom of Norway (The Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of the Kingdom of Norway. Norway also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land).
1940–1945: Occupied by Germany (Reichskommissariat). |
Oslo | ||
| Asia | 8 December 1958 | 1626[note 37] | 1743 | 1970–present 1856-1970: 749-1959: 1744: House of Busaid 1696-1856: 1624: Ya'rubids are a native people of Oman 1507-1656: 1154-1624: Nabhani Dynasty they were rulers of Oman from 1154 until 1624, when the Yaruba dynasty came to power. One of its most visible legacies is Bahla Fort, a large complex of mud-brick buildings on stone foundations that is registered as a UNESCO world heritage site. The Nabhanid dynasty may be a possible ancestor of the Nabhan family, a family of Syrian and Lebanese descent that has influential members in the United States, some of whom immigrated and settled in New York City in the mid-20th century, and some who have influence in Brazil. Previously occupied by Great Seljuq Empire, Ottoman Empire, Portugal (1508–1650), etc. 1400: Azd |
Mascate | ||
| Asia | 14 August 1947 | 14 Aug 1947 | 14 Aug 1947 | 1956–present: 1947–1956: |
Islamabade | ||
| Australia | 1 January 1981 | 1 Oct 1994 | 1 Oct 1994 | Previously ruled by Spain, Germany, Japan. | Ngerulmud | ||
| Asia | 15 June 2007 | Sovereignty disputed by |
15 Nov 1988 | On 15 November 1988, the Palestinian Liberation Organization also proclaimed its independence of the State of Palestine and attained its autonomy as the Palestinian National Authority in 1994 in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, the territories that are occupied by Israel since 1967.
Parts of West Bank are controlled by Israel, except for the Area A of the Palestinian National Authority. The Gaza Strip has been occupied by Hamas since the 2007 war after Israeli disengagement from Gaza in 2005. The West Bank was occupied by Jordan from 1948 to 1967, and the Gaza Strip was occupied by Egypt from 1957 to 1967. |
Ramalá | ||
| The Americas | 31 December 1999 | 3 Nov 1903 | 31 Jan 1990 | 1990–present: 1989–1990: American Invasion 1903–1989: 1886–1903:Part of the 1863–1886: Federated state of the 1858–1863: In union with other 7 states in the 1831–1858: Part of the 1819–1831: Part of the 1717–1819: 1542–1776 : 1528–1542: Before Europeans arrived Panama was widely settled by Chibchan, Chocoan, and Cueva peoples. |
Panama City | ||
| Australia | 1 December 1973 | 16 Sep 1975 | 16 Sep 1975 | Papuan, Polynesians, and Melanesians before then. | Port Moresby | ||
| The Americas | 1938 | 14 May 1811 (de facto) Nov 25, 1845 (formal declaration of Independence) |
1876 | 1876–present: Republic of Paraguay Occupied 1870–1876 by Brazil, in Triple Alliance with Argentina and Uruguay.[112] (Paraguayan independence was assured only after the War of the Triple Alliance, when Brazil resisted Argentine offers to divide and annex the country) |
Asunción | ||
| The Americas | 26 February 1942 | 28 July 1821 | 25 Aug 1839 | 1839–Present: 1836–1839: Divided in North Peru and South Peru, in union with Bolivia in the |
Lima | ||
| Asia | 2012[23][113] | 4 July 1946[note 38] | 4 July 1946[note 39] | 1986–present: Fifth Philippine Republic 1981–1986: Fourth Philippine Republic 1973–1981: Under the Martial Law |
Manila | ||
| Europe | 15 February 1951 | 11 November 1918 (as a new state, not as a nation) | 1945 |
1989–present: Since 498,000 BC humans have been settled in Poland starting with Homo species, and later settled by Lusatian culture, Celts, Germanics, and others. |
Warsaw | ||
| Europe | 20 May 2002 | 25 July 1139 | 30 Aug 1808 | 1975–present: 1974–1975: |
Lisbon | ||
| Asia | 4 November 2021 | 3 Sep 1971 | 3 Sep 1971 | Ottoman Empire Abbasid Caliphate Umayyad Caliphate Rashidun Caliphate Various nomadic Arab tribesmen before that. |
Doha | ||
| Europe | 10 February 1947 | 13 July 1878 | 13 July 1878 | 1944–1958. Ottoman Empire Wallachia |
Bucharest | ||
| Asia/Europe | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | 1471 (Grand Duchy of Moscow) | 26 Dec 1991 (de facto) 12 Dec 1993 (de jure)[note 40] |
1993–present: 1991–1993: |
Moscow | ||
| Africa | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | Became German East Africa (1885–1918), Rwanda-Urundi (1916–1962), became independent on 1 July 1962 | Kigali | ||
| The Americas | 19 December 1980 | 19 Sep 1983 | 19 Sep 1983 | 1882-1983: 1689-1782: British West Indies and French West Indies In the 18th century it was owned by Britain and France, who claimed it as an island of the French and East Indies, and Britain claimed it as part of the British West Indies. |
Basseterre | ||
| The Americas | 27 February 1967 | 22 Feb 1979 | 22 Feb 1979 | 1833-1959: |
Castries | ||
| The Americas | 27 October 1969 | 27 Oct 1979 | 27 Oct 1979 | War in Saint Vicent: Os habitantes indígenas das ilhas de São Vicente e Granadinas eram vários grupos ameríndios . A chegada dos europeus no início do século XVI não levou a um assentamento de longo prazo, apenas em 1717 os franceses ocuparam a ilha de Barrouallie, embora os ingleses tenham reivindicado São Vicente em 1627. O Tratado de Paris (1763) viu São Vicente ... Vincent cedeu à Grã-Bretanha . Os atritos com os britânicos levaram à Primeira e à Segunda Guerra do Caribe em meados do século XVIII | Kingstown | ||
| Australia | 1 June 1962 | 1 Jan 1962 | 1 Jan 1962 | German colony 1900 to 1914; occupied by New Zealand 1914; Trust Territory first of the League of Nations, then of the United Nations and administered by New Zealand, 1920 to 1962. | Apia | ||
| Europe | 1463 | 1243 | 21 Sep 1944 | World War II Allies | 1944: Brief occupation by Germany, then Allies during Battle of San Marino 1739: Brief occupation by the Papal States |
San Marino | |
| Africa | 12 July 1975 | 12 July 1975 | 12 July 1975 | 1975-1991: Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe
1485-1975: |
São Tomé | ||
| Asia | 4 November 2021 | 13 Jan 1902 (Emirate of Riyadh)[note 41] | 23 Sep 1932 | 1932–present: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 1926–1932: Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd, a dual monarchy that was the precursor to the modern day Saudi Arabia |
Riyadh | ||
| Africa | 20 August 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | Independent first as Mali Federation with capital in Dakar. Previously part of Ghana, Mali and Songhai Empires. | Dakar | ||
| Europe | 17 February 2008 (disputed)[40] | 13 July 1878 (as a new state, not as a nation.)[note 42] | 3 June 2006 | 2006–present: 2003–2006: Republic of Serbia, federated state of the Serbia and Montenegro (successor state of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia) |
Belgrade | ||
| Africa | 29 June 1976 | 29 June 1976 | 29 June 1976 | Perhaps sovereign 1790–1794 | Victoria | ||
| Africa | 27 April 1961 | 27 Apr 1961 | 27 Apr 1961 | Colony of United Kingdom | Freetown | ||
| Asia | 9 August 1965 | 9 Aug 1965 | 9 Aug 1965 | British colony 1824–1963; occupied by Japan 1942–1945; declared independence, then merged with Malaysia[12][18] from 1963 until 1965.[15][17] | Singapore | ||
| Europe | 1 January 1993 | 1 Jan 1993 | 1 Jan 1993 | 1945–1993: Part of the Czechoslovakia (interrupted by Warsaw Pact armies in 1968) 1945: Occupied by WWII Allies in 1945 |
Bratislava | ||
| Europe | 19 February 1945 | 25 June 1991 | 25 June 1991 | 1991–present: Republic of Slovenia 1945–1991: Part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia 1918–1945: Part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes 1918–1918: Part of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs 1806–1918: Duchy of Carinthia (as part of the Austria-Hungary Empire) 976–1806: Duchy of Carinthia (as part of the Holy Roman Empire) 889–976: March of Carinthia (as part of the Carolingian Empire) |
Ljubljana | ||
| Australia | 2 January 1976 | 7 July 1978 | 7 July 1978 | Colony of German New Guinea from 1884 to 1920, turning the Solomon Islands into the British after Germany's tragic defeat in the First World War, in the Second World War Japan invaded the islands starting the Solomon Islands Campaign and the Guadalcanal Campaign. | Honiara | ||
| Africa | 18 May 1991 (disputed) | 1 July 1960 | 1 July 1960 | 1 July 1960: Union of Trust Territory of Somalia (former Italian Somaliland) and State of Somaliland (former British Somaliland) 19th century: Part of Sultanate of Hobyo 18th century: Part of Majeerteen Sultanate 15th century: Part of Adal Sultanate 13th century: Part of Ajuran Sultanate 13th century: Part of Warsangali Sultanate 13th century: Part of Ifat Sultanate 10th century: Part of Sultanate of Mogadishu 200 BC: Somali city-states |
Mogadishu | ||
| Africa | 27 April 1994 | 11 Dec 1931[note 43] | 11 Dec 1931 | 1961–present: Republic of South Africa (Democratization in 1994)
1931–1961: Union of South Africa, monarchy in personal union with the United Kingdom |
Bloemfontein (judicial), Cape Town (legislative) and Pretoria (executive) | ||
| Africa | 9 July 2011 | 9 July 2011 | 9 July 2011 | 2011: 1991–present: 1983-2018: |
Juba | ||
| Europe | 26 February 1976 | 542 (Visigothic Spain of Toledo)[note 44][117] | 1813 | 1975–present: 1939–1977:
13th century – 1516: Spain has been divided between two monarchies: the |
Madri | ||
| Asia | 18 May 2009 | 4 Feb 1948 | 4 Feb 1948 | It was not until the reign of Dutthagamani (161–137 BC) that the whole country was unified under his kingdom. | Colombo (executive, judicial) and Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte (official) | ||
| Africa | 9 July 2011 | 1 Jan 1956[note 46] | 1 Jan 1956 | After King Kashta ("the Kushite") invaded Egypt in the eighth century BC, the Kushite kings ruled as pharaohs of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt for a century before being defeated and driven out by the Assyrians. Later ruled by the Ottoman Empire, Egypt, and then as Anglo-Egyptian Sudan 1899–1956. | Khartoum | ||
| The Americas | 15 December 1954 | 25 Nov 1975 | 25 Nov 1975 | Paramaribo | |||
| Europe | 29 March 1809 | 970 c. | 970 | (none) | No exact date for consolidation of Sweden. The beginning of the reign of the first Swedish king proven to have existed historically dates from circa 970 AD. The Kalmar Union (1397–1523) was a personal union of Scandinavian states (Denmark, Sweden and Norway). In states in personal unions their sovereignties and international identity remain intact, just sharing the same head of state.) | Stockholm | |
| Europe | 4 August 1815 | 1599 | 1815 | 1848–present: 1814–1848: |
Bern | ||
| Asia | 10 June 1967 | April 17, 1946 | 28 Sep 1961[note 47] | 1961–present: 1958–1961: |
Damascus | ||
| Asia | 5 December 1929 | 9 Sep 1991 | 9 Sep 1991 | Independent in 1991 of Soviet Union
RSSA Tajique 1929-1991 Russian Empire 1860 Samanid Empire 875-999 |
Dushanbe | ||
| Africa | 26 April 1964 | 9 Dec 1961 | 9 Dec 1961 | Independent in 1961 as Tanganyika, added Zanzibar in 1963. | Dodoma | ||
| Asia | 10 March 1909 | 4 Mar 1351 (Ayutthaya Kingdom) | 1945 | The Ayutthaya Kingdom is considered to be the precursor of modern Thailand. Briefly occupied by Burma in 1767. Occupied by Japan 1941–1945. | Bangkok | ||
| Asia | 1914 | 28 Nov 1975 | 20 May 2002 | 2002–present: 1999–2002: |
Dili | ||
| Africa | 30 August 1958 | 27 Apr 1960 | 27 Apr 1960 | Lomé | |||
| Australia | 4 December 1845 | 4 June 1970 | 4 June 1970 | United 1845 by George Tupou I. British protectorate 1900–1970.
950-1865: Tuʻi Tonga Empire |
Nukuʻalofa | ||
| The Americas | 31 August 1962 | 31 Aug 1962 | 31 Aug 1962 | Port of Spain | |||
| Africa | 20 March 1956 | 20 Mar 1956 | 20 Mar 1956 | 1956–present: Republic of Tunisia
1956-1957: Kingdom of Tunisia The modern state of Tunisia was implemented in 1956 by France 1881-1956: French Tunisia was a French protectorate established in what is now the Republic of Tunisia, it was a protectorate that began with the occupation of Tunisia from 1881 until Tunisia's independence in 1956. 19th century: Bey of Tunis 1705-1881: Beylik of Tunis 1574-1705: Ottoman Tunisia Ottoman Tunisia, also known as the Regency of Tunis, refers to the Ottoman presence in Ifriqiya from the 16th to 19th centuries, when Tunis was officially integrated into the Ottoman Empire as the Eyalet of Tunis. The Ottoman presence in the Maghreb began with the takeover of Algiers in 1516 by the Ottoman Turkish corsair and beylerbey Aruj (Oruç Reis), eventually expanding across the entire region except for Morocco. 1229-1574: Hafsid 1121-1229: Almohad Caliphate During the 13th century, the Almohad chalfiate conquered Tunisia The Kingdom of Africa was a Tunisian kingdom located in North Africa and Italy, Tunisia was conquered by the kingdom in the 12th century, by Roger II During the first millennium, Tunisia was conquered by several Muslim dynasties and caliphates based in Carthage, after the loss of the Umayyad Caliphate 972-1148: Zirid dynasty 909-973: Fatimid Caliphate 800-909: Aghlabids 750-800: Abbasid Caliphate The third Islamic state, the Abbasid Caliphate, was the successor to the Umayyad and Rashidun Caliphates. 698-750: Umayyad Caliphate 590-698: Exarchate of Africa 534-590: Praetorian Prefecture of Africa 435-534: Vandal Kingdom 146 BC-435: Roman Tunisia 12th C.- 146 BC: Ancient Carthage 12th C.-North African culture |
Tunis | ||
| Asia/Europe | 29 June 1939 | 1299[note 48] | 1923 | 1923–present: 1920–1923: |
Ankara | ||
| Asia | 7 August 1921 | 27 Oct 1991 | 27 Oct 1991 | 1991–present: Turkmenistan
1925-1991: Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic 1918-1925: Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic 1789-1925: (part of the) Qajar Iran |
Ashgabat | ||
| Australia | 7 February 1979 | 1 Oct 1978 | 1 Oct 1978 | 1978–present: Tuvalu
1976–1978: Part of the 1892–1976: Part of the |
Funafuti | ||
| Africa | 1 March 1962 | 9 Oct 1962 | 9 Oct 1962 | 1963–present: Republic of Uganda
1962–1963: 1894–1962: Part of the |
Kampala | ||
| Europe | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | 24 August 1991[note 49] | 24 Aug 1991 | 1991–present: 1944–1991: Part of the |
Kyiv | ||
| Asia | 11 February 1972 | 2 Dec 1971 | 2 Dec 1971 | 1971–present: United Arab Emirates
1820–1971: Part of the 1258–1820: Bani Yas 750–1258: Part of the Abbasid Caliphate 661–750: Part of the Umayyad Caliphate 632–661: Part of the Rashidun Caliphate 629–632: Part of the Caliphate of Muhammad 224–629: Part of the |
Abu Dhabi | ||
| Europe | 2 December 1999 | 498 (Dál Riata)[note 50] | 1066 | 1922–present: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland [the later one is variously described as a country, province or region] are the constituent countries of the Kingdom) 1801–1922: Note: The British Empire was founded by the order of Elizabeth I who granted a patent to Humphrey Gilbert for discovery and overseas exploration in 1578.[125] On 1 of May 1707, the kingdoms are united from |
London | ||
| The Americas | 7 September 1981 | 4 July 1776 | 19 Oct 1781 | 1776–present: 1763–1776: |
Washington, D.C. | ||
| The Americas | 1861 | 25 Aug 1825 | 27 Aug 1828 | 1830–present: Oriental Republic of Uruguay
1828–1830: |
Montevideo | ||
| Asia | 24 October 1924 | 1 Sep 1991 | 1 Sep 1991 |
1991–present: 1924–1991: Part of the Soviet Union as 1920–1924: Khorezm People's Soviet Republic 1917–1920: Khanate of Khiva 1873–1917: Part of the Russian Empire as Khanate of Khiva 1511–1873: Khanate of Khiva 1370–1511: Part of the Timurid Empire 1226–1370: Part of the Chagatai Khanate 1206–1226: Part of the Mongol Empire 1100–1206: Part of the Khwarazmian Empire 1037–1100: Part of the Seljuk Empire 840–1037: Part of the Kara-Khanid Khanate 819–840: Part of the Samanid Empire 750–819: Part of the Abbasid Caliphate 661–750: Part of the Umayyad Caliphate 440–661: Part of the Hephthalite Empire 125 BCE-440: Nomadic Tribes 256 BCE-125 BCE: Part of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom 312 BCE-63 BCE: Part of the Seleucid Empire 330 BCE-312 BCE: Part of the Macedonian Empire 530 BCE-330 BCE: Part of the Achaemenid Empire |
Tashkent | ||
| Australia | 30 July 1980 | 30 July 1980 | 30 July 1980 | 1980–present: Republic of Vanuatu
1906–1980: Part of the 1890–1906: Part of the 1889–1890: Independent Commune of Franceville 1887–1889: Part of the |
Port Vila | ||
| Europe | 11 February 1929 | 11 Feb 1929 | 11 Feb 1929 | 1929–present: 1870–1929: States of the Church (in prison) |
Vatican City | ||
| The Americas | 3 October 1899 | 13 Jan 1830 | 13 Jan 1830 |
1999–Present |
Caracas | ||
| Asia | 2 July 1976 | 2 Sep 1945 | 2 July 1976 | 1945–1954: the second French rule, which was ended by the Geneva Conference of 1954
1940–1945: Japanese occupation 1887–1940: French rule 1802–1945: Nguyễn dynasty, effective independence from 1802 to 1887, afterwards becoming puppet of the French rule 1778–1802: Tây Sơn dynasty 1428–1788: Later Le dynasty 1407–1428: annexed by Ming dynasty in the Fourth Era of Northern Domination 1400–1407: Hồ dynasty 1225–1400: Trần dynasty 1009–1225: Lý dynasty 980–1009: Early Lê dynasty 968–979: Đinh dynasty 938–965: Ngô dynasty 544–602: The region gained a longer period of independence as Vạn Xuân under the Anterior Lý dynasty 2879 BC: Văn Lang confederacy arose under Kinh Dương Vương, who was the founder of the Hồng Bàng dynasty |
Hanoi | ||
| Asia | 26 April 2020 | 1 Nov 1918 | 22 May 1990 | North Yemen independent from Ottoman Empire 1918; South Yemen from UK in 1967; unified 1990 | Aden (de facto, temporary) and Sanaa (de jure) | ||
| Africa | 24 October 1964 | 24 Oct 1964 | 24 Oct 1964 | 1964–present: Republic of Zambia
1963–1964: Part of the 1953–1963: Part of the 1911–1953: Part of the 1890–1911: Part of the 1823–1890: Part of the Kingdom of Mthwakazi 1660–1823: Part of the Rozvi Empire 1430–1660: Part of the Kingdom of Mutapa |
Lusaka | ||
| Africa | 1901 | 11 Nov 1965 | 18 Apr 1980 | 1980–present: Republic of Zimbabwe
1979–1980: Part of the 1979: 1970–1979: 1965–1970: 1963–1965: Part of the 1953–1963: Part of the 1923–1953: Part of the 1890–1923: Part of the 1823–1890: Kingdom of Mthwakazi 1660–1823: Rozvi Empire 1430–1660: Part of the Kingdom of Mutapa 1220–1430: Kingdom of Zimbabwe 1075–1220: Kingdom of Mapungubwe The British colony of Southern Rhodesia unilaterally declared Independence as Rhodesia 1965; known as Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979; unrecognised until 1980. |
Harare |
See also
[edit]- Declaration of independence
- List of active autonomist and secessionist movements
- List of national independence days
- List of wars of independence (national liberation)
- List of former European colonies
- List of former national capitals
- List of former sovereign states
- List of national constitutions
- List of sovereign states
- List of world map changes
- Political history of the world
- Succession of states
- Timeline of country and capital changes
- Timeline of national independence
Notes
[edit]- ^ Listed are the six UN member states with limited recognition: China (Bhutan neither recognizes PRC nor ROC; the ROC was recognized as a sovereign country by just 11 countries and Vatican City/Holy See as of Jan 2024,[1] Israel (not recognized by 32 members), North and South Korea (no mutual recognition), Armenia (not recognized by Pakistan) and Cyprus (not recognized by Turkey).
- ^ Since the beginning of the Second Libyan Civil War in 2014, various areas of Libya are under the control of competing groups. These include domestic groups such as New General National Congress and local Tuareg groups, and foreign groups such as ISIL.
- ^ With the ongoing Somali Civil War, significant areas remain outside federal control.
- ^ A new constitution was approved in 2013, but most changes will not enter effect for another decade.
- ^ In the Dominican Republic, every constitutional amendment is considered a new constitution. The most recent amendment was the 2010 constitution.
- ^ a b Following the Northern Iraq offensive in June 2014, large areas of Iraq are de facto under the control of Iraqi Kurds or the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.
- ^ This constitution cut North Korean ties with the Soviet Union. Several new constitutions and amendments have followed (most recently in 2013), creating new titles for the national leader such as Eternal President and Chairman of the National Defence Commission. However, power has remained with the Kim dynasty since 1948.
- ^ See the Declaration of independence article: "... the state from which the territory wishes to secede may regard the declaration as rebellion, which may lead to a war of independence or a constitutional settlement to resolve the crisis."
- ^ See also Sovereignty of the Philippines § Peace protocol, U.S. military government, Treaty of Paris, and other points in that article for clarification.
- ^ a b Due to the ongoing Syrian Civil War, large areas of Syria are de facto under the control of other parties such as the Syrian opposition and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.
- ^ a b c d e According to the Badinter Arbitration Committee, the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was dissolved into five states. This is the result when the Serb-dominated Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) was formed on 27 April 1992 as a rump state, consisting only of the former Socialist Republics of Serbia and Montenegro. Its government claimed continuity to the former country, however, the international community refused to recognize it as such. The stance of the international community was that Yugoslavia had dissolved into its separate states. The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was prevented by a UN resolution on 22 September 1992 from continuing to occupy the United Nations seat as successor state to SFRY. This question was important for claims on SFRY's international assets, including embassies in many countries. Only in 1996 had the FRY abandoned its claim to continuity from the SFRY. The FRY was dominated by Slobodan Milošević and his political allies. This was reaffirmed in the Succession Agreement signed in June 2001.
- ^ The Faroe Islands and Greenland were administered by Denmark until 24 March 1948 and 1 May 1979 respectively. They are now autonomous countries with home rule, but remain part of the Kingdom of Denmark.
- ^ a b c The annexation of the Baltic states in 1940 is considered an illegal occupation by the current governments of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania and by a number of Western countries, including the United States and the European Union, who assert that the states were independent countries occupied by the Soviet Union. The three corresponding Soviet republics were officially sovereign entities in a federation, according to Article 76 of the Constitution of the Soviet Union. However, the Soviet Union was heavily centralized and was de facto a single federal state and the three states consider the corresponding Soviet republics to have been illegitimate entities.
- ^ The breaking-through of the Channel Tunnel on 31 October 1990 created a new land border between the UK and France.[34] However, the Channel Tunnel runs underwater and did not change the above-ground territory of either nation.
- ^ France swapped a small area of land with Andorra in 2001 to allow Andorra to construct the Envalira Tunnel access bridge.
- ^ Prior to 1999, the Constitution of Ireland claimed that "The national territory consists of the whole island of Ireland", but that its laws were only valid in the counties of the Republic.
- ^ East Timor had been under Indonesian occupation since 1975, but this occupation was not recognized by the wider global community.
- ^ The breaking-through of the Channel Tunnel on 31 October 1990 created a new land border between the UK and France.[34] However, the Channel Tunnel runs underwater and did not change the above-ground territory of either nation.
- ^ France swapped a small area of land with Andorra in 2001 to allow Andorra to construct the Envalira Tunnel access bridge.
- ^ Baikonur is treated as a federal subject of Russia, but its exact status is a topic of dispute between the two countries.[54]
- ^ Full sovereignty. Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ Austrians date their national identity back to the establishment of the Duchy of Austria (later the Archduchy of Austria) in the Middle Ages (a state of the Holy Roman Empire that only had full sovereignty after the dissolution of the Empire in the 19th century). Another important states in the identity of the Austrian nation is the Austrian Empire, Cisleithania, Republic of German-Austria, the First Austrian Republic, Federal State of Austria (this later annexed by Nazi Germany). As an independent and sovereign state the current Austrian state dates back to 1945, when the country seceded from Nazi Germany after the end of World War II. However the Moscow Conference of 1943 declared the German annexation of Austria in 1938 null and void
- ^ The medieval Principality of Polotsk became an extinct state after its dissolution. Modern state of Belarus dates from 1991
- ^ Full sovereignty. Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Canada becomes completely sovereign, having consulates and embassies in other countries
- ^ The Kingdom of Chile (Patria Vieja) became an extinct state after its reconquest by Spain. Modern state of Chile dates from 1818
- ^ 20 January 1955 for Taiwan.
- ^ People's Republic of China consider itself the successor state of the Republic of China, the latter considers itself the successor state of the Qing Empire, and through the mandate of heaven all Chinese imperial states considered themselves successors to previous dynasties, with the Shang dynasty being historically the first non-legendary dynasty of that country.
- ^ The Republic of Spanish Haiti became an extinct state after its reconquest by Haiti. Modern state of Dominican Republic dates from 1844
- ^ Egypt is one of the oldest nations in the world, its national identity dating back to the First Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. But it is important to stress the difference between state and nation. As a state the nation lost its sovereignty and was conquered by other states several times in History. The current Egyptian state, as an independent sovereign state, dates from 1922
- ^ Zagwe was one of the kingdoms that emerged from the collapse of the Kingdom of Aksum, that became an extinct or abolished state in 960 AD. It is the direct historical predecessor of the Ethiopian Empire, regardless of the Solomonic dynasty of the ancient Kingdom of Aksum having overthrown the Zagwe dynasty in 1270 and assumed their throne. Dynastic lineages are irrelevant to current international law, mainly because of the fact of the majority of the states in the current world scenario are republics.
- ^ Some historians refer to the beginning of the Holy Roman Empire as 800, with the crowning of Frankish king Charlemagne considered as the first Holy Roman Emperor. Others refer to the beginning as the coronation of Otto I in 962.
- ^ Iran is one of the oldest nations in the world, its national identity dating back to the Median Empire and the Achaemenid Empire. But it is important to stress the difference between state and nation. As a state the nation lost its sovereignty and was conquered by other states several times in History. The current Iranian state, as an independent state in a contiguous way, dates from 1501
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Internationally recognized independence, by nations that aren't members of the Commonwealth of Nations
- ^ Beginning of the reign of the first Japanese emperor proven to have existed historically
- ^ Montenegrins date their national identity to the founding of Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro in 1516. However, the Montenegrin state became an extinct state at the time of the Podgorica Assembly, which led to the annexation and extinction of the Kingdom of Montenegro by the Kingdom of Serbia. The current Montenegrin state emerged in 2006 after separating from Serbia.
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ The region was conquered by Portuguese forces under the command of Afonso de Albuquerque in 1507, and remained under Portuguese control until they were expelled by the Ya'rubids.
- ^ The First Philippine Republic was an unrecognized state and became an extinct state after being terminated by the United States. Modern state of Philippines dates from 1946. However, Filipinos celebrate their independence date on June 12 (the date of establishment of the First Philippine Republic) in order to avoid celebrating their national date on the same day that their former colonizers (the USA) celebrate their national date (July 4).
- ^ Independence recognized via the Treaty of Manila (1946).
- ^ Russia dates its national identity back to the Kievan Rus, medieval state that was extinguished when it was conquered by the Mongols of the Golden Horde. A new Russian state arose and existed continuously and without loss of sovereignty from 1480 until 1922, when of its own accord it ceased to be a sovereign state and became a subnational unit of the Soviet Union. With the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the nation again had a sovereign state, with the current Russian sovereign state dating back to 1991. The Russian Federation is regarded as the successor state to the former Soviet Union, inheriting its seat as a UN member state, after a letter by president Boris Yeltsin was received by the secretary-general Javier Pérez de Cuéllar.
- ^ Saudi Arabia dates its national identity from the establishment of the Emirate of Diriya (First Saudi State), however this state later became extinct, as did the Emirate of Nejd (the Second Saudi State). The current and Third Saudi State came into being in 1903 when it separated from the Emirate of Jabal Shammar. Through wars of conquest it conquered other states and made a real union with Hejaz before adopting the current name Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932
- ^ Serbia consider itself as the successor state of Yugoslavia. The current Serbian state emerged in 1878, after independence de jure from the Ottoman Empire. Other Serbian states existed before this date, but ceased to exist due to the conquest of other states. It is important not to confuse the concept of state with that of the nation, as a nation the Serbian people have existed since the Middle Ages, and just like other ethnic groups (such as the Greeks, Jews, Egyptians, etc.) it went through periods of its history in which it was a Stateless nation
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ During the Visigoth kingdom of Toledo, the names of the Visigoth kingdom (Regnum Gothorum) and Spain (Hispaniae or Spaniae) were used more and more frequently as synonymous terms, beginning to have not only a geographical meaning, but also a political one (especially since the year 624, when Swinthila finally defeated the Byzantines and the Visigoths dominated the entire Iberian Peninsula). Historiographers of the time such as Isidore of Seville, Julian of Toledo, John of Biclaro, as well as from abroad, the Franks Gregory of Tours, Fredegar, or Pope Leo II, referred to the Visigoth kingdom or its kings, as Hispania or kings of Hispania. On the other hand, there was an adoption by the Visigoths of the Hispano-Roman culture, with a progressive intention to merge the Gothic and Hispano-Roman societies into a common one, politically (kingdom administered from the capital of Toledo, and in accordance with Roman ecclesiastical power through the Councils of Toledo), religiously (Reccared I converted from Arianism to Chalcedonian Christianity in 589), common legislation (Code of Leovigild, and later Visigothic Code), militarily (army composed of Hispano-Romans and Visigoths), with a monetary unit (Visigothic royal currency from 580 to 710), and linguistically (Visigoths spoke Latin), taking advantage of the pre-existing cohesion left by the Hispania of the Roman Empire.[116] Spain is a unitary state that emerged from the political union by incorporating union of different states throughout history. Using the modern criteria of the United Nations, which considers the date of admission of other states that emerged from political unions (such as Tanzania, Malaysia and Yemen) as the date of the oldest predecessor state to be admitted, it will soon be seen that the oldest state that merged to form modern Spain is the Kingdom of León, one of the states in personal union that integrated the Crown of Castile, with such state dating its origins directly from the Kingdom of Asturias. Spain was until 1715 a composite monarchy, i.e. several small states in personal union, only passing through a political union in 1715 with the Nueva Planta decrees
- ^ During Napoleon's invasion of Spain, Spain was a governorship of France. In fear of invasion, the King of Portugal went to Rio de Janeiro, in Brazil.
- ^ Sudan dates its national identity to the Kingdom of Kerma, Kingdom of Kush and other ancient kingdoms that existed in its territory, i.e Nubia (mentioned in ancient Egyptian texts). However, as an independent sovereign state, the current Sudanese state dates back to 1956.
- ^ By uniting with Egypt to form the United Arab Republic into a political union, the Second Syrian Republic ceased to exist as a sovereign state and became an extinct state, with Syria becoming a subnational unit of the United Arab Republic. The current Syrian state emerged as a new state when it broke up politically in 1961. However, Syrians celebrate April 17 as their independence day, as it was on April 17, 1946 that the nation ceased to be a colony of France.
- ^ The Republic of Turkey is the successor state of the Ottoman Empire. Despite being known in English as the Turkish War of Independence, Turks call it in their language Kurtuluş Savaşı (lit. Liberation War). "War of Independence" in Turkish is "bağımsızlık savaşı". The country's national date is the Republic Day (Cumhuriyet Bayramı), which commemorates the change of government regime from a monarchy to a republic.
- ^ Ukraine dates its national identity back to the Kievan Rus, however this state became an extinct state when it was conquered by the Mongols of the Golden Horde. Another state with historical importance for Ukrainians in their national identity is the medieval Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, which however also became an extinct state. In the 17th century the Ukrainian nation established another Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, however this state became extinct upon being conquered by the Russian Empire. Between 1917 and 1919, two new Ukrainian states was established, being unified in 1919 but again lost its sovereignty by becoming a subnational unit of the Soviet Union. The current Ukrainian sovereign state dates from 1991, emerging after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- ^ The United Kingdom is a unitary state that emerged from the political union by incorporating union of different states throughout history. Northern Ireland has been part of this political union since 1922, when the rest of Ireland separated from the United Kingdom. Ireland had united with Great Britain in 1800 to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The Kingdom of Great Britain itself emerged from the political union between the Kingdom of England (which had already conquered and annexed the Principality of Wales centuries before) and the Kingdom of Scotland. Using the modern criteria of the United Nations, which considers the date of admission of other states that emerged from political unions (such as Tanzania, Malaysia and Yemen) as the date of the oldest predecessor state to be admitted, it will soon be seen that of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom (today subnational units and not sovereign countries) the oldest is Scotland (unified in 843), which dates its origin to the Dál Riata, which conquered the existing small Pictish states in future Scotland to form the Kingdom of Scotland, which existed until 1707 when it merged with England (originated in 927, when the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (r. 924–939), unifying most of modern England under a single king
References
[edit]- ^ "Countries That Recognize Taiwan 2022". worlpopulationreview.com. Countries that Recognize Taiwan as a Sovereign Country – 2021. Archived from the original on March 15, 2023. Retrieved May 1, 2022.)
- ^ David Armitage, The Declaration of Independence in World Context, Organization of American Historians, Magazine of History, Volume 18, Issue 3, Pp. 61–66 (2004)
- ^ Manning, Patrick (1990). Slavery and African Life: Occidental, Oriental, and African Slave Trades. London: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Lovejoy, Paul E. (2012). Transformations of Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa. London: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Martin Klein, "Slave Descent and Social Status in Sahara and Sudan", in Reconfiguring Slavery: West African Trajectories, ed. Benedetta Rossi (Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 2009), 29.
- ^ Country Profile: Cuba Archived 2014-04-10 at the Wayback Machine, September 2006, U.S. Library of Congress – Federal Research Division.
- ^ "19 de abril de 1810". Venezuela Tuya. Archived from the original on 2019-04-18. Retrieved 2014-11-17.
- ^ "Armenia - The Artaxiads". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2023-05-31. Retrieved 2024-04-14.
- ^ "Cambodia - Khmer Empire, Angkor, Temples". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2024-04-04. Retrieved 2024-04-11.
- ^ Gavlak, Dale (12 June 2011). "Jordan's King Abdullah vows to allow elected cabinets". BBC News. Archived from the original on 13 June 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j The Republics of the Soviet Union were officially sovereign entities in a federation, according to Article 76 of the Constitution of the Soviet Union. However, the Soviet Union was heavily centralized and was de facto a single federal state.
- ^ a b c Malaysia Act 1963
- ^ United Nations Member States
- ^ a b Federation of Malaya Independence Act 1957
- ^ a b c d Agreement relating to the separation of Singapore from Malaysia as an independent and sovereign state
- ^ a b Agreement relating to the separation of Singapore from Malaysia as an independent and sovereign state/proclamation of singapore
- ^ a b c Singapore Act 1966
- ^ a b Agreement relating to Malaysia between United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Federation of Malaya, North Borneo, Sarawak and Singapore
- ^ "Myanmar - Pyu State, Ancient Cities, Irrigation | The kingdom of Pagan (849–c. 1300)". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2024-04-04. Retrieved 2024-04-04.
- ^ "Philippines". The World Factbook. CIA. Archived from the original on July 26, 2009.
- ^ "Country Profile: Philippines" (PDF). Federal Research Division of the U.S. Library of Congress. March 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 10, 2012. said: "The Philippines attained independence from Spain on 12 June 1898, and from the United States on 4 July 1946.". Other sources (e.g. The CIA Factbook Archived 2021-01-10 at the Wayback Machine ) say that the Philippine Islands were ceded to the US by Spain in 1898 following the Spanish–American War.
- ^ Republic of the Philippines[permanent dead link], Philippine Government website.
- ^ a b Bautista, Lowell B. (3 September 2009). "The Historical Context and Legal Basis of the Philippine Treaty Limits" (PDF). Aegean Review of the Law of the Sea and Maritime Law. 1: 3. doi:10.1007/s12180-009-0003-5. ISSN 1864-9610. S2CID 153653227. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2010.
The sovereignty of a State is co-extensive with its territorial limits.
- ^ a b "UN approves PH territorial claim to Benham Rise". 28 April 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ Bautista 2009: "Although by today's standards the 1898 annexation of the Philippines by the U.S. was unlawful, it does not follow that the U.S. claims of sovereignty are unfounded. Under the doctrine of intertemporal law, 'a juridical fact must be appreciated in light of the law contemporary with it, and not the law in force at the time when a dispute in regard to it arises or falls to be settled.' Thus, the legality of any act should be determined in accordance with the law of the time the act was committed, and not by reference to law as it might have become at a later date.'"
- ^ "Qatar completes border demarcation with Saudi Arabia". Doha News. 4 November 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Deeley, Furness, and Schofield (2001) The International Boundaries of East Timor p. 8
- ^ Tuchscherer, Michel (2000-07-01). "Chronologie du Yémen (1506-1635)". Arabian Humanities. Revue internationale d'archéologie et de sciences sociales sur la péninsule Arabique/International Journal of Archaeology and Social Sciences in the Arabian Peninsula (in French). 8 (8). doi:10.4000/cy.11. ISSN 1248-0568. Archived from the original on 2022-06-17. Retrieved 2024-04-07.
- ^ a b "Hrvatska povijest". Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Grboslovlje u Hrvata >> Krunisani". Archived from the original on 24 November 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Hrvatski Vladari / Croatian rulers – Geni". Archived from the original on 31 March 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ a b "TOPLI DOM JADRANA – PRIMORSKA HRVATSKA – Visite Croatia – Stema Guide". Archived from the original on 21 August 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Croatia – World Leaders Index". Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ a b Under the Channel, traffic soon to roll . Baltimore Sun. 1 May 1994.
- ^ "Peloponnesian League | Athenian, Spartan, Confederacy | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-21. Retrieved 2024-04-03.
- ^ "Delian League". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2023-12-10. Retrieved 2024-04-03.
- ^ "League of Corinth". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2020-10-17. Retrieved 2024-04-03.
- ^ "King's Collections : Exhibitions & Conferences : The London Protocol of 3 February 1830". kingscollections.org. Archived from the original on 2023-12-25. Retrieved 2024-04-03.
- ^ "Liechtenstein prince wins powers". BBC News. 2003-03-16. Archived from the original on 2015-12-15. Retrieved 2015-10-26.
- ^ a b Rettman, Andrew (6 February 2013). "Kosovo: EU meeting is 'de facto recognition' by Serbia". EUobserver. Brussels. Archived from the original on 22 March 2019. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ a b Manuel Alvarez-Valdés y Valdés (1991). La Extranjería en la Historia Del Derecho Español (in Spanish). Universidad de Oviedo. p. 151. ISBN 978-84-7468-737-8.
- ^ Ross, D. (2002). Chronology of Scottish History. Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-85534-380-1
- ^ Hearn, J. (2002). Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture. Edinburgh University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-902930-16-9
- ^ Davies (1994) p. 100[citation not found]
- ^ Davies (1994) p. 128[citation not found]
- ^ "Background Note: United Kingdom". bbc.co.uk Acts of Union: The creation of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 2018-12-20. Retrieved 2011-08-06.
- ^ Allan I. Macinnes (2007). Union and empire: the making of the United Kingdom in 1707. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-85079-7.
- ^ David Armitage; Michael J. Braddick (2002). The British Atlantic world, 1500–1800. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-333-96340-1.
- ^ Finlayson, Christopher (2021). He Kupu Taurangi: Treaty settlements and the future of Aotearoa New Zealand. Huia Publishers. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-77550-615-7. OCLC 1238026659.
- ^ "U.S. Relations With Vanuatu". U.S. Department of State. 9 March 2016. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ Wolff, Stefan (2004). Disputed Territories: The Transnational Dynamics of Ethnic Conflict Settlement. Berghahn Books. pp. 30–31. ISBN 978-1-57181-657-3. Archived from the original on 2023-03-26. Retrieved 2023-03-23.
- ^ Wippman, David (1998). "Practical and Legal Constraints on Internal Power Sharing". In Wippman, David (ed.). International Law and Ethnic Conflict. Cornell University Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-8014-3433-4. Archived from the original on 2023-03-26. Retrieved 2023-03-23.
- ^ Bahcheli, Tozun; Noel, Sid (2005). "Power Sharing for Cyprus (Again)? European Union Accession and the Prospects for Reunification". In Noel, Sid (ed.). Relations of Ruling: Class and Gender in Postindustrial Societies. McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-7735-2948-9.
- ^ Kumkova, Katya (29 January 2013). "Russia and Kazakhstan: What's Behind the Baikonur Spat?". EurasiaNet.org. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-10-28.
- ^ Christopher A Whatley (2001). Bought and Sold for English Gold: The Union of 1707 (Tuckwell Press, 2001)
- ^ An Outline of the People's Republic of Albania. 8 Nëntori. 1978. p. 47.
- ^ Ceka, N. (2013). The Illyrians to the Albanians. Migjeni. p. 25. ISBN 978-9928-4074-6-7. Retrieved 2022-04-01.
- ^ The Regency of Algiers ceased to exist and became an extinct or abolished state when France conquered Algeria. The People's Democratic Republic of Algeria is a new state that emerged after separating from the French Republic
- ^ Shillington, Kevin (2005). Encyclopedia of African history. CRC Press. p. 60. ISBN 1-57958-453-5. Archived from the original on 2023-01-12. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ "The Site of Ain Hanech Revisited: New Investigations at this Lower Pleistocene Site in Northern Algeria" (PDF). Gi.ulpgc.es. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-10. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- ^ Blaustein, Albert P.; Sigler, Jay A.; Beede, Benjamin R. (1977). Independence documents of the world. Brill Archive. p. 11. ISBN 0-379-00794-0.
- ^ Whittlesey, Derwent (June 1934). "Andorra's Autonomy". The Journal of Modern History. 6 (2): 147–155. doi:10.1086/236113. S2CID 145133794.
- ^ Archambault, G.H. (Nov 16, 1944). "Andorra Occupied by French Police; De Gaulle Acts Under Historic Authority to Keep Order in Pyrenees Republic". The New York Times. p. 5. Archived from the original on February 19, 2014. Retrieved April 25, 2009.
- ^ "1975: Divided Angola gets independence". BBC On This Day. 1975-11-11. Archived from the original on 2009-02-22. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Background Note: Antigua and Barbuda". state.gov. US Department of State. Archived from the original on 2017-01-22. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Congress of Tucumán". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2009-07-01. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Howe, G. Melvyn; Dowsett, Charles James Frank; Mints, Aleksey Aleksandrovich; Suny, Ronald Grigor (23 April 2019). "Armenia: Independence". Britannica.com. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ "Federation". australia.gov.au. Australian Government. Archived from the original on 2019-03-12. Retrieved 2019-06-06.
- ^ Kurian, George Thomas (1987). The Encyclopedia of the Third World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Facts on File. p. 115. ISBN 0-8160-1118-4.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (12 February 2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-511-99741-9.
- ^ "U.S. Relations With Belize". state.gov. US Department of State. December 22, 2016. Archived from the original on June 11, 2018. Retrieved May 23, 2019.
- ^ Rose, Leo E. (1977). The Politics of Bhutan. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. p. 24. ISBN 0-8014-0909-8.
[T]here can be no doubt that since at least the tenth century no external power has controlled Bhutan, although there have been periods when various of its neighbors have been able to exert a strong cultural and/or political influence there.
- ^ Bisht, Ramesh Chandra (2008). International Encyclopaedia of Himalayas. Vol. 2. New Delhi: Mittal Publications. p. 12. ISBN 978-81-8324-265-3.
- ^ "Botswana". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2010-07-15. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ "Brazil". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ "Bulgaria". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2009-07-11. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ Guadelli, Jean-Luc; Kovacheva, Mary Kovatcheva or most frequently; Krumov, Ivaylo; Miteva, Viviana; Taneva, Stanimira; Dimitrova, Irena; Guadelli, Aleta (2010). "An ancient continuous human presence in the Balkans and the beginnings of human settlement in western Eurasia: A Lower Pleistocene example of the Lower Palaeolithic levels in Kozarnika cave (North-western Bulgaria)". Quaternary International. 223–224: 94. Bibcode:2010QuInt.223...94S. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2010.02.023. Archived from the original on 2022-12-06. Retrieved 2020-05-28 – via www.academia.edu.
- ^ "Burkina Faso". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2010-05-21. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer (1999). Vietnam. Routledge. pp. 196–197. ISBN 1-85728-922-6.
- ^ "Statute of Westminster: Canada's Declaration of Independence". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on August 13, 2014. Retrieved April 19, 2009. and the last province to join the Canadian Confederation being Newfoundland and Labrador
- ^ Colin G. Calloway (2006). The Scratch of a Pen: 1763 and the Transformation of North America. Oxford U.P. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-804119-1.
- ^ "Background Note: Cape Verde". state.gov. US Department of State. June 2008. Archived from the original on 4 June 2019. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ "Stone Age wells found in Cyprus". BBC News. 25 June 2009. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- ^ McKitterick, Rosamond, ed. (1995). The New Cambridge Medieval History. Volume II c.700–c.900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 205. ISBN 0-521-36292 X.
- ^ Langer, William L., ed. (1972). An Encyclopedia of World History (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 9. ISBN 0-395-13592-3.
- ^ "Estonian Declaration of Independence, 24 February 1918". President of the Republic of Estonia. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ a b A. Berhe. (2003). Revisiting resistance in Italian-occupied Ethiopia: the Patriots' Movement (1936–1941) and the redefinition of post-war Ethiopia. African dynamics, ISSN 1568-1777; vol. 2. Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-12624-4.
- ^ Becker, Marc (2011). "History of U.S. Interventions in Latin America". Marc Becker. Archived from the original on 7 November 2019. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^ Price and Brown, 1985, Bettinger, 1991
- ^ Bose, Sugata; Jalal, Ayesha (2004). Modern South Asia: History, Culture, Political Economy (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-203-71253-5.
- ^ Chauhan, Partha R. (2010). "The Indian Subcontinent and 'Out of Africa 1'". In Fleagle, John G.; Shea, John J.; Grine, Frederick E.; Baden, Andrea L.; Leakey, Richard E. (eds.). Out of Africa I: The First Hominin Colonization of Eurasia. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 145–164. ISBN 978-90-481-9036-2.
- ^ Petraglia, Michael D.; Allchin, Bridget (2007). The Evolution and History of Human Populations in South Asia: Inter-disciplinary Studies in Archaeology, Biological Anthropology, Linguistics and Genetics. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-1-4020-5562-1.
- ^ Petraglia, Michael D. (2010). "The Early Paleolithic of the Indian Subcontinent: Hominin Colonization, Dispersals and Occupation History". In Fleagle, John G.; Shea, John J.; Grine, Frederick E.; Baden, Andrea L.; Leakey, Richard E. (eds.). Out of Africa I: The First Hominin Colonization of Eurasia. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 165–179. ISBN 978-90-481-9036-2.
- ^ Campbell Robertson; Stephen Farrell (31 December 2008), "Green Zone, Heart of U.S. Occupation, Reverts to Iraqi Control", The New York Times, archived from the original on 20 October 2017, retrieved 10 February 2017
- ^ Genealogies from Bodleian Library, MS Rawlinson B 502 and the Book of Leinster
- ^ "National Geographic Italia – Erano padani i primi abitanti d'Italia". Archived from the original on June 26, 2019.
- ^ Hoshino Iseki Museum, Tochigi Pref.
- ^ "Wonders of the African World". PBS. Archived from the original on 1 March 2020. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ a b Eckert, Carter J.; Lee, Ki-Baik (1990). Korea, old and new: a history. Korea Institute Series. Published for the Korea Institute, Harvard University by Ilchokak. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-9627713-0-9.
- ^ a b Christopher J. Norton, "The Current State of Korean Paleoanthropology", (2000), Journal of Human Evolution, 38: 803–825.
- ^ "November 18, 1918 – Proclamation of Latvia's independence". LETA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2008. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ "Colonization". The African-American Mosaic. Library of Congress. July 5, 2005. Archived from the original on 2011-02-26. Retrieved 2009-04-25.
Liberia ... was neither a sovereign power nor a bona fide colony of any sovereign nation. ... the United States refused to claim sovereignty over Liberia.
- ^ At the end of World War II, the region was abandoned by the Italians. The French and British occupy the region militarily, with the French settling in Fezzan, the British in Tripolitania and the Emirate of Cyrenaica being established as an independent country. King Idris I unified the country on December 24, 1951, uniting the territories into a single federal state, named the United Kingdom of Libya, later becoming the unitary Kingdom of Libya
- ^ The independent government of the Moroccan Sultan still existed, in nominal form, during the period when the country was a protectorate of European colonial powers. Source: Treaty of Fes
- ^ Rose, Leo E.; Margaret W. Fisher (1970). The Politics of Nepal. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. p. xi. ISBN 0-8014-0574-2.
Nepal is of special interest, partly because it is an Asian country that was never reduced to colonial status.
- ^ "Neanderthal fossil discovered in Zeeland province | Radio Netherlands Worldwide". Rnw.nl. 16 June 2009. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ^ "What changed?". Archived from the original on 2020-06-14. Retrieved 2020-10-10.
- ^ "New Zealand Parliament – New Zealand sovereignty: 1857, 1907, 1947, or 1987?". New Zealand Parliament Research Papers. Archived from the original on April 15, 2012. Retrieved April 19, 2009.
- ^ "Breve Reseña Histórica" [Brief History]. Asociación Indígena para la Integración y Desarrollo de la Región Autónoma de la Costa Atlántica (in Spanish). n.d. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "Palaeolithic and Pleistocene of Pakistan". Department of Archaeology, University of Sheffield. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2019.
- ^ Murray, Tim (1999). Time and archaeology. London; New York: Routledge. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-415-11762-3.
- ^ Painter, James E.; Butland, Gilbert James; Service, Elman R.; Nickson, R. Andrew; Williams, John Hoyt (10 May 2019). "Paraguay". Britannica.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ "UN approves PH territorial claim to Benham Rise". 28 April 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ "400,000-year-old fossil human cranium is oldest ever found in Portugal". phys.org. Archived from the original on 16 August 2018. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ Koenig 1971; Payne 1983: Briggs 2009
- ^ ""El concepto de España en la historiografía visigoda y asturiana" (The concept of Spain in Visigothic and Asturian historiography). Alexander Pierre Bronisch, 2006". Archived from the original on 2023-10-31. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
- ^ Hispania-Spania. El nacimiento de España. Conciencia hispana en el reino visigodo de Toledo (Santiago Cantera Montenegro). Hispania-Spania. The birth of Spain. Hispanic consciousness in the Visigothic Kingdom of Toledo. (Santiago Cantera Montenegro)
- ^ Sáez Juárez, Juana (December 2002). "Los primeros pobladores de la Península Ibérica. Cronología y posibles rutas". Página de Historia (in Spanish). Universidad de Valencia. Archived from the original on 29 May 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ Baselland, Archäologie. "Der Faustkeil von Pratteln". Archäologie Baselland. Archived from the original on 2018-11-16. Retrieved 2019-07-14.
- ^ Francis Pryor, Britain BC, 2003.
- ^ "Signs of Earliest Scots Unearthed". BBC News. 9 April 2009. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ "Biggar Archaeology News – Early Mesolithic flint assemblage found". biggararchaeology.org.uk. Archived from the original on 10 October 2010. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ "Gathering the Jewels". Early Neanderthal jaw fragment, c. 230,000 years old. Culturenet Cymru. 2008. Archived from the original on 29 February 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ Davies, J A History of Wales, p. 3.[citation not found]
- ^ Andrews, p. 187.
