New Spain
Viceroyalty of New Spain
| |
|---|---|
| 1521–1821 | |
Coat of arms of the viceroyalty of New Spain[1]
| |
| Motto: Plus ultra "Further Beyond" | |
| Anthem: Marcha Real "Royal March" (1775–1821) | |
Left: Flag of Spain (18th century): first national flag, naval and fortress flag, the last flag to float in continental America, in the Fortress of San Juan de Ulúa; Right: Military flag of the Viceroyalty of New Spain with Cross of Burgundy and Royal or Duchy Crown (military flag)  | |
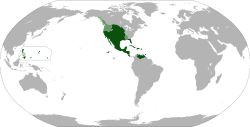 Anachronistic map showing all territories that were ever part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain (dark green). The areas in light green were territories claimed but not controlled by New Spain. | |
| Status | Governorate of the Columbian Viceroyalty (1521–1535) Viceroyalty of the Spanish Empire (1535–1821) |
| Capital | México |
| Official languages | Spanish[2] Nahuatl[3] |
| Regional languages | |
| Religion | Roman Catholicism (official) |
| King | |
• 1521–1556 | Charles I (first) |
• 1813–1821 | Ferdinand VII (last) |
| Viceroy | |
• 1535–1550 | Antonio de Mendoza (first) |
• 1821 | Juan O'Donojú (as Political chief superior) |
| Legislature | Council of the Indies |
| Historical era | Colonial era |
| 1519–1521 | |
| 13 August 1521 | |
• Venezuela annexed to Viceroyalty of New Granada | 27 May 1717 |
• Panama annexed to New Kingdom of Granada | 1739 |
| 1762 | |
| 1 October 1800 | |
| 22 February 1819 | |
• Trienio Liberal abolished the Kingdom of New Spain | 31 May 1820 |
| 28 September 1821 | |
| Area | |
| 1790 | 7,657,000 km2 (2,956,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1790 | 7 million |
• 1810 | 8 million |
| Currency | Spanish colonial real |
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain (Spanish: Virreinato de Nueva España [birejˈnato ðe ˈnweβa esˈpaɲa] ; Nahuatl: Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl),[4] originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several domains established during the Spanish conquest of the Americas, and had its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a large area of the southern and western portions of North America, mainly what became Mexico and the Southwestern United States, but also California, Florida and Louisiana; Central America, the Caribbean, and northern parts of South America; several Pacific archipelagos, including the Philippines and Guam. Additional Asian colonies included "Spanish Formosa," on the island of Taiwan.
After the 1521 Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, conqueror Hernán Cortés named the territory New Spain, and established the new capital, Mexico City, on the site of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Mexica (Aztec) Empire. Central Mexico became the base of expeditions of exploration and conquest, expanding the territory claimed by the Spanish Empire. With the political and economic importance of the conquest, the crown asserted direct control over the densely populated realm. The crown established New Spain as a viceroyalty in 1535, appointing as viceroy Antonio de Mendoza, an aristocrat loyal to the monarch rather than the conqueror Cortés. New Spain was the first of the viceroyalties that Spain created, the second being Peru in 1542, following the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire. Both New Spain and Peru had dense indigenous populations at conquest as a source of labor and material wealth in the form of vast silver deposits, discovered and exploited beginning in the mid-1500s.
New Spain developed strong regional divisions based on local climate, topography, distance from the capital and the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz, size and complexity of indigenous populations, and the presence or absence of mineral resources. Central and southern Mexico had dense indigenous populations, each with complex social, political, and economic organization, but no large-scale deposits of silver to draw Spanish settlers. By contrast, the northern area of Mexico was arid and mountainous, a region of nomadic and semi-nomadic indigenous populations, which do not easily support human settlement. In the 1540s, the discovery of silver in Zacatecas attracted Spanish mining entrepreneurs and workers, to exploit the mines, as well as crown officials to ensure the crown received its share of revenue. Silver mining became integral not only to the development of New Spain, but also to the enrichment of the Spanish crown, which marked a transformation in the global economy. New Spain's port of Acapulco became the New World terminus of the transpacific trade with the Philippines via the Manila galleon. New Spain became a vital link between Spain's New World empire and its East Indies empire.
From the beginning of the 19th century, the kingdom fell into crisis, aggravated by the 1808 Napoleonic invasion of Iberia and the forced abdication of the Bourbon monarch, Charles IV. This resulted in a political crisis in New Spain and much of the Spanish Empire in 1808, which ended with the government of Viceroy José de Iturrigaray. Conspiracies of American-born Spaniards sought to take power, leading to the Mexican War of Independence, 1810–1821. At its conclusion in 1821, the viceroyalty was dissolved and the Mexican Empire was established. Former royalist military officer turned insurgent for independence Agustín de Iturbide would be crowned as emperor.
The Crown and the Viceroyalty of New Spain
[edit]The Kingdom of New Spain was established on 18 August 1521, following the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, as a New World kingdom ruled by the Crown of Castile. The initial funds for exploration came from Queen Isabella.[5][6] Although New Spain was a dependency of Castile, it (Mexico) was a kingdom and not a colony, subject to the presiding monarch on the Iberian Peninsula.[7][8]
The monarch had sweeping power in the overseas territories, with not just sovereignty over the realm but also property rights. All power over the state came from the monarch. The crown had sweeping powers over the Catholic Church in its overseas territories, and via the Patronato real, a grant by the papacy to the crown to oversee the Church in all aspects save doctrine. The Viceroyalty of New Spain was created by royal decree on October 12, 1535, in the Kingdom of New Spain with a viceroy appointed as the king's "deputy" or substitute. This was the first New World viceroyalty and one of only two that the Spanish Rmpire administered in the continent until the 18th-century Bourbon Reforms.
Territorial extent of the overseas Spanish Empire
[edit]
At its greatest extent, the Spanish crown claimed on the mainland of the Americas much of North America south of Canada, that is: all of modern Mexico and Central America except Panama; most of the United States west of the Mississippi River, plus the Floridas. The Spanish West Indies, settled prior to the conquest of the Aztec Empire, also came under New Spain's jurisdiction: Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, the Cayman Islands, Trinidad, and the Bay Islands.[9][10][11] New Spain also claimed jurisdiction over the overseas territories of the Spanish East Indies in Asia and Oceania: the Philippine Islands, the Mariana Islands, the Caroline Islands, parts of Taiwan, and parts of the Moluccas. Although asserting sovereignty over this vast realm, it did not effectively control large swaths. Other European powers, including England, France, and the Netherlands established colonies in territories Spain claimed.
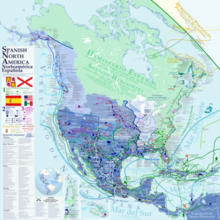
Much of what was called in the United States the "Spanish borderlands", is territory that attracted few Spanish settlers, with less dense indigenous populations and apparently lacking in mineral wealth. Huge deposits of gold in California were discovered immediately after it was incorporated into the U.S. following the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The northern region of New Spain in the colonial era was considered marginal to Spanish interests compared to the most densely populated and lucrative areas of central Mexico. To shore up its claims in North America in the eighteenth century as other powers encroached on its claims, the crown sent expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, which explored and claimed the coast of British Columbia and Alaska.[12]
Religious missions and fortified presidios were established to shore up Spanish control on the ground. On the mainland, the administrative units included Las Californias, that is, the Baja California peninsula, still part of Mexico and divided into Baja California and Baja California Sur; Alta California (modern Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, western Colorado, and southern Wyoming); (from the 1760s) Louisiana (including the western Mississippi River basin and the Missouri River basin); Nueva Extremadura (the modern states of Coahuila and Texas); and Santa Fe de Nuevo México (parts of Texas and New Mexico).[13]
Government
[edit]

Viceroyalty
[edit]The Viceroyalty was administered by a viceroy residing in Mexico City and appointed by the Spanish monarch, who had administrative oversight of all of these regions, although most matters were handled by the local governmental bodies, which ruled the various regions of the viceroyalty. First among these were the audiencias, which were primarily superior tribunals, but which also had administrative and legislative functions. Each of these was responsible to the Viceroy of New Spain in administrative matters (though not in judicial ones), but they also answered directly to the Council of the Indies.
Captaincies general and governorates
[edit]The Captaincy Generals were the second-level administrative divisions and these were relatively autonomous from the viceroyalty. The viceroy was captain-general of those provinces that remained directly under his command. Santo Domingo (1535); Philippines (1565); Puerto Rico (1580); Cuba (1608); Guatemala (1609); Yucatán (1617); Commandancy General of the Provincias Internas (1776) (analogous to a dependent captaincy general). Two governorates, third-level administrative divisions, were established, the Governorate of Spanish Florida (Spanish: La Florida) and the Governorate of Spanish Louisiana (Spanish: Luisiana).
High courts
[edit]The high courts, or audiencias, were established in major areas of Spanish settlement. In New Spain the high court was established in 1527, prior to the establishment of the viceroyalty. The First Audiencia was headed by Hernán Cortés's rival Nuño de Guzmán, who used the court to deprive Cortés of power and property. The crown dissolved the First Audiencia and established the Second Audiencia.[14] The audiencias of New Spain were Santo Domingo (1511, effective 1526, predated the Viceroyalty); Mexico (1527, predated the Viceroyalty); Panama (1st one, 1538–1543); Guatemala (1543); Guadalajara (1548); Manila (1583).
Audiencia districts further incorporated the older, smaller divisions known as governorates (gobernaciones, roughly equivalent to provinces), which had been originally established by conquistador-governors known as adelantados. Provinces which were under military threat were grouped into captaincies general, such as the Captaincies General of the Philippines (established 1574) and Guatemala (established in 1609), which were joint military and political commands with a certain level of autonomy. The viceroy was captain-general of those provinces that remained directly under his command.

Local-level administration
[edit]At the local level there were over two hundred districts, in both indigenous and Spanish areas, which were headed by either a corregidor (also known as an alcalde mayor) or a cabildo (town council), both of which had judicial and administrative powers. In the late 18th century the Bourbon dynasty began phasing out the corregidores and introduced intendants, whose broad fiscal powers cut into the authority of the viceroys, governors and cabildos. Despite their late creation, these intendancies so affected the formation of regional identity that they became the basis for the nations of Central America and the first Mexican states after independence.
Intendancies of the 1780s
[edit]As part of the sweeping eighteenth-century administrative and economic changes known as the Bourbon Reforms, the Spanish crown created new administrative units called intendancies, to strengthen central control over the viceroyalty. Some measures aimed to break the power of local elites in order to improve the economy of the empire. Reforms included the improvement of public participation in communal affairs, distribution of undeveloped lands to the indigenous and Spaniards, ending the corrupt practices of local crown officials, encouraging trade and mining, and establishing a system of territorial division similar to the model created by the government of France, already adopted in Spain.[15][16]
The establishment of intendancies was strongly resisted by the viceroyalties and general captaincies similar to the opposition in the Iberian Peninsula when the reform was adopted. Royal audiencias and ecclesiastical hierarchs opposed the reform for its intervention in economic issues, for its centralist politics, and the forced ceding of many of their functions to the intendants. In New Spain, these units generally corresponded to the regions or provinces that had developed earlier in the center, South, and North.[17][18]
Many of the intendancy boundaries became Mexican state boundaries after independence. The intendancies were created between 1764 and 1789, with the greatest number in the mainland in 1786: 1764 La Habana (later subdivided); 1766 Nueva Orleans; 1784 Puerto Rico; 1786 México, Veracruz, Puebla de Los Ángeles, Guadalajara, Guanajuato, Zacatecas, San Luis Potosí, Sonora, Durango, Oaxaca, Guatemala, San Salvador, Comayagua, León, Santiago de Cuba, Puerto Príncipe; 1789 Mérida.[19][20]
History of New Spain
[edit]The history of mainland New Spain spans three hundred years from the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521) to the collapse of Spanish rule in the Mexican War of Independence (1810–1821).
Beginning with the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire in 1521 by Hernán Cortés, Spanish rule was established, leading to the creation of governing bodies like the Council of the Indies and the Audiencia to maintain control. It involved the forced conversion of indigenous populations to Catholicism and the blending of Spanish and indigenous cultures.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, Spanish settlers founded major cities such as Mexico City, Puebla, and Guadalajara, turning New Spain into a vital part of the Spanish Empire. The discovery of silver in Zacatecas and Guanajuato significantly boosted the economy, leading to conflicts like the Chichimeca War. Missions and presidios were established in northern frontiers, aiding in the expansion and control of territories that later became part of the southwestern United States. The 18th century saw the implementation of the Bourbon Reforms, which aimed to modernize and strengthen the colonial administration and economy. These reforms included the creation of intendancies, increased military presence, and the centralization of royal authority. The expulsion of the Jesuits and the establishment of economic societies, were part of the efforts to enhance efficiency and revenue for the crown.
The decline of New Spain culminated in the early 19th century with the Mexican War of Independence. Following Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla's 1810 Cry of Dolores, the insurgent army waged an eleven-year war against Spanish rule. The eventual alliance between royalist military officer Agustín de Iturbide and insurgent leader Vicente Guerrero led to the successful campaign for independence. In 1821, New Spain officially became the independent nation of Mexico, ending three centuries of Spanish colonial rule.
Economy
[edit]



During the era of the conquest, in order to pay off the debts incurred by the conquistadors and their companies, the new Spanish governors awarded their men grants of native tribute and labor, known as encomiendas. In New Spain these grants were modeled after the tribute and corvee labor that the Mexica rulers had demanded from native communities. This system came to signify the oppression and exploitation of natives, although its originators may not have set out with such intent. In short order the upper echelons of patrons and priests in the society lived off the work of the lower classes. Due to some horrifying instances of abuse against the indigenous peoples, Bishop Bartolomé de las Casas suggested bringing black slaves to replace them. Fray Bartolomé later repented when he saw the even worse treatment given to the black slaves.
In colonial Mexico, Encomenderos de Negros were specialized middlemen during the first half of the seventeenth century. While encomendero (alternatively, encomenderos de indios) generally refers to men granted the labor and tribute of a particular indigenous group in the immediate post-conquest era, encomenderos de negros were Portuguese slave dealers who were permitted to operate in Mexico for the slave trade.[citation needed]
In Peru, the other discovery that perpetuated the system of forced labor, the mit'a, was the enormously rich single silver mine discovered at Potosí, but in New Spain, labor recruitment differed significantly. With the exception of silver mines worked in the Aztec period at Taxco, southwest of Tenochtitlan, the Mexico's mining region was outside the area of dense indigenous settlement. Labor for the mines in the north of Mexico had a workforce of black slave labor and indigenous wage labor, not draft labor.[21] Indigenous who were drawn to the mining areas were from different regions of the center of Mexico, with a few from the north itself. With such diversity they did not have a common ethnic identity or language and rapidly assimilated to Hispanic culture. Although mining was difficult and dangerous, the wages were good, which is what drew the indigenous labor.[21]
The Viceroyalty of New Spain was the principal source of income for Spain in the eighteenth century, with the revival of mining under the Bourbon Reforms. Important mining centers like Zacatecas, Guanajuato, San Luis Potosí and Hidalgo had been established in the sixteenth century and suffered decline for a variety of reasons in the seventeenth century, but silver mining in Mexico out-performed all other Spanish overseas territories in revenues for the royal coffers.
The fast red dye cochineal was an important export in areas such as central Mexico and Oaxaca in terms of revenues to the crown and stimulation of the internal market of New Spain. Cacao and indigo were also important exports for the New Spain, but was used through rather the vice royalties rather than contact with European countries due to piracy, and smuggling.[22] The indigo industry in particular also helped to temporarily unite communities throughout the Kingdom of Guatemala due to the smuggling.[22]
There were two major ports in New Spain, Veracruz the viceroyalty's principal port on the Atlantic, and Acapulco on the Pacific, terminus of the Manila galleon. In the Philippines Manila near the South China Sea was the main port. The ports were fundamental for overseas trade, stretching a trade route from Asia, through the Manila galleon to the Spanish mainland.
These were ships that made voyages from the Philippines to Mexico, whose goods were then transported overland from Acapulco to Veracruz and later reshipped from Veracruz to Cádiz in Spain. So then, the ships that set sail from Veracruz were generally loaded with merchandise from the East Indies originating from the commercial centers of the Philippines, plus the precious metals and natural resources of Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. During the 16th century, Spain held the equivalent of US$1.5 trillion (1990 terms) in gold and silver received from New Spain.
However, these resources did not translate into development for the Metropolis (mother country) due to Spanish Roman Catholic Monarchy's frequent preoccupation with European wars (enormous amounts of this wealth were spent hiring mercenaries to fight the Protestant Reformation), as well as the incessant decrease in overseas transportation caused by assaults from companies of British buccaneers, Dutch corsairs and pirates of various origin. These companies were initially financed by, at first, by the Amsterdam stock market, the first in history and whose origin is owed precisely to the need for funds to finance pirate expeditions, as later by the London market. The above is what some authors call the "historical process of the transfer of wealth from the south to the north."
Regions of mainland New Spain
[edit]In the colonial period, basic patterns of regional development emerged and strengthened.[23] European settlement and institutional life was built in the Mesoamerican heartland of the Aztec Empire in Central Mexico. The South (Oaxaca, Michoacán, Yucatán, and Central America) was a region of dense indigenous settlement of Mesoamerica, but without exploitable resources of interest to Europeans, the area attracted few Europeans, while the indigenous presence remained strong.
The North was outside the area of complex indigenous populations, inhabited primarily by nomadic and hostile northern indigenous groups. With the discovery of silver in the north, the Spanish sought to conquer or pacify those peoples in order to exploit the mines and develop enterprises to supply them. Nonetheless, much of northern New Spain had sparse indigenous population and attracted few Europeans. The Spanish crown and later the Republic of Mexico did not effectively exert sovereignty over the region, leaving it vulnerable to the expansionism of the United States in the nineteenth century.
Regional characteristics of colonial Mexico have been the focus of considerable study.[23][24] For those based in the vice-regal capital of Mexico City, everywhere else were the "provinces." Even in the modern era, "Mexico" for many refers solely to Mexico City, with the pejorative view that anywhere outside the capital is a hopeless backwater.[25] "Fuera de México, todo es Cuauhtitlán" ["outside of Mexico City, it's all Podunk"],[26][27] that is, poor, marginal, and backward, in short, the periphery.
The picture is far more complex, however; while the capital is enormously important as the center of institutional, economic, and social power, the provinces played a significant role in colonial Mexico. Regions (provinces) developed and thrived to the extent that they became sites of economic production and tied into networks of trade. "Spanish society in the Indies was import-export oriented at the very base and in every aspect," and the development of many regional economies was typically centered on support of that export sector.[28]
Central region
[edit]Mexico City, capital of the viceroyalty
[edit]
Mexico City was the center of the Central region, and the hub of New Spain. The development of Mexico City itself was vitally important to the development of New Spain as a whole. It was the seat of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, the Archdiocese of the Catholic Church, the Holy Office of the Inquisition, the merchants' guild (consulado), and home of the most elite families in the Kingdom of New Spain. Mexico City was the single most populous city, not just in New Spain, but for many years the entire Western Hemisphere, with a high concentration of mixed-race castas.
Veracruz to Mexico City
[edit]Significant regional development grew along the main transportation route from the capital east to the port of Veracruz. Alexander von Humboldt called this area, Mesa de Anahuac, which can be defined as the adjacent valleys of Puebla, Mexico, and Toluca, enclosed by high mountains, along with their connections to the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz and the Pacific port of Acapulco, where over half the population of New Spain lived.[29] These valleys were linked trunk lines, or main routes, facilitating the movement of vital goods and people to get to key areas.[30]
Even in the relatively richly endowed region of Mexico, the difficulty of transit of people and goods in the absence of rivers and level terrain remained a major challenge to the economy of New Spain. This challenge persisted during the post-independence years until the late nineteenth-century construction of railroads. In the colonial era and up until the railroads were built in key areas in post-independence in the late nineteenth century, mule trains were the main mode of transporting goods. Pack mules were used because unpaved roads, mountainous terrain, and seasonal flooding could not generally accommodate carts.
In the late eighteenth century, the crown devoted some resources to study and remedy the poor roads. The Camino Real (royal road) between the port of Veracruz and the capital had some short sections paved and bridges constructed. The construction was done despite protests from some indigenous settlements when the infrastructure improvements, which sometimes included rerouting the road through communal lands. The Spanish crown finally decided that road improvement was in the interests of the state for military purposes, as well as for fostering commerce, agriculture, and industry, but the lack of state involvement in the development of physical infrastructure was to have lasting effects, constraining development until the late nineteenth century.[31][32] Despite the road improvements, transit was still difficult, particularly for heavy military equipment.
Although the crown had ambitious plans for both the Toluca and Veracruz portions of the king's highway, improvements were limited to a localized network.[33] Even where infrastructure was improved, transit on the Veracruz-Puebla main road had other obstacles, with wolves attacking mule trains, killing animals, and rendering some sacks of foodstuffs unsellable because they were smeared with blood.[34] The north-south Acapulco route remained a mule track through mountainous terrain.
Veracruz, port city and province
[edit]Veracruz was the first Spanish settlement founded in what became New Spain, and it endured as the only viable Gulf Coast port, the gateway for Spain to New Spain. The difficult topography around the port affected local development and New Spain as a whole. Going from the port to the central plateau entailed a daunting 2000 meter climb from the narrow tropical coastal plain in just over a hundred kilometers. The narrow, slippery road in the mountain mists was treacherous for mule trains, and in some cases mules were hoisted by ropes. Many tumbled with their cargo to their deaths.[35]
Given the transport constraints, only high-value, low-bulk goods continued to be shipped in the transatlantic trade, which stimulated local production of foodstuffs, rough textiles, and other products for a mass market. Although New Spain produced considerable sugar and wheat, these were consumed exclusively in the colony even though there was demand elsewhere. Philadelphia, not New Spain, supplied Cuba with wheat.[36]
The Caribbean port of Veracruz was small, with its hot, pestilential climate not a draw for permanent settlers: its population never topped 10,000.[37] Many Spanish merchants preferred living in the pleasant highland town of Jalapa (1,500 m). For a brief period (1722–76) the town of Jalapa became even more important than Veracruz, after it was granted the right to hold the royal trade fair for New Spain, serving as the entre for goods from Asia via Manila galleon through the port of Acapulco and European goods via the flota (convoy) from the Spanish port of Cádiz.[38]
Spaniards also settled in the temperate area of Orizaba, east of the Citlaltepetl volcano. Orizaba varied considerably in elevation from 800 metres (2,600 ft) to 5,700 metres (18,700 ft) (the summit of the Citlaltepetl volcano), but "most of the inhabited part is temperate."[39] Some Spaniards lived in semitropical Córdoba, which was founded as a villa in 1618, to serve as a Spanish base against runaway slave (cimarrón) predations on mule trains traveling the route from the port to the capital. Some cimarrón settlements sought autonomy, such as one led by Gaspar Yanga, with whom the crown concluded a treaty leading to the recognition of a largely black town, San Lorenzo de los Negros de Cerralvo, later called the municipality of Yanga.[40]
European diseases immediately affected the multiethnic Indian populations in the Veracruz area and for that reason Spaniards imported black slaves as either an alternative to indigenous labor or its complete replacement in the event of a repetition of the Caribbean die-off. A few Spaniards acquired prime agricultural lands left vacant by the indigenous demographic disaster. Portions of the province could support sugar cultivation and as early as the 1530s sugar production was underway. New Spain's first viceroy, Don Antonio de Mendoza established an hacienda on lands taken from Orizaba.[41]
Indians resisted cultivating sugarcane themselves, preferring to tend their subsistence crops. As in the Caribbean, black slave labor became crucial to the development of sugar estates. During the period 1580–1640 when Spain and Portugal were ruled by the same monarch and Portuguese slave traders had access to Spanish markets, African slaves were imported in large numbers to New Spain and many of them remained in the region of Veracruz. But even when that connection was broken and prices rose, black slaves remained an important component of Córdoba's labor sector even after 1700. Rural estates in Córdoba depended on African slave labor, who were 20% of the population there, a far greater proportion than any other area of New Spain, and greater than even nearby Jalapa.[42]
In 1765 the crown created a monopoly on tobacco, which directly affected agriculture and manufacturing in the Veracruz region. Tobacco was a valuable, high-demand product. Men, women, and even children smoked, something commented on by foreign travelers and depicted in eighteenth-century casta paintings.[43] The crown calculated that tobacco could produce a steady stream of tax revenues by supplying the huge Mexican demand, so the crown limited zones of tobacco cultivation. It also established a small number of factories of finished products, and licensed distribution outlets (estanquillos).[44] The crown also set up warehouses to store up to a year's worth of supplies, including paper for cigarettes, for the factories.[45] With the establishment of the monopoly, crown revenues increased and there is evidence that despite high prices and expanding rates of poverty, tobacco consumption rose while at the same time, general consumption fell.[46]
In 1787 during the Bourbon Reforms Veracruz became an intendancy, a new administrative unit.
Valley of Puebla
[edit]Founded in 1531 as a Spanish settlement, Puebla de los Angeles quickly rose to the status of Mexico's second-most important city. Its location on the main route between the viceregal capital and the port of Veracruz, in a fertile basin with a dense indigenous population, largely not held in encomienda, made Puebla a destination for later arriving Spaniards. If there had been significant mineral wealth in Puebla, it could have been even more prominent a center for New Spain, but its first century established its importance. In 1786 it became the capital of an intendancy of the same name.[47]
It became the seat of the richest diocese in New Spain in its first century, with the seat of the first diocese, formerly in Tlaxcala, moved there in 1543.[48] Bishop Juan de Palafox asserted that the income from the diocese of Puebla was twice that of the archbishopic of Mexico, due to the tithe income derived from agriculture.[49] In its first hundred years, Puebla was prosperous from wheat farming and other agriculture, as the ample tithe income indicates, plus manufacturing woolen cloth for the domestic market. Merchants, manufacturers, and artisans were important to the city's economic fortunes, but its early prosperity was followed by stagnation and decline in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.[50]
The foundation of the town of Puebla was a pragmatic social experiment to settle Spanish immigrants without encomiendas to pursue farming and industry.[51] Puebla was privileged in a number of ways, starting with its status as a Spanish settlement not founded on existing indigenous city-state, but with a significant indigenous population. It was located in a fertile basin on a temperate plateau in the nexus of the key trade triangle of Veracruz–Mexico City–Antequera (Oaxaca). Although there were no encomiendas in Puebla itself, encomenderos with nearby labor grants settled in Puebla. And despite its foundation as a Spanish city, sixteenth-century Puebla had Indians resident in the central core.[51]
Administratively Puebla was far enough from Mexico City (approximately 160 km or 100 mi) so as not to be under its direct influence. Puebla's Spanish town council (cabildo) had considerable autonomy and was not dominated by encomenderos. The administrative structure of Puebla "may be seen as a subtle expression of royal absolutism, the granting of extensive privileges to a town of commoners, amounting almost to republican self-government, in order to curtail the potential authority of encomenderos and the religious orders, as well as to counterbalance the power of the viceregal capital."[52]

During the "golden century" from its founding in 1531 until the early 1600s, Puebla's agricultural sector flourished, with small-scale Spanish farmers plowing the land for the first time, planting wheat and vaulting Puebla to importance as New Spain's breadbasket, a role assumed by the Bajío (including Querétaro) in the seventeenth century, and Guadalajara in the eighteenth.[53] Puebla's wheat production was the initial source of its prosperity, but it emerged as a manufacturing and commercial center, "serving as the inland port of Mexico's Atlantic trade."[54] Economically, the city was exempted from the alcabala (sales tax) and almojarifazgo (import/export duties) for its first century (1531–1630), which helped promote commerce.
Puebla built significant textile production in workshops (obrajes) supplying New Spain and markets as far away as Guatemala and Peru. Transatlantic ties between a particular Spanish town, Brihuega, and Puebla demonstrated the close connection between the two settlements. The growth in Puebla's manufacturing sector did not simply coincide with immigration from Brihuega but was crucial to "shaping and driving Puebla's economic development".[55]
Brihuega immigrants came to Mexico with expertise in textile production, and the transplanted briocenses provided capital to create large-scale obrajes. Although obrajes in Brihuega were small-scale enterprises, quite a number of them in Puebla employed up to 100 workers. Supplies of wool, water for fulling mills, and labor (free indigenous, incarcerated Indians, black slaves) were available. Although much of Puebla's textile output was rough cloth, it also produced higher quality dyed cloth with cochineal from Oaxaca and indigo from Guatemala.[56] But by the eighteenth century, Querétaro had displaced Puebla as the mainstay of woolen textile production.[57]
In 1787, Puebla became an intendancy as part of the new administrative structuring of the Bourbon Reforms.
Valley of Mexico
[edit]Mexico City dominated the Valley of Mexico, but the valley continued to have dense indigenous populations challenged by growing, increasingly dense Spanish settlement. The Valley of Mexico had many former Indian city-states that became Indian towns in the colonial era. These towns continued to be ruled by indigenous elites under the Spanish crown, with an indigenous governor and a town councils.[58][59] The Indian towns close to the capital were the most desirable ones for encomenderos to hold and for the friars to evangelize.
The capital was provisioned by the indigenous towns, and its labor was available for enterprises that ultimately created a colonial economy. The gradual drying up of the central lake system created more dry land for farming, but the sixteenth-century population declines allowed Spaniards to expand their acquisition of land. One region that retained strong Indian land holding was the southern fresh water area, with important suppliers of fresh produce to the capital. The area was characterized by intensely cultivated chinampas, human-made extensions of cultivable land into the lake system. These chinampa towns retained a strong indigenous character, and Indians continued to hold the majority of that land, despite its closeness to the Spanish capital. A key example is Xochimilco.[60][61][62]
Texcoco in the pre-conquest period was one of the three members of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the cultural center of the empire. It fell on hard times in the colonial period as an economic backwater. Spaniards with any ambition or connections would be lured by the closeness of Mexico City, so that the Spanish presence was minimal and marginal.[63]
Tlaxcala, the major ally of the Spanish against the Aztecs of Tenochtitlan, also became something of a backwater, but like Puebla it did not come under the control of Spanish encomenderos. No elite Spaniards settled there, but like many other Indian towns in the Valley of Mexico, it had an assortment of small-scale merchants, artisans, farmers and ranchers, and textile workshops (obrajes).[64]
North
[edit]Since portions of northern New Spain became part of the United States' Southwest region, there has been considerable scholarship on the Spanish borderlands in the north. The motor of the Spanish colonial economy was the extraction of silver. In Bolivia, it was from the single rich mountain of Potosí; but in New Spain, there were two major mining sites, one in Zacatecas, the other in Guanajuato.
The region farther north of the main mining zones attracted few Spanish settlers. Where there were settled indigenous populations, such as in the present-day state of New Mexico and in coastal regions of Baja and Alta California, indigenous culture retained considerable integrity.
Bajío, Mexico's breadbasket
[edit]The Bajío, a rich, fertile lowland just north of central Mexico, was nonetheless a frontier region between the densely populated plateaus and valleys of Mexico's center and south and the harsh northern desert controlled by nomadic Chichimeca. Devoid of settled indigenous populations in the early sixteenth century, the Bajío did not initially attract Spaniards, who were much more interested in exploiting labor and collecting tribute whenever possible. The region did not have indigenous populations that practiced subsistence agriculture. The Bajío developed in the colonial period as a region of commercial agriculture.
The discovery of mining deposits in Zacatecas and Guanajuato in the mid-sixteenth century and later in San Luis Potosí stimulated the Bajío's development to supply the mines with food and livestock. A network of Spanish towns was established in this region of commercial agriculture, with Querétaro also becoming a center of textile production. Although there were no dense indigenous populations or network of settlements, Indians migrated to the Bajío to work as resident employees on the region's haciendas and ranchos or rented land (terrasguerros). From diverse cultural backgrounds and with no sustaining indigenous communities, these indios were quickly hispanized, but largely remained at the bottom of the economic hierarchy.[65] Although Indians migrated willingly to the region, they did so in such small numbers that labor shortages prompted Spanish hacendados to provide incentives to attract workers, especially in the initial boom period of the early seventeenth century. Land owners lent workers money, which could be seen as a perpetual indebtedness, but it can be seen not as coercing Indians to stay but a way estate owners sweetened their terms of employment, beyond their basic wage labor.[66][67] For example, in 1775 the Spanish administrator of a San Luis Potosí estate "had to scour both Mexico City and the northern towns to find enough blue French linen to satisfy the resident employees."[68] Other types of goods they received on credit were textiles, hats, shoes, candles, meat, beans, and a guaranteed ration of maize. However, where labor was more abundant or market conditions depressed, estate owners paid lower wages. The more sparsely populated northern Bajío tended to pay higher wages than the southern Bajío, which was increasingly integrated in the economy of central Mexico.[69] The credit-based employment system often privileged those holding higher ranked positions on the estate (supervisors, craftsmen, other specialists) who were mostly white, and the estates did not demand repayment.[70]
In the late colonial period, renting complemented estate employment for many non-Indians in more central areas of the Bajío with access to markets. As with hacendados, renters produced for the commercial market. While these Bajío renters could prosper in good times and achieved a level of independence, drought and other disasters made their choice more risky than beneficial.[71]
Many renters retained ties to the estates, diversifying their household's sources of income and level of economic security. In San Luis Potosí, rentals were fewer and estate employment the norm. After a number of years of drought and bad harvests in the first decade of the nineteenth century Hidalgo's 1810 grito appealed more in the Bajío than in San Luis Potosí. In the Bajío estate owners were evicting tenants in favor of renters better able to pay more for land, there was a disruption of previous patterns of mutual benefit between estate owners and renters.[69]
Spanish borderlands
[edit]
Areas of northern Mexico were incorporated into the United States in the mid-nineteenth century, following Texas independence and the Mexican–American War (1846–48) and generally known as the "Spanish Borderlands."[72][73] Scholars in the United States have extensively studied this northern region, which became the states of Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, and California.[74][75][76][77] During the period of Spanish rule, this area was sparsely populated even by indigenous peoples.[78]
The Presidios (forts), pueblos (civilian towns) and the misiones (missions) were the three major agencies employed by the Spanish crown to extend its borders and consolidate its colonial holdings in these territories.
Missions and the northern frontier
[edit]The town of Albuquerque (modern Albuquerque, New Mexico) was founded in 1706. Other Mexican towns in the region included Paso del Norte (modern Ciudad Juárez), founded in 1667; Santiago de la Monclova in 1689; Panzacola, Tejas in 1681; and San Francisco de Cuéllar (modern city of Chihuahua) in 1709. From 1687, Father Eusebio Francisco Kino, with funding from the Marqués de Villapuente, founded over twenty missions in the Sonoran Desert (in modern Sonora and Arizona).
From 1697, Jesuits established eighteen missions throughout the Baja California peninsula. Between 1687 and 1700 several missions were founded in Trinidad, but only four survived as Amerindian villages throughout the 18th century. In 1691, explorers and missionaries visited the interior of Texas and came upon a river and Amerindian settlement on 13 June, the feast day of St. Anthony, and named the location and river San Antonio in his honor.
New Mexico
[edit]
During the term of viceroy Don Luis de Velasco, marqués de Salinas the crown ended the long-running Chichimeca War by making peace with the semi-nomadic Chichimeca indigenous tribes of northern México in 1591. This allowed expansion into the 'Province of New Mexico' or Provincia de Nuevo México. In 1595, Don Juan de Oñate, son of one of the key figures in the silver remining region of Zacatecas, received official permission from the viceroy to explore and conquer New Mexico. As was the pattern of such expeditions, the leader assumed the greatest risk but would reap the largest rewards, so that Oñate would become capitán general of New Mexico and had the authority to distribute rewards to those in the expedition.[79]
Oñate pioneered 'The Royal Road of the Interior Land' or El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro between Mexico City and the Tewa village of Ohkay Owingeh, or San Juan Pueblo. He also founded the Spanish settlement of San Gabriel de Yungue-Ouinge on the Rio Grande near the Native American Pueblo, located just north of the modern city of Española, New Mexico.[80] Oñate eventually learned that New Mexico, while it had a settled indigenous population, had little arable land, no silver mines, and possessed few other resources to exploit that would merit large scale colonization. He resigned as governor in 1607 and left New Mexico, having lost much of his personal wealth on the enterprise.[81]
In 1610, Pedro de Peralta, a later governor of the Province of New Mexico, established the settlement of Santa Fe near the southern end of the Sangre de Cristo mountain range. Missions were established to convert the indigenous peoples and manage the agricultural industry. The territory's indigenous population resented their forced conversion to Catholicism and suppression of their religion, and the imposition of encomienda system of forced labor. The unrest led to the Pueblo Revolt in 1680, expelling the Spanish, who retreated to Paso del Norte, modern-day Ciudad Juárez.[82]
After the return of the Spanish in 1692, the final resolution included a marked reduction of Spanish efforts to eradicate native culture and religion, the issuing of substantial communal land grants to each Pueblo, and a public defender of their rights and for their legal cases in Spanish courts. In 1776 the New Mexico came under the new Provincias Internas jurisdiction. In the late 18th century the Spanish land grant encouraged the settlement by individuals of large land parcels outside Mission and Pueblo boundaries, many of which became ranchos.[83]
California
[edit]In 1602, Sebastián Vizcaíno, the first Spanish presence in the 'New California' (Nueva California) region of the frontier Las Californias province since Cabrillo in 1542, sailed as far north up the Pacific Coast as present-day Oregon, and named California coastal features from San Diego to as far north as the Bay of Monterrey.
Not until the eighteenth century was California of much interest to the Spanish crown, since it had no known rich mineral deposits or indigenous populations sufficiently organized to render tribute and do labor for Spaniards. The discovery of huge deposits of gold in the Sierra Nevada foothills did not come until after the U.S. had added California following the Mexican–American War (1846–48).
By the middle of the 1700s, the Catholic order of Jesuits had established a number of missions on the Baja (lower) California peninsula. Then, in 1767, King Charles III ordered all Jesuits expelled from all Spanish possessions, including New Spain.[84] New Spain's Visitador General José de Gálvez replaced them with the Dominican Order in Baja California, and the Franciscans were chosen to establish new northern missions in Alta (upper) California.
In 1768, Gálvez received the order to "Occupy and fortify San Diego and Monterey for God and the King of Spain." The Spanish colonies there, having far fewer known natural resources and less cultural development than Mexico or Peru, were to combine establishing posts to defend the territory with a perceived responsibility to convert the indigenous people to Catholicism.
The method used to "occupy and fortify" was the established Spanish colonial system: missions (misiones, between 1769 and 1833 twenty-one missions were established) aimed at converting the Native Californians to Catholicism, forts (presidios, four total) to protect the missionaries, and secular municipalities (pueblos, three total). Due to the region's great distance from supplies and support in México, the system had to be largely self-sufficient. As a result, the colonial population of California remained small, widely scattered and near the coast.
In 1776, the north-western frontier areas came under the administration of the new 'Commandancy General of the Internal Provinces of the North' (Provincias Internas), designed to streamline administration and invigorate growth. The crown created two new provincial governments from the former Las Californias in 1804; the southern peninsula became Baja California, and the ill-defined northern mainland frontier area became Alta California.
Once missions and protective presidios were established in an area, large land grants encouraged settlement and establishment of California ranchos. The Spanish system of land grants was not very successful; however, because the grants were merely royal concessions—not actual land ownership. Under later Mexican rule, land grants conveyed ownership, and were more successful at promoting settlement.
Rancho activities centered on cattle-raising; many grantees emulated the Dons of Spain, with cattle, horses and sheep the source of wealth. The work was usually done by Native Americans, sometimes displaced and/or relocated from their villages. Native-born descendants of the resident Spanish-heritage rancho grantees, soldiers, servants, merchants, craftsmen and others became the Californios. Many of the less-affluent men took native wives, and many daughters married later English, French and American settlers.
After the Mexican War of Independence (1821) and subsequent secularization ("disestablishment") of the missions (1834), Mexican land grant transactions increased the spread of the rancho system. The land grants and ranchos established mapping and land-ownership patterns that are still recognizable in present-day California and New Mexico.[85]
South
[edit]Yucatán
[edit]
The Yucatán Peninsula can be considered a cul-de-sac,[86] and it has unique features, but it also has strong similarities to other areas in the South. The Yucatán Peninsula extends into the Gulf of Mexico and was connected to Caribbean trade routes and Mexico City, far more than some other southern regions, such as Oaxaca.[87] The main Spanish settlements included the inland city of Mérida, where Spanish civil and religious officials had their headquarters and where the many Spaniards in the province lived. The villa of Campeche was the peninsula's port, the key gateway for the whole region. A merchant group developed and expanded dramatically as trade flourished during the seventeenth century.[88] Although that period was once characterized as New Spain's "century of depression", for Yucatán this was certainly not the case, with sustained growth from the early seventeenth century to the end of the colonial period.[89]
With dense indigenous Maya populations, Yucatán's encomienda system was established early and persisted far longer than in central Mexico, since fewer Spaniards migrated to the region than in the center.[90] Although Yucatán was a more peripheral area to the colony, since it lacked rich mining areas and no agricultural or other export product, it did have a complex of Spanish settlement, with a whole range of social types in the main settlements of Mérida and the villas of Campeche and Valladolid.[91] There was an important sector of mixed-race "castas", some of whom were fully at home in both the indigenous and Hispanic worlds. Blacks were an important component of Yucatecan society.[92] The largest population in the province was indigenous Maya, who lived in their communities, but which were in contact with the Hispanic sphere via labor demands and commerce.[93]
In Yucatán, Spanish rule was largely indirect, allowing these communities considerable political and cultural autonomy. The Maya community, the cah, was the means by which indigenous cultural integrity was maintained. In the economic sphere, unlike many other regions and ethnic groups in Mesoamerica, the Yucatec Maya did not have a pre-conquest network of regular markets to exchange different types of food and craft goods. Perhaps because the peninsula was uniform in its ecosystem local niche production did not develop.[94] Production of cotton textiles, largely by Maya women, helped pay households' tribute obligations, but basic crops were the basis of the economy. The cah retained considerable land under the control of religious brotherhoods or confraternities (cofradías), the device by which Maya communities avoided colonial officials, the clergy, or even indigenous rulers (gobernadores) from diverting of community revenues in their cajas de comunidad (literally community-owned chests that had locks and keys). Cofradías were traditionally lay pious organizations and burial societies, but in Yucatán they became significant holders of land, a source of revenue for pious purposes kept under cah control. "[I]n Yucatán the cofradía in its modified form was the community."[95] Local Spanish clergy had no reason to object to the arrangement since much of the revenue went for payment for masses or other spiritual matters controlled by the priest.
A limiting factor in Yucatán's economy was the poor quality of the limestone soil, which could only support crops for two to three years with land cleared through slash-and-burn agriculture. Access to water was also a limiting factor on agriculture, with the limestone escarpment giving way in water filled sinkholes (locally called cenotes), but rivers and streams were generally absent on the peninsula. Individuals had rights to land so long as they cleared and tilled them and when the soil was exhausted, they repeated the process. In general, the Indians lived in a dispersed pattern, which Spanish congregación or forced resettlement attempted to alter. Collective labor cultivated the confraternities' lands, which included raising the traditional maize, beans, and cotton. But confraternities also later pursued cattle ranching, as well as mule and horse breeding, depending on the local situation. There is evidence that cofradías in southern Campeche were involved in inter-regional trade in cacao as well as cattle ranching.[96] Although generally the revenues from crops and animals were devoted to expenses in the spiritual sphere, cofradías' cattle were used for direct aid to community members during droughts, stabilizing the community's food supply.[97]
In the seventeenth century, patterns shifted in Yucatán and Tabasco, as the English took territory the Spanish claimed but did not control, especially what became British Honduras (now Belize) and in Laguna de Términos (Isla del Carmen) where they cut logwood. In 1716–17 viceroy of New Spain organized a sufficient ships to expel the foreigners, where the crown subsequently built a fortress at Isla del Carmen.[98] But the British held onto their territory in the eastern portion of the peninsula into the twentieth century. In the nineteenth century, the enclave supplied guns to the rebellious Maya in the Caste War of Yucatan.[99]
Valley of Oaxaca
[edit]
Since Oaxaca was lacking in mineral deposits and it had an abundant sedentary indigenous population, it developed without European or mixed-race population and large-scale Spanish haciendas, so the indigenous communities retained their land, indigenous languages, and distinct ethnic identities. Antequera (Oaxaca City) was a Spanish settlement founded in 1529, but the rest of Oaxaca consisted of indigenous towns. Despite its remoteness from Mexico City, "throughout the colonial era, Oaxaca was one of Mexico's most prosperous provinces."[100][Note 1] In the eighteenth century, the value of crown offices (alcalde mayor or corregidor) were the highest for two Oaxaca jurisdictions, with Jicayan and Villa Alta each worth 7,500 pesos, Cuicatlan-Papalotipac, 4,500; Teposcolula and Chichicapa, each 4,200 pesos.[Note 2]q
The most important commodity for Oaxaca was cochineal red dye. Cochineal's commodity chain is interesting, with indigenous peasants in the remote areas of Oaxaca ultimately linked to Amsterdam and London commodity exchanges and the European production of luxury cloth.[102] The most extensive study of Oaxaca's eighteenth-century economy deals with the nexus between the local crown officials (alcaldes mayores), merchant investors (aviadores), the repartimiento (forced labor), and indigenous products, particularly cochineal. The rich, color-fast red dye produced from insects, was harvested from nopal cacti. Cochineal was a high-value, low-volume product that became the second-most valuable Mexican export after silver. Although it could be produced elsewhere in central and southern Mexico, its main region of production was Oaxaca. For the indigenous in Oaxaca, cochineal was the only one "with which the [tributaries] maintain themselves and pay their debts" but it also had other advantages.[Note 3] Producing cochineal was time-consuming labor, but it was not particularly difficult and could be done by the elderly, women, and children.[104] It was also important to households and communities because it initially did not require the indigenous to displace their existing crops or migrate elsewhere.[105]
Although the repartimiento has historically been seen as an imposition on the indigenous, forcing them into economic relations they would rather have avoided and maintained by force,[106] recent work on eighteenth-century Oaxaca analyzes the nexus of crown officials (the alcaldes mayores) and Spanish merchants, and indigenous via the repartimiento. cash loaned by local crown officials (the alcalde mayor and his teniente), usually to individual Indians but sometimes to communities, in exchange for a fixed amount of a good (cochineal or cotton mantles) at a later date. Indigenous elites were an integral part of the repartimiento, often being recipients of large extensions of credit. As authority figures in their community, they were in a good position to collect on the debt, the most risky part of the business from the Spanish point of view.
Tehuantepec
[edit]The Isthmus of Tehuantepec region of Oaxaca was strategically important for its short transit between the Gulf Coast and the Pacific, facilitating both overland and sea trade. The province of Tehuantepec was the Pacific side of the isthmus and the headwaters of the Coatzacoalcos River.[107] Hernán Cortés acquired holdings for his entailed estate including Huatulco,[Note 4] once the main Pacific Coast port before Acapulco replaced it in 1563.
Gold mining was an early draw for Spaniards, who directed indigenous labor to its extraction, but did not continue beyond the mid-sixteenth century. Over the long run, ranching and commerce were the most important economic activities, with the settlement of Tehuantepec becoming the hub. The region's history can be divided into three distinct periods, an initial period of engagement with Spanish colonial rule to 1563, during which there was a working relationship with the Zapotec ruling line and the establishment of Cortés's economic enterprises. This early period came to a close with the death of the last native king in 1562 and the escheatment of Cortés's Tehuantepec encomiendas to the crown in 1563. The second period of approximately a century (1563–1660) saw the decline of the indigenous entailed estate (cacicazgo) and indigenous political power and development of the colonial economy and imposition of Spanish political and religious structures. The final period is the maturation of these structures (1660–1750). The 1660 rebellion can be a dividing line between the two later periods.[109]
The Villa of Tehuantepec, the largest settlement on the isthmus, was an important prehispanic Zapotec trade and religious center, which was not under the jurisdiction of the Aztecs.[107] The early colonial history of Tehuantepec and the larger province was dominated by Cortés and the Marquesado, but the crown realized the importance of the area and concluded an agreement in 1563 with the second Marqués by which the crown took control of the Tehuantepec encomienda. The Marquesado continued to have major private holdings in the province. The Villa of Tehuantepec became a center of Spanish and mixed-race settlement, crown administration, and trade.
The Cortés haciendas in Tehuantepec were key components of the province's economy, and they were directly linked to other Marquesado enterprises in greater Mexico in an integrated fashion.[110] The Dominicans also had significant holdings in Tehuantepec, but there has been little research on these. However important the Marquesado and the Dominican enterprises were, there were also other economic players in the region, including individual Spaniards as well as existing indigenous communities. Ranching emerged as the dominant rural enterprise in most of Tehuantepec with a ranching boom in the period 1580–1640. Since Tehuantepec experienced significant indigenous population loss in the sixteenth century conforming to the general pattern, ranching made possible for Spaniards to thrive in Tehuantepec because ranching was not dependent on significant amounts of indigenous labor.[111]
The most detailed economic records for the region are of the Marquesado's ranching haciendas, which produced draft animals (horses, mules, burros, and oxen) and sheep and goats, for meat and wool. Cattle ranching for meat, tallow, and leather were also important. Tallow for candles used in churches and residences and leather used in a variety of ways (saddles, other tack, boots, furniture, machinery) were significant items in the larger colonial economy, finding markets well beyond Tehuantepec. Since the Marquesado operated as an integrated enterprise, draft animals were used in other holdings for transport, agriculture, and mining in Oaxaca, Morelos, Toluca, and Mexico City as well as sold. Raised in Tehuantepec, the animals were driven to other Marquesado holdings for use and distribution.[112]
Although colonial population decline affected the indigenous in Tehuantepec, their communities remained important in the colonial era and remain distinctly Indian to the current era. There were differences in the three distinct linguistic and ethnic groups in colonial Tehuantepec, the Zapotec, the Zoque, and the Huave. The Zapotecs concluded an alliance with the Spaniards at contact, and they had already expanded their territory into Zoque and Huave regions.
Under Spanish rule, the Zapotecs not only survived, but flourished, unlike the other two. They continued to pursue agriculture, some of it irrigated, which was not disrupted by the growing ranching economy. Generally Zapotec elites protected their communities from Spanish incursions and community cohesion remained strong as shown in members' performance of regular community service for social ends. Zapotec elites engaged in the market economy early on, which undermined to an extent the bonds between commoners and elites who colluded with the Spanish. In contrast to the Zapotecs, the Zoque generally declined as a group during the ranching boom, with interloping animals eating their maize crops. Zoque response was to take up being vaqueros themselves. They had access to the trade to Guatemala. Of the three indigenous groups, the Huave were the most isolated from the Spanish ranching economy and labor demands.[113] With little arable or grazing land, they exploited the lagoons of the Pacific coast, using shore and beach resources. They traded dried shrimp and fish, as well as purple dye from shells to Oaxaca, likely acquiring foodstuffs that they were unable to cultivate themselves.[111]
Not well documented is the number of African slaves and their descendants, who were artisans in urban areas and did hard manual labor in rural areas.[114] In a pattern recognizable elsewhere, coastal populations were mainly African, including an unknown number of cimarrón (runaway slave) settlements, while inland the indigenous communities were more prominent. On the Cortés haciendas, blacks and mulattoes were essential to the profitability of the enterprises.[115]
In general, Tehuantepec was not a site of major historical events, but in 1660–61, there was a significant rebellion stemming from increased repartimiento Spanish demands.[116]
Central America
[edit]
With the growth of a sufficient Spanish population and the crown's desire to better govern the area, it established the Captaincy General of Guatemala, which had primary jurisdiction over what became Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. The region was diverse, and outlying provinces were resentful for elites in capital of Antigua Guatemala, destroyed by an earthquake in 1773. There was a high court Audiencia in the Kingdom of Guatemala. Given the region's distance from major centers of power in New Spain and Spain itself, local strongmen in the early were only nominally subject to royal authority. The indigenous population was very large in comparison to the Spanish, and there were relatively few Africans. Spaniards continued to employ forced labor in the region starting with the conquest era and exact tribute from the indigenous.[117] Compared to the mining areas of New Spain's North, this region was generally poor in mineral resources, although Honduras had a brief boom in gold mining, and in the colonial period had little potential to develop an export product, except for cacao and the blue dye indigo.[118]


Cacao had been cultivated in the prehispanic period. Orchards of cacao trees, which took a number of years to come to maturity and produce fruit. Cacao boomed in the late sixteenth century, and then was displaced by indigo as the most important export product. Indigo, like cacao, was native to the region, and the indigenous peoples gathered wild indigo, used for dying cloth and as a trade good. After the arrival of the Spanish, they domesticated indigo and created plantations for its cultivation in Yucatan, El Salvador, and Guatemala. The indigo industry thrived, since there was high demand in Europe for a high quality, color-fast blue dye. In the region, cultivation and processing was done by indigenous workers, but the owners of plantations, añileros, were Spanish.
It was a dangerous work environment, with toxins in the indigo plants that sickened and sometimes killed workers. It was profitable, especially following the Bourbon Reforms, which allowed trade within the Spanish empire. In the late eighteenth century, indigo growers organized in a trade organization, the Consulado de Comercio.[119] There were regions that were not subjugated to Spanish rule, such as the Petén and the Mosquito Coast, and the English took advantage of weak Spanish control to establish a commercial presence on the Gulf Coast, later seizing Belize. An American-born Spanish elite (criollos) accumulated land and built fortunes on wheat, sugar, and cattle, all of which were consumed within the region.[120]
Demographics
[edit]The role of epidemics
[edit]
Spanish settlers brought to the American continent smallpox, measles, typhoid fever, and other infectious diseases. Most of the Spanish settlers had developed an immunity to these diseases from childhood, but the indigenous peoples lacked the needed antibodies since these diseases were totally alien to the native population. There were at least three separate, major epidemics that devastated the population: smallpox (1520–1521), measles (1545–1548) and typhus (1576–1581).
During the 16th century, the native population of Mexico fell from an estimated pre-Columbian population of 8 to 20 million to less than two million. Therefore, at the start of the 17th century, continental New Spain was a depopulated region with abandoned cities and maize fields. These diseases did not affect the Philippines in the same way because they were already present; Pre-Hispanic Filipinos had contact with other foreign nationalities prior to the arrival of the Spaniards.
Population in early 1800s
[edit]


While different intendancies would conduct censuses to get insights into their inhabitants (namely occupation, number of persons per household, ethnicity etc.), it was not until 1793 that the results of the first national census would be published. That census is known as the "Revillagigedo census" because its creation was ordered by the Count of the same name. Most of the census' original datasets have reportedly been lost; thus most of what is known about it comes from essays and field investigations made by academics who had access to the census data and used it as reference for their works, such as Prussian geographer Alexander von Humboldt. Each author gives different estimates for the total population, ranging from 3,799,561 to 6,122,354[121][122] (more recent data suggest that the population of New Spain in 1810 was 5 to 5.5 million individuals)[123] and not much variation in ethnic composition, with Europeans ranging from 18% to 23% of New Spain's population, Mestizos ranging from 21% to 25%, Amerindians ranging from 51% to 61% and Africans being between 6,000 and 10,000. It is concluded then, that across nearly three centuries of colonization, the population growth trends of Europeans and Mestizos were steady, while the percentage of the indigenous population decreased at a rate of 13%–17% per century. The authors assert that rather than Europeans and Mestizos having higher birthrates, the reason for the indigenous population's decrease lies with their higher mortality, due to living in remote locations rather than in cities and towns founded by the Spanish colonists, or being at war with them. It is also for these reasons that the number of indigenous Mexicans presents a greater variation between publications, with their numbers in a given location estimated rather than counted, leading to possible overestimations in some provinces and underestimations in others.[124]
| Intendancy/territory | European population (%) | Indigenous population (%) | Mestizo population (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| México (only State of Mexico and capital) | 16.9% | 66.1% | 16.7% |
| Puebla | 10.1% | 74.3% | 15.3% |
| Oaxaca | 06.3% | 88.2% | 05.2% |
| Guanajuato | 25.8% | 44.0% | 29.9% |
| San Luis Potosí | 13.0% | 51.2% | 35.7% |
| Zacatecas | 15.8% | 29.0% | 55.1% |
| Durango | 20.2% | 36.0% | 43.5% |
| Sonora | 28.5% | 44.9% | 26.4% |
| Yucatán | 14.8% | 72.6% | 12.3% |
| Guadalajara | 31.7% | 33.3% | 34.7% |
| Veracruz | 10.4% | 74.0% | 15.2% |
| Valladolid | 27.6% | 42.5% | 29.6% |
| Nuevo México | ~ | 30.8% | 69.0% |
| Vieja California | ~ | 51.7% | 47.9% |
| Nueva California | ~ | 89.9% | 09.8% |
| Coahuila | 30.9% | 28.9% | 40.0% |
| Nuevo León | 62.6% | 05.5% | 31.6% |
| Nuevo Santander | 25.8% | 23.3% | 50.8% |
| Texas | 39.7% | 27.3% | 32.4% |
| Tlaxcala | 13.6% | 72.4% | 13.8% |
~Europeans are included within the Mestizo category.
Regardless of the imprecision related to the counting of indigenous peoples living outside of the colonized areas, the effort that New Spain's authorities put into considering them as subjects is worth mentioning, as censuses made by other colonial or post-colonial countries did not consider American Indians to be citizens/subjects. For example the censuses made by the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata would only count the inhabitants of the colonized settlements.[125] Another example would be the censuses made by the United States, that did not count Indigenous peoples living among the general population until 1860, and indigenous peoples as a whole until 1900.[126]
Once New Spain achieved independence, the legal basis of the colonial caste system was abolished and mentions of a person's caste in official documents was also abandoned, which led to the exclusion of racial classification from future censuses, and made it difficult to track demographic development of each ethnicity in the country. More than a century would pass before Mexico conducted a new census on which a person's race was listed, in 1921,[127] but even then, due to its huge inconsistencies with other official registers as well as its historic context, modern investigators have deemed it inaccurate.[128][129] Almost a century after the 1921 census, Mexico's government has begun to conduct ethno-racial surveys again, with results suggesting that the population growth trends for each major ethnic group haven't changed significantly since the 1793 census.
Culture, art, and architecture
[edit]The capital of Viceroyalty of New Spain, Mexico City, was one of the principal centers of European cultural expansion in the Americas. Some of the most important early buildings in New Spain were churches and other religious architecture. Civil architecture included the viceregal palace, now the National Palace, and the Mexico City town council (cabildo), both located on the main square in the capital.
The first printing press in the New World was brought to Mexico in 1539, by printer Juan Pablos (Giovanni Paoli). The first book printed in Mexico was entitled "La escala espiritual de San Juan Clímaco". In 1568, Bernal Díaz del Castillo finished La Historia Verdadera de la Conquista de la Nueva España. Figures such as Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, Juan Ruiz de Alarcón, and don Carlos de Sigüenza y Góngora, stand out as some of the viceroyalty's most notable contributors to Spanish literature. In 1693, Sigüenza y Góngora published El Mercurio Volante, the first newspaper in New Spain.
Architects Pedro Martínez Vázquez and Lorenzo Rodriguez produced some visually frenetic architecture known as churrigueresque in the capital, Ocotlan, Puebla and some remote silver-mining towns. Composers including Manuel de Zumaya, Juan Gutiérrez de Padilla, and Antonio de Salazar were active from the early 1500s through the Baroque period of music.
See also
[edit]- Criollo people
- Economic history of Mexico
- Filipino immigration to Mexico
- Governor-General of the Philippines
- Historiography of Colonial Spanish America
- History of democracy in Mexico
- History of Honduras
- Index of Mexico-related articles
- List of governors in the Viceroyalty of New Spain
- List of viceroys of New Spain
- Mexican settlement in the Philippines
- Spanish American Enlightenment
- History of Mexico
- History of Guatemala
- History of El Salvador
- List of viceroys of New Spain
Notes
[edit]- ^ Brian R. Hamnett says that "José de Gálvez considered Oaxaca one of New Spain's richest provinces".[101]
- ^ The crown sold public offices, with their purchasers expecting to quickly recoup the costs. For a complete chart, see Hamnett (1971), p. 16.
- ^ Baskes suggests the crown restricted its production to Oaxaca until 1819, which likely contributed to artificially high prices.[103]
- ^ The crown did not wish to have the main west coast port in private hands and an agreement was worked out with Cortés heir, Don Martín Cortés, to relinquish the Tehuantepec encomienda.[108]
References
[edit]- ^ Sierra López, Alejandro. "El rincón de la heráldica. Escudos de ciudades y regiones americanas" [The heraldry corner Coats of arms of American cities and regions]. Gobierno de España. Ministerio de Cultura y Deporte (in Spanish).
Both the coat of arms of Lima and Mexico City were taken as a symbol of the kingdoms of which they were the capital, as can be seen in the Hall of Kingdoms in Madrid, where both appear representing the kingdoms of Peru and Mexico. Spanish: Tanto el escudo de Lima como el de la ciudad de México fueron tomados como sinécdoque de los reinos de los que eran capital, tal y como puede observarse en el Salón de Reinos de Madrid donde ambos aparecen representando a los reinos de Perú y México.
- ^ Wright-Carr, David Charles (September 2007). "La política lingüística en la Nueva España". ResearchGate (in Spanish).
- ^ Wright-Carr, David Charles (September 2007). "La política lingüística en la Nueva España". ResearchGate (in Spanish).
- ^ Figueroa Saavedra, Miguel (December 2022). "Imomachtilis iwan itlachihchiwalis in masewalyewehkahtlahtoh ipan Yankuik Kaxtillan". ResearchGate (in Nahuatl).
- ^ Haring (1947), pp. 7, 105
- ^ Liss (1975), p. 33
- ^ Haring (1947), p. 7
- ^ Mark A. Burkholder (2016) "Spain's America: from kingdoms to colonies", Colonial Latin American Review, 25:2, 125–153, doi:10.1080/10609164.2016.1205241
- ^ "Colección Juan Bautista Muñoz. Archivo de la Real Academia de la Historia – España". LANIC (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 6 September 2019. Retrieved 20 March 2008.
- ^ de la Mota Padilla (1870)
- ^ de Solís (1771)
- ^ "Viceroyalty of New Spain (historical territory, Mexico)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ "Viceroyalty of New Spain (historical territory, Mexico)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ Altman, Cline & Pescador (2003), p. 69
- ^ Haring (1947), pp. 133–135
- ^ Lombardi, Lombardi & Stoner (1983), p. 50
- ^ Haring (1947), pp. 133–135
- ^ Lombardi, Lombardi & Stoner (1983), p. 50
- ^ Haring (1947), pp. 133–135
- ^ Lombardi, Lombardi & Stoner (1983), p. 50
- ^ a b Altman, Cline & Pescador (2003), p. 172
- ^ a b Foster (2000), pp. 101–103
- ^ a b Lockhart & Altman (1976)
- ^ Van Young (1992)
- ^ Monsivaís (1992), pp. 247–254
- ^ Van Young (1992), p. 3 n. 3
- ^ Van Young (2006), p. xxviii
- ^ Lockhart (1976)
- ^ Ouweneel (1997), map 2 p. 6; p. 288
- ^ Lockhart (1991)
- ^ Castleman (2005), p. 10
- ^ Coatsworth (1998), p. 34
- ^ Castleman (2005), p. 31
- ^ Ouweneel (1997), p. 90
- ^ Ouweneel (1997), p. 68
- ^ Ouweneel (1997), p. 67, quoting Alexander von Humboldt.
- ^ Carroll (1991), p. 3
- ^ Carroll (1979), p. 124
- ^ Gerhard (1993), p. 205
- ^ Gerhard (1993), pp. 83–85
- ^ Gerhard (1993), p. 206
- ^ Carroll (1991), p. 93
- ^ Ouweneel (1997), pp. 188–189
- ^ Deans-Smith (1992) (a definitive study of the tobacco monopoly)
- ^ Deans-Smith (1992), p. 106
- ^ Deans-Smith (1992), p. 157
- ^ Gerhard (1993), pp. 220–224
- ^ Gibson (1952), pp. 55–56
- ^ Israel (1975), p. 219
- ^ Thomson (1989), p. 16
- ^ a b Hirschberg (1979)
- ^ Thomson (1989), p. 6
- ^ Thomson (1989), p. 12
- ^ Thomson (1989), citing Pierre Chaunu Seville et l'Atlantique 1504–1650, Pt. 2, vol. VIII 1959, 714.
- ^ Altman (2000), p. 51
- ^ Altman (2000), p. 62
- ^ Salvucci (1987), p. 80
- ^ Gibson (1964)
- ^ Lockhart (1992)
- ^ Gibson (1964), p. 409
- ^ Cline (1991), pp. 265–274
- ^ Rojas Rabiela (1991)
- ^ Lewis (1976)
- ^ Szewczyk (1976)
- ^ Tutino (1986), pp. 52–54
- ^ Brading (1978), pp. 76–77
- ^ Tutino (1979), pp. 339–378
- ^ Tutino (1979), p. 354
- ^ a b Tutino (1979), p. 364
- ^ Tutino (1979), p. 363
- ^ Tutino (1979), p. 366
- ^ Bannon (1974)
- ^ Weber (1991)
- ^ Bolton (1956)
- ^ Cutter (1995)
- ^ Spicer (1962)
- ^ Weber (1992)
- ^ Jackson (1994)
- ^ Altman, Cline & Pescador (2003), pp. 193–194
- ^ Sanchez & Spude (2013), Chapters 2 & 3
- ^ Altman, Cline & Pescador (2003), p. 194
- ^ Gonzales (2003)
- ^ Gonzales (2003)
- ^ Weber (1992), p. 242
- ^ Robinson (1979)
- ^ Gerhard (1993), p. 3
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 59–60
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 38–42
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 39, 59–60
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 50–51
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 33–51
- ^ Restall (2009)
- ^ Hunt (1976), pp. 42–46
- ^ Restall (1997), p. 185
- ^ Farriss (1984), p. 266
- ^ Farriss (1984), p. 267
- ^ Farriss (1984), p. 270
- ^ Gerhard (1993), pp. 50–52
- ^ Reed (1964)
- ^ Baskes (2000), p. 186
- ^ Hamnett (1971), p. 40
- ^ Marichal (2006)
- ^ Baskes (2000), p. 185
- ^ Chance (1989), p. 121
- ^ Baskes (2000), pp. 18–19
- ^ For instance, Chance (1989), pp. 121–122.
- ^ a b Gerhard (1993), p. 264
- ^ Gerhard (1993), p. 265.
- ^ Zeitlin (2005), pp. xiv–xv
- ^ Gutiérrez Brockington (1989)
- ^ a b Zeitlin (1989)
- ^ Gutiérrez Brockington (1989), p. 9
- ^ Zeitlin (1989), p. 55
- ^ Gutiérrez Brockington (1989), p. 15
- ^ Gutiérrez Brockington (1989), p. 16
- ^ Zeitlin (2005), esp. Chapter 5
- ^ Sherman, William L. Forced Native Labor in Sixteenth-Century Central America. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1979.
- ^ MacLeod, Murdo J., Spanish Central America: A Socioeconomic History, 1520–1720. Berkeley: University of California Press 1973.
- ^ Woodward, Ralph Lee. Class Privilege and Economic Development: The Consulado de Comercio of Guatemala, 1793–1871. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press 1966.
- ^ Webre, Stephen. "Audiencia of Guatemala" in Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture, vol. 3, pp.130–31. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons 1996.
- ^ Navarro y Noriega (1820)
- ^ von Humboldt (1811)
- ^ McCaa (2000)
- ^ Lerner, Victoria (1968). Consideraciones sobre la población de la Nueva España: 1793–1810, según Humboldt y Navarro y Noriega [Considerations on the population of New Spain: 1793–1810, according to Humboldt and Navarro and Noriega] (PDF) (in Spanish). pp. 328–348. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2017. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ^ Historical Dictionary of Argentina. London: Scarecrow Press, 1978. pp. 239–40.
- ^ "American Indians in the Federal Decennial Census". Retrieved on 25 July 2017.
- ^ Censo General De Habitantes (1921 Census) (PDF) (Report). Departamento de la Estadistica Nacional. p. 62. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
- ^ "El mestizaje es un mito, la identidad cultural sí importa" Istmo, Mexico, Retrieved on 25 July 2017.
- ^ Federico Navarrete (2016). Mexico Racista. Penguin Random house Grupo Editorial Mexico. p. 86. ISBN 978-6073143646. Retrieved 23 February 2018.
Bibliography
[edit]General histories
[edit]- Altman, Ida; Lockhart, James, eds. (1976). The Provinces of Early Mexico. Los Angeles, CA: UCLA Latin American Center. ISBN 0-87903-036-4.
- Altman, Ida; Cline, Sarah; Pescador, Juan Javier (2003). The Early History of Greater Mexico. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-1309-1543-6.
- Haring, Clarence Henry (1947). The Spanish Empire in America. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Israel, Jonathan I. (1975). Race, Class, and Politics in Colonial Mexico. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Knight, Alan (2002). Mexico: The Colonial Era. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521891967.
- Liss, Peggy K. (1975). Mexico Under Spain: Society and the Origins of Nationality. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press.
- Lockhart, James; Schwartz, Stuart (1983). Early Latin America. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Meyer, Michael C., William L. Sherman, and Susan M. Deeds. (2014) The Course of Mexican History Tenth edition, esp. chapters 6–15. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Van Young, Eric. Stormy Passage: Mexico from Colony to Republic, 1750-1850. Lanham MD: Rowman and Littlefield 2022. ISBN 9781442209015.
More specialized works
[edit]- Altman, Ida (2000). Transatlantic Ties in the Spanish Empire: Brihuega, Spain & Puebla, Mexico, 1560–1620. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Bannon, John Francis (1974). The Spanish Borderlands Frontier: 1513-1821. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press.
- Baskes, Jeremy (2000). Indians, Merchants, and Markets: A Reinterpretation of the Repartimiento and Spanish-Indian Economic Relations in Colonial Oaxaca 1750–1821. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Bolton, Herbert Eugene, ed. (1956). Spanish Explorations in the Southwest, 1542–1706. New York, NY: Barnes and Noble.
- Brading, D. A. (1978). Haciendas and Ranchos in the Mexican Bajío: León 1700–1860. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Carroll, Patrick J. (1991). Blacks in Colonial Veracruz: Race, Ethnicity, and Regional Development. Austin, TX: University of Texas Press.
- Castleman, Bruce A. (2005). Building the King's Highway: Labor, Society, and Family on Mexico's Caminos Reales 1757–1804. Tucson, AZ: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 9780816524396.
- Chance, John (1989). Conquest of the Sierra: Spaniards and Indians in Colonial Oaxaca. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press.
- Cutter, Charles R. (1995). The Legal Culture of Northern New Spain, 1700–1810. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press. ISBN 9780826316417.
- Deans-Smith, Susan (1992). Bureaucrats, Planters, and Workers: The Making of the Tobacco Monopoly in Bourbon Mexico. Austin, TX: University of Texas Press.
- Farriss, Nancy (1984). Maya Society under Colonial Rule: The Collective Enterprise of Survival. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Foster, Lynn V. (2000). A Brief History of Central America. New York, NY: Facts on File. ISBN 0-8160-3962-3.
- Gibson, Charles (1964). The Aztecs Under Spanish Rule: a History of the Indians of the Valley of Mexico, 1519–1810. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Gonzales, Phillip B. (2003). "Struggle for survival: the Hispanic land grants of New Mexico, 1848–2001". Agricultural History. 77 (2): 293–324. doi:10.1525/ah.2003.77.2.293. JSTOR 3744837. S2CID 154553608.
- Gutiérrez Brockington, Lolita (1989). The Leverage of Labor: Managing the Cortés Haciendas of Tehuantepec, 1588–1688. Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Hamnett, Brian R. (1971). Politics and Trade in Southern Mexico 1750–1821. Cambridge University Press.
- von Humboldt, Alexander (1811). Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain (in French). Paris: F. Schoell.
- Hunt, Marta Espejo Ponce (1976). "The Processes of the Development of Yucatan, 1600–1700". In Altman, Ida; Lockhart, James (eds.). The Provinces of Early Mexico: Variants of Spanish American Regional Evolution. Los Angeles, CA: UCLA Latin American Center.
- Jackson, Robert H. (1994). Indian Population Decline: the Missions of Northwestern New Spain, 1687–1840. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press.
- Lockhart, James (1991). "Trunk lines and feeder lines: The Spanish Reaction to American Resources". In James Lockhart (ed.). Of Things of the Indies: Essays Old and New in Early Latin American History. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Lockhart, James (1992). The Nahuas After the Conquest: A Social and Cultural History of the Indians of Mexico, Sixteenth Through Eighteenth Centuries. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Marichal, Carlos (2006). "Mexican Cochineal and the European Demand for American Dyes, 1550–1850". In Steven Topik; Carlos Marichal; Zephyr Frank (eds.). From Silver to Cocaine: Latin American Commodity Chains and the Building of the World Economy, 1500–2000. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. pp. 76–92.
- McCaa, Robert (2000). "The peopling of Mexico from origins to revolution". In Michael R. Haines; Richard H. Steckel (eds.). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. pp. 241–304. ISBN 9780521496667.
- Monsivaís, Carlos (1992). "'Just Over That Hill'": Notes on Centralism and Regional Cultures". In Eric Van Young (ed.). Mexico's Regions. Center for U.S.-Mexican Studies, UCSD.
- Ouweneel, Arij (1997). Shadows over Anahuac: an Ecological Interpretation of Crisis and Development in Central Mexico, 1730–1800. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press.
- Reed, Nelson A. (1964). The Caste War of Yucatan. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Restall, Matthew (1997). The Maya World: Yucatec Culture and Society, 1550–1850. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Restall, Matthew (2009). The Black Middle: Africans, Mayas, and Spaniards in Colonial Yucatan. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Robinson, William Wilcox (1979). Land in California: the story of mission lands, ranchos, squatters, mining claims, railroad grants, land scrip and homesteads. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520038752.
- Salvucci, Richard (1987). Textiles and Capitalism in Mexico: An Economic History of the Obraje. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Sanchez, Joseph P.; Spude, Robert L. (2013). New Mexico: A History.
- de Solís, Antonio (1771). Historia de la conquista de México, poblacion y progresos de la América Septentrional, conocida por el nombre de Nueva España (in Spanish). Barcelona: Thomas Piferrer.
- Spicer, Edward H. (1962). Cycles of Conquest: The Impact of Spain, Mexico, and the United States on the Indians of the Southwest, 1533–1960. Tucson, AZ: University of Arizona Press.
- Thomson, Guy P. C. (1989). Puebla de Los Angeles: Industry and Society in a Mexican City, 1700–1850. Westview Press.
- Tovell, Freeman M. (2008). At the Far Reaches of Empire: the Life of Juan Francisco De La Bodega Y Quadra. University of British Columbia Press. ISBN 978-0-7748-1367-9.
- Tutino, John (1979). "Life and Labor on North Mexican Haciendas: The Queretaro-San Luis Potosi Region, 1775-1810". El trabajo y los trabajadores en la historia de Mexico. Mexico City: El Colegio de Mexico. pp. 339–378.
- Tutino, John (1986). From Insurrection to Revolution: Social Bases of Agrarian Violence 1750–1940. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Van Young, Eric (2006). "Introduction to the 25th Anniversary Edition". Hacienda and Market in Eighteenth-Century Mexico (2nd ed.).
- Weber, David J. (1992). The Spanish Frontier in North America. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300059175.
- Zeitlin, Judith Francis (2005). Cultural Politics in Colonial Tehuantepec: Community and State among the Isthmus Zapotec, 1500–1750. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Historiography
[edit]- Hanke, Lewis. Do the Americas Have a Common History? A Critique of the Bolton Theory (1964).
- Hurtado, Albert L. "Bolton and Turner: The Borderlands and American Exceptionalism." Western Historical Quarterly 44#1 (2013): 4–20. online.
- Hurtado, Albert L. Herbert Eugene Bolton: Historian of the American Borderlands (University of California Press; 2012).
- Van Young, Eric (1992). "Are Regions Good to Think?". In Eric Van Young (ed.). Mexico's Regions. Center for U.S.-Mexican Studies, UCSD.
- Van Young, Eric. "Two Decades of Anglophone Historical Writing on Colonial Mexico: Continuity and Change since 1980". Mexican Studies/Estudios Mexicanos. (2004) vol. 20, No. 2 (summer), 275–326.
- Weber, David. J., ed. (1991). The Idea of the Spanish Borderlands. New York, NY: Garland Publishers.
Reference works
[edit]- Encyclopedia of Mexico. 2 vols. (1997) Chicago.
- Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture. 5 vols. (1996) New York.
- Gerhard, Peter (1993). The Historical Geography of New Spain (2nd ed.). Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press.
- Lombardi, Cathryn L.; Lombardi, John V.; Stoner, K. Lynn (1983). Latin American History: a Teaching Atlas. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0-299-09714-5.
External links
[edit]- MEXICO'S COLONIAL ERA—PART I: The Settlement of New Spain Archived 1 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine at mexconnect.com
- Index to the DeWitt Colony Region under New Spain Archived 3 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine at Texas A&M University
- 1492 – Middle America at ibiblio.org the public's library and digital archive
- Encyclopædia Britannica: Hispanic Heritage in The Americas
- Map of the Border of the King's Dominion in the Northern America is a map by José de Urrútia and Nicolas de la Fora.
- New Spain
- 1519 establishments in North America
- 1519 in North America
- 1510s establishments in Mexico
- 1520s establishments in Mexico
- 1821 disestablishments in Mexico
- 1821 disestablishments in New Spain
- 1821 in North America
- Colonial Mexico
- Colonial United States (Spanish)
- Colonization history of the United States
- Former colonies in North America
- Former countries of the United States
- Former regions and territories of the United States
- Former Spanish colonies
- History of North America
- History of New Spain
- History of the Philippines (1565–1898)
- Latin American history
- Pre-statehood history of Arizona
- Pre-statehood history of New Mexico
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Spanish exploration in the Age of Discovery
- Spanish-speaking countries and territories
- Spanish Texas
- Spanish East Indies
- Spanish West Indies
- States and territories established in 1519
- States and territories established in 1535
- States and territories disestablished in 1821
- The Californias
- Viceroyalties of the Spanish Empire

![Coat of arms of the viceroyalty of New Spain[1] of New Spain](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/Escudo_del_Reino_de_M%C3%A9xico.svg/85px-Escudo_del_Reino_de_M%C3%A9xico.svg.png)