Giacomo Gastaldi
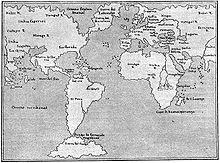
Giacomo Gastaldi (c. 1500 in Villafranca Piemonte – October 1566 in Venice) was an Italian cartographer, astronomer and engineer of the 16th century.[1] Gastaldi (sometimes referred to as Jacopo[2] or Iacobo[3]) began his career as an engineer, serving the Venetian Republic in that capacity until the fourth decade of the sixteenth century. From about 1544 he turned his attention entirely to mapmaking, and his work represents several important turning points in cartographic development.[4]


According to the author Philip Burden, Gastaldi's 1548 edition of Ptolemy's Geography, "was the most comprehensive atlas produced between Martin Waldseemüller's Geographia of 1513, and the Abraham Ortelius Theatrum of 1570," because it included regional maps of the Americas.[5] Yet Gastaldi's detailed attention to the new world was not his only contribution to the development of map production. The Ptolemy edition of 1548 was also an innovation in that Gastaldi and his publisher reduced the size of the volume, thereby making the first 'pocket' atlas.[3] Finally, Gastaldi's work also indicated a shift in cartographical technique via its use of the copper engraving. Prior to this period, most maps had been printed from woodcuts; by using a copper plate rather than a woodblock to print, the engraver could render a much higher level of finesse and detail.[6]
Gastaldi was described by one contemporary as the 'most excellent Piedmontese cosmographer'.[2] As a cartographer, Gastaldi worked for various publishers, such as Nicolo Bascarini and Giovanbattista Pedrezano.[7] But he also occasionally accepted private commissions, for example, that from Venice's Council of Ten, who invited him to fresco maps of Asia and Africa on the walls of a room in the Doge's Palace.[2]
Among his other works is the Asiae Nova Descriptio, engraved in copper in 1574.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ "The Drawing of the Modern Geography of the Whole Africa". World Digital Library. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ^ a b c Tooley, R.V, and Charles Bricker, Landmarks of Mapmaking, (Elsevier-Sequoia, Amsterdam, 1968).
- ^ a b Nordenskiöld, Adolf Erik, Facsimile-Atlas to the Early History of Cartography, (Dover Publications, New York, Reprint 1973), p. 40.
- ^ Moreland, Carl & David Bannister, Antique Maps - A Collector's Guide, (Phaidon-Christie's, Oxford, 1983), p. 66.
- ^ Burden, Philip D, The Mapping of North America: A list of printed maps 1511-1670, (Raleigh, England, 1996), p. 16. See also: Nordenskiöld, Adolf Erik, Facsimile-Atlas to the Early History of Cartography, (Dover Publications, New York, Reprint 1973), p. 28.
- ^ Burden, Philip D. The Mapping of North America: A list of printed maps 1511-1670, (Raleigh, England, 1996), p. 16. See also Moreland, Carl & David Bannister, Antique Maps - A Collector's Guide, (Phaidon-Christie's, Oxford, 1983), p. 66.
- ^ Tooley, R.V, and Charles Bricker, Landmarks of Mapmaking, (Elsevier-Sequoia, Amsterdam, 1968); Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, Facsimile-Atlas to the Early History of Cartography, (Dover Publications, New York, Reprint 1973), p. 40.
External links
[edit]- 1564 Map of Africa by Gastaldi at the World Digital Library
- Maps by Gastaldi at the Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, the National Library of Israel
