1952 United States presidential election in Massachusetts
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 75.0%[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Massachusetts |
|---|
 |
|
|
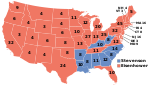
The 1952 United States presidential election in Massachusetts took place on November 4, 1952, as part of the 1952 United States presidential election, which was held throughout all contemporary 48 states. Voters chose 16 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Massachusetts voted for the Republican nominee, General Dwight D. Eisenhower of New York, over the Democratic nominee, former Governor Adlai Stevenson of Illinois. Eisenhower ran with the Senator Richard Nixon of California, while Stevenson's running mate was Senator John Sparkman of Alabama.
Eisenhower carried the state with 54.22% of the vote to Stevenson’s 45.46%, a Republican victory margin of 8.76%.
As Eisenhower won a comfortable victory nationwide, Massachusetts still weighed in for this election as about 2% more Democratic than the national average.
Once a typical Yankee Republican bastion in the wake of the Civil War, Massachusetts, had been a Democratic-leaning state since 1928, when a coalition of Irish Catholic and other ethnic immigrant voters primarily based in urban areas turned Massachusetts and neighboring Rhode Island into New England's only reliably Democratic states. Massachusetts voted for Al Smith in 1928, for Franklin D. Roosevelt four times in the 1930s and 1940s, and for Harry S. Truman in 1948. However General Dwight Eisenhower, a war hero and moderate Republican who pledged to support and continue popular New Deal Democratic policies, was finally able to appeal to a broad enough coalition both to win back the White House and to flip Massachusetts back into the Republican column.
Eisenhower carried 13 of the state’s 14 counties, Stevenson’s only victory coming from urban Suffolk County, home to the state’s capital and largest city, Boston.
This was the first time that Massachusetts was won by a Republican presidential candidate since 1924.
Results
[edit]| 1952 United States presidential election in Massachusetts[3] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Republican | Dwight D. Eisenhower | 1,292,325 | 54.22% | 16 | |
| Democratic | Adlai Stevenson | 1,083,525 | 45.46% | 0 | |
| Progressive | Vincent Hallinan | 4,636 | 0.19% | 0 | |
| Socialist Labor | Eric Hass | 1,957 | 0.08% | 0 | |
| Prohibition | Stuart Hamblen | 886 | 0.04% | 0 | |
| Write-ins | Write-ins | 69 | 0.00% | 0 | |
| Totals | 2,383,398 | 100.00% | 16 | ||
Results by county
[edit]| County | Dwight D. Eisenhower Republican |
Adlai Stevenson Democratic |
Various candidates Other parties |
Margin | Total votes cast[4] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Barnstable | 20,943 | 80.64% | 4,984 | 19.19% | 44 | 0.17% | 15,959 | 61.45% | 25,971 |
| Berkshire | 38,413 | 56.13% | 29,785 | 43.52% | 243 | 0.36% | 8,628 | 12.61% | 68,441 |
| Bristol | 98,105 | 51.09% | 93,444 | 48.67% | 462 | 0.24% | 4,661 | 2.42% | 192,011 |
| Dukes | 2,432 | 76.05% | 760 | 23.76% | 6 | 0.19% | 1,672 | 52.29% | 3,198 |
| Essex | 156,030 | 55.64% | 123,334 | 43.98% | 1,045 | 0.37% | 32,696 | 11.66% | 280,409 |
| Franklin | 19,489 | 68.94% | 8,729 | 30.88% | 50 | 0.18% | 10,760 | 38.06% | 28,268 |
| Hampden | 98,641 | 51.86% | 90,936 | 47.81% | 616 | 0.32% | 7,705 | 4.05% | 190,193 |
| Hampshire | 24,141 | 58.19% | 17,247 | 41.57% | 98 | 0.24% | 6,894 | 16.62% | 41,486 |
| Middlesex | 316,069 | 56.99% | 236,910 | 42.72% | 1,626 | 0.29% | 79,159 | 14.27% | 554,605 |
| Nantucket | 1,490 | 78.55% | 405 | 21.35% | 2 | 0.11% | 1,085 | 57.20% | 1,897 |
| Norfolk | 140,409 | 65.20% | 74,321 | 34.51% | 631 | 0.29% | 66,088 | 30.69% | 215,361 |
| Plymouth | 67,922 | 67.22% | 32,815 | 32.48% | 305 | 0.30% | 35,107 | 34.74% | 101,042 |
| Suffolk | 162,147 | 40.05% | 240,957 | 59.51% | 1,775 | 0.44% | -78,810 | -19.46% | 404,879 |
| Worcester | 146,094 | 53.00% | 128,898 | 46.76% | 645 | 0.23% | 17,196 | 6.24% | 275,637 |
| Totals | 1,292,325 | 54.22% | 1,083,525 | 45.46% | 7,548 | 0.32% | 208,800 | 8.76% | 2,383,398 |
Counties that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Bicentennial Edition: Historical Statistics of the United States, Colonial Times to 1970, part 2, p. 1072.
- ^ "U.S. presidential election, 1952". Facts on File. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2013.
Eisenhower, born in Texas, considered a resident of New York, and headquartered at the time in Paris, finally decided to run for the Republican nomination
- ^ "1952 Presidential General Election Results - Massachusetts". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved February 7, 2013.
- ^ Scammon, Richard M. (compiler); America at the Polls: A Handbook of Presidential Election Statistics 1920-1964; p. 215 ISBN 0405077114