User:Ajzahuranec/sandbox
Appearance
| Alben W. Barkley | James Farley | John Nance Garner | Millard Tydings | Joseph P. Kennedy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Senate Majority Leader
(1937–1945) |
Postmaster General
(1933–1940) |
Vice President (1933-1941)
|
Ambassador to the United Kingdom
(1938–1940) | |

 Top left: The US Senate passes the Security Assistance Act Right: Norman Rockwell's Freedom from Fear; Bottom left: Wanted poster for Silver Legion leader William Dudley Pelley | |
| Type | National security program |
|---|---|
| Cause | The Quiet War |
| Organized by | President Alben W. Barkley |
| Outcome | Expansion of police authority; surveillance of suspected radicals and saboteurs; creation of the American Broadcasting Company; restitution for victims of vigilante violence |
| Part of the Second Interwar Period and The Quiet War | |
 Lindbergh delivering the speech | |
| Date | January 12, 1949 |
|---|---|
| Time | 7:00 pm (Eastern Time, UTC–5) |
| Duration | 55 minutes |
| Venue | Madison Square Garden |
| Location | New York, New York |
| Also known as | The New York speech, On the Thieves and Their Goals |
| Type | Speech |
| Participants | President Charles Lindbergh |
| Outcome | Widespread condemnation of President Lindbergh Reports of antisemitic and white supremacist violence |
| Media | audio, transcript |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Italian. (August 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Ajzahuranec/sandbox | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Second Interwar Period | |||||||
 Aftermath of the bombing of Sacred Heart Catholic School in St. James, Louisiana in August 1952 which killed 198 people, the deadliest event during the Quiet War. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Supported by: |
Supported by:
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
National Guard: Police: Knights of Columbus: 2 killed
|
| ||||||
| Total deaths (including civilians): 600-1,200, c. 8,000 physical and psychological injuries[25] | |||||||
| History of Italy |
|---|
 |
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 54.7%[26] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
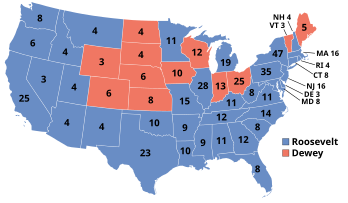 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes those won by Barkley/Wallace, red denotes states won by Lindbergh/Vandenberg. Orange denotes states won by Winant/Benson. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1945 contingent U.S. presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
48 state delegations of the House of Representatives 25 state votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 House of Representatives votes by state.
States in Blue voted for Barkley, states in red voted for Lindbergh, and states in orange voted for Winant. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 55.1%[27] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
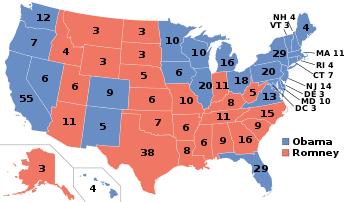 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Obama/Biden and red denotes those won by Romney/Ryan. Numbers indicate electoral votes cast by each state and the District of Columbia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Democratic Party | |
|---|---|
| Republican Party | |
| Minor parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
- ^ a b c d Willan, Philip (March 26, 2001). "Terrorists 'helped by CIA' to stop rise of left in Italy". The Guardian. Cite error: The named reference "Willan" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ It was dismantled and became inactive.
- ^ "Italian minister falls victim to corruption". The Independent. February 11, 1993. Archived from the original on May 7, 2022.
- ^ Willan, Puppetmasters, p. 161
- ^ a b "NAR: lo spontaneismo armato neofascista". Ariannaeditrice.it.
- ^ Vulliamy, Ed (December 5, 1990). "Secret agents, freemasons, fascists ... and a top-level campaign of political 'destabilisation'". The Guardian. Retrieved June 10, 2021.
- ^ "Terrorists 'helped by CIA' to stop rise of left in Italy". TheGuardian.com. March 26, 2001.
- ^ "Strage di Piazza Fontana spunta un agente Usa". February 11, 1998.
- ^ "Il Terrorismo, le stragi ed il contesto storico-politico" (PDF). August 19, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 19, 2006.
- ^ "The Battle of Valle Giulia 50 Years After – 1 March 1968".
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Zavoliwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ F. Stefani, The history of the doctrine and the regulations of the Italian Army, Historical Office of the Army General Staff
- ^ A. Viotti, S. Ales, Structure, uniforms and badges of the Italian Army 1946–1970, Historical Office of the General Staff of the Army
- ^ "New Order | Mapping Militant Organizations". stanford.edu.
- ^ "National Vanguard | Mapping Militant Organizations". web.stanford.edu.
- ^ Adinolfi, Gabriele; Fiore, Roberto (2000). Noi Terza posizione (in Italian). Settimo Sigillo.
- ^ a b "Salerno non dimentica l'attentato delle Brigate Rosse | Dentro Salerno | L'informazione di Salerno e provincia è on line". www.dentrosalerno.it. Archived from the original on May 26, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Sergio Zavoli 1992was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The Peteano massacre: "Great example of dedication to duty", on ilgazzettino.it .
- ^ Indro Montanelli and Mario Cervi, Italy of the years of mud, Milan, Rizzoli, 1993.
- ^ Armando Spataro, (in French) "La culpabilité de Battisti repose sur des preuves" Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. in L'Express, 15/3/2004
- ^ Indro Montanelli and Mario Cervi, Italy of the years of mud, Milan, Rizzoli, 1993.
- ^ Armando Spataro, (in French) "La culpabilité de Battisti repose sur des preuves" Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. in L'Express, 15/3/2004
- ^ "Fioravanti e lo spontaneismo armato dei Nar – Corriere della Sera". www.corriere.it.
- ^ "Anni di piombo, le vittime dimenticate dallo Stato". Lettera43 (in Italian). March 16, 2014.
- ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
FEC 2013was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=N> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=N}} template (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).








