Prokaryotic cytoskeleton
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s.[2] Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered.[3][4][5][6] Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.[7][8]
Tubulin superfamily
[edit]FtsZ
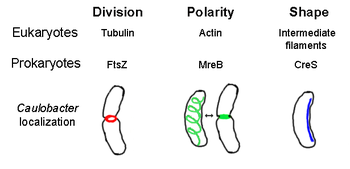
[edit]FtsZ, the first identified prokaryotic cytoskeletal element, forms a filamentous ring structure located in the middle of the cell called the Z-ring that constricts during cell division, similar to the actin-myosin contractile ring in eukaryotes.[2] The Z-ring is a highly dynamic structure that consists of numerous bundles of protofilaments that extend and shrink, although the mechanism behind Z-ring contraction and the number of protofilaments involved are unclear.[1] FtsZ acts as an organizer protein and is required for cell division. It is the first component of the septum during cytokinesis, and it recruits all other known cell division proteins to the division site.[9]
Despite this functional similarity to actin, FtsZ is homologous to eukaryal tubulin. Although comparison of the primary structures of FtsZ and tubulin reveal a weak relationship, their 3-dimensional structures are remarkably similar. Furthermore, like tubulin, monomeric FtsZ is bound to GTP and polymerizes with other FtsZ monomers with the hydrolysis of GTP in a mechanism similar to tubulin dimerization.[10] Since FtsZ is essential for cell division in bacteria, this protein is a target for the design of new antibiotics.[11] There currently exist several models and mechanisms that regulate Z-ring formation, but these mechanisms depend on the species. Several rod shaped species, including Escherichia coli and Caulobacter crescentus, use one or more inhibitors of FtsZ assembly that form a bipolar gradient in the cell, enhancing polymerization of FtsZ at the cell center.[12] One of these gradient-forming systems consists of MinCDE proteins (see below).
Actin superfamily
[edit]MreB
[edit]MreB is a bacterial protein believed to be homologous to eukaryal actin. MreB and actin have a weak primary structure match, but are very similar in terms of 3-D structure and filament polymerization.
Almost all non-spherical bacteria rely on MreB to determine their shape. MreB assembles into a helical network of filamentous structures just under the cytoplasmic membrane, covering the whole length of the cell.[13] MreB determines cell shape by mediating the position and activity of enzymes that synthesize peptidoglycan and by acting as a rigid filament under the cell membrane that exerts outward pressure to sculpt and bolster the cell.[1] MreB condenses from its normal helical network and forms a tight ring at the septum in Caulobacter crescentus right before cell division, a mechanism that is believed to help locate its off-center septum.[14] MreB is also important for polarity determination in polar bacteria, as it is responsible for the correct positioning of at least four different polar proteins in C. crescentus.[14]
ParM and SopA
[edit]ParM is a cytoskeletal element that possesses a similar structure to actin, although it behaves functionally like tubulin. Further, it polymerizes bidirectionally and it exhibits dynamic instability, which are both behaviors characteristic of tubulin polymerization.[4][15] It forms a system with ParR and parC that is responsible for R1 plasmid separation. ParM affixes to ParR, a DNA-binding protein that specifically binds to 10 direct repeats in the parC region on the R1 plasmid. This binding occurs on both ends of the ParM filament. This filament is then extended, separating the plasmids.[16] The system is analogous to eukaryotic chromosome segregation as ParM acts like eukaryotic tubulin in the mitotic spindle, ParR acts like the kinetochore complex, and parC acts like the centromere of the chromosome.[17]
F plasmid segregation occurs in a similar system where SopA acts as the cytoskeletal filament and SopB binds to the sopC sequence in the F plasmid, like the kinetochore and centromere respectively.[17] Lately an actin-like ParM homolog has been found in a gram-positive bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis, which assembles into a microtubule-like structure and is involved in plasmid segregation.[18]
Archaeal actin
[edit]Crenactin is an actin homologue unique to the archaeal kingdom Thermoproteota (formerly Crenarchaeota) that has been found in the orders Thermoproteales and Candidatus Korarchaeum.[19] At the time of its discovery in 2009, it has the highest sequence similarity to eukaryotic actins of any known actin homologue.[20] Crenactin has been well characterized in Pyryobaculum calidifontis (A3MWN5) and shown to have high specificity for ATP and GTP.[19] Species containing crenactin are all rod or needle shaped. In P. calidifontis, crenactin has been shown to form helical structures that span the length of the cell, suggesting a role for crenactin in shape determination similar to that of MreB in other prokaryotes.[19][21]
Even closer to the eukaryotic actin system is found in the proposed superphylum of Asgardarchaeota. They use primitive versions of profilin, gelsolin, and cofilin to regulate the cytoskeleton.[22]
Unique groups
[edit]Crescentin
[edit]Crescentin (encoded by creS gene) is an analogue of eukaryotic intermediate filaments (IFs). Unlike the other analogous relationships discussed here, crescentin has a rather large primary homology with IF proteins in addition to three-dimensional similarity - the sequence of creS has a 25% identity match and 40% similarity to cytokeratin 19 and a 24% identity match and 40% similarity to nuclear lamin A. Furthermore, crescentin filaments are roughly 10 nm in diameter and thus fall within diameter range for eukaryal IFs (8-15 nm).[23] Crescentin forms a continuous filament from pole to pole alongside the inner, concave side of the crescent-shaped bacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Both MreB and crescentin are necessary for C. crescentus to exist in its characteristic shape; it is believed that MreB molds the cell into a rod shape and crescentin bends this shape into a crescent.[1]
MinCDE system
[edit]The MinCDE system is a filament system that properly positions the septum in the middle of the cell in Escherichia coli. According to Shih et al., MinC inhibits the formation of the septum by prohibiting the polymerization of the Z-ring. MinC, MinD, and MinE form a helix structure that winds around the cell and is bound to the membrane by MinD. The MinCDE helix occupies a pole and terminates in a filamentous structure called the E-ring made of MinE at the middle-most edge of the polar zone. From this configuration, the E-ring will contract and move toward that pole, disassembling the MinCDE helix as it moves along. Concomitantly, the disassembled fragments will reassemble at the opposite polar end, reforming the MinCDE coil on the opposite pole while the current MinCDE helix is broken down. This process then repeats, with the MinCDE helix oscillating from pole to pole. This oscillation occurs repeatedly during the cell cycle, thereby keeping MinC (and its septum inhibiting effect) at a lower time-averaged concentration at the middle of the cell than at the ends of the cell.[24]
The dynamic behavior of the Min proteins has been reconstituted in vitro using an artificial lipid bilayer as mimic for the cell membrane. MinE and MinD self-organized into parallel and spiral protein waves by a reaction-diffusion like mechanism.[25]
Bactofilin
[edit]Bactofilin (InterPro: IPR007607) is a β-helical cytoskeletal element that forms filaments throughout the cells of the rod-shaped proteobacterium Myxococcus xanthus.[26] The bactofilin protein, BacM, is required for proper cell shape maintenance and cell wall integrity. M. xanthus cells lacking BacM have a deformed morphology characterized by a bent cell body, and bacM mutants have decreased resistance to antibiotics targeting the bacterial cell wall. M. xanthus BacM protein is cleaved from its full-length form to allow polymerization. Bactofilins have been implicated in cell shape regulation in other bacteria, including curvature of Proteus mirabilis cells,[27] stalk formation by Caulobacter crescentus,[28] and helical shape of Helicobacter pylori.[29]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Gitai Z (March 2005). "The new bacterial cell biology: moving parts and subcellular architecture". Cell. 120 (5): 577–86. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.026. PMID 15766522. S2CID 8894304.
- ^ a b Bi EF, Lutkenhaus J (November 1991). "FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli". Nature. 354 (6349): 161–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.354..161B. doi:10.1038/354161a0. PMID 1944597. S2CID 4329947.
- ^ Gunning PW, Ghoshdastider U, Whitaker S, Popp D, Robinson RC (June 2015). "The evolution of compositionally and functionally distinct actin filaments". Journal of Cell Science. 128 (11): 2009–19. doi:10.1242/jcs.165563. PMID 25788699.
- ^ a b Popp D, Narita A, Lee LJ, Ghoshdastider U, Xue B, Srinivasan R, Balasubramanian MK, Tanaka T, Robinson RC (June 2012). "Novel actin-like filament structure from Clostridium tetani". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (25): 21121–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.341016. PMC 3375535. PMID 22514279.
- ^ Popp D, Narita A, Ghoshdastider U, Maeda K, Maéda Y, Oda T, Fujisawa T, Onishi H, Ito K, Robinson RC (April 2010). "Polymeric structures and dynamic properties of the bacterial actin AlfA". Journal of Molecular Biology. 397 (4): 1031–41. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.010. PMID 20156449.
- ^ Wickstead B, Gull K (August 2011). "The evolution of the cytoskeleton". The Journal of Cell Biology. 194 (4): 513–25. doi:10.1083/jcb.201102065. PMC 3160578. PMID 21859859.
- ^ Shih YL, Rothfield L (September 2006). "The bacterial cytoskeleton". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 70 (3): 729–54. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00017-06. PMC 1594594. PMID 16959967.
- ^ Michie KA, Löwe J (2006). "Dynamic filaments of the bacterial cytoskeleton" (PDF). Annual Review of Biochemistry. 75: 467–92. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142452. PMID 16756499. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 17, 2006.
- ^ Graumann PL (December 2004). "Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria". Current Opinion in Microbiology. 7 (6): 565–71. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.010. PMID 15556027.
- ^ Desai A, Mitchison TJ (July 1998). "Tubulin and FtsZ structures: functional and therapeutic implications". BioEssays. 20 (7): 523–7. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199807)20:7<523::AID-BIES1>3.0.CO;2-L. PMID 9722999.
- ^ Haydon DJ, Stokes NR, Ure R, Galbraith G, Bennett JM, Brown DR, Baker PJ, Barynin VV, Rice DW, Sedelnikova SE, Heal JR, Sheridan JM, Aiwale ST, Chauhan PK, Srivastava A, Taneja A, Collins I, Errington J, Czaplewski LG (September 2008). "An inhibitor of FtsZ with potent and selective anti-staphylococcal activity". Science. 321 (5896): 1673–5. Bibcode:2008Sci...321.1673H. doi:10.1126/science.1159961. PMID 18801997. S2CID 7878853.
- ^ Haeusser DP, Margolin W (April 2016). "Splitsville: structural and functional insights into the dynamic bacterial Z ring". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 14 (5): 305–19. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.26. PMC 5290750. PMID 27040757.
- ^ Kürner J, Medalia O, Linaroudis AA, Baumeister W (November 2004). "New insights into the structural organization of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cytoskeletons using cryo-electron tomography". Experimental Cell Research. 301 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.005. PMID 15501443.
- ^ a b Gitai Z, Dye N, Shapiro L (June 2004). "An actin-like gene can determine cell polarity in bacteria". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (23): 8643–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0402638101. PMC 423248. PMID 15159537.
- ^ Garner EC, Campbell CS, Mullins RD (November 2004). "Dynamic instability in a DNA-segregating prokaryotic actin homolog". Science. 306 (5698): 1021–5. Bibcode:2004Sci...306.1021G. doi:10.1126/science.1101313. PMID 15528442. S2CID 14032209.
- ^ Møller-Jensen J, Jensen RB, Löwe J, Gerdes K (June 2002). "Prokaryotic DNA segregation by an actin-like filament". The EMBO Journal. 21 (12): 3119–27. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf320. PMC 126073. PMID 12065424.
- ^ a b Gitai Z (February 2006). "Plasmid segregation: a new class of cytoskeletal proteins emerges". Current Biology. 16 (4): R133-6. Bibcode:2006CBio...16.R133G. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.02.007. PMID 16488865.
- ^ Jiang S, Narita A, Popp D, Ghoshdastider U, Lee LJ, Srinivasan R, Balasubramanian MK, Oda T, Koh F, Larsson M, Robinson RC (March 2016). "Novel actin filaments from Bacillus thuringiensis form nanotubules for plasmid DNA segregation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (9): E1200-5. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113E1200J. doi:10.1073/pnas.1600129113. PMC 4780641. PMID 26873105.
- ^ a b c Ettema TJ, Lindås AC, Bernander R (May 2011). "An actin-based cytoskeleton in archaea". Molecular Microbiology. 80 (4): 1052–61. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07635.x. PMID 21414041.
- ^ Yutin N, Wolf MY, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (February 2009). "The origins of phagocytosis and eukaryogenesis". Biology Direct. 4: 9. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-4-9. PMC 2651865. PMID 19245710.
- ^ Ghoshdastider U, Jiang S, Popp D, Robinson RC (July 2015). "In search of the primordial actin filament". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (30): 9150–1. doi:10.1073/pnas.1511568112. PMC 4522752. PMID 26178194.
- ^ Akıl, Caner; Tran, Linh T.; Orhant-Prioux, Magali; Baskaran, Yohendran; Manser, Edward; Blanchoin, Laurent; Robinson, Robert C. (18 August 2020). "Insights into the evolution of regulated actin dynamics via characterization of primitive gelsolin/cofilin proteins from Asgard archaea". PNAS. 117 (33): 19904–19913. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11719904A. bioRxiv 10.1101/768580. doi:10.1073/pnas.2009167117. PMC 7444086. PMID 32747565.
- ^ Ausmees N, Kuhn JR, Jacobs-Wagner C (December 2003). "The bacterial cytoskeleton: an intermediate filament-like function in cell shape". Cell. 115 (6): 705–13. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00935-8. PMID 14675535. S2CID 14459851.
- ^ Shih YL, Le T, Rothfield L (June 2003). "Division site selection in Escherichia coli involves dynamic redistribution of Min proteins within coiled structures that extend between the two cell poles". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (13): 7865–70. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.7865S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1232225100. PMC 164679. PMID 12766229.
- ^ Loose M, Fischer-Friedrich E, Ries J, Kruse K, Schwille P (May 2008). "Spatial regulators for bacterial cell division self-organize into surface waves in vitro". Science. 320 (5877): 789–92. Bibcode:2008Sci...320..789L. doi:10.1126/science.1154413. PMID 18467587. S2CID 27134918.
- ^ Koch MK, McHugh CA, Hoiczyk E (May 2011). "BacM, an N-terminally processed bactofilin of Myxococcus xanthus, is crucial for proper cell shape". Molecular Microbiology. 80 (4): 1031–51. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07629.x. PMC 3091990. PMID 21414039.
- ^ Hay NA, Tipper DJ, Gygi D, Hughes C (April 1999). "A novel membrane protein influencing cell shape and multicellular swarming of Proteus mirabilis". Journal of Bacteriology. 181 (7): 2008–16. doi:10.1128/JB.181.7.2008-2016.1999. PMC 93611. PMID 10094676.
- ^ Kühn J, Briegel A, Mörschel E, Kahnt J, Leser K, Wick S, Jensen GJ, Thanbichler M (January 2010). "Bactofilins, a ubiquitous class of cytoskeletal proteins mediating polar localization of a cell wall synthase in Caulobacter crescentus". The EMBO Journal. 29 (2): 327–39. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.358. PMC 2824468. PMID 19959992.
- ^ Sycuro LK, Pincus Z, Gutierrez KD, Biboy J, Stern CA, Vollmer W, Salama NR (May 2010). "Peptidoglycan crosslinking relaxation promotes Helicobacter pylori's helical shape and stomach colonization". Cell. 141 (5): 822–33. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.046. PMC 2920535. PMID 20510929.
