Zirconium acetylacetonate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
tetrakis(acetylacetonato)zirconium, zirconium tetraacetylacetonate, zirconium tetrakis(acetylacetonate), tetrakis(acetylacetonato) zirconium, Zirconium(IV) 2,4-pentanedionate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.721 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H28O8Zr | |
| Molar mass | 487.660 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.419 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 194–195 °C (381–383 °F; 467–468 K) |
| 140 °C in vacuo | |
| Solubility in benzene | 200 g/L |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
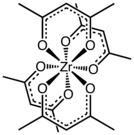
Zirconium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Zr(C5H7O2)4. It is a common acetylacetonate of zirconium. It is a white solid that exhibits high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons.[1]
The complex is prepared by treating zirconium oxychloride with acetylacetone:[1]
- ZrOCl2 + 4 Hacac → Zr(acac)4 + 2 HCl + H2O
The complex has a square antiprismatic geometry with eight nearly equivalent Zr-O bonds of length 2.19 Å. The molecular symmetry is D2, i.e. the complex is chiral.[2] Compounds of high coordination number tend to be stereochemically nonrigid as indicated by the observation of one methyl signal by proton NMR spectroscopy.[3]
More volatile than Zr(acac)4 is the related complex of 1,1,1-trifluoroacetylacetonate.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Young, R. C.; Arch, Arnold (1946). "Zirconium Acetylacetonate [Tetrakis(2,4-pentanediono)zirconium]". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 2. pp. 121–148. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch35. ISBN 978-0-470-13233-3.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Clegg, William (1987). "Redetermination of the structure of tetrakis(acetylacetonato)zirconium(IV)". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 43 (4): 789–91. doi:10.1107/S0108270187094083.
- ^ a b Morris, Melvin L.; Moshier, Ross W.; Sievers, Robert E. (1967). "Tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedionato)zirconium(and Hafnium)". Tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedionato)zirconium (and Hafnium). Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 9. pp. 50–52. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch15. ISBN 978-0-470-13168-8.
