Spanish–Portuguese War (1776–1777)
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2014) |
| Spanish–Portuguese War (1776–1777) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Spanish–Portuguese wars | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
1,450 initially 9,000 expeditionary corps | 6,000 | ||||||
The Spanish-Portuguese War, also known as the Second Cevallos expedition, was fought between 1776 and 1777 over the border between Spanish and Portuguese South America.
Portuguese attack
[edit]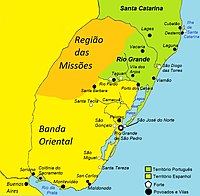
In the previous Spanish-Portuguese War 1762–1763, Spanish forces had conquered Colonia del Sacramento, Santa Tecla, San Miguel, Santa Teresa and Rio Grande de São Pedro in the First Cevallos expedition.
Colonia del Sacramento was returned to Portugal in the Treaty of Paris, but Santa Tecla, San Miguel, Santa Teresa and Rio Grande de São Pedro remained in Spanish hands.

The Portuguese started assembling troops and harassing the Spanish in 1767. Over the years, the Portuguese built up an army of 6,000 men, considerably more than the 1,450 Spanish troops in the area. The matter escalated in February 1776 when two Portuguese fleets under Robert MacDouall and Jorge Hardcastle landed troops near the fortress of Rio Grande de São Pedro, and started shelling the Spanish fort. A Spanish fleet under Francisco Javier Morales drove off the Portuguese fleet after a three-hour battle in which the Spanish fleet suffered 6 men killed and 24 wounded, and the Portuguese lost two ships.
However, the Portuguese land forces advanced on the fortified position, and the Spanish commander, Juan José de Vértiz y Salcedo, was forced to withdraw and give up the entire Rio Grande area.
Spanish response
[edit]The response of the Spanish King Charles III was swift. There was little fear that Portugal's old ally, the British, would come to its aid, as they were fully occupied by the American Revolutionary War.
King Charles III promoted Governor Pedro Antonio de Cevallos to Viceroy of the Río de la Plata and gave him the leadership of the expedition. Cevallos had already proven his ability to organise and command military forces in the First Cevallos expedition (1762–1763), when he had conquered Colonia del Sacramento and had marched deep into Portuguese territory before the peace settlement returned most of the territory that he had conquered.
Cevallos was in Spain and personally organised the expedition from Cádiz. He had 9,000 men, and a fleet of six warships (Poderoso, 70 guns, Santiago la América, 64, San Dámaso, 70, Septentrión, 64, Monarca, 68, and San José, 70), six frigates, a number of smaller ships and a hundred transport ships at his disposal. The commander of the fleet was Francisco Javier Everardo Tilly y García de Paredes, marqués de Casa Tilly. The fleet left Cádiz on 20 November, arrived in South America on 18 February 1777 and captured several Portuguese ships on the way.
There they encountered the Portuguese fleet of Robert MacDouall, which was much smaller and managed to escape.
Cevallos decided to take the island of Santa Catarina as his northern base on 23 February. When the Portuguese saw the formidable Spanish fleet disembark its troops, the garrison fled to the mainland without firing a shot. On 20 March, Cevallos sailed towards his second target, Rio Grande de São Pedro, but the fleet was dispersed by a storm and had to return to Montevideo.
There, he split up his forces and sailed with all the artillery to Colonia de Sacramento and besieged the Portuguese on May 23. The town capitulated on June 3.
The rest of the fleet was sent to check the fleet of MacDouall, which was still a menace to be counted with. In fact, the fleet surprised and captured the lone San Agustín and renamed the ship Santo Agostinho. The new captain, who also played an important role in capturing the ship, was an Englishman in Portuguese service, Arthur Phillip, who later founded Port Jackson (Sydney).
After taking Sacramento, Cevallos marched towards Rio Grande de São Pedro and joined forces with the troops of Juan José Vertiz in Santa Teresa but was ordered to turn back as peace negotiations had started.
Peace
[edit]On 24 February 1777, King Joseph I died, and his daughter and successor Maria I dismissed Pombal and concluded on 1 October the First Treaty of San Ildefonso with Spain.
Spain returned the island of Santa Catarina to Portugal and recognised Rio Grande de São Pedro as Portuguese territory but kept the strategically-important River Plate port town of Colonia del Sacramento, which the Portuguese had founded in 1680,[1] with the rest of the Banda Oriental (Uruguay), and also kept the Misiones Orientales. In return, Spain acknowledged that the Portuguese territories in Brazil extended far west of the line that had been set in the Treaty of Tordesillas.[2]
In the Treaty of El Pardo, signed on 11 March 1778, Spain gained Spanish Guinea[3] (Equatorial Guinea), which would be administered from Buenos Aires from 1778 to 1810 and was held by Spain until 1968.
Aftermath
[edit]One of the results of the war was that the Portuguese remained neutral when the American War of Independence became a global war in 1778 with the entry of the French and the Spanish in 1779. The Portuguese were bound to the British by treaty but disappointed by the lack of British support against Spain, Portugal did not itself enter the war. Instead Portugal joined the First League of Armed Neutrality in 1781, to resist British seizures of cargo from neutral ships.[4]
See also
[edit]- Military history of Spain
- Military history of Portugal
- List of wars involving Spain
- List of wars involving Portugal
- Portuguese Armed Forces
- Spanish Armed Forces
- Spanish special operations
- Spanish military orders
- Spanish Military Hospital Museum
- M1752 Musket
- Service rifle
- List of battle rifles
References
[edit]- ^ Robert S. Chamberlain, "Latin America", in An Encyclopedia of History (1948), Revised Edition, Boston: Houghton Mifflin, p. 501.
- ^ Robert S. Chamberlain, "Latin America", in An Encyclopedia of History (1948), Revised Edition, Boston: Houghton Mifflin, p. 502.
- ^ "Spanish Guinea", in The Columbia-Viking Desk Encyclopedia (1953), New York: Viking.
- ^ John D. Grainger, The Battle of Yorktown, 1781: A Reassessment, Bognor Regis, West Sussex: Boydell & Brewer, p. 10.
