Regions of Indonesia
This is a list of some of the regions of Indonesia. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the central government. At different times of Indonesia's history, the nation has been designated as having regions that do not necessarily correlate to the current administrative or physical geography of the territory of the nation.
Geographical units
[edit]
According to ISO 3166-2:ID, Indonesia is divided into seven geographical units, with each unit consisting of major islands or an island group. These geographical units are as follows:
Eastern Indonesia and Western Indonesia
[edit]
During the last stages of the Dutch colonial era, the area east of Java and Kalimantan was known as the Great East and later known as Eastern Indonesia. On 24 December 1946, the State of East Indonesia was formed covering the same area (excluding Western New Guinea). It was a component of the United States of Indonesia, and was dissolved into the unitary Republic of Indonesia in 17 August 1950.[2] Currently, Eastern Indonesia consists of 17 provinces: Bali, East Nusa Tenggara, West Nusa Tenggara, Central Sulawesi, Gorontalo, North Sulawesi, South Sulawesi, Southeast Sulawesi, West Sulawesi, Maluku, North Maluku, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua.[3][4][5] Meanwhile, the region comprising the other 21 provinces in Sumatra, Java, and Kalimantan is known as Western Indonesia.[6]
Development regions
[edit]According to the National Development Planning Agency, Indonesia is divided into four main development regions, with each being led by the major cities of Medan, Jakarta, Surabaya, and Makassar.[7][8][9]
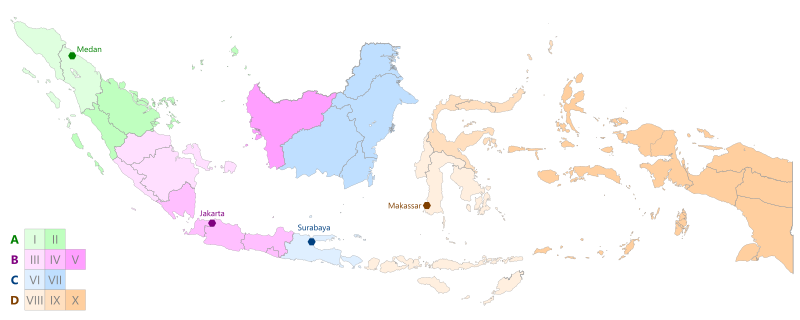
| Main development region | Central city | Development region | Province(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Development Region A (Wilayah Pembangunan Utama A) |
Medan | Development Region I | Aceh and North Sumatra |
| Development Region II | Riau, the Riau Islands, and West Sumatra | ||
| Main Development Region B (Wilayah Pembangunan Utama B) |
Jakarta | Development Region III | The Bangka Belitung Islands, Bengkulu, Jambi, and South Sumatra |
| Development Region IV | Lampung, Banten, Central Java, the Special Capital Region of Jakarta, the Special Region of Yogyakarta, and West Java | ||
| Development Region V | West Kalimantan | ||
| Main Development Region C (Wilayah Pembangunan Utama C) |
Surabaya | Development Region VI | East Java and Bali |
| Development Region VII | Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, and South Kalimantan | ||
| Main Development Region D (Wilayah Pembangunan Utama D) |
Makassar | Development Region VIII | East Nusa Tenggara, West Nusa Tenggara, South Sulawesi, Southeast Sulawesi, and West Sulawesi |
| Development Region IX | Central Sulawesi, Gorontalo, and North Sulawesi | ||
| Development Region X | Maluku, North Maluku, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua |
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2024.
- ^ Ricklefs 2008, pp. 362, 374.
- ^ Media, Kompas Cyber (6 March 2012). "13 Provinsi di Indonesia Timur Gelar Konsultasi Regional - Kompas.com".
- ^ Agency, ANTARA News. "BI Catat Bali Raih Inflasi Terendah KTI - ANTARA News Bali".
- ^ "Bawaslu Siap Kelola Keuangan Pilkada 2018 Secara Akuntabel - Badan Pengawas Pemilihan Umum Republik Indonesia". bawaslu.go.id.
- ^ Badan Riset dan Inovasi Nasional Republik Indonesia (2021-03-19). "Sosialisasi dan Bimtek Indeks Daya Saing Daerah untuk Kawasan Barat Indonesia (Sumatera, Jawa dan Kalimantan) | Berita - Index Daya Saing Daerah (IDSD)". Indeks-inovasi.brin.go.id. Retrieved 2022-04-23.
- ^ "26. Z. Irian Jaya". bappenas.go.id (Word DOC) (in Indonesian).
- ^ Geografi. Grasindo. ISBN 9789797596194.
- ^ Geografi: Jelajah Bumi dan Alam Semesta. PT Grafindo Media Pratama. ISBN 9789799281623.
References
[edit]- Ricklefs, M.C. (2008) [1981]. A History of Modern Indonesia Since c.1300 (4th ed.). London: MacMillan. ISBN 978-0-230-54685-1.
