Pirandamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
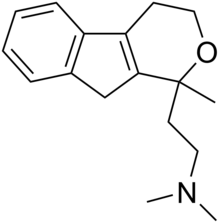
| Formula | C17H23NO |
| Molar mass | 257.377 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Pirandamine (AY-23,713) is a tricyclic derivative which acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).[1][2][3] It was investigated in the 1970s as a potential antidepressant but clinical development was not commenced and it was never marketed.[1] Pirandamine is structurally related to tandamine, which, in contrast, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.[1][3]
Synthesis
[edit]Pirandamine can be synthesized starting from 1-indanone.[4] The Reformatsky reaction between 1-indanone (1) and ethyl bromoacetate in the presence of zinc gives ethyl 2-(1-hydroxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-yl)acetate (2). The reduction of the ester with ester with lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) gives 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dihydroinden-1-ol (3). Acid-catalyzed dehydration then leads to indene-3-ethanol (4). Acid-catalyzed condensation with ethyl acetoacetate then gives (5). The saponification of the ester then gives the corresponding acid. The reaction of this with ethyl chloroformate gives a mixed anhydride, and further reaction of this with dimethylamine then leads to the amide (6). Reduction with lithium aluminium hydride completes the synthesis of pirandamine (7).

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Pugsley T, Lippmann W (May 1976). "Effects of tandamine and pirandamine, new potential antidepressants, on the brain uptake of norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine and related activities". Psychopharmacology. 47 (1): 33–41. doi:10.1007/BF00428698. PMID 1085452. S2CID 8354739.
- ^ Lippmann W, Pugsley TA (August 1976). "Pirandamine, a relatively selective 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor". Pharmacological Research Communications. 8 (4): 387–405. doi:10.1016/0031-6989(76)90039-4. PMID 1088377.
- ^ a b Lippmann W, Seethaler K (April 1977). "Effects of tandamine and pirandamine, selective blockers of biogenic amine uptake mechanisms, on gastric acid secretion and ulcer formation in the rat". Life Sciences. 20 (8): 1393–400. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(77)90367-8. PMID 853871.
- ^ I. Jirkovsky, L. G. Humber and R. Noureldin,Eur. J. Med. Chem., 11, 571 (1976).
