Meilen–Rorenhaab
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 The site of the prehistoric settlement | |
| Location | Meilen, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland |
| Part of | Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps |
| Criteria | Cultural: (iv), (v) |
| Reference | 1363-052 |
| Inscription | 2011 (35th Session) |
| Area | 0.7 ha (1.7 acres) |
| Buffer zone | 4.8 ha (12 acres) |
| Website | www |
| Coordinates | 47°15′50.16″N 8°39′36.82″E / 47.2639333°N 8.6602278°E |

Meilen–Rorenhaab is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, of which 56 are located in Switzerland.[1][2]
Geography
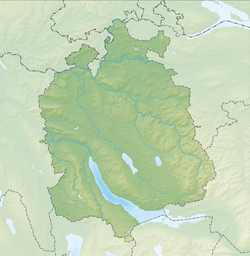
[edit]The site is located on Lake Zurich {Zürichsee) lakeshore in Rohrenhaab, a locality of the municipality of Meilen in the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. Because the lake has grown in size over time, the original piles are now around 4 metres (13 ft) to 7 metres (23 ft) below the water level of 406 metres (1,332 ft). The settlement comprises 0.7 hectares (1.73 acres), and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises 4.8 hectares (11.86 acres) in all. During the winter of 1853–54, in the context of lowered water levels at the lake, archaeologist Ferdinand Keller discovered the remains of the site.[3][4]
Description
[edit]As mentioned, this site was the starting point of pile-dwelling research and therefore interesting from the point of view of research history. It is one of several sites in a small area illustrating the typical settlement dynamics of a micro-region during the Neolithic. All periods are represented here, usually with several settlement phases, but particularly from the Early Bronze Age interesting are numerous dendrochronological dates, which allow to study the development of this period.[5]
Protection
[edit]As well as being part of the 56 Swiss sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, the settlement is also listed in the Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance as a Class A object of national importance.[6] Hence, the area is provided as a historical site under federal protection, within the meaning of the Swiss Federal Act on the nature and cultural heritage (German: Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz NHG) of 1 July 1966. Unauthorised researching and purposeful gathering of findings represent a criminal offense according to Art. 24.[7]
See also
[edit]Literature
[edit]- Peter J. Suter, Helmut Schlichtherle et al.: Pfahlbauten – Palafittes – Palafitte. Palafittes, Biel 2009. ISBN 978-3-906140-84-1.
- Beat Eberschweiler: Ur- und frühgeschichtliche Verkehrswege über den Zürichsee: Erste Ergebnisse aus den Taucharchäologischen Untersuchungen beim Seedamm. In: Mitteilungen des Historischen Vereins des Kantons Schwyz, Volume 96, Schwyz 2004.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ "Prehistoric Pile Dwellings in Switzerland". Swiss Coordination Group UNESCO Palafittes (palafittes.org). Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ "World Heritage". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-12-09. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ Keller, Ferdinand (1854). "Die keltischen Pfahlbauten in den Schweizerseen". Mittheilungen der Antiquarischen Gesellschaft in Zürich. 1.
- ^ Wood, James, ed. (1907). . The Nuttall Encyclopædia. London and New York: Frederick Warne.
- ^ "Sites Switzerland: Meilen–Rorenhaab (CH-ZH-06)". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ "A-Objekte KGS-Inventar" (PDF). Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, Amt für Bevölkerungsschutz. 2015-01-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-10-01. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ^ "Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz (NHG)" (PDF) (in German). Hochbaudepartement Stadt Zürich. 2014-10-12. Retrieved 2015-08-21.
- ^ Beat Eberschweiler (2004). "Ur- und frühgeschichtliche Verkehrswege über den Zürichsee: Erste Ergebnisse aus den Taucharchäologischen Untersuchungen beim Seedamm" (in German). ETH Bibliothek. Retrieved 2014-12-10.