Greifensee–Storen/Wildsberg
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 The site of the prehistoric settlement | |
| Location | Greifensee, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland |
| Part of | Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps |
| Criteria | Cultural: (iv), (v) |
| Reference | 1363-051 |
| Inscription | 2011 (35th Session) |
| Area | 9.59 ha (23.7 acres) |
| Buffer zone | 11.7 ha (29 acres) |
| Website | www |
| Coordinates | 47°21′37.81″N 8°40′51.51″E / 47.3605028°N 8.6809750°E |
Greifensee–Storen–Wildsberg is one of the 111 serial sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, of which are 56 located in Switzerland.[1][2]
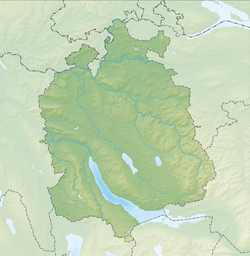
Geography
[edit]The site is located on Greifensee lakeshore in Wildsberg, a locality of the municipality of Greifensee in the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. Because the lake has grown in size over time, the original piles are now around 4 metres (13 ft) to 7 metres (23 ft) under the water level of 435 metres (1,427 ft). The settlement comprises 9.59 hectares (23.70 acres), and the buffer zone including the lake area comprises 11.70 hectares (28.91 acres) in all.
Settlements in Greifensee date back to 4000 BC. In 1975, the Neolithic stilt house village located on the northern lakeshore area called Böschen was discovered by recreational divers. Initially, they found ceramics, lavishly decorated pots and bowls, and simple, large food tanks. In scientific dives, the remains of a village with 24 huts have been revealed. The excellent condition of the timber relicts allows dendrochronological dating to the year 1051 BC. Weaving spindles made of clay, tools, needles and fishing hooks from bronze, charred wild apples and cereals have been conserved. Ten years after its construction, the settlement was destroyed by a fire and not rebuilt.
Description
[edit]Characterized is the settlement Storen–Wildsberg, around 1.1 kilometres (1 mi) in the east of Böschen by a large settlement area on a very steep slope on Greifensee lakeshore. From a scientific point of view and besides the location, a particularly interesting aspect is a phase of occupation dating from the Late Horgen culture. Furthermore, a copper spiral coil and a copper dagger from the Pfyn culture bear early witness to the processing of metal in this region. The settlement is largely undisturbed and thus holds great scientific potential for future research.[3]
Protection
[edit]As well as being part of the 56 Swiss sites of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, the settlement is also listed in the Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance as a Class A object of national importance.[4] Hence, the area is provided as a historical site under federal protection, within the meaning of the Swiss Federal Act on the nature and cultural heritage (German: Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz NHG) of 1 July 1966. Unauthorised researching and purposeful gathering of findings represent a criminal offense according to Art. 24.[5]
Image gallery
[edit]-
Path to the observation platform
-
Observation platform
-
Information board
-
Neolithic findings #1
-
Neolithic findings #2
See also
[edit]Literature
[edit]- Peter J. Suter, Helmut Schlichtherle et al.: Pfahlbauten – Palafittes – Palafitte. Palafittes, Biel 2009. ISBN 978-3-906140-84-1.
References
[edit]- ^ "Prehistoric Pile Dwellings in Switzerland". Swiss Coordination Group UNESCO Palafittes (palafittes.org). Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ "World Heritage". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-12-09. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ "Sites Switzerland: Greifensee–Storen/Wildsberg (CH-ZH-02)". palafittes.org. Archived from the original on 2014-10-07. Retrieved 2014-12-10.
- ^ "A-Objekte KGS-Inventar" (PDF). Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, Amt für Bevölkerungsschutz. 2015-01-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-10-01. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ^ "Bundesgesetz über den Natur- und Heimatschutz (NHG)" (PDF) (in German). Hochbaudepartement Stadt Zürich. 2014-10-12. Retrieved 2015-08-21.