Coastal Konjo language
Tools
Actions
General
Print/export
In other projects
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Language spoken in Indonesia
| Coastal Konjo | |
|---|---|
| Konjo Ilau’, Konjo Bulukkumba | |
| Native to | Indonesia |
| Region | South Sulawesi |
Native speakers | 170,000 (2010 census)[1] |
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | kjc |
| Glottolog | coas1295 |
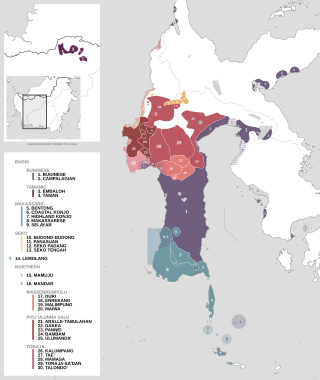 Map showing the distribution of the South Sulawesi languages in Sulawesi and Kalimantan. Bentong language is marked with number 6 in the Makassar languages group. | |
| Coordinates: 5°25′0.00″S 120°18′0.01″E / 5.4166667°S 120.3000028°E / -5.4166667; 120.3000028 | |
Coastal Konjo is an Austronesian language of Sulawesi, Indonesia, which belongs to the Makassaric branch of the South Sulawesi subgroup. It is spoken along the coast in the southeastern corner of South Sulawesi in the regencies of Sinjai, Bulukumba and Bantaeng.[2][3] It is closely related to, but distinct from Highland Konjo, which also belongs to the Makassaric languages.
Phonology
[edit]The following sound inventory is based on Friberg & Friberg (1991).[4]
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| High | i | u |
| Mid | e | o |
| Low | a | |
The vowel /a/ is realized as [ə] before geminate nasals.
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | t͡ʃ | k | ʔ |
| voiced | b | d | d͡ʒ | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | s | h | ||||
| Semivowel | j | w | ||||
| Lateral | l | |||||
| Trill | r | |||||
Only [ŋ] and [ʔ] can appear in final position. Words with underlying final /s/, /l/ or /r/ add an echo vowel, e.g. /nipis/ ['nipisi] 'thin'.
Grammar
[edit]Personal pronouns in Coastal Konjo have one independent form, and three bound forms.[5]
| free | ergative | absolutive | possessive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.sg./1.pl.excl. | nakke | ku- | -a | -ku |
| 1.pl.incl./2.honorific | gitte | ki- | -ki | -ta |
| 2.familiar | kau | nu- | -ko | -mu |
| 3. | ia | na- | -i | -na |
References
[edit]- ^ Coastal Konjo at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Grimes, C. E.; Grimes, B. E. (1987). Languages of South Sulawesi. Pacific Linguistics Series D - No. 78. Canberra: Australian National University. doi:10.15144/PL-D78. hdl:1885/145413. ISBN 0-85883-352-2.
- ^ Friberg, T.; Laskowske, T. V. (1989). "South Sulawesi Languages" (PDF). In Sneddon, J. N. (ed.). Studies in Sulawesi Linguistics Part I. NUSA 31. Jakarta: Universitas Atma Jaya. pp. 1–17.
- ^ a b c Friberg, Barbara; Friberg, Timothy (1991). "Notes on Konjo Phonology" (PDF). In Sneddon, James N. (ed.). Studies in Sulawesi Linguistics, Part II. NUSA 33. Jakarta: Universitas Atma Jaya. pp. 71–115.
- ^ Friberg, Barbara (1996). "Konjo's Peripatetic Person Markers" (PDF). In Steinhauer, Hein (ed.). Papers in Austronesian Linguistics No. 3. Canberra: Australian National University. pp. 137–171.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
† indicate extinct languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
