Ahin Posh
| Ahin Posh | |
|---|---|
 Ahin Posh stupa reconstitution, by William Simpson in 1878 | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Buddhism |
| Region | Gandhara |
| Ecclesiastical or organizational status | Stupa ruins |
| Year consecrated | 2nd century CE |
| Status | Artifacts removed |
| Location | |
| Location | Afghanistan |
| Geographic coordinates | 34°24′43″N 70°27′08″E / 34.412045°N 70.452130°E |
Ahan Posh or Ahan Posh Tape (Persian: آهن پوش (âhan puš) "iron-covered (place)") is an ancient Buddhist stupa and monastery complex in the vicinity of Jalalabad, Afghanistan, dated to circa 150-160 CE, at the time of the Kushan Empire.
The stupa was first excavated by William Simpson in February 1879. He cleared the base of the stupa and dug a tunnel to the center. The excavation found the remains of a colossal Buddha statue in clay covered with stucco at the entrance of the principal gateway, with feet measuring 58 centimeters in length.[1] The stupa was decorated with Indo-Corinthian capitals, "Indo-Persian" capitals, and capitals of the Ionic order typical of the Roman period.[1][2] Some of the Indo-Corinthian capitals had Buddhas seated among the foliage.[2]
A relic deposit compartment was found at the center of the stupa Ahin Posh, which was reached by a tunnel dug by Simpson. The deposit included a Gandharan golden amulet inset with garnets, in which two coins were found: one of Wima Kadphises and one of Kanishka.[3] Overall, numerous coins of Kushan kings were found in the central deposit compartment: ten coins of Wima Kadphises (c. 113–127 CE), six coins of Kanishka I, including one with an image of the standing Buddha, and one coin of Huvishka (circa 150–190 CE).[3]
Roman coins were also found in the deposit: a gold aureus of Roman emperor Domitian (81–96 CE), a gold coin of the Roman emperor Trajan (98-117 CE) and a gold aureus of Sabina, wife of Hadrian (117-138 CE).[3] In the coin of Sabina, she is entitled "Agusta", a title she received in 117 CE, at the time Hadrian was proclaimed Emperor. Therefore, the final dedication of the Ahin Posh stupa necessarily occurred after this date, probably during the few decades after 120 CE.[4]
This deposit now forms part of the collections of the British Museum.[5][6]
-
The three Roman coins found in the central deposit at Ahin Posh
-
A coin of the Roman Emperor Trajan, found together with coins of Kanishka, at Ahin Posh.
-
The golden amulet which contained coins of Wima Kadphises and Kanishka, now in the British Museum.[1]
-
Ahin Posh stupa Buddha, Simpson 1878
-
View of the ruins of Ahin Posh stupa, Illustrated London News August 16, 1879
-
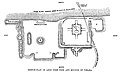
Plan of Ahin Posh stupa, by William Simpson in 1878
-
Ahin Posh stupa and vihara next to it, Simpson 1878
-
All the coins found in the central chamber at Ahin Posh.[9]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Errington, Elizabeth (2017). Charles Masson and the Buddhist Sites of Afghanistan: Explorations, Excavations, Collections 1832–1835. British Museum. pp. 156–159.
- ^ a b Cunningham, Alexander (1879). Proceedings of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. Asiatic Society of Bengal. p. 209.
- ^ a b c d e Errington, Elizabeth (2017). Charles Masson and the Buddhist Sites of Afghanistan: Explorations, Excavations, Collections 1832–1835. British Museum. p. 159.
- ^ Cunningham, Alexander. Proceedings of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. Asiatic Society of Bengal. p. 209.
- ^ Documents Epigraphiques Kushans G. Fussman p.48
- ^ British Museum Collection
- ^ See listing of coins, and obverse and reverse of the coin
- ^ "Coin, British Museum". The British Museum.
- ^ Errington, Elizabeth (2017). Charles Masson and the Buddhist Sites of Afghanistan (PDF). London: British Museum Research Publications. p. 59, Fig. 242 "Gold coins from the Ahinposh relic deposit".
Sources
[edit]- Errington, Elizabeth (2017). Charles Masson and the Buddhist Sites of Afghanistan: Explorations, Excavations, Collections 1832–1835. British Museum. pp. 156–159.
- "Documents Epigraphiques Kushans" G. Fussman





![Coin of Kanishka, found at Ahin Posh. This one has goddess Selene ("ϹΑΛΗΝΗ") on the reverse .[3][7]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b8/KanishkaICoinFoundInAhinposhAfghanistan.jpg/120px-KanishkaICoinFoundInAhinposhAfghanistan.jpg)
![The golden amulet which contained coins of Wima Kadphises and Kanishka, now in the British Museum.[1]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/33/AhinPoshGoldenAmulet2ndCenturyCE.jpg/120px-AhinPoshGoldenAmulet2ndCenturyCE.jpg)
![Gold coin of Kanishka, with depiction of the Buddha, found in Ahin Posh.[8][3]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fa/Ahin_Posh%2C_coin_of_Kanishka_with_the_Buddha.jpg/120px-Ahin_Posh%2C_coin_of_Kanishka_with_the_Buddha.jpg)



![All the coins found in the central chamber at Ahin Posh.[9]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3f/Gold_coins_found_at_Ahin_Posh.jpg/120px-Gold_coins_found_at_Ahin_Posh.jpg)