User:Tfmbty/2017 Pacific typhoon season
| Tfmbty/2017 Pacific typhoon season | |
|---|---|
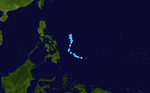
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | January 7, 2017 |
| Last system dissipated | January 4, 2018 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Lan |
| • Maximum winds | 260 km/h (160 mph) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 915 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 41 official, 1 unofficial |
| Total storms | 27 |
| Typhoons | 11 |
| Super typhoons | 2 (unofficial) |
| Total fatalities | 864 total |
| Total damage | $15.7 billion (2017 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2017 Pacific typhoon season was a below-average season in terms of Accumulated Cyclone Energy and the number of typhoons and super typhoons. The season produced a total of 27 named storms, 11 typhoons, and only two super typhoons, making it an average season in terms of storm numbers. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2017, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Muifa, developed on April 25, while the season's last named storm, Tembin, dissipated on December 26. However, Tropical Storm Bolaven developed as a tropical depression on December 30 and persisted into 2018, when it strengthened to a tropical storm before dissipating on January 4. This season also featured the latest occurrence of the first typhoon of the year since 1998, with Noru reaching this intensity on July 23.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, to the north of the equator between 100°E and the 180th meridian. Within the northwestern Pacific Ocean, there are two separate agencies that assign names to tropical cyclones, which can often result in a cyclone having two names. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) will name a tropical cyclone should it be judged to have 10-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph) anywhere in the basin. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) are given a numerical designation with a "W" suffix.
Seasonal forecast
[edit]| TSR forecasts Date |
Tropical storms |
Total Typhoons |
Intense TCs |
ACE | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (1965–2016) | 26 | 16 | 9 | 297 | [1] |
| May 5, 2017 | 27 | 17 | 10 | 357 | [1] |
| July 6, 2017 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 250 | [2] |
| August 8, 2017 | 26 | 14 | 7 | 255 | [3] |
| Other forecasts Date |
Forecast Center |
Period | Systems | Ref | |
| January 20, 2017 | PAGASA | January — March | 1–2 tropical cyclones | [4] | |
| January 20, 2017 | PAGASA | April — June | 2–4 tropical cyclones | [4] | |
| June 26, 2017 | CWB | January 1 — December 31 | 21–25 tropical storms | [5] | |
| July 6, 2017 | PAGASA | July — September | 6–9 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| July 6, 2017 | PAGASA | October — December | 3–5 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| 2017 season | Forecast Center |
Tropical cyclones |
Tropical storms |
Typhoons | Ref |
| Actual activity: | JMA | 41 | 27 | 11 | |
| Actual activity: | JTWC | 33 | 26 | 12 | |
| Actual activity: | PAGASA | 22 | 16 | 4 | |
During the year, several national meteorological services and scientific agencies forecast how many tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons will form during a season and/or how many tropical cyclones will affect a particular country. These agencies include the Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) Consortium of University College London, PAGASA and Taiwan's Central Weather Bureau. The first forecast of the year was released by PAGASA during January 20, within its seasonal climate outlook for the period January – June.[4] The outlook noted that one to two tropical cyclones were expected between January and March, while two to four were expected to develop or enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility between April and June.[4] During March 23, the Hong Kong Observatory predicted that the tropical cyclone season in Hong Kong would be near-normal, with four to seven tropical cyclones coming within 500 km (310 mi) of the territory, compared to an average of six, which was revised to six to nine tropical cyclones in August.[7]
On May 5, Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) issued their first forecast for the season, anticipating an activity of slightly above normal with 27 named storms, 17 typhoons and 10 intense typhoons, including an Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) of 357.[1] On June 26, Taiwan's Central Weather Bureau (CWB) predicted a normal season with 21—25 tropical storms developing over the basin, while three — five systems were expected to affect Taiwan itself.[5] In the same day, the Thai Meteorological Department (TMD) predicted that 2 tropical cyclones would move towards the northern or northeastern parts of Thailand during August or September.[8] On July 6, TSR released their second forecast for the season, reducing the predicted numbers to 25 named storms, 15 typhoons, and 7 intense typhoons, with an ACE Index of 250.[2] During the same day, the PAGASA issued their second and final outlook for the season for the period of July – December, where six to nine tropical cyclones were expected to develop or entered their area of responsibility between July and September, while three to five were forecast during October to December. During August 8, the TSR released their third and final forecast for the season, slightly raising their forecast named storms to 26, with 14 reaching typhoon intensity and 7 reaching intense typhoon intensity. ACE Indices were slightly raised to 255.[3]
Season summary
[edit]
The first half of the season was relatively inactive, with only seven systems developing, of which only two intensified into tropical storms. The first system of 2017 developed on January 7, and was named Auring by PAGASA. Tropical Depression Bising developed during the first week of February, and was a factor in, and worsened the effects of, the 2017 Visayas and Mindanao floods. This was followed by Crising, the third system unofficially named by PAGASA. Heavy rains from the depression caused flooding that led to the deaths of 10 people in Cebu, Philippines. Shortly after the dissipation of Crising came the formation of the first tropical storm of the season — Muifa. The system was not strong, however, and was located away from all major land areas, so it caused no damage. No systems formed during the month of May, the first such occurrence since 2013. The next cyclone, Merbok, formed during mid-June, and made landfall in Shenzhen in China. The cyclone was short-lived; however, it was relatively strong, producing winds of 100 km/h (65 mph) at its peak. Nanmadol passed over the Ryukyu Islands and progressed to make landfall in Nagasaki on Japan's island of Kyushu during early July. Torrential rainfall and strong winds from the cyclone itself and from the stormy weather that persisted for a number of days were responsible for major damage and 41 fatalities across mainland Japan.
By the middle of July, tropical activity had increased with simultaneous tropical storms developing after July 14. Severe Tropical Storm Talas formed during mid-July near the Paracel Islands in the South China Sea, and traveled generally westwards. It made landfall in Vietnam after brushing China's Hainan province and, unusually, continued to track far inland to the Laos–Thailand border before weakening to a depression. At least 14 deaths were attributed to the storm, primarily as a result of flooding. Later, the season was very active with 7 storms in late July-early August. Typhoon Noru reached Category 5 super typhoon in peak intensity and made landfall in Japan, causing $100 million in damage. Tropical Storm Sonca made landfall in Quảng Trị, Vietnam; 2017 was the first year since 1971 where 2 storms made landfall in Central Vietnam in July. Sonca brought heavy rainfall in Northeast Thailand and caused extreme flooding in the region with estimated costs of over US$300 million. Typhoon Nesat and Tropical storm Haitang made landfall in Taiwan and Fujian (a province in China), respectively, 2 days apart. In mid-late August, Typhoon Hato and Tropical Storm Pakhar made landfall in Macau and Guangdong respectively while they were at peak intensity. So far Typhoon Hato is the costliest tropical cyclone in Northwest Pacific in 2017 with damages totalling $6.82 billion.
The season was weaker in September. Typhoon Talim made landfall in Japan as a minimal typhoon and caused US$700 million in damage. Typhoon Doksuri made landfall in Quảng Bình, Vietnam as a Category 3 typhoon; damage was very major as the total was estimated at over US$814 million. In early October a tropical depression made landfall in Northern and North Central Vietnam, which brought very heavy rainfall and was responsible for the worst flooding in Northern and North-Central Vietnam, with 109 deaths and total damages of over US$570 million. Later, Typhoon Khanun made landfall in Southern China. So far Typhoon Lan has been the strongest tropical cyclone in the basin in 2017, and became the second largest tropical cyclone on record.
In November, La Nina was returned and tropical activity had increased with simultaneous tropical storms developing, and most of them moved west and affected Philippines and Vietnam. Typhoon Damrey made landfall in Khánh Hoà, Vietnam and became one of the costliest typhoon in Vietnam since 1975; and it is one of the costliest and deadliest typhoon in the basin in 2017 with total damage reached US$1.03 billion and 151 deaths. Later, two weak storms affected Philippines. In December, Tropical storm Kai-tak caused flooding in Central Philippines. Typhoon Tembin was responsible for severe flooding and landslides in South Philippines, it became the deadliest tropical cyclone in 2017 with over 250 deaths. Typhoon Tembin moved South China Sea, so 2017 became the most tropical cyclone in South China Sea with 22 Tropical cyclones, and Tembin affected Southern Vietnam.
A new record low of zero typhoons made landfall over the Philippines, although above-average tropical cyclone activity was observed in the South China Sea, resulting in more impacts to southern China and Vietnam.
Systems
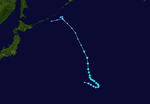
[edit]Tropical Depression 01W
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 7 – January 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
On January 7, both PAGASA and the JMA reported that a Tropical Depression developed about 400 km (250 mi) to the northeast of Davao City on Mindanao, Philippines.[9][10] During that day, the system moved along the southern periphery of a subtropical ridge of high pressure, before the JTWC initiated advisories on the system and designated it as Tropical Depression 01W.[11] It later made landfall in the Philippines the next day, and was assessed to have degenerated into a remnant low by the JTWC.[12] The JMA however tracked the system until it emerged into the South China Sea.[citation needed] By January 15, the JTWC re-issued advisories as it was located to the east of Vietnam.[13] However, convection dissipated due to wind shear and land interaction, the JTWC issued their final warnings on January 16.[14]
Flooding from the TD killed a total of 11 people.[15] Damages from Tropical Depression Auring were totaled at Ph₱7.14 million (US$143,000) from agriculture and fishing in Negros Occidental.[16]
Tropical Depression
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 3 – February 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
On February 3, a tropical depression developed near Palau.[17] The system dissipated on the 7th.[citation needed]
Tropical Depression 02W
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | April 13 – April 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min); 1006 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2017) |
A tropical depression formed over Palau on April 13.[18] During the next 2 days, the system moved toward the Philippines.[citation needed]
As of April 17, at least ten people were reported to be killed in Cebu by flooding caused by the system.[19] Total damages throughout the Philippines reached Ph₱84.8 million (US$1.7 million), mostly from Danao, Cebu.[20]
Tropical Storm Muifa
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | April 22 – April 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
During April 22, the JMA started to monitor a tropical depression that had developed near Guam.[21] After moving westward for a couple of days, the JTWC began issuing advisories, and designated the storm 03W. By April 25, 03W organized and began consolidating further as the JMA upgraded the depression to a tropical storm, giving it the name Muifa.[21] Muifa entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility the following day, and was named Dante by PAGASA.[22] The storm, however, started moving northwards and immediately tracked out of the area by April 27. Following this, both the JMA and the JTWC downgraded Muifa to a tropical depression. Muifa fully dissipated early on April 29, and the JMA issued their final advisory on the storm.[21]
Tropical Storm Merbok
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 10 – June 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
On June 10, the JMA started to track a tropical depression to the west of Manila, Philippines.[23] After the system entered a region favorable for further development, the depression rapidly organized, prompting the JTWC to start issuing advisories and give it the designation of 04W.[citation needed] A few hours later, 04W had intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name Merbok as it starts to move in a north-northwestward direction.[23] During June 12, Merbok reached its peak intensity with 10-minute winds of 100 km/h (65 mph) and a minimum pressure of 985 hPa, shortly before making landfall in Eastern Shenzen.[23][24] On June 13, the JMA issued its final warning on Merbok, as the system dissipated over China.[24][23]
Sustained winds of 51.3 knots (95.0 km/h; 59.0 mph) and a minimum pressure of 990.3 hPa (29.24 inHg) were recorded in Hong Kong as the eye passed nearby.[24] Across Guangdong Province, 32 homes were destroyed, 122,000 people reported property damage, and 13,000 hectares of crops flooded. Total economic losses in South China were counted to be CN¥600 million (US$88.2 million).[25]
Typhoon Nanmadol
[edit]| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 1 – July 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (1-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
On July 1, the JMA upgraded a low-pressure area it had been monitoring to a tropical depression, located south-southwest of Okinotorishima.[26] Later that day, the JMA began issuing advisories once the depression's sustained winds were estimated at 55 km/h (35 mph).[27] Shortly thereafter, the PAGASA classified the system as a tropical depression, assigning the local name Emong. On July 2, the JMA classified the system as a tropical storm, and assigned the official name Nanmadol.[26] The JTWC followed suit and gave the internal designation of 05W. The cyclone continued to intensify, and was upgraded by the JMA to a severe tropical storm later that day.[26] Nanmadol reached peak intensity at about 06:00 UTC on July 3,[26] and maintained this strength until making landfall on the western coast of Kyushu several hours later. The cyclone began to accelerate while following a generally eastward course across the south of Japan. After brushing the southern coast of Japan, the JTWC issued its final advisory during the next day. The JMA followed suit late on July 4, when it had become extratropical.[26] Its remnants moved out of the basin three days later.[26]
Evacuation advisories were issued to at least 20,000 residents due to fears of possible flooding and landslides, especially in the prefectures of Niigata, Toyama and Nagano, which had experienced rainfall accumulations of up to 300 mm (12 in) in the preceding hours.[28][29] At least three people were injured during the storm—a young boy's hand was injured when a school window broke in the city of Kumamoto, and two adults in Oita prefecture sustained minor injuries after falling due to the strong winds.[28][29][30] A total of 41 people have been confirmed dead due to torrential rains which caused landslides and flooding, particularly in Kyushu.[31] Total damages from the storm in Japan were amounted to be JP¥224 billion (US$2.04 billion).[32]
Tropical Storm Talas
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 14 – July 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
Early on July 14, the JMA upgraded a low-pressure area in the South China Sea to a tropical depression after the system began to organize.[33] Late the same day, the JMA began issuing advisories on the depression, and forecast it to develop into a tropical storm within the next 24 hours.[34]
Talas made landfall near Vinh of Nghệ An Province in Central Vietnam at 01:00 ICT on July 17 (18:00 UTC on July 16) as a severe tropical storm.[35] In Vietnam, the storm left 14 people dead and damaged around 2,700 houses. A coal ship with 13 crew members sank off the coast of Cửa Lò, leaving 3 dead and another 3 still unaccounted for.[36] Damages in Vietnam were counted to be 1 trillion₫ (US$44 million).[37] Total economic losses in Hainan Province reached CNY 60 million (US$8.9 million).[25]
Typhoon Noru
[edit]| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 19 – August 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 260 km/h (160 mph) (1-min); 930 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
The JMA reported that a non-tropical low had transitioned into a tropical depression north-northwest of Wake Island early on July 19.[38] Fluctuations in intensity occurred until late on July 29, when explosive intensification ensued. Total economic losses in Japan were counted to be US$100 million.[39]
Tropical Storm Kulap
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 20 – July 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
On July 20, the JMA started to monitor a tropical depression that formed over to the southwest of Midway Atoll, just to the west of the International Date Line.[40] The JTWC classified the system as subtropical, however.[41] By July 21, the subtropical storm started to show tropical characteristics, where it prompted both agencies to start issuing advisories, receiving the designation of 09W and the name Kulap.[42][40] During the next day, Kulap briefly reached its peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 95 km/h (60 mph) after imagery depicted some convection over near its compact center.[43] After moving westward in a marginally favorable environment, the JMA had reported a minimum pressure of 1002 hPa with peak 10-minute winds of 75 km/h (45 mph) during the early hours of July 24. However several hours later, Kulap had entered in a very unfavorable environment such as cooler waters of 25 °C (77 °F).[44] Due to strong shear and an interaction with Typhoon Noru to its south, Kulap had rapidly weakened; therefore, both agencies issued their final advisory on July 26.[45] The JMA, however, tracked Kulap's remnants until July 28 when it was absorbed by the outflow of Typhoon Noru.[40]
Tropical Storm Sonca
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 21 – July 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
On July 21, both the JMA and the JTWC reported that Tropical Depression 08W had developed approximately 582 km (361 mi) to the south of Hong Kong.[46][47] After moving westward for a couple of days, the system strengthened into a tropical storm by both agencies while nearing the island province of Hainan, receiving the name Sonca.[48][46] By July 24, Sonca reached its maximum intensity with a minimum pressure of 994 hPa.[46] Early on July 25, the JTWC issued its final advisory as the system made landfall over in Quảng Trị Province, Vietnam.[49][50] The JMA issued its final advisory a few hours later when it had weakened into a tropical depression,[46] although Sonca maintained its intensity over land until it had fully dissipated on July 29.[46]
Flooding in Northern Cambodia drowned two people, blocked many roads and flooded several hundred houses.[51] Damage across Sakon Nakhon, Thailand exceeded 100 million baht (US$3 million)[52] and killed 23 people across Thailand.[53]
Tropical Storm Roke
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 21 – July 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
The JMA noted the formation of a tropical depression southeast of Taiwan early on July 21.[54] Assigning the numerical designation 10W, the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical depression at about 18:00 UTC the same day.[55] The system traveled in a generally northwesterly direction, and passed through the Luzon Strait, between Taiwan and the Philippines.[55] Around the same time, the PAGASA began issuing advisories on the depression, and contributed the unofficial name Fabian. Early the next day, after the system had emerged into the South China Sea, both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded the system to a tropical storm, naming it Roke.[55][54] Roke assumed a more westerly course, and tracked obliquely towards China's Guangdong coast.[56] The JTWC downgraded the system to a tropical depression just 12 hours later, at 18:00 UTC,[55] but the JMA maintained the cyclone's category as a tropical storm. Roke made landfall just east of the Hong Kong central business district at about 01:30 UTC on July 23, and passed over Shenzhen one to two hours later.[56] Roke weakened to a depression a few hours later, though the JMA declared that it had dissipated on 18:00 UTC of the same day.[54]
Schools, businesses and government offices were closed in Hong Kong as the Hong Kong Observatory (HKO) raised its typhoon warning signal to 8—the third highest of five levels—in preparation for Tropical Storm Roke.[57] Ferry services in the city were suspended, and more than 50 flights were delayed.[58] However, winds in the city were relatively light and no significant damage was reported.
Typhoon Nesat
[edit]| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 25 – July 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (1-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
The JMA upgraded a low-pressure area to a tropical depression east of the Philippines early on July 25.[59]
Despite the storm not making landfall over in the Philippines, Nesat enhanced the southwest monsoon which brought torrential rainfall over most of the country. As of July 30, the NDRRMC had reported a total of Php 105.02 million (US$2.08 million) worth of damages.[60] Total damages in Taiwan were counted to be NT$60 million(USD 2 million).[61] Total damages in Mainland China were counted to be CNY 1.83 billion(USD 277.27 million).[25]
Tropical Storm Haitang
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 27 – August 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
A low-pressure area over the northern portion of the South China Sea was upgraded to a tropical depression by the JMA early on July 27.[62] Despite an exposed LLCC with disorganized banding, the JTWC started initiating advisories, assigning the designation of 12W.[63] During the next day, the system had strengthened into a tropical storm, with the JMA naming it as Haitang, after ASCAT image depicted 40 knot winds over in the southern portion of the storm.[64] Due to the nearby Typhoon Nesat and moderate wind shear, Haitang maintained its intensity for several hours,[65] until on July 30 when the system had deepened and reached its peak intensity with 10-minute sustained winds of 85 km/h (50 mph) with a minimum pressure of 985 hPa. Around the same time, Haitang entered the Philippine area of Responsibility, receiving the name Huaning by PAGASA, although the system had left the area during 12:00 UTC of the same day. Three hours later, the JTWC downgraded the system to a tropical depression,[66] though it was re-upgraded into a tropical storm six hours later.[67] By July 31, the JTWC issued their final advisory on Haitang after the system had made landfall over in the Pingtan County in Taiwan.[68] During 06:00 UTC of that day, the JMA issued their final advisory after Haitang weakened into a remnant low.[citation needed]
Tropical Storm Nalgae
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 31 – August 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
During July 31, the JMA started to monitor a tropical depression located about 1,106 km (687 mi) to the northeast of Wake Island.[69] During the next day, the JTWC started issuing advisories and designated it as 13W.[70] By August 2, both agencies upgraded 13W to Tropical Storm Nalgae after imagery showed flaring convection and the storm was located in a region of low to moderate wind shear and warm SSTs.[71][72] Moving in a northward direction, Nalgae slowly intensified for several days. Nalgae reached its peak intensity with 10-minute sustained winds of 85 km/h (55 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 988 hPa during August 5 for a brief time, as it was beginning to transition into an extratropical cyclone. The JTWC downgraded Nalgae to a tropical depression later that day and issued their final advisory after the storm was located in very unfavorable environments.[73] The JMA followed suit early on August 6 when Nalgae fully transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, after which its remnants moved further north and were last noted during August 9.[citation needed]
Typhoon Banyan
[edit]| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 10 – August 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (1-min); 945 hPa (mbar) |
On August 11, a tropical depression had formed. The system then tracked north-west. On August 12th, the systems turned north and underwent intensification (and was named Banyan) until it reached its peak of category 2 at 140km/h (85mp/h) and a pressure of 970 hPa, the storm had not developed an eye wall fully yet. After heading north, the system was disrupted by moderate-strong wind shear caused the system to weaken back to a tropical depression, now tracking north-east. Banyan managed to strengthen again into category 2 (eye did not form here) but was again affected by wind shear and cooler waters, still tracking north-east. Then Banyan headed for Alaska as a tropical storm and before being extra tropical, it dissipated.
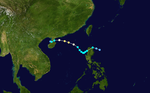
Typhoon Hato
[edit]| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 19 – August 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min); 950 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
A low-pressure area developed into a tropical depression on August 19 while located to the southeast of Taiwan.[74]
It gradually intensified and reached typhoon status on the afternoon of August 22 after entering the northeastern part of the South China Sea. On August 23, 07:00 HKT, Hato was approximately 100 km southeast of Hong Kong, bringing rain to the mainland as well as Hainan to the west. At 11:00 HKT the eye was approximately 60 km southwest of Hong Kong with the typhoon heading onto the mainland in a west-northwesterly direction.[75]
Hong Kong Observatory issued Hurricane Signal No. 10 at 09:10 HKT, the first time since 2012.[76] A total of 11 people were killed while total damages in Mainland China were counted to CN¥28.91 billion (US$4.38 billion).[25] No people were killed in Hong Kong, while estimated damages in Hong Kong amounted to HK$8 billion (US$1.02 billion).[77] In Macau, losses of 11.47 billion patacas (US$1.42 billion) were incurred when high tides exacerbated flooding in most of the lower lying areas, inundating ground floor shops and businesses. There were 12 deaths as a result of the typhoon including a number of people who drowned in flooded underground car-parks.[78] Despite making landfall in South China, Hato triggered floods in Northern Vietnam and killed 1 person. The total damage by heavy rainfall in Bắc Kạn Province, were counted to be 25 billion₫ (US$1.12 million).[79]
Tropical Storm Pakhar
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 24 – August 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
On August 26, Pakhar passed over the Philippines heading westward toward mainland China where it gathered strength before making landfall in Tianshan on August 27.
Total economic losses in South China have amounted to CN¥760 million (US$115 million) while a total of twelve people have been killed.[25] Moreover, damages in the Philippines were recorded at PhP41.27 million (US$808 thousand) and 2 billion₫ (US$85,000) in Vietnam.[80][81]
Typhoon Sanvu
[edit]| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 26 – September 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min); 955 hPa (mbar) |
On August 27, the JMA began to monitor a tropical depression that had developed about 441 km (274 mi) north-northeast of Saipan, although the system's nature was more of a monsoon depression.[82] The JTWC followed suit on the following day, designating the system as 17W.[83] Around the same time, the system had intensified into Tropical Storm Sanvu. By August 29, Sanvu increased in size, and therefore it prompted the JMA to upgrade it to a severe tropical storm. After moving in a westward direction, Sanvu stalled and entered a region of favorable conditions. As a ragged eye developed, both agencies upgraded Sanvu to a typhoon during August 31.[84] Sanvu reached its peak intensity on September 1 as a Category 2 typhoon.[85] Thereafter, the system steadily weakened as it started to move northwards with JTWC immediately downgrading the system to a tropical storm and issuing their final advisory late on September 2. The JMA still classified Sanvu as a typhoon until they issued their final advisory as the system had transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on September 3.
Sanvu did not caused any significant damage in the Mariana Islands, though a 33-year-old woman drowned at Obyan beach due to large waves on August 29.[86]
Tropical Storm Mawar
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 30 – September 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
On August 30, the JMA started to track a tropical depression to the north-northeast of Luzon, Philippines. Given the international designation of 18W by the JTWC,[87] the JMA upgraded the system immediately to Tropical Storm Mawar. Slowly organizing, convection had rapidly developed and Mawar strengthened into a severe tropical storm early on September 2. On September 3, Mawar had weakened to a tropical storm after environments started to become unfavorable due to high wind shear.[88] Later that day, Mawar weakened to a tropical depression and the JTWC issued their final advisory while making landfall over in Southeastern China between the cities of Shanwei and Shantou.[89][90] The JMA followed suit early on September 4 when Mawar had fully dissipated.
The China's National Meteorological Center (NMC) issued a blue alert for the southern parts of Guangdong on September 1.[91] During 2:00 a.m. local time on September 2, the Hong Kong Observatory issued a Tropical Cyclone Warning Signal No. 1 over in Hong Kong.[92] Chinese authorities activated a natural disaster alert and response to help local civil affairs departments in areas such as the provinces of Fujian and Guandong to prepare for relief work.[93] By September 3, the NMC had raised their warning signal to a yellow alert.[94] Flooding from Mavar was a major concern with reports of rainfall of up to 80 mm (3.1 in) in some places which were impacted by Hato and Pakhar.[90] Total economic losses in South China were counted to be CNY 10 million(USD 1.51 million).[25]
Tropical Storm Guchol
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 3 – September 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
On September 3, the JMA started to track a tropical depression that had developed to the east of Luzon, Philippines. During the next day, the PAGASA initiated advisories and gave the local name Kiko,[95] while the JTWC followed suit by giving it the designation 19W.[96] However, due to increased wind shear along with an exposed circulation, the JTWC issued its final advisory on 03:00 UTC September 5.[97] Several hours later, deep convection was depicted and despite moderate to high shear, the JTWC re-initiated advisories,[98] while the JMA had upgraded the system to a tropical storm, naming it as Guchol early on the next day. On 21:00 UTC of that day, the JTWC stopped issuing warnings on the system after convection significantly weakened.[99] JMA later followed suit early in the next day by declaring it a remnant low as it neared Putian, Fujian on Strait of Taiwan. The remnant low would then make landfall over Pingtan County of Fujian in China late in the following day before it transitioned into an extratropical storm near Zhejiang as it merged with the cold front on September 8.[citation needed]
Typhoon Talim
[edit]| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 8 – September 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 220 km/h (140 mph) (1-min); 930 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical depression formed east of Guam on September 7.[100] By the next day, the JTWC began issuing advisories on Tropical Depression 20W.[101] On September 9, 20W organized into a tropical storm, with the JMA naming the system as Talim.[102] With gradual intensification, the JMA upgraded Talim to a severe tropical storm. Talim further strengthened to a typhoon on September 11 where it simultaneously entered the PAR, with PAGASA naming it as Lannie.[103] The JTWC, however, delayed their upgrade until September 12.[104] Due to an ill-defined eye, Talim maintained its intensity until its eye became much clearer as rapid deepening ensued, as Talim became a Category 4 on September 14, and reached its peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 220 km/h (140 mph).[105] Talim began to curve eastward as it rapidly weakened to a tropical storm thereafter, making landfall in Kyushu on September 17, with a path of heavy rainfall up to the region east of Tokyo.[106]
In total, 5 people were killed in Japan, and total damages were counted to be US$750 million.[107]
Typhoon Doksuri
[edit]| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 10 – September 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
As of September 19, the NDRRMC confirmed a total of 8 dead due to landslides and flooding while total damages were up to Ph₱267 million (US$5.23 million).[108]
On September 15, Typhoon Doksuri made landfall in Quảng Bình Province, Vietnam as a Category 3 typhoon. Doksuri killed 15 people so far in Vietnam while estimated damages were about ₫16.36 trillion (US$720 million).[109][110][111] Despite making landfall in Indochina, Doksuri affected Hainan and total economic losses were estimated to be CNY 100 million(USD 15.1 million).[25]
Tropical Depression 22W
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 23 – September 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical depression formed to the west of Luzon on September 23, and was named "Nando" by PAGASA. The tropical depression quickly moved west-northwest and made landfall in Quảng Ninh, Vietnam, on September 25, before dissipating later on the same day.[citation needed]
The China Observatory issued a "yellow" alert over in the eastern and southern regions due to rainstorms. Some areas have warned a possible precipitation of about 140 mm (5.5 in).[112] Typhoon Signal No. 1 was raised over in Hong Kong during September 24, with expected gusts of up to 70 km/h (42 mph) including rough swells.[113] A voltage dip also occurred, causing 17 people to be trapped in lifts.[114] As the depression approached Vietnam on September 25, the Vietnam National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting of Vietnam forecast rainfall of about 150 mm (5.9 in) in Hanoi and surrounding provinces, with rough waves up to 3 m (9.8 ft) in Ha Long Bay.[115]
Tropical Depression 23W
[edit]| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 7 – October 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
Early on October 7, a tropical depression formed to the west of the Philippines.[116]
Early on October 10, the tropical depression made landfall in Hà Tĩnh Province, Vietnam, and dissipated shortly afterward. Consequently, both the JMA and the JTWC issued their final advisories for the storm.[citation needed]
Tropical Depression 23W caused severe flooding over provinces of Northern and Central Vietnam. Roughly more than 700 houses have been destroyed, while rescue efforts have saved 28 people from the danger zone. In total, 100 people were killed, and damages were about 13 trillion₫ (US$573 million).[117][118] During October 10, the Red River was forecast to have waters exceed to the levels of 3–50 cm (2–20 in).[119][120] In Hoàng Long river (Ninh Bình Province) flooding was the most severe since 1985.[121]
Typhoon Khanun
[edit]| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 11 – October 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min); 955 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
According to the NDRRMC, Khanun killed only one person, with total damages of Php4.45 million (US$86,400).[122] Authorities in Hong Kong and Macau raised the number 8 tropical cyclone warning on October 15 as gale-force winds affected the region. In total, damages from Khanun in South China were counted to be CNY2.46 billion (US$372.33 million).[25]
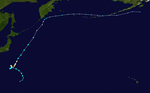
Typhoon Lan
[edit]| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 15 – October 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 250 km/h (155 mph) (1-min); 915 hPa (mbar) |
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) initially mentioned a tropical disturbance over Chuuk on October 11.[123] After the slow consolidation, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert to the elongated system early on October 14,[124] shortly after the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) started to monitor it as a low-pressure area.[125] The agency upgraded it to a tropical depression almost one day later and began to issue tropical cyclone warnings since 06:00 UTC on October 15.[126][127] In the afternoon, the JTWC also upgraded it to a tropical depression assigning the designation 25W, which formative but shallow convective bands had become more organized, and symmetrically wrapped into a defined low-level circulation center.[128] About three hours later, the JMA upgraded it to the twenty-first Northwest Pacific tropical storm in 2017 and assigned the international name Lan, when it was located approximately 310 km (190 mi) to the northeast of Palau.[129] Early on October 16, the JTWC upgraded Lan to a tropical storm too, based on T-number 2.5 of the Dvorak technique,[130] shortly before it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and received the name Paolo from PAGASA.[131] In total, 17 people were killed in Mainland Japan and total economic losses were counted to be US$2 billion.[107]
Tropical Depression 26W
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 18 – October 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
Originating from an enhanced monsoon trough, a tropical disturbance developed just to the northwest of Palawan on October 17.[132] On October 18, the JTWC had issued a TCFA on the system.[133] By 21:00 UTC of that day, the JTWC began issuing advisories as they classified it as a tropical depression, assigning the identifier 26W.[134] This was due to deep convection found near the storm's center with formative banding, along with its location over in a favorable environment.[135] Initially, its forecast stated that 26W would intensify into a weak tropical storm, although due to a disorganized center with strong shear, the JTWC issued their final advisory on October 19 as it was being absorbed by the outflow of nearby Typhoon Lan.[136]
Associated with the rainbands of a nearby typhoon, 26W helped spread scattered rainfall throughout most of Visayas and northern Mindanao. Residents in some areas were alerted against possible flash floods and landslides.[137] 14 people were dead from heavy rainfall from the system and its precursor, and raised a state of calamity in Zamboanga City on October 23.[138][139]
Typhoon Saola
[edit]| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 22 – October 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min); 970 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
A tropical depression formed north of Guam, the next day, the Tropical Depression transitioned into a Tropical Storm and the Japan Meteorological Agency named it Tropical Storm Saola. By evening of that day, Saola entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR). The PAGASA gave the local name "Quedan" to the storm. By the next day, Saola moved slowly and strengthened into a severe tropical storm. Its intensity did not change, even as high wind shear occurred to the north of Saola and the strengthening northeast monsoon while heading to Japan. It started weakening while in cold waters and brought rains to Southern Japan but did not make landfall. It dissipated after avoiding Japan and heading northeast.[citation needed]
Tropical Depression 29W
[edit]| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 30 – November 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1006 hPa (mbar) |
The JMA upgraded a low-pressure area to a tropical depression over the southern portion of the South China Sea, on October 30.[140] The JTWC issued a TCFA during the next day as it gathered strength. Initially forecast to intensify to a tropical storm, the system rapidly deteriorated and degenerated to a remnant low on November 3 as it tracked into the Gulf of Thailand.[141] Over in the course of two days, after re-curving back to the gulf, the JTWC re-issued a TCFA.[142] By November 6, the JTWC classified the system as Tropical Depression 29W.[143] On November 8, 29W made landfall over the Malay Peninsula, before dissipating soon afterward.
Tropical Depression 29W caused unusually heavy rains and flash floods to occur in the state of Penang, killing 7 people.[144] Flood waters in parts of the city reached 3.7 m (12 ft), submerging entire homes.
Typhoon Damrey
[edit]| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 31 – November 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (1-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
The JMA upgraded a low-pressure area to a tropical depression east of Visayas on October 31. PAGASA gave warnings to the system and named it Ramil. The storm brought rainy weather on the All Saints's Day (November 1) to Visayas. The tropical depression made landfall over Busuanga, Palawan at midnight on November 1. On November 2, Ramil strengthened, and the JTWC and JMA upgraded Ramil to a tropical storm, and gave the system the international name Damrey.[145]
As of November 8, a total of 112 people were confirmed dead due to the storm.[146][147]
Tropical Storm Haikui
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 7 – November 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
A Tropical Depression formed over Samar on November 9, and PAGASA gave the name Salome to the system. Salome damaged boats in Sorsogon with large waves. On the next day, after Salome made landfall, the system intensified into a tropical storm, and the JMA gave the international name Haikui to the system. Haikui dropped heavy rainfall over Southern Luzon and Visayas. Haikui was a weak, but deadly system, especially in Philippines.[citation needed]
No casualties were reported, though damages were totaled up to Php218.5 million (US$4.3 million). In addition, only five houses were fully damaged in Dipaculao, Aurora.[148]
Tropical Storm Kirogi
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 16 – November 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
On November 16, a tropical Depression formed on Sulu Sea, with the PAGASA naming it Tino. At midnight on the same day, the system made landfall on Puerto Princesa. At about that time, the system intensified into a tropical storm, and the system was given the international name Kirogi by the JMA.[citation needed]
Total economic losses in Vietnam were amounted to be US$10 million.[149] The remnant energy of Tropical Storm Kirogi eventually contributed to the formation of Very Severe Cyclonic Storm Ockhi in the North Indian Ocean.[150][151]
Tropical Storm Kai-tak
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 13 – December 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
A low pressure area developed into a tropical depression east of Mindanao late on December 11, and the JMA began to issue tropical cyclone warnings early on the next day.[152]
The NDRRMC confirmed a total of 83 people dead and calculated a total of Php3.747 billion (US$75 million) worth of infrastructure and agricultural damages.[153][107]
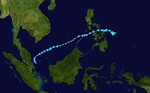
Typhoon Tembin
[edit]| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 20 – December 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min); 965 hPa (mbar) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2018) |
A low-pressure area (LPA) was upgraded to a tropical depression south of Elato by the JMA early on December 16,[154] yet it degenerated into an LPA two days later.[155] It was upgraded to a tropical depression by the JMA again early on December 20,[156] when it was located to the east-northeast of Palau, shortly before the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert.[157] It also received the local name Vinta from PAGASA.[158]
Rough waves caused by Tembin sank a ferry on December 22, killing five people.[159] An additional 261 people were also killed due to flooding in Mindanao.[160] Estimated damages are around ₱2.1 billion (US$42.4 million).[161]
Other systems
[edit]On March 19, a tropical depression formed close to the northeast of Mindanao, Philippines, and dissipated over the Sibuyan Sea two days later.[162][163] Early on June 29, the JMA initiated advisories on a newly formed tropical depression located about 138 km (86 mi) south of Okinawa Island.[164] The system re-curved and started moving in a northeastward direction until it dissipated to the southwest of Tokyo on July 1.[165] Early on July 4, the JMA indicated that a tropical depression had formed about 505 km (314 mi) south of Okinotorishima.[166] During the next day, the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) on the system, although it was canceled several hours later.[167] After moving northward, the depression rapidly weakened as it was absorbed by a stationary front on July 7.[168]
Early on July 13, the JMA reported that a non-tropical low had transitioned into a tropical depression about 75 km (45 mi) north-northeast of Iwo Jima.[169] The depression moved in a generally northeasterly direction until weakening to a low-pressure area by 06:00 UTC on July 16.[170] A tropical depression formed about 700 km (435 mi) northeast of Wake Island late on July 25, though the JTWC indicated it as a subtropical system with estimated recorded winds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[171][172] After several days, the system had already transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on July 29, without becoming a tropical storm.[173] Early on August 25 the JMA started to track a tropical depression over in the South China Sea,[174] although it was last monitored during the next day when it was absorbed by the outflow of Tropical Storm Pakhar.[175] On August 28, the JMA started to issue advisories on a tropical depression that had developed about 1,217 km (756 mi) east-northeast of Tuguegarao City.[176] The JMA predicted that the system would become a tropical storm within the next 24 hours, although because the system did not develop further, the JMA issued their final advisory on 03:00 UTC of August 29 when the system had weakened into a low-pressure area.[177] The remnants of the system helped with formation of Tropical Storm Mawar.[178]
On December 29, a tropical depression formed, which later strengthened to Tropical Storm Bolaven in January 2018.[citation needed]
Storm names
[edit]Within the Northwest Pacific Ocean, both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and PAGASA assign names to tropical cyclones that develop in the Western Pacific, which can result in a tropical cyclone having two names.[179] The Japan Meteorological Agency's RSMC Tokyo — Typhoon Center assigns international names to tropical cyclones on behalf of the World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee, should they be judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[180] PAGASA assigns names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in their area of responsibility located between 135°E–115°E and between 5°N–25°N even if the cyclone has had an international name assigned to it.[179] The names of significant tropical cyclones are retired, by both PAGASA and the Typhoon Committee.[180] Should the list of names for the Philippine region be exhausted then names will be taken from an auxiliary list of which the first ten are published each season. Unused names are marked in gray.
International names
[edit]During the season 27 tropical storms developed in the Western Pacific and each one was named by the JMA, when the system was judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph). The JMA selected the names from a list of 140 names, that had been developed by the 14 members nations and territories of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee.[181] During the season, the names Hato and Lan were used for the first time, after they had replaced the names Washi and Vicente, which were retired after the 2011 and 2012 seasons, respectively.
| Muifa | Merbok | Nanmadol | Talas | Noru | Kulap | Roke | Sonca | Nesat | Haitang | Nalgae | Banyan | Hato | Pakhar |
| Sanvu | Mawar | Guchol | Talim | Doksuri | Khanun | Lan | Saola | Damrey | Haikui | Kirogi | Kai-tak | Tembin |
After the season the Typhoon Committee retired the names Hato, Kai-tak and Tembin from the naming lists, while their replacement names will be announced in 2019.[182]
Season effects
[edit]This table summarizes all the systems that developed within or moved into the northern Pacific Ocean, to the west of the International Date Line during 2017. The tables also provide an overview of a systems intensity, duration, land areas affected and any deaths or damages associated with the system.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| 01W | January 7 – 16 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines, Vietnam, Cambodia | $140,000 | 11 | [15][16] |
| TD | February 3 – 7 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | March 19 – 21 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1008 hPa (29.77 inHg) | Philippines | None | None | |
| 02W | April 13 – 20 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan | $1.7 million | 10 | [19][20] |
| Muifa | April 22 – 29 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Caroline Islands | None | None | |
| Merbok | June 10 – 13 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Philippines, South China[nb 1] | $90.8 million | None | [25] |
| TD | June 29 – July 1 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1008 hPa (29.77 inHg) | Japan | None | None | |
| Nanmadol | July 1 – 4 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Japan | $1.99 billion | 41 | [31][32] |
| TD | July 4 – 7 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1010 hPa (29.83 inHg) | Taiwan, Ryukyu Islands | None | None | |
| TD | July 13 – 16 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Talas | July 14 – 17 | Severe tropical storm | 95 km/h (60 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | South China, Indochina[nb 2] | $80.1 million | 14 | [183][184] [37][185][25] |
| Noru | July 19 – August 8 | Typhoon | 175 km/h (110 mph) | 935 hPa (27.61 inHg) | Japan | $100 million | 2 | [39] |
| Kulap | July 20 – 28 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Sonca | July 21 – 29 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 994 hPa (29.35 inHg) | Hainan, Indochina | $306 million | 37 | [186][187] [188][189] [190][191] |
| Roke | July 21 – 23 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, South China | None | None | |
| Nesat | July 25 – 30 | Typhoon | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 960 hPa (28.35 inHg) | Philippines, Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan, East China |
$281 million | 3 | [60][61][192][25] |
| TD | July 25 – 29 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Haitang | July 27 – August 2 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, East China | $3.83 million | None | [61][193] |
| Nalgae | July 31 – August 5 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Banyan | August 10 – 17 | Typhoon | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Wake Island | None | None | |
| Hato | August 19 – 24 | Typhoon | 140 km/h (85 mph) | 965 hPa (28.50 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, South China, Vietnam | $6.82 billion | 24 | [25][77][78][79] |
| Pakhar | August 24 – 27 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Vietnam, Thailand | $116 million | 13 | [25][81][80][107] |
| TD | August 25 – 26 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Vietnam | None | None | |
| Sanvu | August 27 – September 3 | Typhoon | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Mariana Islands, Japan, Russian Far East | Unknown | 1 | [86] |
| TD | August 28 – 29 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines | None | None | |
| Mawar | August 30 – September 4 | Severe tropical storm | 95 km/h (60 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, South China | $1.51 million | None | [25] |
| Guchol | September 3 – 7 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, East China | None | None | |
| Talim | September 8 – 17 | Typhoon | 175 km/h (110 mph) | 935 hPa (27.61 inHg) | Mariana Islands, Taiwan, Japan, East China, Russian Far East | $750 million | 5 | [107] |
| Doksuri | September 10 – 16 | Typhoon | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Indochina, Bangladesh | $814 million | 45 | [108][109][110][111][194][25][195] |
| 22W | September 23 – 25 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Vietnam | Minimal | None | |
| 23W | October 7 – 10 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Indochina | $603 million | 109 | [195][196] |
| Khanun | October 11 – 16 | Typhoon | 140 km/h (85 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, South China, Vietnam | $372 million | 1 | [25][122] |
| Lan | October 15 – 23 | Typhoon | 185 km/h (115 mph) | 915 hPa (27.02 inHg) | Caroline Islands, South Korea, Philippines, Japan, Russian Far East | $2 billion | 17 | [107] |
| 26W | October 18 – 19 | Tropical depression | 45 km/h (30 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines | Minimal | 14 | [139] |
| Saola | October 22 – 29 | Severe tropical storm | 110 km/h (70 mph) | 975 hPa (28.79 inHg) | Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands, Japan | $250 million | None | [107] |
| 29W | October 30 – November 8 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, Northern Malaysia | Minimal | 7 | [144] |
| Damrey | October 31 – November 4 | Typhoon | 130 km/h (80 mph) | 970 hPa (28.64 inHg) | Philippines, Vietnam, Cambodia | $1.03 billion | 151 | [197][198][199] |
| Haikui | November 7 – 13 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Central Vietnam | $4.3 million | None | [148] |
| Kirogi | November 16 – 19 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Philippines, East Malaysia, Indochina | $10 million | 10 | [200][149] |
| Kai-tak | December 13 – 23 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 994 hPa (29.35 inHg) | Philippines, Malaysia, Southern Vietnam | $75 million | 83 | [201] |
| Tembin | December 20 – 26 | Typhoon | 130 km/h (80 mph) | 970 hPa (28.64 inHg) | Caroline Islands, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam | $42.4 million | 266 | [159][160][161]
|
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 42 systems | January 7, 2017 – January 4, 2018 |
185 km/h (115 mph) | 915 hPa (27.02 inHg) | $15.7 billion | 864 | |||
See also
[edit]- 2017 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2017 Pacific hurricane season
- 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2016–17, 2017–18
- South Atlantic tropical cyclone
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (May 5, 2017). Extended Range Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2017 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ^ a b Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (July 6, 2017). July Forecast Forecast Update for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2017 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (August 7, 2017). August Forecast Forecast Update for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2017 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved August 8, 2017.
- ^ a b c d Malano, Vicente B (January 20, 2017). January — June 2017 (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on January 29, 2017. Retrieved January 29, 2017.
- ^ a b Cheng, Ming-Dean (June 26, 2017). "Normal Number of Typhoons Expected for 2017; Three to Five May Hit Taiwan" (doc) (Press release). Taiwan Central Weather Bureau. Retrieved June 26, 2017.
- ^ a b July – December 2017Malano, Vicente B (July 6, 2017). July — December 2017 (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration.
- ^ Chi-ming, Shun (March 23, 2017). "Director of the Hong Kong Observatory highlights Observatory's latest developments March 23, 2017". Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved April 14, 2017.
- ^ "The Seasonal forecast of Thailand during the Rainy Season of 2017". Thai Meteorological Department. Ministry of Digital Economy and Society. 26 June 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-01-09. Retrieved 2017-01-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6nLHT1u8P?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WWJP25-RJTD_201701070000.htm
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 8, 2017. Archived from the original on January 8, 2017. Retrieved January 8, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 007". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 8, 2017. Archived from the original on January 9, 2017. Retrieved January 8, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 008". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 15, 2017. Archived from the original on January 16, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 012". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. January 16, 2017. Archived from the original on January 16, 2017. Retrieved January 16, 2017.
- ^ a b "Global Catastrophe Recap January 2017" (PDF). thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com. Aon Benfield. Retrieved February 8, 2017.
- ^ a b "'Auring' damage to agro-fishery in Negros Occidental reaches P7.14M". Sunstar. January 21, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Advisory for Analysis and Forecast 2017-02-03T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved February 3, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-04-13T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved April 13, 2017.
- ^ a b "'Crising' death toll in Cebu rises to 10". Philstar. April 17, 2017.
- ^ a b "Capitol pegs Crising damage at P84.8M". Inquirer. April 25, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1701 Muifa (1701)". Japan Meteorological Agency. June 9, 2017. Archived from the original on June 9, 2017.
- ^ "'Dante' intensifies into tropical storm as it enters PAR". Inquirer.net. April 26, 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1702 Merbok (1702)". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 19, 2017. Archived from the original on July 19, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Tropical Storm 04W (Merbok) Warning NR 008". usno.navy.mil. Archived from the original on 2017-06-12. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p China Meteorological Agency (November 26, 2017). Member Report: China (PDF). ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee: 12th Integrated Workshop. ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 26, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1703 Nanmadol (1703)". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 28, 2017. Archived from the original on August 28, 2017.
- ^ "WebCite query result". www.webcitation.org. Archived from the original on 2017-07-01. Retrieved 2017-07-01.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ a b "Typhoon rips through Japan archipelago, causing mudslides, blackouts". Mainichi Daily News. 2017-07-05. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ a b hermesauto (2017-07-04). "Japan typhoon grounds flights, injures 3". The Straits Times. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ "Typhoon causes mudslides, blackouts". Japan Today. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ a b "浸水想定区域外14人犠牲 山あいの水流強く". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). January 11, 2017. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- ^ a b "福岡県被害1941億円 先月調査より744億円増". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). August 25, 2017. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-14T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 14, 2017.
- ^ "WebCite query result". www.webcitation.org. Archived from the original on 2017-07-14. Retrieved 2017-07-14.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Tropical Storm Talas (06W)". Reactions. 17 July 2017. Archived from the original on 17 July 2017. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- ^ "Storm Talas kills 14 in Vietnam, destroys homes". The Straits Times. 19 July 2017. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Storm-ravaged Vietnamese province closes beaches with Sonca bearing down". VN Express. July 25, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-19T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- ^ a b "Global Catastrophe Recap August 2017" (PDF). thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com. Aon Benfield. Retrieved September 7, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1706 Kulap (1706)". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 4, 2017. Archived from the original on September 4, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6s5rpCQiO?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/ABPW10-PGTW_201707200600.htm
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 09W (Kulap) Warning Nr 01". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2017. Archived from the original on July 23, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 09W (Kulap) Warning Nr 005". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2017. Archived from the original on July 22, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 09W (Kulap) Warning Nr 15". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2017. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 09W (Kulap) Warning Nr 020". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 26, 2017. Archived from the original on July 28, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1708 Sonca (1708)". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 5, 2017. Archived from the original on September 5, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 08W (Eight) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2017. Archived from the original on July 21, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 08W (Eight) Warning Nr 009". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2017. Archived from the original on July 23, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 08W (Sonca) Warning Nr 018". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 25, 2017. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017.
- ^ "VIDEO Cập nhật bão số 4: Đổ bộ vào Quảng Trị và gây mưa lớn". Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ Khouth Sophak Chakrya (27 July 2017). "Flooded areas vacated". Phnom Penh Post. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ^ "Sakon Nakhon flood damage estimated at over Bt100 million - The Nation". Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ Ltd, Australian News Channel Pty. "Thailand flash flooding kills 23". Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ a b c "Tropical Cyclone Best Track 1707 Roke (1707)". Japan Meteorological Agency. September 4, 2017. Archived from the original on September 4, 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Tropical Storm Roke Track File".
- ^ a b "WebCite query result". www.webcitation.org. Archived from the original on 2017-07-23. Retrieved 2017-07-23.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Hong Kong raises alert as Typhoon Roke approaches". Channel NewsAsia. Retrieved 2017-07-23.
- ^ "Hong Kong Raises Storm Warning as Cyclone Roke Approaches". Bloomberg.com. 2017-07-23. Retrieved 2017-07-23.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-25T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ a b "Sitrep No.06 re Southwest Monsoon Enhanced by TY "GORIO"" (PDF). NDRRMC. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Agricultural losses from Typhoon Nesat exceed NT$60 million – Focus Taiwan".
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-27T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 12W (Twelve) Warning Nr 01". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 28, 2017. Archived from the original on July 28, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 12W (Haitang) Warning Nr 05". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 29, 2017. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 12W (Haitang) Warning Nr 06". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 29, 2017. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 12W (Haitang) Warning Nr 10". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 30, 2017. Archived from the original on July 30, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 12W (Haitang) Warning Nr 011". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 30, 2017. Archived from the original on July 31, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 12W (Haitang) Warning Nr 012". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 31, 2017. Archived from the original on July 31, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6sNNNO3wi?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/ABPW10-PGTW_201707311400.htm
- ^ "Tropical Depression 13W (Thirteen) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2017. Archived from the original on August 1, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 13W (Nalgae) Warning Nr 05". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2017. Archived from the original on August 2, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 13W (Nalgae) Warning Nr 007". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2017. Archived from the original on August 2, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 13W (Nalgae) Warning Nr 019". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2017. Archived from the original on August 5, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-08-19T12:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- ^ "Weather Satellite Imagery". www.weather.gov.hk.
- ^ "TROPICAL CYCLONE WARNING". www.weather.gov.hk. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ a b "Typhoon Hato could cause HK$8 billion in losses after No 10 signal storm brought Hong Kong to standstill". South China Moring Post. August 24, 2017.
- ^ a b "Macau suffers US$1.42 billion economic loss in Typhoon Hato's wake". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 2017-09-07.
- ^ a b NAM, BAO NONG NGHIEP VIET (29 August 2017). "Bắc Kạn thiệt hại nặng do mưa bão số 6". Nongnghiep.vn. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- ^ a b web24h.vn. "Hoàn lưu bão số 7 gây thiệt hại khoảng 2 tỷ đồng". backantv.vn.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Storm Pakhar displaces 929 families in Philippines". Anadolu Agency. August 27, 2017.
- ^ http://ftp.emc.ncep.noaa.gov/wd20vxt/hwrf-init/decks/bwp172017.dat
- ^ "Tropical Depression 17W (Sanvu) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 28, 2017. Archived from the original on August 28, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon 17W (Sanvu) Warning Nr 012". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 31, 2017. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon 17W (Sanvu) Warning Nr 015". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2017. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017.
- ^ a b "'Drowning victim swimming with brother when they got swept outside reef'".
- ^ "Tropical Depression 18W (Mawar) Warning Nr 001". August 31, 2017. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 18W (Mawar) Warning Nr 10". September 1, 2017. Archived from the original on September 3, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 18W (Mawar) Warning Nr 013". September 3, 2017. Archived from the original on September 3, 2017.
- ^ a b "Mawar brings flooding to southeast China". AlJazeera. September 4, 2017.
- ^ "Blue alert issued for Typhoon Mawar". Global Times. September 1, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon Mawar – T1 warning signal issued in Hong Kong". Asia Times. September 2, 2017.
- ^ "China activates emergency response mechanism for Typhoon Mawar". Xinhua. September 2, 2017.
- ^ "China renews yellow alert for Typhoon Mawar". Xinhua. September 3, 2017.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin No.01 re Tropical Depression KIKO" (PDF). NDRRMC. September 4, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 19W (Nineteen) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 4, 2017. Archived from the original on September 5, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 19W (Nineteen) Warning Nr 002". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 5, 2017. Archived from the original on September 5, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 19W (Nineteen) Warning Nr 03". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 5, 2017. Archived from the original on September 6, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 19W (Guchol) Warning Nr 007". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2017. Archived from the original on September 6, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-09-07T12:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 20W (Twenty) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 8, 2017. Archived from the original on September 8, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Storm 20W (Talim) Warning Nr 004". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 9, 2017. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon 'Lannie' enters PAR". Inquirer. September 11, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon 20W (Talim) Warning Nr 014". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 12, 2017. Archived from the original on September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon 20W (Talim) Warning Nr 023". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 14, 2017. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017.
- ^ Lisa Twaronite; Simon Cameron-Moore (September 17, 2017). "Weaker Typhoon Talim disrupts transport in southwestern Japan". reuters.com. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Companion Volume to Weather, Climate & Catastrophe Insight" (PDF). Aon Benfield. Retrieved 30 January 2018.
- ^ a b "Summary Report on the Effects of Tropical Storm Cosme" (PDF). NDRRMC. September 19, 2017.
- ^ a b "Miền Trung thiệt hại hơn 11 nghìn tỷ đồng do bão Doksuri". VN Express. September 19, 2017.
- ^ a b "Bão số 10 làm 11 người chết, 1 người mất tích và 28 người bị thương". 16 September 2017.
- ^ a b Tư, Báo Điện tử Nhà Đầu. "Miền Trung thiệt hại hơn 16.000 tỷ đồng, nhiều gia đình vườn không nhà trống do bão số 10".
- ^ "China renews yellow alert for rainstorms". Xinhua. September 24, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon signal No 1 issued for Hong Kong as squalls expected". South China Morning Post. September 24, 2017.
- ^ "'Sudden dip in voltage' traps 17 people in Hong Kong lifts for almost an hour". South China Morning Post. September 24, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical pressure system on course to hit Vietnam's Ha Long Bay". VN Express. September 25, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-10-07T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- ^ "Death toll from worst Vietnam floods in years rises to 54". Channel News Asia. October 13, 2017.
- ^ "Floods and landslides kill 43, leave 34 missing in Vietnam". ABC News. October 12, 2017.
- ^ "Lũ dữ tàn phá miền tây Yên Bái, thiệt hại hơn 100 tỷ đồng" (in Vietnamese). Tiênphong. October 10, 2017.
- ^ "29 người thiệt mạng trong mưa lũ dồn dập" (in Vietnamese). VN Express. October 10, 2017.
- ^ VCCorp.vn. "Thủ tướng khen Ninh Bình trắng đêm canh từng cm lũ, sáng suốt chưa xả tràn".
- ^ a b "SitRep No.09 re Preparedness Measures and Effects of Tropical Storm "ODETTE"" (PDF). NDRRMC. October 20, 2017.
- ^ "Index of /tcdat/tc17/WPAC/25W.LAN/ir/geo/1km". United States Naval Research Laboratory. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 14, 2017. Archived from the original on October 14, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-10-13T18:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. October 13, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-10-14T18:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. October 14, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "WTPQ21 RJTD 150600 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 15, 2017. Archived from the original on October 15, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 25W (Twentyfive) Warning Nr 01". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 15, 2017. Archived from the original on October 15, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "WTPQ21 RJTD 151800 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 15, 2017. Archived from the original on October 15, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Lan) Warning Nr 03". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 16, 2017. Archived from the original on October 17, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #2 for Tropical Storm Paolo (Lan)". PAGASA. October 16, 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 21, 2017. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ^ http://ftp.emc.ncep.noaa.gov/wd20vxt/hwrf-init/decks/bwp262017.dat
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6uJRdQBON?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WTPN21-PGTW_201710180830.htm
- ^ "Tropical Depression 26W (Twenty-six) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 18, 2017. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 26W (Twenty-six) Warning Nr 01". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 18, 2017. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 26W (Twenty-six) Warning Nr 003". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 19, 2017. Archived from the original on October 19, 2017.
- ^ "Paolo maintains strength while LPA intensifies into tropical depression". GMA News. October 19, 2017.
- ^ "Zamboanga City in state of calamity as thousands evacuate due to Typhoon Paolo and LPA". CNN Philippines. October 19, 2017.
- ^ a b "Landslides, floods leave 14 dead in Zamboanga". Malaya. October 22, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-10-30T12:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6uhDPPetI?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WWJP25-RJTD_201711030000.htm
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6ukQtwtjp?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WTPN21-PGTW_201711050730.htm
- ^ "Tropical Depression 29W (Twenty-nine) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 6, 2017. Archived from the original on November 6, 2017.
- ^ a b "Umno man wants Penang govt to give RM2,000 to flood victims".
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-10-31T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved October 31, 2017.
- ^ "Typhoon Damrey damage: Vietnam wrecked by strongest deadly typhoon in 16 years - 106 dead". The Daily Express. 8 November 2017 – via http://www.express.co.uk.
{{cite web}}: External link in|via= - ^ Press, Associated (2017-11-04). "Typhoon Damrey hits Vietnam with deadly force". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2017-11-04.
- ^ a b "Update SitRep No.7 re Preparedness Measures and Effects of Tropical Storm SALOME" (PDF). NDRRMC. November 14, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ a b "Global Catastrophe Recap November 2017" (PDF). thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com. Aon Benfield. Retrieved December 7, 2017.
- ^ "Low from kirogi in Bay of Bengal". Hindu Business Line. November 20, 2017. Retrieved November 29, 2017.
- ^ "IMD Bulletin for Cyclone Ockhi #16". December 1, 2017. Retrieved December 1, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-12-11T18:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 12, 2017.
- ^ "SitRep_No_28_re_Preparedness_Measures_and_Effects_of_Tropical_Storm-URDUJA_KAI-TAK" (PDF). NDRRMC. February 7, 2018.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-12-16T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-12-18T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-12-20T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 20, 2017. Archived from the original on December 20, 2017. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ "SEVER WEATHER BULLETIN #1 FOR:Tropical Depression Vinta". PAGASA. December 20, 2017. Archived from the original on December 20, 2017. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ a b "Search for ferry accident survivors continues, 5 dead". ABS CBN. December 22, 2017.
- ^ a b "Death toll from Tropical Storm Vinta breaches 200". Rappler. Retrieved December 24, 2017.
- ^ a b "SitRep No.26 for Preparedness Measures and Effects of Typhoon "VINTA"" (PDF). NDRRMC. NDRRMC. Retrieved February 4, 2017.
- ^ "Digital Typhoon: List of weather charts on March 19, 2017 (Sun)". agora.ex.nii.ac.jp.
- ^ "Digital Typhoon: List of weather charts on March 21, 2017 (Tue)". agora.ex.nii.ac.jp.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-06-29T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved June 29, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6rcq7wf0F?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WWJP25-RJTD_201707010000.htm
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-04T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 4, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6rm7A74CM?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WTPN21-PGTW_201707051900.htm
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6rm7GJy1q?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WWJP25-RJTD_201707070000.htm
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-13T00:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-16T06:00:00Z « WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo". www.wis-jma.go.jp. Retrieved 2017-07-16.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-25T18:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ https://www.webcitation.org/6sIiPiGm6?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/ABPW10-PGTW_201707261400.htm
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-07-29T06:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-08-25T18:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2017-08-26T12:00:00Z". WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo. Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory TD". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 28, 2017. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory TD". Japan Meteorological Agency. August 29, 2017. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017.
- ^ "Digital Typhoon: Typhoon 201716 (MAWAR) - General Information (Pressure and Track Charts)". agora.ex.nii.ac.jp.
- ^ a b Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary December 1999". Australian Severe Weather. Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ a b The Typhoon Committee (February 21, 2013). "Typhoon Committee Operational Manual 2013" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. pp. 37–38. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ Zhou, Xiao; Lei, Xiaotu (2012). "Summary of retired typhoons within the Western North Pacific Ocean". Tropical Cyclone Research and Review. 1 (1). The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific/World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee: 23–32. doi:10.6057/2012TCRR01.03. ISSN 2225-6032. Retrieved December 21, 2014.
- ^ "Replacement Names of HAIMA, SARIKA, NOCK-TEN and MERANTI in the Tropical Cyclone Name List" (PDF). ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee. February 21, 2018.
- ^ "gulftoday.ae – Tropical Storm Talas hits Vietnam, leaves one dead". gulftoday.ae.
- ^ VnExpress. "9 dead or missing in Vietnam as infrastructure is damaged – VnExpress International".
- ^ "Tổng cục Thống kê". www.gso.gov.vn.
- ^ "Sonca storm leaves ruinous signature". 28 July 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ Limited, Bangkok Post Public Company. "Worst floods in 2 decades hit Sakon Nakhon (Updated)". Retrieved 23 August 2017.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "AHA Centre Flash Update: Flooding, Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar & Thailand". 2 August 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ "Viet Nam, The Impact of Tropical Storm "Sonca"". 31 July 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ "Thailand floods kill 23, cause damage estimated at $300 million". 3 August 2017 – via Reuters.
- ^ "Nghệ An: Bão số 4 gây thiệt hại trên 127 tỷ đồng".
- ^ Ltd, Australian News Channel Pty. "Typhoon Nesat sweeps through Taiwan". Retrieved 23 August 2017.
- ^ "Typhoons Nesat, Haitang inflict NT$176 million in damages to agriculture".
- ^ "Vientiane Times". www.vientianetimes.org.la.
- ^ a b https://www.gso.gov.vn/default.aspx?tabid=621&ItemID=18668
- ^ "Global Catastrophe Recap October 2017" (PDF). thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com. Aon Benfield. Retrieved November 9, 2017.
- ^ http://sggp.org.vn/thiet-hai-do-thien-tai-gay-ra-len-den-53200-ty-dong-485282.html
- ^ Jason De Asis (November 4, 2017). "Ramil-triggered floods damage P1-M agri crops in Baler". Philippine Canadian Inuirer.
- ^ "8 dead from latest storm". Press Reader. November 4, 2017.
- ^ http://sggp.org.vn/10-nguoi-chet-va-mat-tich-o-mien-trung-vi-mua-lu-khong-khi-lanh-484914.html
- ^ "SitRep_No_28_re_Preparedness_Measures_and_Effects_of_Tropical_Storm-URDUJA_KAI-TAK" (PDF). NDRRMC. February 7, 2018.
External links
[edit]- China Meteorological Agency
- Digital Typhoon
- Hong Kong Observatory
- Japan Meteorological Agency
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center
- Korea Meteorological Administration
- Malaysian Meteorological Department
- National Weather Service Guam
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
- Taiwan Central Weather Bureau
- TCWC Jakarta
- Thai Meteorological Department
- Typhoon2000
- Vietnam's National Hydro-Meteorological Service