User:Abyssal/Portal:Silurian
IntroductionSelected article on the Silurian world and its legacies
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata which is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals but others replicate by budding and become colonies, each unit being known as a zooid. They are marine filter feeders with a water-filled, sac-like body structure and two tubular openings, known as siphons, through which they draw in and expel water. During their respiration and feeding they take in water through the incurrent (or inhalant) siphon and expel the filtered water through the excurrent (or exhalant) siphon. Most adult tunicates are sessile and are permanently attached to rocks or other hard surfaces on the ocean floor; others such as salps, doliolids and pyrosomes swim in the pelagic zone of the sea as adults. Various species are commonly known as sea squirts, sea pork, sea liver or sea tulips.
The Tunicata first appear in the fossil record in the early Cambrian period. Despite their simple appearance and very different adult form, their close relationship to the vertebrates is shown by the fact that during their mobile larval stage, they possess a notochord or stiffening rod and resemble a tadpole. Their name derives from their unique outer covering or "tunic" which is formed from proteins and carbohydrates and acts as an exoskeleton. In some species it is thin, translucent and gelatinous while in others it is thick, tough and stiff. (see more...) Selected article on the Silurian in human science, culture and economics
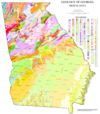
The geologic map of Georgia (a state within the United States) is a special-purpose map made to show geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by colors or symbols to indicate where they are exposed at the surface. Structural features such as faults and shear zones are also shown. Since the first national geological map, in 1809, there have been numerous maps which included the geology of Georgia. The first Georgia specific geologic map was created in 1825. The most recent state-produced geologic map of Georgia, by the Georgia Department of Natural Resources is 1:500,000 scale, and was created in 1976 by the department's Georgia Geological Survey. It was generated from a base map produced by the United States Geological Survey. The state geologist and Director of the Geological Survey of Georgia was Sam M. Pickering, Jr. Since 1976, several geological maps of Georgia, featuring the state's five distinct geologic regions, have been produced by the federal government. (see more...)
Selected image
Did you know?
Need help?Do you have a question about Abyssal/Portal:Silurian that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk. GeochronologyEpochs - Llandovery - Wenlock - Ludlow - Pridoli Plants - Lycopods - Rhyniophytes - Vascular plants Fossil sites - Yea Flora Fossil Site Researchers - Increase A. Lapham - Roderick Murchison Quality ContentFeatured Silurian articles - Fungus SubcategoriesRelated contentAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
|