User:A.h. king/Sandbox2
Template:Featured article is only for Wikipedia:Featured articles.
Рэспубліка Беларусь Республика Беларусь Republic of Belarus | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Мы, беларусы (Belarusian) My, Belarusy (transliteration) We Belarusians | |
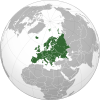
![Location of A.h. king/Sandbox2 (green) in Europe (dark grey) – [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/Location_Belarus_Europe.png/250px-Location_Belarus_Europe.png) | |
| Capital and largest city | Minsk 53°55′N 27°33′E / 53.917°N 27.550°E |
| Official languages | Belarusian, Russian |
| Demonym(s) | Belarusian |
| Government | Presidential republic |
| Alexander Lukashenko | |
| Sergey Sidorsky | |
| Independence from the Soviet Union | |
• Declared | 27 July 1990 |
• Established | 25 August 1991 |
• Completed | 25 December 1991 |
| Area | |
• Total | 207,600 km2 (80,200 sq mi) (85th) |
• Water (%) | negligible (2.830 km²)1 |
| Population | |
• 2008 estimate | 9,689,800[1] (86th) |
• 1999 census | 10,045,200 |
• Density | 46.7/km2 (121.0/sq mi) (142nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
• Total | $119.096 billion[2] (58th) |
• Per capita | $12,313[2] (65th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
• Total | $60.302 billion[2] |
• Per capita | $6,234[2] |
| Gini (2002) | 29.7 low inequality |
| HDI (2006) | Error: Invalid HDI value (67th) |
| Currency | Belarusian ruble (BYR) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | 375 |
| ISO 3166 code | BY |
| Internet TLD | .by |
| |
Belarus (Belarusian: Беларусь, Russian: Беларусь or Белоруссия) is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe,[3] bordered by Russia to the north and east, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the north. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno (Hrodna), Gomel (Homiel), Mahilyow (Mahiloŭ) and Vitebsk (Viciebsk). Forty percent of the country is forested,[4] and its strongest economic sectors are agriculture and manufacturing.
Until the 20th century, the Belarusians lacked the opportunity to create a distinctive national identity because for centuries the lands of modern-day Belarus belonged to several ethnically different countries, including the Duchy of Polatsk, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the short-lived Belarusian People's Republic (1918–19), Belarus became a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, the Byelorussian SSR.
The final unification of Belarusian lands within its modern borders took place in 1939, when the ethnically Belarusian-Russian lands held by the Second Polish Republic (interwar Poland) were annexed into the USSR under the terms of the Nazi-Soviet pact,[5] and attached to Soviet Belarus. The territory and its nation were devastated in World War II, during which Belarus lost about a third of its population and more than half of its economic resources;[6] the republic was redeveloped in the post-war years. The parliament of the republic declared the sovereignty of Belarus on 27 July 1990, and following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Belarus declared independence on 25 August 1991. Alexander Lukashenko has been the country's president since 1994. During his presidency, Lukashenko has implemented Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership of the economy, despite objections from Western governments. Since 2000, Belarus and Russia signed a treaty for greater cooperation, with some hints of forming a Union State.
Most of Belarus's population of 9.85 million reside in the urban areas surrounding Minsk and other oblast (regional) capitals.[7] More than 80% of the population are native Belarusians, with sizable minorities of Russians, Poles and Ukrainians. Since a referendum in 1995, the country has had two official languages: Belarusian and Russian. The Constitution of Belarus does not declare an official religion, although the primary religion in the country is Russian Orthodox Christianity and the second most popular is Roman Catholicism. Both Orthodox and Catholic Christmas and Easter are officially respected as national holidays.
Etymology
[edit]The name Belarus derives from the term White Rus, which first appeared in German and Latin medieval literature. The Latin term for the area was Alba Ruthenia. Historically, the country was referred to in English as White Ruthenia. It is also claimed by some people[who?] that it describes the area of Eastern Europe populated by Slavic people or the states that occupied the area.[8] The first known use of White Russia to refer to Belarus was in the late-16th century by Englishman Sir Jerome Horsey.[9] During the 17th century, Russian tsars used White Rus', asserting that they were trying to recapture their heritage from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.[9]
Belarus was named Belorussia (Russian: Белоруссия) in the days of Imperial Russia, and the Russian tsar was usually styled Tsar of All the Russias—Great, Little, and White. Belorussia was the only Russian language name of the country (its names in other languages such as English being based on the Russian form) until 1991, when the Supreme Soviet of the Belorussian Soviet Socialist Republic decreed by law that the new independent republic should be called Belarus (Беларусь) in Russian and in all other language transcriptions of its name. The change was made to reflect adequately the Belarusian language form of the name.[10] Accordingly, the name Belorussia was replaced by Belarus in English, and, to some extent, in Russian (although the traditional name still persists in that language as well); likewise, the adjective Belorussian or Byelorussian was replaced by Belarusian in English (though Russian has not developed a new adjective). Some Belarusians object to the name Belorussia as an unwelcome reminder of the days under Russian and Soviet rule.[11] However, several popular newspapers published locally still retain the old name of the country in Russian in their names, for example Komsomolskaya Pravda v Byelorussii, which is the localised publication of a popular Russian tabloid. Officially, the full name of the country is Republic of Belarus (Рэспубліка Беларусь, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Byelarus').[12]
History
[edit]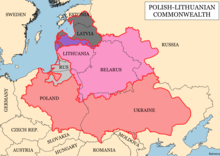
The region that is now modern-day Belarus was first settled by Slavic tribes in the 6th century. They gradually came into contact with the Varangians, a band of warriors consisting of Scandinavians and Slavs from the Baltics.[13] Though defeated and briefly exiled by the local population, the Varangians were later asked to return[13] and helped to form a polity—commonly referred to as the Kievan Rus'—in exchange for tribute. The Kievan Rus' state began in about 862 at the present-day city of Novgorod,[14] or alternatively at Kiev.[14]
Upon the death of Kievan Rus' ruler, Prince Yaroslav the Wise, the state split into independent principalities.[15] These Ruthenian principalities were badly affected by a Mongol invasion in the 13th century, and many were later incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.[16] Of the principalities held by the Duchy, nine were settled by ancestors of the Belarusian people.[17] During this time, the Duchy was involved in several military campaigns, including fighting on the side of Poland against the Teutonic Knights at the Battle of Grunwald in 1410; the joint victory allowed the Duchy to control the northwestern border lands of Eastern Europe.[18]
On 2 February 1386, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland were joined in a personal union through a marriage of their rulers.[19] This union set in motion the developments that eventually resulted in the formation of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, created in 1569. The Russians, led by Tsar Ivan the III, began military conquests in 1486 in an attempt to reunite the Kievan Rus' lands, specifically the missing Belarus and Ukraine.[20] The union between Poland and Lithuania ended in 1795, and the commonwealth was partitioned by Imperial Russia, Prussia, and Austria, dividing Belarus.[21] Belarusian territories were acquired by the Russian Empire during the reign of Catherine II[22] and held until their occupation by Germany during World War I.[23]

During the negotiations of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, Belarus first declared independence on 25 March 1918, forming the Belarusian People's Republic. The Germans supported the BPR, which lasted for about ten months.[24] Soon after the Germans were defeated, the BPR fell under the influence of the Bolsheviks and the Red Army and became the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1919.[24] After Russian occupation of eastern and northern Lithuania, it was merged into the Lithuanian-Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. Byelorussian lands were then split between Poland and the Soviets after the Polish-Soviet War ended in 1921, and the recreated Byelorussian SSR became a founding member of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922.[24] At the same time Western Belarus remained occupied by Poland.[25][26][26]
A set of agricultural reforms, culminating in the Belarusian phase of Soviet collectivization, began in the 1920s. A process of rapid industrialization was undertaken during the 1930s, following the model of Soviet five-year plans.
In 1939, West Belarus, the territory of modern Belarus that Poland had acquired from the Soviets pursuant to Treaty of Riga two decades earlier, was reunited with Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic.[27][28][29][30][31][32] The area was a part of the territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union as a result of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact and Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939.[33] The decision was made by the Soviet controlled Belarusian People Council on October 28, 1939 in Bialystok[32]
Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941 – the Fortress of Brest in western Belarus receiving one of the fiercest of the war's opening blows, with its notable defense in 1941 coming to be remembered as an act of heroism in countering the German aggression. Statistically, Byelorussia was the hardest hit Soviet Republic in the war and remained in Nazi hands until 1944. During that time, Germany destroyed 209 out of 290 cities in the republic, 85% of the republic's industry, and more than one million buildings.[6] Casualties were estimated to between two and three million (about a quarter to one-third of the total population), while the Jewish population of Byelorussia was devastated during The Holocaust and never recovered.[6][34] The population of Belarus did not regain its pre-war level until 1971.[34] After the war ended, Byelorussia was officially among the 51 founding countries of the United Nations Charter in 1945. Intense post-war reconstruction was initiated promptly. During this time, the Byelorussian SSR became a major center of manufacturing in the western region of the USSR, increasing jobs and bringing an influx of ethnic Russians into the republic.[35] The borders of Byelorussian SSR and Poland were redrawn to a point known as the Curzon Line.[33]
Joseph Stalin implemented a policy of Sovietization to isolate the Byelorussian SSR from Western influences.[34] This policy involved sending Russians from various parts of the Soviet Union and placing them in key positions in the Byelorussian SSR government. The official use of the Belarusian language and other cultural aspects were limited by Moscow. After Stalin died in 1953, successor Nikita Khrushchev continued this program, stating, "The sooner we all start speaking Russian, the faster we shall build communism."[34] The Byelorussian SSR was significantly exposed to nuclear fallout from the explosion at the Chernobyl power plant in neighboring Ukrainian SSR in 1986.[36] In June 1988 at the rural site of Kurapaty near Minsk, archaeologist Zianon Pazniak, the leader of Christian Conservative Party of the BPF, discovered mass graves which contained about 250,000 bodies of victims executed in 1937-1941.[36] Some nationalists contend that this discovery is proof that the Soviet government was trying to erase the Belarusian people, causing Belarusian nationalists to seek independence.[37]
Two years later, in March 1990, elections for seats in the Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR took place. Though the pro-independence Belarusian Popular Front took only 10% of the seats, the populace was content with the selection of the delegates.[38] Belarus declared itself sovereign on 27 July 1990, by issuing the Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic. With the support of the Communist Party, the country's name was changed to the Republic of Belarus on 25 August 1991.[38] Stanislav Shushkevich, the Chairman of the Supreme Soviet of Belarus, met with Boris Yeltsin of Russia and Leonid Kravchuk of Ukraine on 8 December 1991, in Belavezhskaya Pushcha to formally declare the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States.[38] A national constitution was adopted in March 1994, in which the functions of prime minister were given to the president.
Two-round elections for the presidency (24 June 1994 and 10 July 1994)[39] resulted in the politically unknown Alexander Lukashenko winning more than 45% of the vote in the first round and 80%[38] in the second round, beating Vyacheslav Kebich who got 14%. Lukashenko was reelected in 2001 and in 2006.
Politics
[edit]
Belarus is a presidential republic, governed by a president and the National Assembly. In accordance with the constitution, the president is elected once every five years. The National Assembly is a bicameral parliament comprising the 110-member House of Representatives (the lower house) and the 64-member Council of the Republic (the upper house). The House of Representatives has the power to appoint the prime minister, make constitutional amendments, call for a vote of confidence on the prime minister, and make suggestions on foreign and domestic policy. The Council of the Republic has the power to select various government officials, conduct an impeachment trial of the president, and accept or reject the bills passed by the House of Representatives. Each chamber has the ability to veto any law passed by local officials if it is contrary to the Constitution of Belarus.[40] Since 1994, Alexander Lukashenko has been the president of Belarus. The government includes a Council of Ministers, headed by the prime minister. The members of this council need not be members of the legislature and are appointed by the president. The judiciary comprises the Supreme Court and specialized courts such as the Constitutional Court, which deals with specific issues related to constitutional and business law. The judges of national courts are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Council of the Republic. For criminal cases, the highest court of appeal is the Supreme Court. The Belarusian Constitution forbids the use of special extrajudicial courts.[40]
As of 2007, 98 of the 110 members of the House of Representatives are not affiliated with any political party and of the remaining twelve members, eight belong to the Communist Party of Belarus, three to the Agrarian Party of Belarus, and one to the Liberal Democratic Party of Belarus. Most of the non-partisans represent a wide scope of social organizations such as workers' collectives, public associations and civil society organizations. Neither the pro-Lukashenko parties, such as the Belarusian Socialist Sporting Party and the Republican Party of Labor and Justice, nor the People's Coalition 5 Plus opposition parties, such as the Belarusian People's Front and the United Civil Party of Belarus, won any seats in the 2004 elections. Groups such as the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) declared the election "un-free" because of the opposition parties' poor results and media bias in favor of the government.[41] In the country's 2006 presidential election, Lukashenko was opposed by Alaksandar Milinkievič, a candidate representing a coalition of opposition parties, and by Alaksandar Kazulin of the Social Democrats. Kazulin was detained and beaten by police during protests surrounding the All Belarusian People's Assembly. Lukashenko won the election with 80% of the vote, but the OSCE and other organizations called the election unfair.[42]
Lukashenko has described himself as having an "authoritarian ruling style."[43] Western countries have described Belarus under Lukashenko as a dictatorship; the government has accused the same Western powers of trying to oust Lukashenko.[44] The Council of Europe has barred Belarus from membership since 1997 for undemocratic voting and election irregularities in the November 1996 constitutional referendum and parliament by-elections.[45] The Belarusian government is also criticized for human rights violations and its actions against non-governmental organizations, independent journalists, national minorities, and opposition politicians.[46][47] Belarus is the only nation in Europe that retains the death penalty for certain crimes during times of peace and war.[48] As noted, Lukashenko has even gone as far as changing the country's constitution to allow him to remain in office for an unlimited amount of time after each election. In testimony to the U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations, United States Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice labeled Belarus among the six nations of the "outposts of tyranny."[49] In response, the Belarusian government called the assessment "quite far from reality."[50]
Foreign relations and military
[edit]
Belarus and Russia have been close trading partners and diplomatic allies since the breakup of the Soviet Union. Belarus is dependent on Russia for imports of raw materials and for its export market.[51] The Union of Russia and Belarus, a supranational confederation, was established in a 1996–99 series of treaties that called for monetary union, equal rights, single citizenship, and a common foreign and defense policy.[51] Although the future of the Union was in doubt because of Belarus's repeated delays of monetary union, the lack of a referendum date for the draft constitution, and a 2006–07 dispute about petroleum trade.[51] On 11 December 2007, reports emerged that a framework for the new state was discussed between both countries.[52] On 27 May 2008, Belarusian President Lukashenko said that he had named Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin the "prime minister" of the Russia-Belarus alliance. The meaning of the move was not immediately clear; however, there was speculation that Putin might become President of a unified state of Russia and Belarus after stepping down as Russian president in May 2008, although this has not happened.[53]
Belarus was a founding member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS); however, recently other CIS members have questioned the effectiveness of the organization.[54] Belarus has trade agreements with several European Union member states (despite other member states' travel ban on Lukashenko and top officials),[55] as well as with its neighbors Lithuania, Poland and Latvia (all of whom are EU members).[56]
Bilateral relations with the United States are strained because the U.S. Department of State supports various pro-democracy NGOs and because the Belarusian government has made it harder for US-based organizations to operate within the country.[57] The 2004 US Belarus Democracy Act continued this trend, authorizing funding for pro-democracy Belarusian NGOs and forbidding loans to the Belarusian government except for humanitarian purposes.[58] Despite this, the two nations cooperate on intellectual property protection, prevention of human trafficking and technology crime, and disaster relief.[59]
Belarus has increased cooperation with China, strengthened by the visit of President Lukashenko to China in October 2005.[60] Belarus has strong ties with Syria,[61] which President Lukashenko considers a key partner in the Middle East.[62] In addition to the CIS, Belarus has membership in the Eurasian Economic Community and the Collective Security Treaty Organization.[56] Belarus has been a member of the international Non-Aligned Movement since 1998[63] and a member of the United Nations since its founding in 1945.[64]
The Armed Forces of Belarus have three branches: the Army, the Air Force, and the Ministry of Defense joint staff. Colonel-General Leonid Maltsev heads the Ministry of Defense,[65] and Alexander Lukashenko (as president) serves as Commander-in-Chief.[66] The Armed Forces were formed in 1992 using parts of the former Soviet Armed Forces on the new republic's territory. The transformation of the ex-Soviet forces into the Armed Forces of Belarus, which was completed in 1997, reduced the number of its soldiers by 30,000 and restructured its leadership and military formations.[67] Most of Belarus's service members are conscripts, who serve for 12 months if they have higher education or 18 months if they do not.[68] However, demographic decreases in the Belarusians of conscription age have increased the importance of contract soldiers, who numbered 12,000 as of 2001.[69] In 2005, about 1.4% of Belarus's gross domestic product was devoted to military expenditures.[70] Belarus has not expressed a desire to join NATO but has participated in the Individual Partnership Program since 1997.[71]
Provinces and districts
[edit]
Belarus is divided into six voblasts (vobłaść), or provinces, which are named after the cities that serve as their administrative centers.[72] Each voblast has a provincial legislative authority, called an oblsovet (oblast council), which is elected by the voblast's residents, and a provincial executive authority called a voblast administration, whose leader is appointed by the president.[73] Voblasts are further subdivided into raions (commonly translated as districts or regions).[72] As with voblasts, each raion has its own legislative authority (raisovet, or raion council) elected by its residents, and an executive authority (raion administration) appointed by higher executive powers. As of 2002, there are six voblasts, 118 raions, 102 towns and 108 urbanized settlements.[74] Minsk is given a special status, due to the city serving as the national capital. Minsk City is run by an executive committee and granted a charter of self-rule by the national government.[75]
Voblasts (with administrative centers):
- Brest Voblast (Brest)
- Gomel Voblast (Gomel)
- Grodno Voblast (Grodno)
- Mogilev Voblast (Mogilev)
- Minsk Voblast (Minsk)
- Vitebsk Voblast (Vitebsk)
Special administrative district:
Geography
[edit]
Belarus is landlocked, relatively flat, and contains large tracts of marshy land.[76] According to a 2005 estimate by the United Nations, 40% of Belarus is covered by forests.[77] Many streams and 11,000 lakes are found in Belarus.[76] Three major rivers run through the country: the Neman, the Pripyat, and the Dnepr. The Neman flows westward towards the Baltic sea and the Pripyat flows eastward to the Dnepr; the Dnepr flows southward towards the Black Sea.[78] Belarus's highest point is Dzyarzhynskaya Hara (Dzyarzhynsk Hill) at 345 metres (1,132 ft), and its lowest point is on the Neman River at 90 metres (295 ft).[76] The average elevation of Belarus is 525 feet (160 m) above sea level.[79] The climate ranges from harsh winters, with average January temperatures at −6 °C (21.2 °F), to cool and moist summers with an average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F).[80] Belarus has an average annual rainfall of 550 to 700 mm (21.7 to 27.6 in).[80] The country experiences a yearly transition from a continental climate to a maritime climate.[76]

Belarus's natural resources include peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomite (limestone), marl, chalk, sand, gravel, and clay.[76] About 70% of the radiation from neighboring Ukraine's 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster entered Belarusian territory, and as of 2005 about a fifth of Belarusian land (principally farmland and forests in the southeastern provinces) continues to be affected by radiation fallout.[81] The United Nations and other agencies have aimed to reduce the level of radiation in affected areas, especially through the use of caesium binders and rapeseed cultivation, which are meant to decrease soil levels of caesium-137.[82][83]
Belarus is bordered by Latvia on the north, Lithuania to the northwest, Poland to the west, Russia to the north and east and Ukraine to the south. Treaties in 1995 and 1996 demarcated Belarus's borders with Latvia and Lithuania, but Belarus failed to ratify a 1997 treaty establishing the Belarus-Ukraine border.[84] Belarus and Lithuania ratified final border demarcation documents in February 2007.[85]
Economy
[edit]
Most of the Belarusian economy remains state-controlled,[51] and has been described as "Soviet-style."[86] Thus, 51.2% of Belarusians are employed by state-controlled companies, 47.4% are employed by private Belarusian companies (of which 5.7% are partially foreign-owned), and 1.4% are employed by foreign companies.[87] The country relies on imports such as oil from Russia.[88][89] Important agricultural products include potatoes and cattle byproducts, including meat.[90] As of 1994, the biggest exports from Belarus were heavy machinery (especially tractors), agricultural products, and energy products.[91]

Historically important branches of industry include textiles and wood processing.[92] As of the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union, Belarus was one of the world's most industrially developed states by percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) as well as the richest CIS state.[93] Economically, Belarus involved itself in the CIS, Eurasian Economic Community, and Union with Russia. During the 1990s, however, industrial production plunged because of decreases in imported inputs, in investment, and in demand for exports from traditional trading partners.[94] It took until 1996 for the gross domestic product to rise;[95] this coincided with the government putting more emphasis on using the GDP for social welfare and state subsidies.[95] The GDP for 2006 was US$83.1 billion in purchasing power parity (PPP) dollars (estimate), or about $8,100 per capita.[90] In 2005, the gross domestic product increased by about 9.9%, with the inflation rate averaging about 9.5%.[90]
Belarus's largest trading partner is Russia, accounting for nearly half of total trade in 2006.[96] As of 2006, the European Union is Belarus's next largest trading partner, with nearly a third of foreign trade.[96][97] Because of its failure to protect labor rights, however, Belarus lost its E.U. Generalized System of Preferences status on 21 June 2007, which raised tariff rates to their prior most-favored nation levels.[97] Belarus applied to become a member of the World Trade Organization in 1993.[98]

The labor force consists of more than four million people, among whom women hold slightly more jobs than men.[99] In 2005, nearly a quarter of the population was employed by industrial factories.[99] Employment is also high in agriculture, manufacturing sales, trading goods, and education. The unemployment rate, according to Belarusian government statistics, was about 1.5% in 2005.[99] The number of unemployed persons totaled 679,000 of whom about two-thirds are women.[99] The rate of unemployment has been decreasing since 2003, and the overall rate is the highest since statistics were first compiled in 1995.[99]
The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble (BYR). The currency was introduced in May 1992, replacing the Soviet ruble. The ruble was reintroduced with new values in 2000 and has been in use ever since.[100] As part of the Union of Russia and Belarus, both states have discussed using a single currency along the same lines as the Euro. This has led to the proposal that the Belarusian ruble be discontinued in favor of the Russian ruble (RUB), starting as early as 1 January 2008. As of August 2007, the National Bank of Belarus is no longer pegging the Belarusian ruble to the Russian ruble.[101] The banking system of Belarus is composed of 30 state-owned banks and one privatized bank.[102]
Demographics
[edit]
Ethnic Belarusians constitute 81.2% of Belarus's total population.[103] The next largest ethnic groups are Russians (11.4%), Poles (3.9%), and Ukrainians (2.4%).[103] Belarus's two official languages are Russian and Belarusian;[104] Russian is the main language, used by 72% of the population, while Belarusian, the second official language, is only used by 19.2%.[105] Minorities also speak Polish, Ukrainian and Eastern Yiddish.[106]
Belarus has a population density of about 50 people per square kilometre (127 per sq mi); 71.7% of its total population is concentrated in urban areas.[103] Minsk, the nation's capital and largest city, is home to 1,741,400 of Belarus's 9,724,700 residents.[103] Gomel, with 481,000 people, is the second largest city and serves as the capital of the Homel Oblast. Other large cities are Mogilev (365,100), Vitebsk (342,400), Hrodna (314,800) and Brest (298,300).[107]
Like many other European countries, Belarus has a negative population growth rate and a negative natural growth rate. In 2007, Belarus's population declined by 0.41% and its fertility rate was 1.22,[103] well below the replacement rate. Its net migration rate is +0.38 per 1,000, indicating that Belarus experiences slightly more immigration than emigration.[103] As of 2007, 69.7% of Belarus's population is aged 14 to 64; 16% is under 14, and 14.6% is 65 or older.[103] Its population is also aging: while the current median age is 37,[103] it is estimated that Belarusians' median age will be 51 in 2050.[108] There are about 0.88 males per female in Belarus.[103] The average life expectancy is 68.7 years (63.0 years for males and 74.9 years for females).[103] Over 99% of Belarusians are literate.[103][109]

Belarus has historically leaned to different religions, mostly Russian Orthodox (in eastern regions), Catholicism (in western regions), different denominations of Protestantism (especially during the time of union with Protestant Sweden). Sizable minorities practice Judaism and other religions. Many Belarusians converted to the Russian Orthodox Church after Belarus was annexed by Russia after the partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. As a consequence, now Russian Orthodox church has more members than other denominations. Belarus's Roman Catholic minority, which makes up perhaps 10% of the country's population and is concentrated in the western part of the country, especially around Hrodna, is made up of a mixture of Belarusians and the country's Polish and Lithuanian minorities. About 1% belong to the Belarusian Greek Catholic Church.[110] Belarus was a major center of the European Jewish population, with 10% being Jewish, but the population of Jews has been reduced by war, starvation, and the Holocaust to a tiny minority of about 1% or less. Emigration from Belarus is a cause for the shrinking number of Jewish residents.[111] The Lipka Tatars numbering over 15,000 are Muslims. According to Article 16 of the Constitution, Belarus has no official religion. While the freedom of worship is granted in the same article, religious organizations that are deemed harmful to the government or social order of the country can be prohibited.[112]
Culture
[edit]
Literature
[edit]Belarusian literature began with 11th- to 13th century religious writing; the 12th century poetry of Cyril of Turaw is representative.[113] By the 16th century, Polotsk resident Francysk Skaryna translated the Bible into Belarusian. It was published in Prague and Vilnius between 1517 and 1525, making it the first book printed in Belarus or anywhere in Eastern Europe.[114] The modern period of Belarusian literature began in the late 19th century; one important writer was Yanka Kupala. Many notable Belarusian writers of the time, such as Uładzimir Žyłka, Kazimir Svayak, Yakub Kolas, Źmitrok Biadula and Maksim Haretski, wrote for a Belarusian language paper called Nasha Niva, published in Vilnius. After Belarus was incorporated into the Soviet Union, the Soviet government took control of the Republic's cultural affairs. The free development of literature occurred only in Polish-held territory until Soviet occupation in 1939.[114] Several poets and authors went into exile after the Nazi occupation of Belarus, not to return until the 1960s.[114] The last major revival of Belarusian literature occurred in the 1960s with novels published by Vasil Bykaŭ and Uładzimir Karatkievič.
Music
[edit]In the 17th century, Polish composer Stanislaw Moniuszko composed operas and chamber music pieces while living in Minsk. During his stay, he worked with Belarusian poet Vincent Dunin-Marcinkevich and created the opera Sielanka (Peasant Woman). At the end of the 19th century, major Belarusian cities formed their own opera and ballet companies. The ballet Nightingale by M. Kroshner was composed during the Soviet era and became the first Belarusian ballet showcased at the National Academic Bolshoi Ballet Theatre in Minsk.[115] After the Great Patriotic War, music focused on the hardships of the Belarusian people or on those who took up arms in defense of the homeland. During this period, A. Bogatyryov, creator of the opera In Polesye Virgin Forest, served as the "tutor" of Belarusian composers.[116] The National Academic Theatre of Ballet, in Minsk, was awarded the Benois de la Dance Prize in 1996 as the top ballet company in the world.[116] Although rock music has risen in popularity in recent years, the Belarusian government has suppressed the development of popular music through various legal and economic mechanisms.[117] Since 2004, Belarus has been sending artists to the Eurovision Song Contest.[118]
Performances
[edit]
The Belarusian government sponsors annual cultural festivals such as the Slavianski Bazaar in Vitebsk, which showcases Belarusian performers, artists, writers, musicians, and actors. Several state holidays, such as Independence Day and Victory Day, draw big crowds and often include displays such as fireworks and military parades, especially in Vitebsk and Minsk.[119] The government's Ministry of Culture finances events promoting Belarusian arts and culture both inside and outside the country.
Dress
[edit]The traditional Belarusian dress originates from the Kievan Rus' period. Because of the cool climate, clothes, usually composed of flax or wool, were designed to keep the body warm. They are decorated with ornate patterns influenced by the neighboring cultures: Poles, Lithuanians, Latvians, Russians, and other European nations. Each region of Belarus has developed specific design patterns.[120] An ornamental pattern used on some early dresses is currently used to decorate the hoist of the Belarusian national flag, adopted in a disputed referendum in 1995.[121]
Cuisine
[edit]
Belarusian cuisine consists mainly of vegetables, meat (especially pork), and breads. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. A typical Belarusian eats a very light breakfast and two hearty meals, with dinner being the largest meal of the day. Wheat and rye breads are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. To show hospitality, a host traditionally presents an offering of bread and salt when greeting a guest or visitor.[122] Popular drinks in Belarus include Russian wheat vodka and kvass, a soft drink made from malted brown bread or rye flour. Kvass may also be combined with sliced vegetables to create a cold soup called okroshka.[123]
Heritage Sights
[edit]Belarus has four World Heritage Sites: the Mir Castle Complex, the Niasvizh Castle, the Belovezhskaya Pushcha (shared with Poland), and the Struve Geodetic Arc (shared with nine other countries).[124]
TV and Broadcasting
[edit]
The largest media holding group in Belarus is the state-owned National State Teleradiocompany. It operates several television and radio stations that broadcast content domestically and internationally, either through traditional signals or the Internet.[125] The Television Broadcasting Network is one of the major independent television stations in Belarus, mostly showing regional programming. Several newspapers, printed either in Belarusian or Russian, provide general information or special interest content, such as business, politics or sports. In 1998, there were fewer than 100 radio stations in Belarus: 28 AM, 37 FM and 11 shortwave stations.[126]

All media companies are regulated by the Law On Press and Other Mass Media, passed on 13 January 1995.[127] This grants the freedom of press; however, Article 5 states that slander cannot be made against the president of Belarus or other officials outlined in the national constitution.[127] The Belarusian Government has since been criticized for acting against media outlets. Newspapers such as Nasa Niva and the Belaruskaya Delovaya Gazeta have been targeted for closure by the authorities after they published reports critical of President Lukashenko or other government officials.[128][129] The OSCE and Freedom House have commented regarding the loss of press freedom in Belarus. In 2005, Freedom House gave Belarus a score of 6.75 (not free) when it came to dealing with press freedom. Another issue for the Belarusian press is the unresolved disappearance of several journalists.[130]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ The Ministry of Statistics and Analysis of the Republic of Belarus
- ^ a b c d "Belarus". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- ^ UN Statistics Division (2007-08-28). "Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". United Nations Organization. Retrieved 2007-12-07.
- ^ "Belarus: Window of Opportunity (see Table 15, page 66)" (PDF). United Nations.
- ^ Europa Publications Limited, "Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States, Volume 4", Routledge, 1999, pg. 182, [1]
- ^ a b c Axell, Albert (2002). Russia's Heroes, 1941–45. Carroll & Graf Publishers. p. 247. ISBN 078671011X.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "About Belarus - Population". United Nations Office in Belarus. 2003. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ^ Bielawa, Matthew (2002). "An Understanding of the Terms 'Ruthenia' and 'Ruthenians". Genealogy of Halychyna/Eastern Galicia. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
- ^ a b Bely, Alies' (2000). The chronicle of the White Russia: an essay on the history of one geographical name. Minsk, Belarus: Encyclopedix. ISBN 985-6599-12-1.
- ^ "Law of the Republic of Belarus - About the name of the Republic of Belarus" (in Russian). Pravo - Law of the Republic of Belarus. 1991-09-19. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ Katkouski, Uladzimir (2003-02-03). "Belarus: Belarusian and Belarusan the correct adjective forms". Pravapis.org. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ^ "Belarus - Government". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2007-12-13. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ a b Rambaud, Alfred (1902). Russia. P. F. Collier & Son. pp. 46–48.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Treuttel (1841). The Foreign Quarterly Review. New York, New York: Jemia Mason. p. 38.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Plokhy, Serhii (2006). The Origins of the Slavic Nations. Cambridge University Press. pp. 94–95. ISBN 0521864038.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Robinson, Charles Henry (1917). The Conversion of Europe. Longmans, Green. pp. 491–492.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Zaprudnik, Jan (1993). Belarus: At a Crossroads in History. Westview Press. p. 27. ISBN 0813317940.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Lerski, George Jan (1996). Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966–1945. Greenwood Press. pp. 181–182. ISBN 0313260079.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Edited by Michael Jones (2005). The New Cambridge Medieval History (Vol.6). Cambridge University Press. p. 710. ISBN 0521362903.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Nowak, Andrzej (1997-01-01). "The Russo-Polish Historical Confrontation". Sarmatian Review XVII. Rice University. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ Scheuch, E. K. (2000). Societies, Corporations and the Nation State. BRILL. p. 187. ISBN 9004116648.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Birgerson, Susanne Michele (2002). After the Breakup of a Multi-Ethnic Empire. Praeger/Greenwood. p. 101. ISBN 0275969657.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Olson, James Stuart (1994). Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. Greenwood Press. p. 95. ISBN 0313274975.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c (Birgerson 2002:105–106)
- ^ Sorge, Arndt (2005). The global and the local: understanding the dialectics of business systems. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- ^ a b Minahan, James (1998). Miniature empires: a historical dictionary of the newly independent states. Greenwood Press. Retrieved 2009-11-10. Cite error: The named reference "ocu2" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Abdelal, Rawi (2001). National purpose in the world economy: post-Soviet states in comparative perspective. Cornell University Press. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- ^ Taylor & Francis Group (2004). Europa World Year, Book1. Europa publications. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- ^ Клоков В. Я. Великий освободительный поход Красной Армии.(Освобождение Западной Украины и Западной Белоруссии). -Воронеж, 1940.
- ^ Минаев В. Западная Белоруссия и Западная Украина под гнетом панской Польши. — М., 1939.
- ^ Трайнин И.Национальное и социальное освобождение Западной Украины и Западной Белоруссии. — М., 1939. — 80 с.
- ^ a b Гiсторыя Беларусi. Том пяты. — Мiнск, 2006. — с. 449-474
- ^ a b (Olson 1994:95)
- ^ a b c d Fedor, Helen (1995). "Belarus - Stalin and Russification". Belarus: A Country Study. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "Belarus History and Culture". iExplore.com. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ a b Fedor, Helen (1995). "Belarus- Perestroika". Belarus: A Country Study. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-03-26.
- ^ {Birgerson 2002:99)
- ^ a b c d Fedor, Helen (1995). "Belarus - Prelude to Independence". Belarus: A Country Study. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-22. Cite error: The named reference "byind" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "World Factbook: Belarus" (TXT). Central Intelligence Agency. 1994-10-20. Retrieved 2007-12-21.
- ^ a b "Section IV:The President, Parliament, Government, the Courts". Constitution of Belarus. Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus. 2004. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "OSCE Report on the October 2004 parliamentary elections" (PDF). Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. 2004. Retrieved 2007-03-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Belarus rally marred by arrests". BBC News. March 2, 2006. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "Profile: Alexander Lukashenko". BBC News. March 20, 2006. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ Mulvey, Stephen (2001-09-10). "Profile: Europe's last dictator?". BBC News. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2007-12-21.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Belarus suspended from the Council of Europe". Press Service of the Council of Europe. January 17, 1997. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "Essential Background - Belarus". Human Rights Watch. 2005. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "Human rights by country - Belarus". Amnesty International Report 2007. Amnesty International. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Capital Punishment in Belarus and Changes of Belarus Criminal Legislation related thereto". Embassy of the Republic of Belarus in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Opening Statement by Dr. Condoleezza Rice, Senate Foreign Relations Committee" (PDF). January 18, 2005. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "At-a-glance: 'Outposts of tyranny'". BBC News. January 19, 2005. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ a b c d United States Government (2007). "Background Note: Belarus". United States State Department. Retrieved 2007-11-07.
- ^ "Russia-Belarus Union Presidency Dismissed". The Moscow Times. 2007-12-10. Retrieved 2007-12-13.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ AP (2008-05-27). "Putin named PM of Belarus-Russia alliance". Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ Radio Free Europe (2006). "CIS: Foreign Ministers, Heads Of State Gather In Minsk For Summit". Retrieved 2007-11-07.
- ^ "EU imposes Belarus travel ban". BBC News. BBC. 2002-11-19. Retrieved 2007-12-03.)
- ^ a b "Foreign Policy". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "U.S. Government Assistance FY 97 Annual Report". United States Embassy in Minsk, Belarus. 1998. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Belarus Democracy Act Will Help Cause of Freedom, Bush Says". USINO. United States State Department. 2007-10-22. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Relations between Belarus and the United States of America". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ Pan, Letian (2005-12-06). "China, Belarus agree to upgrade economic ties". Xinhua News Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Syria and Belarus agree to promote trade". BBC News. British Broadcasting Corporation. 1998-03-13. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Belarus-Syria report substantial progress in trade and economic relations". Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus. 2007-08-31. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the RB (2007). "Membership of the Republic of Belarus in International Organizations". Retrieved 2007-11-04.
- ^ "Growth in United Nations membership, 1945-present". Department of Public Information. United Nations Organization. 2006-07-03. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "High-ranking Military Officials of the Republic of Belarus". Ministry of Defense of the Republic of Belarus. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Section IV:The President, Parliament, Government, the Courts". Constitution of Belarus. Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus. 2004. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "History" (in Russian). Ministry of Defense of the Republic of Belarus. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ Routledge, IISS Military Balance 2007, p.158–159
- ^ Bykovsky, Pavel (2001–05). "Military Development and the Armed Forces of Belarus". Moscow Defense Brief. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Belarus - Military". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2005. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- ^ "Belarus and NATO". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus. 2002. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- ^ a b "Section I: Principles of the Constitutional System". Constitution of Belarus. Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus. 2004. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Section V: Local government and self-government". Constitution of Belarus. Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus. 2004. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ Carvalho, Fernando Duarte (2004). Defence Related SME's: Analysis and Description of Current Conditions. IOS Press. p. 32. ISBN 1586034081.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "About Minsk". Minsk City Executive Committee. Retrieved 2007-12-20.
- ^ a b c d e "Belarus - Geography". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2007. Retrieved 2007-11-07.
- ^ "Belarus: Window of Opportunity (see Table 15, page 66)" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 2008-09-22.
- ^ Bell, Imogen (2002). Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia 2003. Taylor & Francis. p. 132. ISBN 1857431375.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ (Zaprudnik, xix)
- ^ a b Fedor, Helen (1995). "Belarus - Climate". Belarus: A Country Study. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ Rainsford, Sarah (April 26, 2005). "Belarus cursed by Chernobyl". BBC News. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ "The United Nations and Chernobyl - The Republic of Belarus". United Nations. 2004. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ Smith, Marilyn. "Ecological reservation in Belarus fosters new approaches to soil remediation". International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "State Border - Delimitation History". State Border Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ^ "Lithuania's Cooperation with Belarus". Lithuanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ "Belarus shuns Moscow amid loan row". Al Jazeera Engllish. 29 May 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
Belarus' Soviet-style economy has been propped up in part by cheap Russian gas and oil and Lukashenko has called for his country to reunite with Russia.
- ^ Ministry of Statistics and Analysis of the Republic of Belarus (2006). "Labour". Retrieved 2007-11-06.
- ^ Dr. Kaare Dahl Martinsen (2002). "The Russian-Belarusian Union and the Near Abroad" (PDF). Norwegian Institute for Defence Studies. NATO. Retrieved 2007-11-07.
- ^ "Russia may cut oil supplies to ally Belarus - Putin". Reuters. 2006-10-25. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b c "The World Factbook - Belarus - Economy". Central Intelligence Agency. 2006. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
- ^ Library of Congress (1994). "Belarus - Exports". Country Studies. Retrieved 2007-11-04.
- ^ "Economic and Investment Review" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ World Bank. "Belarus: Prices, Markets, and Enterprise Reform," pp. 1. World Bank, 1997. ISBN 0821339761
- ^ "Belarus - Industry". Country Studies. Library of Congress. 1995. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
- ^ a b World Bank (2006). "Belarus - Country Brief 2003". Retrieved 2007-11-09.
- ^ a b Council of Ministers Foreign trade in goods and services in Belarus up by 11.5% in January-October. Published 2006. Retrieved October 6, 2007.
- ^ a b European Union The EU's Relationship With Belarus - Trade (PDF). Published November 2006. Retrieved October 6, 2007.
- ^ World Trade Organization Accessions - Belarus. Retrieved October 6, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e Ministry of Statistics and Analysis Labor Statistics in Belarus. Published 2005. Retrieved 18 March 2007.
- ^ National Bank of the Republic of Belarus History of the Belarusian Ruble. Retrieved 18 March 2007.
- ^ Pravda.ru Belarus abandons pegging its currency to Russian ruble. Published 23 August 2007. Retrieved 6 October 2007.
- ^ "Heritage Foundation's Index of Economic Freedom - Belarus". Retrieved March 18, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "CIA World Factbook (2007) - Belarus - People". Retrieved 2007-11-07.
- ^ "Languages across Europe." BBC Education at bbc.co.uk. Accessed November 6, 2007.
- ^ "Tres de cada cuatro bielorrusos emplean en su vida cotidiana el ruso (Three of every four Belarusians use Russian in their daily lives)" (in Spanish). Retrieved 2009-10-25.
According to results announced today from an investigation by The Center for Information and Analysis of the Presidency of Belarus... [f]or 72% of the population, Russian in the primary language used in everyday life.... According to the study, only 11.9% of inhabitants primarily speaks Belarusian, while the rest uses a mix of Russian and Belarusian. 29.4%... speaks, reads, and writes in Belorusian, while 52.5% only speaks and reads it.... [O]ne in ten does not understand Belorusian [at all]. (quote translated)
- ^ Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version: http://www.ethnologue.com/.
- ^ World Gazette Largest Cities of Belarus (2007). Published in 2007. Retrieved March 19, 2007.
- ^ "Population Pyramid Summary for Belarus". US Census Bureau. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ The literacy rate is defined as the percentage of people aged 15 and older who can read and write.
- ^ Library of Congress Country Studies Belarus - Religion. Retrieved 9 July 2007.
- ^ Minsk Jewish Campus Jewish Belarus. Retrieved 9 July 2007.
- ^ Webportal of the President of the Republic of Belarus Section One of the Constitution. Published 1994, amended in 1996. Retrieved 6 June 2007.
- ^ "Old Belarusian Poetry". Virtual Guide to Belarus. 1994. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- ^ a b c "Belarus." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. <http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-33482>.
- ^ Zou, Crystal (2003-12-11). "Ballets for Christmas". Shanghai Star. Retrieved 2007-12-20.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b Virtual Guide to Belarus - Classical Music of Belarus. Retrieved March 21, 2007.
- ^ Freemuse Blacklisted bands play in Poland. Published on March 17, 2006. Retrieved March 18, 2007.
- ^ National State Teleradiocompany Page on the 2004 Belarusian entry to the Eurovision Song Contest. Published 2004. Retrieved March 18, 2007.
- ^ "Belarusian National Culture". Embassy of the Republic of Belarus in the United States of America. Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ Virtual Guide to Belarus Belarusian traditional clothing. Retrieved on March 21, 2007.
- ^ Flags of the World Belarus - Ornament. Published November 26, 2006. Retrieved March 21, 2007.
- ^ Canadian Citizenship and Immigration - Cultures Profile Project - Eating the Belarusian Way. Published in 1998. Retrieved March 21, 2007.
- ^ University of Nebraska-Lincoln - Institute of Agriculture and National Resources. Situation and Outlook - People and Their Diets. Published in April 2000. Retrieved March 21, 2007.
- ^ "Belarus - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Retrieved 2006-03-26.
- ^ National State Teleradiocompany About us. Retrieved 5 October 2007.
- ^ "CIA World Factbook (2007) - Belarus - Communications". Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ a b Law of the Republic of Belarus Law On Press and Other Mass Media. Retrieved October 5, 2007.
- ^ Eurozine Independent Belarusian newspaper "Nasha Niva" to close. Published April 19, 2006.
- ^ United States Department of States Media Freedom in Belarus. Press release by Philip T. Reeker. Published May 30, 2003.
- ^ Freedom House Country Report - Belarus. Published 2005. Reviewed October 6, 2007.
Further reading
[edit]- Zaprudnik, Jan, Belarus: At a Crossroads in History, Westview Press, 1993 (ISBN 0813317940)
External links
[edit]- News and media
- Belarusian telegraph agency - news, events, facts
- Minsk Post | Daily diary of Belarus
- Belarus News and Analysis
- Media in Belarus
- (in Belarusian) News of Belarus
- Politics and News from Belarus
- Government
- E-Government in Belarus
- Embassy of Belarus in the United States
- Global Integrity Report: Belarus has information on Belarus anti-corruption efforts.
- Government of Belarus
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- President's official site
- General information
- Official Website of the Republic of Belarus
- "Belarus". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Belarus at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Belarus Miscellany
- The 1st Belarusian Art Gallery
- The Virtual Guide of Belarus
- The World Bank in Belarus
- FAO Country Profiles: Belarus
- Maps