Israel–United States relations
 | |
Israel |
United States |
|---|---|
| Diplomatic mission | |
| Embassy of Israel, Washington, D.C. | Embassy of the United States, Jerusalem |
| Envoy | |
| Ambassador Mike Herzog | Ambassador Jack Lew |


The United States was the first country to recognize the nascent State of Israel on May 14, 1948.[1] Since the 1960s, the Israel–U.S. relationship has grown into a mutually beneficial alliance in economic, strategic and military aspects.[1] The U.S. has provided strong support for Israel: it has played a key role in the promotion of good relations between Israel and its neighbouring Arab states—notably Jordan, Lebanon, Egypt—while holding off hostility from countries such as Syria and Iran. In turn, Israel provides a strategic American foothold in the region as well as intelligence and advanced technological partnerships in both the civilian and military worlds. During the Cold War, Israel was a vital counterweight to Soviet influence in the region.[2] Relations with Israel are an important factor in the U.S. government's overall foreign policy in the Middle East; the U.S. Congress has placed considerable importance on the maintenance of a supportive relationship. The relationship has been marked by the strong influence of the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC), a pro-Israel lobby which has its own political action committee (PAC);[3] it has been called one of the most powerful lobbying groups in the United States.[4][5]
Israel is the largest cumulative recipient of U.S. foreign aid: up to February 2022, the U.S. had provided Israel US$150 billion (non-inflation-adjusted) in assistance.[6] The United States' first free trade agreement was with Israel, in 1985. The free trade agreement with Israel creates the most American jobs per export dollar of all of the United States' free trade agreements.[7] In 1999, the U.S. government signed a commitment to provide Israel with at least US$2.7 billion in military aid annually for ten years; in 2009 it was raised to $3 billion; and in 2019 raised to a minimum of US$3.8 billion.[6] Since 1972, the U.S. has also extended loan guarantees to Israel to assist with housing shortages, absorption of new Jewish immigrants and economic recovery.[6] Moreover, Israel is the United States' 23rd largest trading partner while the United States is Israel's largest trading partner; two-way trade totaled nearly $50 billion by 2023.[8] 300 American mostly technology oriented companies have set up R&D centers in Israel, whilst 650 Israeli technology companies operate in the United States.[9][10] Israeli American partnerships tend to contribute to relatively niche sectors of the American economy with the effect multiplying positively toward the wider economy.[11]
In addition to financial and military aid, the U.S. provides large-scale political support, having used its United Nations Security Council veto power 42 times against resolutions condemning Israel, out of 83 times in which its veto has been used. Between 1991 and 2011, out of the 24 vetoes invoked by the U.S., 15 were used to protect Israel.[12][13] As of 2021[update], the United States remains the only permanent member of the United Nations Security Council to have recognized the Golan Heights as non-occupied Israeli sovereign territory, recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel, and moved its embassy there from Tel Aviv in 2018.[14] Israel is designated by the United States as a major non-NATO ally, the only country in the Middle East other than Egypt to have this designation.
Bilateral relations have evolved from an initial American policy of sympathy and support for the creation of a Jewish homeland in 1948, to a partnership that links a small but powerful state with a superpower attempting to balance influence against competing interests in the region, namely Russia and its allies.[15][16] Some analysts maintain that Israel is a particularly strategic ally for the U.S., and that relations with the former strengthen the latter's influence in the Middle East.[17] They argue the military foothold offered by Israel justifies the expense of American military aid, referring to Israel as "America's aircraft carrier in the Middle East".[18][19]
History

Support for Zionism among American Jews was minimal, until the involvement of Louis Brandeis in the Federation of American Zionists,[20] starting in 1912 and the establishment of the Provisional Executive Committee for General Zionist Affairs in 1914; it was empowered by the Zionist Organization "to deal with all Zionist matters, until better times come".[21]
Woodrow Wilson, who was sympathetic to the plight of Jews in Europe and favorable to Zionist objectives (giving his assent to the text of the Balfour Declaration shortly before its release) stated on March 2, 1919, "I am persuaded that the Allied nations with the fullest concurrence of our own Government and people are agreed that in Palestine shall be laid the foundation of a future Jewish commonwealth" and on April 16, 1919, corroborated the U.S. government's "expressed acquiescence" in the Balfour Declaration.[22] Wilson's statements did not result in a change in policy of the U.S. State Department in favor of Zionist aims. However, the U.S. Congress passed the Lodge-Fish resolution,[23] the first joint resolution stating its support for "the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people" on September 21, 1922.[24][25] The same day, the Mandate of Palestine was approved by the Council of the League of Nations.
During World War II, while U.S. foreign policy decisions were often ad hoc moves and solutions dictated by the demands of the war, the Zionist movement made a fundamental departure from traditional Zionist policy and its stated goals, at the Biltmore Conference in May 1942.[26] Previous stated policy towards establishing a Jewish "national home" in Palestine were gone; these were replaced with its new policy "that Palestine be established as a Jewish Commonwealth" like other nations, in cooperation with the United States, not Britain.[27] Two attempts by Congress in 1944 to pass resolutions declaring U.S. government support for the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine were objected to by the Departments of War and State, because of wartime considerations and Arab opposition to the creation of a Jewish state. The resolutions were permanently dropped.[28]
Following the war, the "new postwar era witnessed an intensive involvement of the United States in the political and economic affairs of the Middle East, in contrast to the hands-off attitude characteristic of the prewar period. In Truman's administration the United States had to face and define its policy in all three sectors that provided the root causes of American interests in the region: the Soviet threat, the birth of Israel, and petroleum."[29]
Recognition of the State of Israel

Previous American presidents, although encouraged by active support from members of the American and world Jewish communities, as well as domestic civic groups, labor unions, and political parties, supported the Jewish homeland concept, alluded to in Britain's 1917 Balfour Declaration, they officially continued to "acquiesce". Throughout the Roosevelt and Truman administrations, the Departments of War and State recognized the possibility of a Soviet-Arab connection and the potential Arab restriction on oil supplies to the U.S., and advised against U.S. intervention on behalf of the Jews.[30] With continuing conflict in the area and worsening humanitarian conditions among Holocaust survivors in Europe, on November 29, 1947, and with U.S. support, the United Nations General Assembly adopted as Resolution 181, the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, which recommended the adoption and implementation of a Plan of Partition with Economic Union.[31] The voting was heavily lobbied by Zionist supporters, which Truman himself later noted,[32] and rejected by the Arabs.

As the end of the mandate approached, the decision to recognize the Jewish state remained contentious, with significant disagreement between President Truman, his domestic and campaign adviser, Clark Clifford, and both the State Department and Defense Department. Truman, while sympathetic to the Zionist cause, was most concerned about relieving the plight of the displaced persons; Secretary of State George Marshall feared U.S. backing of a Jewish state would harm relations with the Muslim world, limit access to Middle Eastern oil, and destabilize the region. On May 12, 1948, Truman met in the Oval Office with Secretary of State Marshall, Under Secretary of State Robert A. Lovett, Counsel to the President Clark Clifford, and several others to discuss the Palestine situation. Clifford argued in favor of recognizing the new Jewish state in accordance with the partition resolution. Marshall opposed Clifford's arguments, contending that they were based on domestic political considerations in the election year. Marshall said that, if Truman followed Clifford's advice and recognized the Jewish state, then he would vote against Truman in the election. Truman did not clearly state his views in the meeting.[33]
Two days later, on May 14, 1948, the United States, under Truman, became the first country to extend any form of recognition. This happened within hours of the Jewish People's Council gathering at the Tel Aviv Museum and David Ben-Gurion declaring "the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz Israel, to be known as the State of Israel". The phrase "in Eretz Israel" is the only place in the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel containing any reference to the location of the new State.[34]
The text of the communication from the provisional government of Israel to Truman was as follows:
MY DEAR MR. PRESIDENT: I have the honor to notify you that the state of Israel has been proclaimed as an independent republic within frontiers approved by the General Assembly of the United Nations in its Resolution of 29 November 1947, and that a provisional government has been charged to assume the rights and duties of government for preserving law and order within the boundaries of Israel, for defending the state against external aggression, and for discharging the obligations of Israel to the other nations of the world in accordance with international law. The Act of Independence will become effective at one minute after six o'clock on the evening of 14 May 1948, Washington time.
With full knowledge of the deep bond of sympathy which has existed and has been strengthened over the past thirty years between the Government of the United States and the Jewish people of Palestine, I have been authorized by the provisional government of the new state to tender this message and to express the hope that your government will recognize and will welcome Israel into the community of nations.
Very respectfully yours,
ELIAHU EPSTEIN
The text of the United States recognition was as follows:
This Government has been informed that a Jewish state has been proclaimed in Palestine, and recognition has been requested by the provisional Government thereof.
The United States recognizes the provisional government as the de facto authority of the new State of Israel.
(sgn.) Harry Truman
Approved,
14 May 1948
6.11[36]
With this unexpected decision, U.S. representative to the United Nations Warren Austin, whose team had been working on an alternative trusteeship proposal, shortly thereafter left his office at the UN and went home. Secretary of State Marshall sent a State Department official to the United Nations to prevent the entire United States delegation from resigning.[33] De jure recognition came on January 31, 1949.
Following UN mediation by American Ralph Bunche, the 1949 Armistice Agreements ended the 1948 Arab Israeli War. Related to enforcement of the armistice, the United States signed the Tripartite Declaration of 1950 with Britain and France. In it, they pledged to take action within and outside the United Nations to prevent violations of the frontiers or armistice lines; outlined their commitment to peace and stability in the area and their opposition to the use or threat of force; and reiterated their opposition to the development of an arms race in the region.
Under rapidly changing geopolitical circumstances, U.S. policy in the Middle East was generally geared toward supporting Arab states' independence; aiding the development of oil-producing countries; preventing Soviet influence from gaining a foothold in Greece, Turkey, and Iran; and preventing an arms race and maintaining a neutral stance in the Arab–Israeli conflict. U.S. policymakers initially used foreign aid to support these objectives.
Foreign policy of the U.S. government
Eisenhower administration (1953–1961)

During these years of austerity, the United States provided Israel moderate amounts of economic aid, mostly as loans for basic foodstuffs; a far greater share of state income derived from German war reparations (86% of Israeli GDP in 1956) which were used for domestic development.
France became Israel's main arms supplier at this time and provided Israel with advanced military equipment and technology. This support was seen by Israel to counter the perceived threat from Egypt under President Gamal Abdel Nasser with respect to the "Czech arms deal" of September 1955. During the 1956 Suez Crisis, the Israeli Defense Forces invaded Egypt and were soon followed by French and British forces. For differing reasons, France, Israel and Britain signed a secret agreement to topple Nasser by regaining control of the Suez Canal, following its nationalization, and to occupy parts of western Sinai assuring free passage of shipping (for Israel) in the Gulf of Aqaba.[37] In response, the U.S., with support from the Soviet Union at the UN intervened on behalf of Egypt to force a withdrawal. Afterward, Nasser expressed a desire to establish closer relations with the United States. Eager to increase its influence in the region, and prevent Nasser from going over to the Soviet Bloc, U.S. policy was to remain neutral and not become too closely allied with Israel. At this time, the only assistance the U.S. provided Israel was food aid. In the early 1960s, the U.S. would begin to sell advanced, but defensive, weapons to Israel, Egypt, and Jordan, including Hawk anti-aircraft missiles.
Kennedy and Johnson administrations (1961–1969)

As president, Kennedy initiated the creation of security ties with Israel, and he was the founder of the U.S.–Israeli military alliance. Kennedy, basing his policy decision on his White House advisors, avoided the State Department with its greater interest in the Arab world. A central issue was the status of Palestinians, split among Israel, Egypt and Jordan. By 1961 there were 1.2 million Palestinian refugees living in Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, and Egypt. The Soviet Union, although it initially supported the creation of Israel, was now an opponent, and looking to the Arab world to build support. The United Nations General assembly was generally anti-Israel, but all decisions were subject to American veto power in the Security Council. According to international law, UNGA resolutions are not legally binding while UNSC resolutions are. Kennedy tried to be evenhanded, but domestic political pressures pushed him to support Israel.[38]
I had forecast that once the Algerian War was over, France would drop Israel like a hot coal and renew its ties with the Arab world. And that, of course, is exactly what happened – Israel adopted the US instead.
Kennedy ended the arms embargo that the Eisenhower and Truman administrations had enforced on Israel. Describing the protection of Israel as a moral and national commitment, he was the first to introduce the concept of a 'special relationship' (as he described it to Golda Meir) between the U.S. and Israel.[40]
President John F. Kennedy in 1962 sold Israel a major weapon system, the Hawk antiaircraft missile. Professor Abraham Ben-Zvi of Tel Aviv University argues that the sale resulted from Kennedy's "need to maintain – and preferably broaden and solidify – the base of Jewish support of the administration on the eve of the November 1962 congressional elections." As soon as the decision was made White House officials told American Jewish leaders about it. However, historian Zachary Wallace argues that the new policy was driven primarily by Kennedy's admiration of the Jewish state. It deserved American support in order to achieve stability in the Middle East.[41]

Kennedy warned the Israeli government against the production of nuclear materials in Dimona, which he believed could instigate a nuclear arms-race in the Middle East. After the existence of a nuclear plant was initially denied by the Israeli government, David Ben-Gurion stated in a speech to the Israeli Knesset on December 21, 1960, that the purpose of the nuclear plant at Beersheba was for "research in problems of arid zones and desert flora and fauna."[42] When Ben-Gurion met with Kennedy in New York, he claimed that Dimona was, for the time being, being developed to provide nuclear power for desalinization and other peaceful purposes. In 1962, the Israeli and U.S. governments agreed to an annual inspection regime. Despite this inspection policy [agreement], Rodger Davies, the director of the State Department's Office of Near Eastern Affairs, concluded in March 1965 that Israel was developing nuclear weapons. He reported that Israel's target date for achieving nuclear capability was 1968–1969.[42] In 1966, when defecting Iraqi pilot Munir Redfa landed in Israel flying a Soviet-built MiG-21 fighter jet, information on the plane was immediately shared with the United States.
During Lyndon B. Johnson's presidency, U.S. policy shifted to a whole-hearted, but not unquestioning, support for Israel. In the lead up to the Six-Day War of 1967, while the Johnson Administration was sympathetic to Israel's need to defend itself against foreign attack, the U.S. worried that Israel's response would be disproportionate and potentially destabilizing. Israel's raid into Jordan after the 1966 Samu Incident was very troubling to the U.S. because Jordan was also an ally and had received over $500 million in aid for construction of the East Ghor Main Canal, which was virtually destroyed in subsequent raids.
The primary concern of the Johnson Administration was that should war break out in the region, the United States and the Soviet Union would be drawn into it. Intense diplomatic negotiations with the nations in the region and the Soviets, including the first use of the Hotline, failed to prevent war. When Israel launched preemptive strikes against the Egyptian Air force, Secretary of State Dean Rusk was disappointed as he felt a diplomatic solution could have been possible.
During the Six-Day War, Israeli jets and torpedo boats attacked USS Liberty, a U.S. Navy spy ship in international waters north of the Sinai Peninsula, about 25.5 nautical miles (47.2 km; 29.3 mi) northwest from the Egyptian city of Arish,[43] killing 34 and wounding 171. Israel, which stated the Liberty had been mistaken as the Egyptian vessel El Quseir, claimed it was an instance of friendly fire. The U.S. government accepted it as such, although the incident raised much controversy, and some still believe it to be deliberate:[44][45] Thomas Hinman Moorer, 7th chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, famously accused President Johnson of having covered up that the attack was a deliberate act, calling it "one of the classic all-American cover-ups".[46]
Prior to the Six-Day War, U.S. administrations had taken considerable care to avoid giving the appearance of favoritism. Writing in American Presidents and the Middle East, George Lenczowski notes, "Johnson's was an unhappy, virtually tragic presidency", regarding "America's standing and posture in the Middle East", and marked a turning point in both U.S.–Israeli and U.S.–Arab relations.[47] He characterizes the Middle Eastern perception of the U.S. as moving from "the most popular of Western countries" before 1948, to having "its glamour diminished, but Eisenhower's standing during the Arab–Israeli Suez Crisis convinced many Middle Eastern moderates that, if not actually lovable, the United States was at least a fair country to deal with; this view of U.S. fairness and impartiality still prevailed during Kennedy's presidency; but during Lyndon B. Johnson's presidency America's policy took a definite turn in the pro-Israeli direction". He added: "The June war of 1967 confirmed this impression, and from 1967 on [writing in 1990] the United States emerged as the most distrusted if not actually hated country in the Middle East."

Following the war, the perception in Washington was that many Arab states (notably Egypt) had permanently drifted toward the Soviets. In 1968, with strong support from Congress, Johnson approved the sale of Phantom fighters to Israel, establishing the precedent for U.S. support for Israel's qualitative military edge over its neighbors. However, the U.S. continued to provide military equipment to Arab states such as Lebanon and Saudi Arabia, to counter Soviet arms sales in the region.
During the Israeli–Egyptian War of Attrition, Israeli commandos captured a Soviet-built P-12 radar station in an operation code-named Rooster 53. Previously unknown information was subsequently shared with the U.S.[49]
When the French government imposed an arms embargo on Israel in 1967, Israeli spies procured designs of the Dassault Mirage 5 from a Swiss Jewish engineer in order to build the IAI Kfir. These designs were also shared with the United States.
Qualitative Military Edge
Qualitative Military Edge (QME) is a concept in U.S. foreign policy. The U.S. commits itself to maintain Israel's qualitative military edge (QME) – that is, the technological, tactical, and other advantages that allow it to deter numerically superior adversaries.[50] This policy is defined in current U.S. law.[51][52][53]
1963 standoff between Israel and United States

Israeli newspaper Haaretz reported in 2019 that, throughout the spring and summer of 1963, the leaders of the United States and Israel – President John F. Kennedy and prime ministers David Ben-Gurion and Levi Eshkol – were engaged in a high-stakes battle of wills over Israel's nuclear program. The tensions were invisible to the publics of both countries, and only a few senior officials, on both sides, were aware of the severity of the situation. According to Yuval Ne'eman, Eshkol, Ben-Gurion's successor, and his associates saw Kennedy as presenting Israel with a real ultimatum. According to Ne’eman, the former Israel Air Force commander Maj. Gen. (res.) Dan Tolkowsky, seriously entertained the fear that Kennedy might send U.S. airborne troops to Dimona, the home of Israel's nuclear complex.[54]
On March 25, 1963, President Kennedy and CIA Director John A. McCone discussed the Israeli nuclear program. According to McCone, Kennedy raised the "question of Israel acquiring nuclear capability," and McCone provided Kennedy with Kent's estimate of the anticipated negative consequences of Israeli nuclearization. According to McCone, Kennedy then instructed National Security Adviser McGeorge Bundy to guide Secretary of State Dean Rusk, in collaboration with the CIA director and the AEC chairman, to submit a proposal "as to how some form of international or bilateral U.S. safeguards could be instituted to protect against the contingency mentioned." That also meant that the "next informal inspection of the Israeli reactor complex [must] ... be undertaken promptly and ... be as thorough as possible."[54]
This presidential request was translated into diplomatic action, on April 2, 1963, Ambassador Barbour met Prime Minister Ben-Gurion and presented the American request for his "assent to semi-annual visits to Dimona perhaps in May and November, with full access to all parts and instruments in the facility, by qualified U.S. scientists." Ben-Gurion, apparently taken by surprise, responded by saying the issue would have to be postponed until after Passover, which that year ended on April 15. To highlight the point further, two days later, Assistant Secretary Talbot summoned Israeli ambassador Harman to the State Department and presented him with a diplomatic démarche on the inspections. This message to Ben-Gurion was the first salvo in what would become "the toughest American-Israeli confrontation over the Israeli nuclear program".[54]
On April 26, 1963, more than three weeks after the original U.S. demand concerning Dimona, Ben-Gurion responded to Kennedy with a seven-page letter that focused on broad issues of Israeli security and regional stability. Claiming that Israel faced an unprecedented threat, Ben-Gurion invoked the specter of "another Holocaust," and insisted that Israel's security should be protected by joint external security guarantees, to be extended by the U.S. and the Soviet Union. Kennedy, however, was determined not to let Ben-Gurion change the subject. On May 4, 1963, he replied to the prime minister, assuring him that "we are watching closely current developments in the Arab world". As to Ben-Gurion's proposal for a joint superpower declaration, Kennedy dismissed both its practicality and its political wisdom. Kennedy was much less worried about an "early Arab attack" than he was by "a successful development of advanced offensive systems which, as you say, could not be dealt with by presently available means."[54]
Kennedy, would not budge on Dimona, and the disagreements became a "pain in the neck" for him, as Robert Komer later wrote. The confrontation with Israel escalated when the State Department transmitted Kennedy's latest letter to the Tel Aviv embassy on June 15 for immediate delivery to Ben-Gurion by Ambassador Barbour. In the letter Kennedy fleshed out his insistence on biannual visits with a set of detailed technical conditions. The letter was akin to an ultimatum: If the U.S. government could not obtain "reliable information" on the state of the Dimona project, Washington's "commitment to and support of Israel" could be "seriously jeopardized." But the letter was never presented to Ben-Gurion. The telegram with Kennedy's letter arrived in Tel Aviv on Saturday, June 15, the day before Ben-Gurion's announcement of his resignation, a decision that stunned his country and the world. Ben-Gurion never explained, in writing or orally, what led him to resign, beyond citing "personal reasons." It is widely believed that the Lavon Affair, a botched Israeli spy mission in Egypt, was the impetus for his resignation. He denied that his move was related to any specific policy issues, but the question of the extent to which Kennedy's Dimona pressure played a role remains open to discussion to the present day.[54]
On July 5, less than 10 days after Levi Eshkol succeeded Ben-Gurion as prime minister, Ambassador Barbour delivered to him a first letter from President Kennedy. The letter was virtually a copy of the undelivered letter of June 15 to Ben-Gurion.[55] As Yuval Ne’eman stated, it was immediately apparent to Eshkol and his advisers that Kennedy's demands were akin to an ultimatum, and thus constituted a crisis in the making. A stunned Eshkol, in his first and interim response, on July 17, requested more time to study the subject and for consultations. The premier noted that while he hoped that U.S-Israeli friendship would grow under his watch, "Israel would do what it had to do for its national security and to safeguard its sovereign rights." Barbour, apparently wanting to mitigate the bluntness of the letter, assured Eshkol that Kennedy's statement was "factual": Critics of strong U.S.-Israel relations might complicate the diplomatic relationship if Dimona was left uninspected.[54]
On August 19, after six weeks of consultations that generated at least eight different drafts, Eshkol handed Barbour his written reply to Kennedy's demands. It began by reiterating Ben-Gurion's past assurances that Dimona's purpose was peaceful. As to Kennedy's request, Eshkol wrote that given the special relationship between the two countries, he had decided to allow regular visits of U.S. representatives to the Dimona site. On the specific issue of the schedule, Eshkol suggested – as Ben-Gurion had in his last letter to Kennedy – that late 1963 would be the time for the first visit: By then, he wrote, "the French group will have handed the reactor over to us and it will be undertaking general tests and measurements of its physical parameters at zero power."[54]
Eshkol was vague on the proposed frequency of visits. Eshkol disregarded Kennedy's demand for biannual tours, while avoiding a frontal challenge to Kennedy's request. "Having considered this request, I believe we shall be able to reach agreement on the future schedule of visits," Eshkol wrote. In sum, the prime minister split the difference: To end the confrontation, he assented to "regular visits" by U.S. scientists, but he did not accept the idea of the prompt visit that Kennedy wanted and avoided making an explicit commitment to biannual inspections. Kennedy's appreciative reply did not mention these divergences, but assumed a basic agreement on "regular visits."[54]
In the wake of Eshkol's letter, the first of the long-sought regular inspection visits to Dimona took place in mid-January 1964, two months after Kennedy's assassination. The Israelis told the American visitors that the reactor had gone critical only a few weeks earlier, but that claim was not accurate. Israel acknowledged years later that the Dimona reactor became operational in mid-1963, as the Kennedy administration had originally assumed.[54]
It turned out that Kennedy's insistence on biannual visits to Dimona was not implemented after his death. U.S. government officials remained interested in such a schedule, and President Lyndon B. Johnson did raise the issue with Eshkol, but he never pressed hard on the subject the way that Kennedy had.[54]
In the end, the confrontation between President Kennedy and two Israeli prime ministers resulted in a series of six American inspections of the Dimona nuclear complex, once a year between 1964 and 1969. They were never conducted under the strict conditions Kennedy laid out in his letters. While Kennedy's successor remained committed to the cause of nuclear nonproliferation and supported American inspection visits at Dimona, he was much less concerned about holding the Israelis to Kennedy's terms. In retrospect, this change of attitude may have saved the Israeli nuclear program.[54]
Nixon and Ford administrations (1969–1977)
On June 19, 1970, Secretary of State William P. Rogers formally proposed the Rogers Plan, which called for a 90-day cease-fire and a military standstill zone on each side of the Suez Canal, to calm the ongoing War of Attrition. It was an effort to reach agreement specifically on the framework of UN Resolution 242, which called for Israeli withdrawal from territories occupied in 1967 and mutual recognition of each state's sovereignty and independence.[56] The Egyptians accepted the Rogers Plan, but the Israelis were split and did not; they failed to get sufficient support within the "unity government". Despite the Labor-dominant Alignments, formal acceptance of UN 242 and "peace for withdrawal" earlier that year, Menachem Begin and the right wing Gahal alliance were adamantly opposed to withdraw from the Palestinian Territories; the second-largest party in the government resigned on August 5, 1970.[57] Ultimately, the plan also failed due to insufficient support from Nixon for his secretary of state's plan, preferring instead the position of his National Security Advisor, Henry Kissinger, not to pursue the initiative.
No breakthrough occurred even after President Sadat of Egypt in 1972 unexpectedly expelled Soviet advisers from Egypt, and again signaled to Washington his willingness to negotiate.[58]
On February 28, 1973, during a visit in Washington, D.C., the then Israeli prime minister Golda Meir agreed with the then U.S. National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger's peace proposal based on "security versus sovereignty": Israel would accept Egyptian sovereignty over all Sinai, while Egypt would accept Israeli presence in some of Sinai strategic positions.[59][60][61][62][63]
Faced with this lack of progress on the diplomatic front, and hoping to force the Nixon administration to become more involved, Egypt prepared for military conflict. In October 1973, Egypt and Syria, simultaneously attacked Israel, thus starting the Yom Kippur War.

Despite intelligence indicating an attack from Egypt and Syria, Prime Minister Golda Meir made the controversial decision not to launch a pre-emptive strike. Meir, among other concerns, feared alienating the United States, if Israel was seen as starting another war, as Israel only trusted the United States to come to its aid. In retrospect, the decision not to strike was probably a sound one, though it is vigorously debated in Israel to this day. Later, according to Secretary of State Henry Kissinger, had Israel struck first, they would not have received "so much as a nail". On October 6, 1973, during the Jewish holiday of Yom Kippur, Egypt and Syria, with the support of Arab expeditionary forces and with backing from the Soviet Union, launched simultaneous attacks against Israel. The resulting conflict is known as the Yom Kippur War. The Egyptian Army was initially able to breach Israeli defenses, advance into the Sinai, and establish defensive positions along the east bank of the Suez Canal, but they were later repulsed in a massive tank battle when they tried to advance further to draw pressure away from Syria. The Israelis then crossed the Suez Canal. Major battles with heavy losses for both sides took place. At the same time, the Syrians almost broke through Israel's thin defenses in the Golan Heights, but were eventually stopped by reinforcements and pushed back, followed by a successful Israeli advance into Syria. Israel also gained the upper hand in the air and at sea early in the war. Days into the war, it has been suggested that Meir authorized the assembly of Israeli nuclear bombs. This was done openly, perhaps in order to draw American attention, but Meir authorized their use against Egyptian and Syrian targets only if Arab forces managed to advance too far.[64][65] The Soviets began to resupply Arab forces, predominantly Syria. Meir asked Nixon for help with military supply. After Israel went on full nuclear alert and loaded their warheads into waiting planes, Nixon ordered the full scale commencement of a strategic airlift operation to deliver weapons and supplies to Israel; this last move is sometimes called "the airlift that saved Israel". However, by the time the supplies arrived, Israel was gaining the upper hand.
Again, the U.S. and Soviets feared that they would be drawn into a Middle East conflict. After the Soviets threatened intervention on the behalf of Egypt, following Israeli advances beyond the cease-fire lines, the U.S. increased the Defense Condition (DEFCON) from four to three, the highest peacetime level. This was prompted after Israel trapped Egypt's Third Army east of the Suez canal.
Kissinger realized the situation presented the United States with a tremendous opportunity—Egypt was totally dependent on the U.S. to prevent Israel from destroying the army, which now had no access to food or water. The position could be parlayed later into allowing the United States to mediate the dispute, and push Egypt out of Soviet influences. As a result, the United States exerted tremendous pressure on the Israelis to refrain from destroying the trapped army. In a phone call with Israeli ambassador Simcha Dinitz, Kissinger told the ambassador that the destruction of the Egyptian Third Army "is an option that does not exist". The Egyptians later withdrew their request for support and the Soviets complied.
After the war, Kissinger pressured the Israelis to withdraw from Arab lands; this contributed to the first phases of a lasting Israeli-Egyptian peace. American support of Israel during the war contributed to the 1973 OPEC embargo against the United States, which was lifted in March 1974.
The Reassessment Crisis
In early 1975, the Israeli government turned down a U.S. initiative for further redeployment in Sinai. President Ford responded on March 21, 1975, by sending Prime Minister Rabin a letter stating that Israeli intransigence has complicated U.S. worldwide interests, and therefore the administration will "reassess" its relations with the Israeli government. In addition, arms shipments to Israel halted. The reassessment crisis came to an end with the Israeli–Egyptian disengagement of forces agreement of September 4, 1975.[66]
Carter administration (1977–1981)

The Carter administration was characterized by very active U.S. involvement in the Middle East peace process. With the May 1977 election of Likud's Menachem Begin as prime minister, after 29 years of leading the Israeli government opposition, major changes took place regarding Israeli withdrawal from the occupied territories.[17] This led to friction in U.S.–Israeli bilateral relations. The two frameworks included in the Carter-initiated Camp David process were viewed by right-wing elements in Israel as creating U.S. pressures on Israel to withdraw from the captured Palestinian territories, as well as forcing it to take risks for the sake of peace with Egypt. The Israeli-Egyptian peace treaty was signed at the White House on March 26, 1979. It led to Israeli withdrawal from Sinai by 1982. Likud governments have since argued that their acceptance of full withdrawal from the Sinai as part of these accords and the eventual Egypt–Israel peace treaty fulfilled the Israeli pledge to withdraw from Sinai.[17] President Carter's support for a Palestinian homeland and for Palestinian political rights particularly created tensions with the Likud government, and little progress was achieved on that front.
Reagan administration (1981–1989)


Israeli supporters expressed concerns early in the first Ronald Reagan term about potential difficulties in U.S.–Israeli relations, in part because several Presidential appointees had ties or past business associations with key Arab countries (for example, Secretaries Caspar Weinberger and George P. Shultz were officers in the Bechtel Corporation, which has strong links to the Arab world; see Arab lobby in the United States.) However, President Reagan's personal support for Israel, and the compatibility between Israeli and Reagan perspectives on terrorism, security cooperation, and the Soviet threat, led to considerable strengthening in bilateral relations.[67]
In 1981, Weinberger and Israeli minister of defense Ariel Sharon signed the Strategic Cooperation Agreement, establishing a framework for continued consultation and cooperation to enhance the national security of both countries. In November 1983, the two sides formed a Joint Political Military Group, which meets twice a year, to implement most provisions of that agreement. Joint air and sea military exercises began in June 1984, and the United States constructed two War Reserve Stock facilities in Israel to stockpile military equipment. Although intended for American forces in the Middle East, the equipment can be transferred to Israeli use if necessary.[67]
U.S.–Israeli ties strengthened during the second Reagan term. Israel was granted "major non-NATO ally" status in 1989, giving it access to expanded weapons systems and opportunities to bid on U.S. defense contracts. The United States maintained grant aid to Israel at $3 billion annually and implemented a free trade agreement in 1985. Since then all customs duties between the two trading partners have been eliminated. However, relations soured when Israel carried out Operation Opera, an Israeli airstrike on the Osirak nuclear reactor in Baghdad. Reagan suspended a shipment of military aircraft to Israel, and harshly criticized the action. Relations also soured during the 1982 Lebanon War, when the United States even contemplated sanctions to stop the Israeli siege of Beirut. The U.S. reminded Israel that weaponry provided by the U.S. was to be used for defensive purposes only, and suspended shipments of cluster munitions to Israel. Although the war exposed some serious differences between Israeli and U.S. policies, such as Israel's rejection of the Reagan peace plan of September 1, 1982, it did not alter the Administration's favoritism for Israel and the emphasis it placed on Israel's importance to the United States. Although critical of Israeli actions, the United States vetoed a Soviet-proposed United Nations Security Council resolution to impose an arms embargo on Israel.[67]
In 1985, the U.S. supported Israel's economic stabilization through roughly $1.5 billion in two-year loan guarantees the creation of a U.S.–Israel bilateral economic forum called the U.S.–Israel Joint Economic Development Group (JEDG).[67]
The second Reagan term ended on what many Israelis considered to be a sour note when the United States opened a dialogue with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) in December 1988. But, despite the U.S.–PLO dialogue, the Pollard spy case, and the Israeli rejection of the Shultz peace initiative in the spring of 1988, pro-Israeli organizations in the United States characterized the Reagan Administration (and the 100th Congress) as the "most pro-Israel ever", and praised the positive overall tone of bilateral relations.[67]
George H. W. Bush administration (1989–1993)

In the midst of the first Intifada, Secretary of State James Baker told an American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC, a pro-Israel lobby group) audience on May 22, 1989, that Israel should abandon its "expansionist policies". President Bush raised the ire of the Likud government when he told a press conference on March 3, 1991, that East Jerusalem was occupied territory and not a sovereign part of Israel as Israel says. Israel had annexed East Jerusalem in 1980, an action which did not gain international recognition. The United States and Israel disagreed over the Israeli interpretation of the Israeli plan to hold elections for a Palestinian peace conference delegation in the summer of 1989, and also disagreed over the need for an investigation of the Jerusalem incident of October 8, 1990, in which Israeli police killed 17 Palestinians.[67]
Amid the Iraq–Kuwait crisis and Iraqi threats against Israel generated by it, former president Bush repeated the U.S. commitment to Israel's security. Israeli–U.S. tension eased after the start of the Persian Gulf War on January 16, 1991, when Israel became a target of Iraqi Scud missiles, suffering over 30 strikes during the war. The United States urged Israel not to retaliate against Iraq for the attacks because it was believed that Iraq wanted to draw Israel into the conflict and force other coalition members, Egypt and Syria in particular, to quit the coalition and join Iraq in a war against Israel. Israel did not retaliate, and gained praise for its restraint.[67]
Following the Gulf War, the administration immediately returned to Arab-Israeli peacemaking, believing there was a window of opportunity to use the political capital generated by the U.S. victory to revitalize the Arab-Israeli peace process. On March 6, 1991, President Bush addressed Congress in a speech often cited as the administration's principal policy statement on the new order in relation to the Middle East, following the expulsion of Iraqi forces from Kuwait.[68][69] Michael Oren summarizes the speech, saying: "The president proceeded to outline his plan for maintaining a permanent U.S. naval presence in the Gulf, for providing funds for Middle East development, and for instituting safeguards against the spread of unconventional weapons. The centerpiece of his program, however, was the achievement of an Arab–Israeli treaty based on the territory-for-peace principle and the fulfillment of Palestinian rights." As a first step, Bush announced his intention to reconvene the international peace conference in Madrid.[68]
However, unlike earlier American peace efforts, no new aid commitments would be used. This was both because President Bush and Secretary Baker felt the coalition victory and increased U.S. prestige would itself induce a new Arab–Israeli dialogue, and because their diplomatic initiative focused on process and procedure rather than on agreements and concessions. From Washington's perspective, economic inducements would not be necessary, although these did enter the process when Israel injected them in May. Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Shamir's request for $10 billion in U.S. loan guarantees added a new dimension to U.S. diplomacy and sparked a political showdown between his government and the Bush administration.[70]
Bush and Baker were thus instrumental in convening the Madrid peace conference in October 1991 and in persuading all the parties to engage in the subsequent peace negotiations. It was reported widely that the Bush Administration did not share an amicable relationship with the Likud government of Yitzhak Shamir. However, the Israeli government did win the repeal of United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, which equated Zionism with racism. After the conference, in December 1991, the UN passed United Nations General Assembly Resolution 46/86; Israel had made revocation of resolution 3379 a condition of its participation in the Madrid peace conference.[71] After the Labor Party won the 1992 election, U.S.–Israel relations appeared to improve. The Labor coalition approved a partial housing construction freeze in the occupied territories on July 19, something the Shamir government had not done despite Bush Administration appeals for a freeze as a condition for the loan guarantees.
Clinton administration (1993–2001)

Israel and the PLO exchanged letters of mutual recognition on September 10, and signed the Declaration of Principles on September 13, 1993. President Bill Clinton announced on September 10 that the United States and the PLO would reestablish their dialogue. On October 26, 1994, President Clinton witnessed the Jordan–Israeli peace treaty signing, and President Clinton, Egyptian president Mubarak, and King Hussein of Jordan witnessed the White House signing of the September 28, 1995, Interim Agreement between Israel and the Palestinians.[67]

President Clinton attended the funeral of assassinated Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin in Jerusalem in November 1995. Following a March 1996 visit to Israel, President Clinton offered $100 million in aid for Israel's anti-terror activities, another $200 million for Arrow anti-missile deployment, and about $50 million for an anti-missile laser weapon.[67]
President Clinton disagreed with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu's policy of expanding Jewish settlements in the Palestinian territories, and it was reported that the President believed that the Prime Minister delayed the peace process. President Clinton hosted negotiations at the Wye River Conference Center in Maryland, ending with the signing of an agreement on October 23, 1998. Israel suspended implementation of the Wye agreement in early December 1998, when the Palestinians violated the Wye Agreement by threatening to declare a state (Palestinian statehood was not mentioned in Wye). In January 1999, the Wye Agreement was delayed until the Israeli elections in May.[67]
Ehud Barak was elected prime minister on May 17, 1999, and won a vote of confidence for his government on July 6, 1999. President Clinton and Prime Minister Barak appeared to establish close personal relations during four days of meetings between July 15 and 20. President Clinton mediated meetings between Prime Minister Barak and Chairman Arafat at the White House, Oslo, Shepherdstown, Camp David, and Sharm al-Shaykh in the search for peace.[67]
George W. Bush administration (2001–2009)

President George W. Bush and Prime Minister Ariel Sharon established good relations in their March and June 2001 meetings. On October 4, 2001, shortly after the September 11 attacks, Sharon accused the Bush Administration of appeasing the Palestinians at Israel's expense in a bid for Arab support for the U.S. anti-terror campaign.[72] The White House said that the remark was unacceptable. Rather than apologize for the remark, Sharon said that the United States failed to understand him. Also, the United States criticized the Israeli practice of assassinating Palestinians believed to be engaged in terrorism, which appeared to some Israelis to be inconsistent with the U.S. policy of pursuing Osama bin Laden "dead or alive".[73] Nonetheless, it was later revealed that Sharon obtained an understanding from the Bush administration that the U.S. government would provide support for Israel while it undertook an extensive campaign of targeted assassinations against Palestinian militants, in exchange for an Israeli undertaking to desist from continuing with the creation of further settlements in the West Bank.[74]
In 2003, in the middle of the Second Intifada and a sharp economic downturn in Israel, the U.S. provided Israel with $9 billion in conditional loan guarantees made available through 2011 and negotiated each year at the U.S.–Israel Joint Economic Development Group.[75]
All recent U.S. administrations have disapproved of Israel's settlement activity as prejudging final status and possibly preventing the emergence of a contiguous Palestinian state. However, President Bush noted in an April 14, 2002 Memorandum which came to be called "the Bush Roadmap" (and which established the parameters for subsequent Israel-Palestinian negotiations) the need to take into account changed "realities on the ground, including already existing major Israeli population centers", as well as Israel's security concerns, asserting that "It is unrealistic to expect that the outcome of final status negotiations will be full and complete return to the armistice lines of 1949."[76] He later emphasized that, within these parameters, details of the borders were subjects for negotiations between the parties.
At times of violence, U.S. officials have urged Israel to withdraw as rapidly as possible from Palestinian areas retaken in security operations. The Bush Administration insisted that United Nations Security Council resolutions be "balanced" by criticizing Palestinian as well as Israeli violence, and it vetoed resolutions which did not meet that standard.[77]
Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice did not name a Special Middle East Envoy and did not say that she would not get involved in direct Israeli-Palestinian negotiations of issues. She said that she preferred to have the Israelis and Palestinians work together, traveling to the region several times in 2005. The Administration supported Israel's disengagement from Gaza as a way to return to the Road Map process to achieve a solution based on two states, Israel and Palestine, living side by side in peace and security.[78] The evacuation of settlers from the Gaza Strip and four small settlements in the northern West Bank was completed on August 23, 2005.
During 2006 Israel–Lebanon conflict
Military relations

On July 14, 2006, as the 2006 Lebanon War broke out, the U.S. Congress was notified of a potential sale of $210 million worth of jet fuel to Israel. The Defense Security Cooperation Agency noted that the sale of the JP-8 fuel, should it be completed, will "enable Israel to maintain the operational capability of its aircraft inventory", and that "The jet fuel will be consumed while the aircraft is in use to keep peace and security in the region".[79] It was reported on July 24 that the United States was in the process of providing Israel with "bunker buster" bombs, which would allegedly be used to target the leader of Lebanon's Hezbollah guerrilla group and destroy its trenches.[80]
American media also questioned whether Israel violated an agreement not to use cluster bombs on civilian targets. Although many of the cluster bombs used were advanced M-85 munitions developed by Israel Military Industries, Israel also used older munitions purchased from the U.S. Evidence during the conflict, hitting civilian areas, although the civilian population had mostly fled. Israel asserts that civilian damage was unavoidable, as Hezbollah ensconced itself in highly populated areas. Simultaneously, indiscriminate Hezbollah rocket fire turned many of its northern towns into virtual ghost towns, in violation of international law. Many bomblets remained undetonated after the war, causing hazard for Lebanese civilians. Israel said that it had not violated any international law because cluster bombs are not illegal and were used only on military targets.[81]
Opposing immediate unconditional ceasefire
On July 15, the United Nations Security Council again rejected pleas from Lebanon that it call for an immediate ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon. The Israeli newspaper Haaretz reported that the U.S. was the only member of out the 15-nation UN body to oppose any council action at all.[82]
On July 19, the Bush administration rejected calls for an immediate ceasefire.[83] Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice said that certain conditions had to be met, not specifying what they were. John Bolton, U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations, rejected the call for a ceasefire, on the grounds that such an action addressed the conflict only superficially: "The notion that you just declare a ceasefire and act as if that is going to solve the problem, I think is simplistic."[84]
On July 26, foreign ministers from the U.S., Europe, and the Middle East that met in Rome vowed "to work immediately to reach with the utmost urgency a ceasefire that puts an end to the current violence and hostilities". However, the U.S. maintained strong support for the Israeli campaign, and the conference's results were reported to have fallen short of Arab and European leaders' expectations.[85]
U.S. veto of Israeli strikes on Iranian nuclear facilities
In September 2008, The Guardian reported that the U.S. vetoed Israeli prime minister Ehud Olmert's plan to bomb Iranian nuclear facilities the previous May.[86]
Obama administration (2009–2017)

Israeli–U.S. relations came under increased strain during Prime Minister Netanyahu's second administration and the new Obama administration. After he took office, President Barack Obama made achieving a peace deal between Israel and the Palestinians a major goal, and pressured Prime Minister Netanyahu into accepting a Palestinian state and entering negotiations. Netanyahu eventually conceded on July 14, 2009. In accordance with U.S. wishes, Israel imposed a ten-month freeze on settlement construction in the West Bank. As the freeze did not include East Jerusalem, which Israel regards as its sovereign territory, or 3,000 pre-approved housing units already under construction, as well as the failure to dismantle already-built Israeli outposts, the Palestinians rejected the freeze as inadequate, and refused to enter negotiations for nine months. Palestinian negotiators signaled a willingness to enter into negotiations weeks before the end of the construction freeze if they were to be extended, but this was rejected by the Israelis.
In 2009, Obama became the first U.S. president to authorize the sale of bunker buster bombs to Israel. The transfer was kept secret to avoid the impression that the United States was arming Israel for an attack on Iran.[87]
In February 2011, the Obama administration vetoed a UN resolution declaring Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal.[88] In 2011, the Obama administration paved the way for the development and production of the Iron Dome missile defense system for Israel, contributing $235 million to its funding.[89][90]
In March 2010, Israel announced that it would continue to build 1,600 new homes that were already under construction in the eastern Jerusalem neighborhood of Ramat Shlomo, during Vice President Joe Biden's visit to Israel. The incident was described as "one of the most serious rows between the two allies in recent decades".[91] Secretary of State Hillary Clinton said that Israel's move was "deeply negative" for US–Israeli relations.[92] East Jerusalem is widely considered by the international community to be occupied territory, while Israel disputes this, as it annexed the territory in 1980.[91] Obama was reported to be "livid" over the announcement.[93]

Shortly afterward, President Obama instructed Secretary of State Hillary Clinton to present Netanyahu with a four-part ultimatum: that Israel cancel the approval of the housing units, freeze all Jewish construction in East Jerusalem, make a gesture to the Palestinians that it wants peace with a recommendation on releasing hundreds of Palestinian prisoners, and agree to discuss a partition of Jerusalem and a solution to the Palestinian refugee problem during the negotiations. Obama threatened that neither he nor any senior administration official would meet Netanyahu and his senior ministers during their upcoming visit to Washington.[94]
On March 26, 2010, Netanyahu and Obama met in the White House. The meeting was conducted without photographers or any press statements. During the meeting, Obama demanded that Israel extend the settlement freeze after its expiration, impose a freeze on Jewish construction in East Jerusalem, and withdraw troops to positions held before the start of the Second Intifada. Netanyahu did not give written concessions on these issues, and presented Obama with a flowchart on how permission for building is granted in the Jerusalem Municipality to reiterate that he had no prior knowledge of the plans. Obama then suggested that Netanyahu and his staff stay at the White House to consider his proposals so that he could inform Obama right away if he changed his mind, and was quoted as saying: "I'm still around, let me know if there is anything new". Netanyahu and his aides went to the Roosevelt Room, spent a further half-hour with Obama, and extended his stay for a day of emergency talks to restart peace negotiations, but left without any official statement from either side.[93][95]
In July 2010, a 2001 video of citizen Netanyahu surfaced; he was speaking to a group of bereaved families in Ofra about relations with the United States and the peace process, and reportedly unaware he was being recorded. He said: "I know what America is; America is a thing you can move very easily, move it in the right direction. They won't get in their way." He also bragged how he undercut the peace process when he was prime minister during the Clinton administration. "They asked me before the election if I'd honor [the Oslo accords]," he said. "I said I would, but ... I'm going to interpret the accords in such a way that would allow me to put an end to this galloping forward to the '67 borders."[96][97] While it created little stir in the press, it was heavily criticized among the Left in Israel.[98]
On May 19, 2011, Obama made a foreign policy speech in which he called for a return to the pre-1967 Israeli borders with mutually agreed land swaps, to which Netanyahu objected.[99] The Republicans criticized Obama for the speech.[100][101] The speech came a day before Obama and Netanyahu were scheduled to meet.[102] In an address to the American Israel Public Affairs Committee on May 22, Obama elaborated on his May 19 speech:
It was my reference to the 1967 lines—with mutually agreed swaps—that received the lion's share of the attention, including just now. And since my position has been misrepresented several times, let me reaffirm what "1967 lines with mutually agreed swaps" means.
By definition, it means that the parties themselves—Israelis and Palestinians—will negotiate a border that is different than the one that existed on 4 June 1967. That's what mutually agreed-upon swaps means. It is a well-known formula to all who have worked on this issue for a generation. It allows the parties themselves to account for the changes that have taken place over the last 44 years.
It allows the parties themselves to take account of those changes, including the new demographic realities on the ground, and the needs of both sides. The ultimate goal is two states for two people: Israel as a Jewish state and the homeland for the Jewish people and the state of Palestine as the homeland for the Palestinian people—each state in joined self-determination, mutual recognition and peace.[103]
In his speech to a joint session of congress on May 24, Netanyahu adopted some of Obama's earlier language:
Now the precise delineation of those borders must be negotiated. We'll be generous about the size of the future Palestinian state. But as President Obama said, the border will be different than the one that existed on 4 June 1967. Israel will not return to the indefensible boundaries of 1967.[103]
On September 20, 2011, President Obama declared that the U.S. would veto any Palestinian application for statehood at the United Nations, asserting that "there can be no shortcut to peace".[104]
In October 2011, the new American defense secretary, Leon Panetta, suggested that Israeli policies were partly responsible for its diplomatic isolation in the Middle East. The Israeli government responded that the problem was the growing radicalism in the region, rather than their own policies.[105]
In 2012, President Obama signed into law a bill that would extend by another three years the program of United States guarantees for Israeli government debt.[106]
Antony Blinken, National Security Advisor to then-U.S. vice president Joe Biden, lamented in 2012 a tendency by U.S. politicians to use the debate over policy toward Israel for political purposes. Until then, Israel had been a bastion of bipartisan consensus in the U.S.[107]
In 2010 and again in July–August 2012, Israeli exports to the United States surpassed those to the European Union, usually the top destination for Israeli exports.[108]
Reaction in Israel was mixed to the Geneva interim agreement on the Iranian nuclear program. Prime Minister Netanyahu strongly criticized it as a "historic mistake",[109] and finance minister Naftali Bennett called it a "very bad deal".[110] However, Kadima Party leader Shaul Mofaz,[111] opposition leader Isaac Herzog,[112] and former Aman chief Amos Yadlin voiced some measure of support for the agreement and suggested that it was more important to maintain good ties to Washington than to publicly rebuke the agreement.[113] According to CNN reporter, Stephen Collinson, Netanyahu's years of meddling in U.S. politics on Iran nuclear program, have alienated many Democrats, and their party's shift to the left has further eroded support for Israel.[114]

On April 2, 2014, U.S. ambassador to the UN Samantha Power reaffirmed the administration's stand that the U.S. opposes all unilateral Palestinian moves to statehood.[115]
During the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict, United States temporarily halted a supply of Hellfire missiles to Israel, sparking tensions between the two countries.[116]
In December 2014, Congress passed the United States–Israel Strategic Partnership Act of 2013.[117] This new category is one notch above the Major Non-NATO Ally classification and adds additional support for defense, energy, and strengthen cooperation business and academics.[118] The bill additionally calls for the U.S. to increase their war reserve stock in Israel $1.8 billion.[119]
Bar Ilan's Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies conducted a study in November 2014 which showed that 96% of the Israeli public feels that the country's relations with the United States are important or very important. It was also felt that Washington is a loyal ally and that America will come to Israel's aid against existential threats. On the other hand, only 37% believe that President Obama has a positive attitude towards Israel (with 24% saying that his attitude is neutral).[120]
On December 23, 2016, the United Nations Security Council passed a resolution calling for an end to Israeli settlements; the Obama administration's UN ambassador, Samantha Power, was instructed to abstain—although the U.S. had previously vetoed a comparable resolution in 2011. President-elect Donald Trump attempted to intercede by publicly advocating the resolution be vetoed and successfully persuading Egypt's Abdel Fattah el-Sisi to temporarily withdraw it from consideration. The resolution was then "proposed again by Malaysia, New Zealand, Senegal and Venezuela"—and passed 14 to 0. Netanyahu's office alleged that "the Obama administration not only failed to protect Israel against this gang-up at the UN, it colluded with it behind the scenes," adding: "Israel looks forward to working with President-elect Trump and with all our friends in Congress, Republicans and Democrats alike, to negate the harmful effects of this absurd resolution."[121][122][123]
On December 28, 2016, U.S. secretary of state John Kerry strongly criticized Israel and its settlement policies in a speech.[124] Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu strongly criticized the UN Resolution[125] and Kerry's speech.[126] On January 6, 2017, the Israeli government withdrew its annual dues from the organization, which totaled $6 million in United States dollars.[127] On January 5, 2017, the United States House of Representatives voted 342–80 to condemn the UN Resolution.[128][129]
U.S.–Israel civilian nuclear deal 2010
According to Army Radio, the U.S. has reportedly pledged to sell Israel materials used to produce electricity, nuclear technology, and other supplies.[130]
First Trump administration (2017–2021)

Trump was inaugurated as U.S. president on January 20, 2017; he appointed a new ambassador to Israel, David M. Friedman. On January 22, 2017, in response to Trump's inauguration, the Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced his intention to lift all restrictions on construction in the West Bank.[131]
Former United States secretary of state Rex Tillerson has said that on May 22, 2017, Benjamin Netanyahu showed Donald Trump a fake and altered video of Palestinian president Mahmoud Abbas calling for the killing of children. This was at a time when Trump was considering if Israel was the obstacle to peace. Netanyahu had showed Trump the fake video to change his position in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.[132] In September 2017 it was announced that the U.S. would open their first permanent military base in Israel.[133]
On December 6, 2017, President Trump recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel.[134] The U.S. Embassy was opened in Jerusalem on May 14, 2018, the 70th anniversary of the Independence of Israel.[135]

In May 2018, President Trump withdrew the United States from the Iran nuclear deal a few days after Netanyahu gave a presentation in which he revealed documents that Mossad smuggled out of Tehran, purportedly showing that Iran lied about its nuclear program.[136] This was followed by a renewal of U.S. sanctions on Iran.[137]
On March 25, 2019, President Trump signed the United States recognition of the Golan Heights as part of Israel, in a joint press conference in Washington with Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu, making the U.S. the first country other than Israel themselves to recognize Israeli sovereignty over the Golan Heights.[138] Israeli officials had lobbied the United States into recognizing "Israeli sovereignty" over the territory.[139]
In August 2020, Trump, Netanyahu and Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan jointly announced the establishment of formal Israel–United Arab Emirates relations.[140] This was followed by Bahrain, Sudan and Morocco establishing relations with Israel through U.S. mediation.[141]
Biden administration (2021–2025)

Early in the Biden administration, the White House confirmed that the U.S. Embassy would remain in Jerusalem, which would remain recognised as the Capital. The administration also expressed support for the Abraham Accords while wanting to expand on them, although it shied away from using that name, instead referring to it simply as "the normalization process".[142][143][144]
On 13 May 2021, in the aftermath of the Al-Aqsa mosque conflict, the Biden administration was accused of being indifferent towards the violent conflict between Israeli statehood and the Palestinian minority there. Critics on both sides have identified the reaction by the White House as "lame and late".[145]
On 21 May 2021, a ceasefire was brokered between Israel and Hamas after eleven days of clashes. According to Biden, the U.S. will be playing a key role to rebuild damaged infrastructure in the Gaza alongside the Palestinian authority.[146][147]
In July 2022, President Biden and Secretary of State Antony Blinken visited Israel as part of a trip to the Middle East. During the official state visit in Jerusalem, Biden and then-Prime Minister Yair Lapid signed a joint declaration extending a 10-year, $38 billion defense package to Israel that had been signed in 2016 under the Obama administration. In addition, the declaration addressed global security issues, such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine and committed both sides to preventing Iran from obtaining a nuclear weapon.[148]
In an interview on Israel's Channel 12, Biden stated that "if that was the last resort" the United States would use force to achieve this[149] and that Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps would remain on the United States' Foreign Terrorist Organizations list even if that meant Iran did not return to the JCPOA under which Iran limited its nuclear program to slow its nuclear weapon program, in return for relief from economic sanctions.[150]
Biden and Lapid also opened the first meeting of I2U2 forum, together with the president of the United Arab Emirates, Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, and the prime minister of India, Narendra Modi, in a virtual conference during which the four countries agreed to collaborate further on issues including food security, clean energy, technology and trade, and reaffirmed their support for the Abraham Accords and other peace and normalization arrangements with Israel. The UAE pledged $2 billion for agricultural development in India using Israeli technologies.[148][151]

On 29 December 2022, after Netanyahu's right-wing government took office and approved the plan to change the structure of the Israeli judiciary, the value gap between many American Jews and Israel increased.[152] On 22 March 2023, the Biden administration summoned Israel's ambassador to the United States to the State Department, voicing its displeasure following the Knesset's passage of a law allowing the resettlement of illegal settlements in critical areas of the occupied West Bank that were evacuated in 2005.[153] The Israeli press considered such a meeting between the two countries very unusual and it reflects the deterioration of relations between the Biden government and the Netanyahu government.[153][154] On 29 March 2023, Biden announced that he does not intend to invite Netanyahu to the White House "in the near term".[155]
2023 Israel–Hamas war


After Hamas launched a surprise attack on Israel in October 2023, Biden issued a statement condemning the attacks and saying he was ready to offer "all appropriate means of support to the Government and people of Israel".[156] Twice in the two months following the attack, Biden publicly declared himself to be a Zionist.[157][158] On 18 October 2023, President Biden arrived in Israel and was received at Ben Gurion Airport by Israeli president Isaac Herzog and Prime Minister Netanyahu.[159] In October 2023, President Biden called on Congress to pass $14.3 billion in emergency military aid to Israel in its war with Hamas.[160] Israel launched a massive bombardment and an invasion of Gaza. The U.S. vetoed three United Nations Security Council resolutions calling for a ceasefire, for various reasons. Domestically, the war began to fracture the left and unite the right. Republicans largely supported Israel's counteroffensive and Netanyahu's government, while Democrats were divided over calls to pressure Israel for a ceasefire.[161] Many Democrats are debating making future U.S. military aid conditional on Israel's behavior in the West Bank and Gaza. According to Steven A. Cook, for the United States, a more normal bilateral relationship with Israel is likely to reduce the moral costs of military aid.[162]

As the war went on, Israel–U.S. relations began to become strained.[164][165] The U.S. government became more critical of Israel and its stance slowly began to change as Palestinian civilian casualties rose and opposition grew. On 8 February 2024, Biden called Israel's actions in Gaza "over the top".[166] Following this, the Biden administration issued a national security directive requiring written assurances from Israel (and other countries) that it was using U.S.-supplied weapons in line with international law.[167][168] On 20 February, the U.S. proposed a draft UN Security Council resolution, calling for a "temporary ceasefire in Gaza as soon as practicable, based on the formula of all hostages being released". It stated that an Israeli offensive on Rafah would have "serious implications" and "should not proceed under current circumstances".[169][170] On 4 March, U.S. vice president Kamala Harris called for "an immediate ceasefire" because of "the immense scale of suffering in Gaza". She said Israel must let more aid into Gaza and was imposing "unnecessary restrictions".[171] In a speech on 14 March, the U.S. Senate majority leader, Chuck Schumer, berated Netanyahu as an "obstacle to peace". He said that Netanyahu "has been too willing to tolerate the civilian toll in Gaza" and that "Israel cannot survive if it becomes a pariah".[172] Schumer added that if Netanyahu stayed in power after the war, "the United States will have no choice but to play a more active role in shaping Israeli policy by using our leverage to change the present course".[173] President Biden praised the speech and said Schumer's "serious concerns" are shared by many Americans.[172] On 25 March, the UN Security Council passed a resolution demanding an immediate temporary ceasefire. The U.S. abstained, allowing the resolution to pass.[174] The Israeli government berated the U.S. for not voting against the resolution, and called off a meeting between an Israeli delegation and U.S. officials in Washington.[175] The U.S. has also voiced its opposition to much of Israel's post-war plan for Gaza.[176] According to CNN's Stephen Collinson, there is a long-standing suspicion among observers in Washington that Netanyahu has a strong personal interest in continuing the war to make amends for his failure to prevent the 7 October attacks and to delay his legal process, as he is facing serious criminal charges.[177]
Economic relations
The United States and Israel's economic relations is currently centered around technology, with aircraft, machinery, diamonds, optic and medical instruments and agricultural products being the main sectors of American-Israeli trade.[178] The United States has provided economic aid to Israel from its founding, until the maturing and success of the Israeli economy with the hightech boom in the 1990s with the U.S. providing $30 billion until 2008 when the last batch of economic aid was provided.[179] Israel is the United States's 23rd largest trade partner as of 2015.[180] Bilateral trade volume in goods amounted to around $35 billion in 2023[181] and the U.S. is Israel's most important trading partner. Israel, accounting for 2.5% of the Middle East's population, imports 20% of American exports in the region.[11] Israel accounts for 50% of the Middle East's investment in the United States.[182] As of 2013, Israel's cumulative FDI in the United States was greater than China's and India's.[180]
The United States signed its first free trade agreement with Israel in 1985.[180] The free trade agreement with Israel supports the most American jobs relative to export dollars of all free trade agreements of the United States.[180] There are several regional American-Israeli chambers of commerce that make it easier for Israeli and American companies to expand into each other's markets. There is U.S.–Israel Joint Economic Development Group, founded in 1985. In the same year, the Israel–United States Free Trade Agreement was signed.
-
Tel Aviv, the center of Israel's Silicon Wadi
-
Israel is New York's fourth largest trade partner
Around 2,500 U.S. companies are active in Israel, and are employing 72,000 people there. Israel has more Nasdaq-listed companies than any other country except China, and U.S. venture capitalists are significant investors in Israel.[183] The United States is the most significant investor in Israel and in turn Israeli investment in the United States amounts to $41.6 billion as of 2021.[184] In California alone, in 2021 there were 140 Israeli companies, employing 6248 people, and paying around $615 million in salaries.[184] Israel, accounting for 2.5% of the Middle East's population imports 20% of American exports in the region.[11] Israel accounts for 50% of the Middle East's investment in the United States.[182] In 2017, the United States Chamber of Commerce launched "Business Israel" to enhance the commercial ties of all 50 states with Israel.[182] Israel and the U.S. hold the Joint Economic Development Group every year to discuss economic cooperation, the countries also work together on exchanges in the scientific and cultural fields.[185] Joint American Israeli projects such as BIRD, BARD and BSF which include scientific collaboration on various fields such as agriculture research and industrial research are held. BIRD received a $2 million investment, its projects have returned $1.7 to the U.S. economy.[180] An ESI study that was described as very conservative concluded that the three joint projects have resulted in 18,000-50,000 American jobs, however the study said the amount of American jobs produced could be about 200,000.[180] The economic addition to the American economy was valued at $7.7 billion.[180]
| 1985 | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. exports to Israel | 2.6 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 1.1 | 3.2 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 9.2 | 9.7 |
| U.S. imports from Israel | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 5.2 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 7.3 | 8.6 | 9.8 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 12.4 | 12.8 | 14.6 | 16.8 |
| Trade balance | 0.5 | −0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | −0.6 | −0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.0 | −0.2 | −0.1 | −0.4 | −1.3 | −1.6 | −2.2 | −2.2 | −4.5 | −5.4 | −5.9 | −5.4 | −7.1 |
| 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||||
| U.S. exports to Israel | 11.0 | 12.9 | 14.5 | 9.6 | 11.3 | 14.0 | 14.3 | 13.7 | 15.1 | 13.6 | 13.2 | 12.5 | 13.7 | 16.3 | 11.2 | 12.9 | 14.2 | 14.0 | |||
| U.S. imports from Israel | 19.2 | 20.8 | 22.3 | 18.7 | 21.0 | 23.0 | 22.1 | 22.8 | 23.0 | 24.5 | 22.2 | 21.0 | 21.8 | 19.5 | 15.3 | 18.7 | 21.4 | 20.8 | |||
| Trade balance | −8.2 | −7.9 | −7.8 | −9.2 | −9.7 | −9.1 | −7.9 | −9.0 | −7.9 | −11.0 | −9.0 | −9.4 | −8.1 | −3.1 | −4.0 | −5.8 | −7.2 | −6.8 |
Technology
Silicon Valley and Israel's Silicon Wadi have had interchangeable relations from the 1970s at least.[186] American technology companies have been prominent in Israel since that time, with Motorola being the first company to have entered Israel.[187] 300 American companies have established research and development centers in Israel,[10] including the likes of Apple, Microsoft, Intel, Cisco and IBM.[11] 18 of the 20 Californian companies investing in Israel were from the Bay Area, these Californian companies from 2003 to 2021 invested about $22.4 billion.[186] Intel is the largest private employer in the country, employing 14,000. Almost half of acquisitions of Israeli companies were by American companies.[186] Israeli companies that wish to go global usually work with American companies and transfer Israeli technology to the United States and create tens of thousands of jobs in the United States, according to the Washington Institute.[11] In total there are 650 Israeli technology companies operating in the United States.[9] Israeli partnerships tend to contribute niche sectors of the American economy, specifically technology related, although the Washington Institute found that the effect is positively multiplied beyond those sectors.[11] Israeli cooperation with the United States ranges from defense to agricultural research.[188]
Current affairs
United States aid
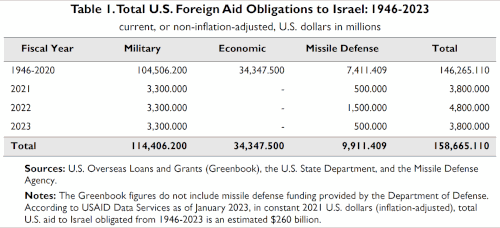
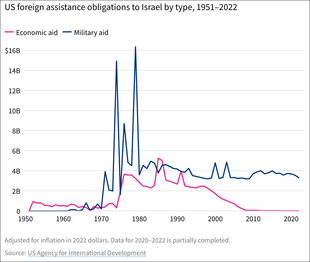

Since the 1970s, Israel has been one of the top recipients of United States foreign aid. In the past, a portion was dedicated to economic assistance, but all economic aid to Israel ended in 2007 due to Israel's growing economy.[190][191] Currently, Israel receives $3 billion annually in U.S. assistance through Foreign Military Financing (FMF).[192] Seventy-four percent of these funds must be spent on the acquisition of U.S. defense equipment, services, and training.[193] Thus, "United States military aid to Israel is seen by many as a subsidy for U.S. industries", according to Kenneth M. Pollack.[194]
FMF is intended to promote U.S. national security by contributing to global stability, strengthening military support for democratically elected governments and containing transnational threats, including terrorism and trafficking of weapons.[192] According to the United States Department of State, these grants enable U.S. allies to improve their defense capabilities and foster closer military relationships between the U.S. and recipient nations. Meanwhile, U.S. Senator Rand Paul (R-KY) has stated, in regards to U.S. foreign military financing to Israel, that "aid hampers Israel's ability to make its own decisions as it sees fit".[195]
In 1998, Israeli, congressional, and Administration officials agreed to reduce US$1.2 billion in Economic Support Funds (ESF) to zero over ten years, while increasing FMF from $1.8 billion to $2.4 billion. Separate from the scheduled cuts, there was an extra $200 million in anti-terror assistance, $1.2 billion to implement the Wye agreement, and the supplemental appropriations bill assisted for another $1 billion in FMF for the 2003 fiscal year. For the 2005 fiscal year, Israel received $2.202 billion in FMF, $357 million in ESF, and migration settlement assistance of $50 million. For 2006, the Administration has requested $240 million in ESF and $2.28 billion in FMF. H.R. 3057, passed in the House on June 28, 2005, and in the Senate on July 20, approved these amounts. House and Senate measures also supported $40 million for the settlement of immigrants from the former Soviet Union and plans to bring the remaining Ethiopian Jews to Israel.[citation needed]
Obama's Fiscal Year 2010 budget proposed $53.8 billion for appropriated international affairs' programs. From that budget, $5.7 billion was appropriated for foreign military financing, military education, and peacekeeping operations. From that $5.7 billion, $2.8 billion, almost 50%, was appropriated for Israel.[196] Israel also has available roughly $3 billion of conditional loan guarantees, with additional funds coming available if Israel meets conditions negotiated at the U.S.–Israel Joint Economic Development Group.
But Eli Lake, the national security correspondent of The Washington Times, reported on September 23, 2011, that Obama had authorized at the beginning of his presidency "significant new aid to the Israeli military that includes the sale of 55 deep-penetrating bombs known as bunker busters".[197]
Former head of the Israeli Air Force, retired major general Eitan Ben Eliyahu, has called the American sale of Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II nuclear capable stealth fighter bombers to Israel a key test of the relationship.[198]
While United States law forbids the use of offset agreements on FMF sales, Israel's Industrial Cooperation Authority attempts to secure industrial participation contracts of around 35 percent of such sales.[199]

In fiscal year 2013, the automatic U.S. budget sequestration process took effect as required by the Budget Control Act of 2011. The process cut appropriations for certain discretionary spending, which reduced foreign military aid to Israel by $157 million, and also reduced funding for Israeli and Israeli–U.S. missile defense programs by $32.7 million.[200]
In November 2013, Steven Strauss (a faculty member at the Harvard Kennedy School) published an editorial calling for the United States to phase out all grant aid to Israel. Strauss argues that the United States should retain a close relationship with Israel, but that Israel is affluent enough to pay for the military equipment it needs.[201]
In 2023, citing "the alarming actions of the new extreme right-wing Israeli government" against Palestinians, U.S. Representative Jamaal Bowman (NY-16) and Senator Bernie Sanders (I-VT)[a] released a letter signed by a dozen of congressional colleagues and supported by numerous advocacy organizations demanding the Biden administration to review the billions of dollars in largely unconditional arms support that the United States provides Israel annually.[202]
The Republican plan, approved by the United States House of Representatives, allocates $14.5 billion in military aid for Israel. Also, Israel has received the highest amount of military assistance from the U.S. compared to any other nation since World War II, with aid exceeding $124 billion.[203]
Settlements

The United States views the growth of Israeli settlements in the West Bank as an impediment to the success of peace negotiations, acknowledging that most world powers view the settlements as illegal. Israel, on the other hand, views the land as a security bulwark and religious Jewish Israelis hold the land is a God-given inheritance. Israel says that it plans to retain blocs of settlements in any peace treaty. In January 2015, Jewish settlers at the "Adei Ad illegal outpost"[204] threw stones at diplomats from a U.S. delegation who had arrived to inspect vandalism reported at a grove of Palestinian-owned trees in the occupied West Bank. It was reported that recently settlers were suspected of uprooting thousands of olive tree saplings, some of which had been planted in honor of senior Palestinian official Ziad Abu Ein, who collapsed and died after an altercation with an Israeli soldier. The American consulate came to inspect the grove because some of the land owners claim U.S. citizenship.[205][206] No injuries were reported.[207] A U.S. State Department spokesman, Jeff Rathke, said: "We can confirm a vehicle from the Consulate General was pelted with stones and confronted by a group of armed settlers today in the West Bank, near the Palestinian village of Turmus Ayya." He added that the U.S. is "deeply concerned" about the attack and that the Israeli authorities recognize "the seriousness of the incident".[208] A police spokeswoman said the police were investigating the incident and no arrests had been made.[209] The U.S. State Department has offered the Israeli authorities a videotape of the incident showing no American drew weapons. Yossi Dagan, head of the Shomron Regional Council, urged Interior Minister Gilad Erdan to expel the American delegation, stating that they were spies.[210] The incident is expected to chill the relationship between the United States and Israel, which is already strained, although this is the first known physical attack against American diplomatic staff.[211]
Nearly 90 US lawmakers sent a letter to Biden in late October 2024 asking him to sanction two far-right Israeli ministers for encouraging violence by Israeli settlers against Palestinian civilians in the occupied West Bank.[212]
Washington pressure towards peace talks with Syria
Syria has repeatedly requested that Israel re-commence peace negotiations with the Syrian government.[213] There is an ongoing internal debate within the Israeli government regarding the seriousness of this Syrian invitation for negotiations. Some Israeli officials asserted that there had been some unpublicized talks with Syria not officially sanctioned by the Israeli government.[214][215][216]
The United States demanded that Israel desist from even exploratory contacts with Syria to test whether Damascus is serious in its declared intentions to hold peace talks with Israel. U.S. secretary of state Condoleezza Rice was forceful in expressing Washington's view on the matter to Israeli officials that even exploratory negotiations with Syria must not be attempted. For years, Israel obeyed Washington's demand to desist from officially returning to peace talks.[213][217] However, around May 2008, Israel informed the U.S. that it was starting peace talks with Syria brokered by Turkey. Syria withdrew from the peace talks several months later in response to the Gaza War.
Washington brokers "peace process"

The United States has taken on the preeminent role in facilitating peace negotiations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. The U.S. has been criticized as acting as the attorney of the Israeli government rather than as an honest broker, catering and coordinating with the Israeli government at the expense of advancing the peace talks.[218] For example, under the U.S.–Israeli "no surprises" policy, the U.S. government must first check with the Israeli government any ideas for advancing the negotiations before publicly proposing them, which allegedly may have stripped the U.S. of the "independence and flexibility required for serious peacemaking".[218]
Military sales to China
Over the years, the United States and Israel have regularly discussed Israel's sale of sensitive security equipment and technology to various countries, especially the People's Republic of China. U.S. administrations believe that such sales are potentially harmful to the security of U.S. forces in Asia. China has looked to Israel to obtain technology it could not acquire from elsewhere, and has purchased a wide array of military equipment and technology, including communications satellites, and Harpy Killer unmanned aerial vehicles in 1999, and which China tested over the Taiwan Strait in 2004. In 2000, the United States persuaded Israel to cancel the sale of the Phalcon. The U.S. was also said to have demanded that Israel provide information on 60 recent arms deals with China, agree to U.S. supervision of arms deals which could be seen as "sensitive" to the U.S.[219]
Democracy
Murtaza Hussain of the Intercept argues that the crackdown on campus protests and other speech opposing Israel in the United States represents an attack on American democracy.[220] He cites a Human Rights Watch statement of concern about the crackdown on these peaceful protests in the United States.[220] He and Shadi Hamid argue that Israel has opposed democracy in the Middle East out of the fear of elections resulting in a hostile foreign policy towards Israel given its unpopularity in the region.[221] Hamid cites this as a source of tension between the United States and Israel over the last 20 years.[221]
Maintenance contract with Venezuela
On 21 October 2005, it was reported that pressure from Washington forced Israel to freeze a major contract with Venezuela to upgrade its 22 U.S.-manufactured F-16 fighter jets. The Israeli government had requested U.S. permission to proceed with the deal, but permission was not granted.[222]
Jerusalem



After capturing East Jerusalem in the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel annexed it and incorporated it into the Jerusalem Municipality, and has built neighborhoods as well as homes in Arab neighborhoods there, along with government offices. Israel has insisted that Jerusalem is its eternal and indivisible capital. The United States does not agree with this position and believes the permanent status of Jerusalem is still subject to negotiations.[citation needed] This is based on the UN's 1947 Partition plan for Palestine, which called for separate international administration of Jerusalem. This position was accepted at the time by most other countries and the Zionist leadership, but rejected by the local Arab leadership as well as Arab countries.[223] Most countries had located their embassies in Tel Aviv before 1967; Jerusalem was also located on the contested border. The Declaration of Principles and subsequent Oslo Accords signed between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization in September 1993 similarly state that it is a subject for permanent status negotiations. U.S. administrations have consistently indicated, by keeping the Embassy of the United States in Israel in Tel Aviv, that Jerusalem's status is unresolved.[citation needed] In 1999 both chambers of Congress recognized Jerusalem as the capital and in 2017, the United States president recognized Jerusalem as the capital of Israel and the embassy was moved to Jerusalem.[224]
In 1995, however, both houses of Congress overwhelmingly passed the Jerusalem Embassy Act to move the embassy to Jerusalem, no later than 31 May 1999, and suggested funding penalties on the State Department for non-compliance. Executive branch opposition to such a move, on constitutional questions of Congressional interference in foreign policy, as well as a series of presidential waivers, based on national security interests, have delayed from the Clinton Administration until 2017.[225][224]

The U.S. Consulate General in Jerusalem was first established in 1844, just inside the Jaffa Gate. A permanent consular office was established in 1856 in this same building. The mission moved to Street of the Prophets in the late 19th century, and to its present location on Agron Street in 1912. The consulate general on Nablus Road in East Jerusalem was built in 1868 by the Vester family, the owners of the American Colony Hotel. In 2006, the U.S. Consulate General on Agron Road leased an adjacent building, a Lazarist monastery built in the 1860s, to provide more office space.[226]
In March 2010, General David Petraeus was quoted by Max Boot saying the lack of progress in the Middle East peace process has "fomented anti-Americanism, undermined moderate Arab regimes, limited the strength and depth of U.S. partnerships, increased the influence of Iran, projected an image of U.S. weakness, and served as a potent recruiting tool for Al Qaeda".[227] When questioned by journalist Philip Klein, Petraeus said Boot "picked apart" and "spun" his speech. He believes there are many important factors standing in the way of peace, including "a whole bunch of extremist organizations, some of which by the way deny Israel's right to exist". He continued: "There's a country that has a nuclear program who denies that the Holocaust took place. So again we have all these factors in there. This [Israel] is just one."[228] U.S.–Israel relations came under strain in March 2010, as Israel announced it was building 1,600 new homes in the eastern Jerusalem neighborhood of Ramat Shlomo as Vice President Joe Biden was visiting.[229] Secretary of State Hillary Clinton described the move as "insulting".[229] Israel apologized for the timing of the announcement.
On 6 December 2017 U.S. President Donald Trump officially recognized Jerusalem as Israel's capital and announced his intention to move the American embassy to Jerusalem.[224] On 22 January 2018 Vice President Mike Pence in an address to the Israeli Knesset announced that the embassy would be moved before the end of 2019.[230] On 18 October 2018, Secretary of State Mike Pompeo announced that the U.S. Consulate-General in Jerusalem would be merged into the U.S. Embassy in Jerusalem. Hitherto, the consulate general had been responsible for conducting U.S. relations with the Palestinians.[231][232] In early March 2019, the consulate general was formally merged into the U.S. Embassy, ending the U.S. practice of assigning separate missions to the Israelis and Palestinians. The consulate general's former Agron Street site will be repurposed as the embassy's new Palestinian Affairs Unit.[233][234][235][236] In October 2024, the Knesset passed a bill banning the creation of new consulates in Jerusalem, in a move interpreted as blocking the creation of consular services for Palestinians in the city.[237]
Public opinion

Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
As of July 2006, a poll stated that 44% of Americans thought that the "United States supports Israel about the right amount", 11% thought "too little", and 38% thought "too much". The same poll asked "In general, do you favor or oppose the establishment of a Palestinian state that is recognized by the United Nations?" with 42% responding in the affirmative with 34% opposed.[240][241][242] Many in the United States question the levels of aid and general commitment to Israel, and argue that a U.S. bias operates at the expense of improved relations with various Arab states. Others maintain that democratic Israel is a helpful and strategic ally, and believe that U.S. relations with Israel strengthen the U.S. presence in the Middle East.[243] A 2002–2006 Gallup Poll of Americans by party affiliation (Republican/Democratic) and ideology (conservative/moderate/liberal) found that, although sympathy for Israel is strongest amongst the right (conservative Republicans), the group most on the left (liberal Democrats) also have a greater percentage sympathizing with Israel. Although proportions are different, each group has most sympathizing more with Israel, followed by both/neither, and lastly more with the Palestinians.[244] These findings support the view that support for Israel in the U.S. is bipartisan. A 2007 Gallup World Affairs poll included the annual update on Americans' ratings of various countries around the world, and asked Americans to rate the overall importance to the United States of what happens in most of these nations, according to that poll, Israel was the only country that a majority of Americans felt both favorably toward (63%) and said that what happens there is vitally important to the United States (55%).[245] A 2013 Gallup poll finds 64% of Americans sympathize with Israelis and 12% with Palestinians. Analysis of the poll data showed that Republicans, conservatives and older Americans were more likely to be partial to Israel. Republicans (78%) were much more likely to sympathize with Israel than Democrats (55%). Democratic support for Israel has increased by four percent since 2001, while Republican support for the Jewish state has jumped 18 percentage points in the same period. The percentage of respondents favoring the Palestinians increases with formal education, ranging from 8% of those with no college experience to 20% of postgraduates. According to Gallup, Palestinians receive the highest sympathy from Democrats, liberals, and postgraduates, but even among these, support tops off at 24%.[246][247] According to a 2013 BBC World Service Poll, the United States is the only Western country surveyed holding favorable views of Israel, and the only country in the survey with a majority of positive ratings, with 51% of Americans viewing Israel's influence positively and 32% expressing a negative view.[248]

Israeli attitudes toward the U.S. are largely positive. In several ways of measuring a country's view of America (American ideas about democracy; ways of doing business; music, movies, and television; science and technology; and spread of U.S. ideas), Israel came on top as the developed country who viewed it most positively.[249]
A 2012 report from The David Project, an Israel advocacy organization in the U.S., found that the strongest anti-Israel behaviour in America is found in universities. Quoting the experience of Jewish students who felt largely comfortable in American universities, the report denied that anti-Israeli feelings were based on antisemitism, as commonly believed. Instead the problem was said to lie in a "drip-drip negativity" about Israel that threatened to erode support over the long term, and might eventually spread from campuses to the population at large.[250] Amongst ethnic groups, the Hispanic and Latino population is believed to be the most hostile towards Israel, according to the Israel Project (TIP), a U.S. nonprofit organization active in Israel advocacy. According to TIP, Israel is more popular among older Americans, Republicans, conservatives and Evangelicals and less popular among "liberal elites", African Americans and Democrats.[251]
Mark Heller, the lead research associate at Tel Aviv's Institute for National Security Studies believes that the American public opinion has shifted over time against Israel and predicts that the relations between the country with the U.S. will deteriorate in the future. To compensate for this loss, he suggests that Israel should strengthen its ties with key Asian countries instead, because, in his view, the major Asian countries "don't seem to indicate much interest about how Israel gets along with the Palestinians, Arabs, or anyone else." He believes that countries like China, India and Singapore would be less committed to the types of liberal and humane concerns that occasionally affect Western policy and are less inclined to protest Israel's settlement construction and its policies towards Palestinians.[252]


In 2012 tensions emerged between the Emergency Committee for Israel and other Jewish charities it argued are hostile to Israel.[253] According to Paul Berger, The group's advertisements against Jewish charities it accuses of supporting anti-Israel organizations seemed unsuccessful. Several people quoted in the Emergency Committee for Israel's New York Times advertisement immediately distanced themselves from the publicity campaign. The Jewish groups the ads targeted reported little change in donor support.[254]
In December 2014, a public opinion poll of Israelis showed a majority of Israelis believe Israel's relationship with the U.S. is "in crisis". The survey found that 61.7 percent of respondents said there was a crisis in U.S.–Israel relations. Less than one quarter of respondents said the relations were "stable and good." A majority of people polled said that Netanyahu's government had "harmed" the relationship.[255] Despite the positive attitudes towards the U.S., the poll found that Israelis are generally mistrustful of the U.S. president, with only 37 percent of respondents calling Obama's views of Israel "positive," while 61% characterized his attitude towards Israel as "negative" or "neutral."[256]
A 2015 Bloomberg Politics poll of Americans asked "When it comes to relations between the U.S. and Israel, which of the following do you agree with more?" 47% of respondents chose "Israel is an ally but we should pursue America's interests when we disagree with them." 45% of respondents chose "Israel is an important ally, the only democracy in the region, and we should support it even if our interests diverge." 8% were unsure.[257]
According to Brookings Institution in 2023, American popular support for Israel has declined in recent years. A March 27-April 5, 2023 Ipsos/University of Maryland poll found that Americans most commonly describe Israel as either "a flawed democracy" or "a state with segregation similar to apartheid."[258]
In November 2023, a Gallup poll found that 50% of respondents in the United States supported Israel's actions in Gaza, while 45% disapproved.[259] The Marist Poll published on 15 November found that American respondents were more likely to sympathize with Israelis (61%) than Palestinians (30%).[260] According to the poll conducted by the Harvard CAPS–Harris Poll on January 17–18, 2024, 67% of American respondents said that a ceasefire in Gaza should only happen after all Israeli hostages are released and Hamas is removed from power. 74% of American respondents believed that the Hamas attack was genocidal, while 34% of respondents believed that Israel was committing genocide.[261]
According to a new poll from The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research, Americans are divided over whether Israel has gone too far in its response to last month's attack.[262]
Immigration
Israel is in large part a nation of Jewish immigrants. Israel has welcomed newcomers inspired by Zionism, the Jewish national movement. Zionism is an expression of the desire of many Jews to live in their historical homeland. The largest numbers of immigrants have come to Israel from countries in the Middle East and Europe.
The United States has played a special role in assisting Israel with the complex task of absorbing and assimilating masses of immigrants in short periods of time. Soon after Israel's establishment, President Truman offered $135 million in loans to help Israel cope with the arrival of thousands of refugees from the Holocaust. Within the first three years of Israel's establishment, the number of immigrants more than doubled the Jewish population of the country.
Mass immigrations have continued throughout Israeli history. Since 1989, Israel absorbed approximately one million Jews from the former Soviet Union. The United States worked with Israel to bring Jews from Arab countries,[citation needed] Ethiopia[citation needed] and the former Soviet Union[citation needed] to Israel, and has assisted in their absorption into Israeli society. In addition, there has been immigration between the two countries, with many American Jews immigrating to Israel annually, while the United States is the top destination for Israelis emigrating abroad (yerida) permanently or for an extended stay.
Corporate exchange
Several regional America–Israel Chambers of Commerce exist to facilitate expansion by Israeli and American companies into each other's markets.[263] American companies such as Motorola, IBM, Microsoft and Intel chose Israel to establish major R&D centers. Israel has more companies listed on the NASDAQ than any country outside North America.
Strategic cooperation

The U.S. and Israel are engaged in extensive strategic, political and military cooperation. This cooperation is broad and includes American aid, intelligence sharing, and joint military exercises. American military aid to Israel comes in different forms, including grants, special project allocations, and loans.
President Obama pledged to maintain Israel's "QME" over the other countries in the region.[264]
Memorandum of Understanding on security
To address threats to security in the Middle East, including joint military exercises and readiness activities, cooperation in defense trade and access to maintenance facilities. The signing of the Memorandum of Understanding marked the beginning of close security cooperation and coordination between the American and Israeli governments. Comprehensive cooperation between Israel and the United States on security issues became official in 1981 when Israel's defense minister Ariel Sharon and American secretary of defense Caspar Weinberger signed a Memorandum of Understanding that recognized "the common bonds of friendship between the United States and Israel and builds on the mutual security relationship that exists between the two nations". The memorandum called for several measures.
Missile defense program
One facet of the U.S.–Israel strategic relationship is the joint development of the Arrow Anti-Ballistic Missile Program, designed to intercept and destroy ballistic missiles. This development is funded by both Israel and the United States. The Arrow has also provided the U.S. with the research and experience necessary to develop additional weapons systems. So far, the development cost has been between $2.4 and $3.6 billion, with the United States picking up 50 percent of the final costs. The U.S. has notably provided funding for Israel's Iron Dome short-range missile defense system: from 2011 until 2022, the United States contributed a total of US$2.6 billion to the Iron Dome defense system.[265][266]
Counter-terrorism

In April 1996, President Bill Clinton and Prime Minister Shimon Peres signed the US–Israel Counter-terrorism Accord. The two countries agreed to further cooperation in information sharing, training, investigations, research and development and policymaking.
Homeland security
At the federal, state and local levels there is close Israeli–American cooperation on homeland security. Israel was one of the first countries to cooperate with the U.S. Department of Homeland Security in developing initiatives to enhance homeland security. In this framework, there are many areas of partnership, including preparedness and protection of travel and trade. American and Israeli law enforcement officers and Homeland Security officials regularly meet in both countries to study counter-terrorism techniques and new ideas regarding intelligence gathering and threat prevention.
In December 2005, the United States and Israel signed an agreement to begin a joint effort to detect the smuggling of nuclear and other radioactive material by installing special equipment in Haifa, Israel's busiest seaport. This effort is part of a nonproliferation program of the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration that works with foreign partners to detect, deter, and interdict illicit trafficking in nuclear and other radioactive materials.
Military bases
The United States maintains six War Reserve Stocks inside Israel, at Airwing 7 air base and maintains some $300 million in military equipment at these sites. The equipment is owned by the United States and is for use by American forces in the Middle East, but can also be transferred to Israeli use during a time of crisis. The United States is also alleged to keep fighter and bomber aircraft at these sites, and one of the bases is thought to contain a 500-bed hospital for U.S. Marines and Special Forces.[267] According to the American military journalist and commentator William Arkin in his book Code Names, the U.S. has prepositioned in at least six sites in Israel, munitions, vehicles, and military equipment, and even a 500-bed hospital, for use by U.S. Marines, Special Forces, and Air Force fighter and bomber aircraft in a wartime contingency in the Middle East.[18] Arkin in his book writes that some of the sites are located at Ben Gurion Airport, Nevatim, Ovda air base, and in Herzliya Pituah. The sites are numbered as "site 51," "site 53," "site 54," "site 55" and "site 56." Some of the depots are underground, others were built as open hangars. According to Arkin, site 51 holds ammunition and equipment in underground depots. Site 53 is munitions storage and war reserve vehicles at Israeli Air Force bases, site 54 is an emergency military hospital near Tel Aviv with 500 beds, and sites 55 and 56 are ammunition depots.[268] However, Israel is not the only country in the Middle East to host U.S. military bases; there are American facilities in Turkey, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia (mostly withdrawn from in 2003), Oman, and the Persian Gulf states of Kuwait, Bahrain (headquarters of the United States Fifth Fleet), Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. The Bahrain headquarters of the United States Fifth Fleet is meant to act as a watchdog and deterrent to potential Iranian aggression in the Persian Gulf region.[18]
The Israeli Mediterranean Port of Haifa hosts regular visits by navy vessels of the United States Sixth Fleet, which is headquartered in Naples, Italy.[269]
The Dimona Radar Facility is an American radar facility in the Negev desert of southern Israel, located near Dimona.[270] The facility has two 120-metre (400-foot) radar towers designed to track ballistic missiles through space and provide ground-based missiles with the targeting data needed to intercept them. It can detect missiles up to 2,400 kilometres (1,500 miles) away. The facility is owned and operated by the U.S. military, and provides only second-hand intelligence to Israel.[citation needed] The towers of the facility are the tallest radar towers in the world, and the tallest towers in Israel.
Intelligence relations
The United States and Israel have cooperated on intelligence matters since the 1950s. Israel was behind the disclosure of Kruschev's secret speech denouncing Stalin in 1956.[271] Throughout the Cold War, Israel provided the U.S. with information on Soviet-built weapons systems captured from the Arabs. Israel also provides the U.S. with much of its Middle Eastern human intelligence. The CIA became more reliant on Israeli intelligence following the Iranian Revolution and the 1983 Beirut barracks bombing.[272] Meanwhile, the U.S. provided Israel with satellite imagery, and in the early 1980s, the CIA reportedly began giving Israel intelligence that it denied its closest NATO allies. In particular, Israel received almost unlimited access to intelligence from the KH-11 Kennan military satellite, though Israeli access was more restricted following Operation Opera.
The National Security Agency has acknowledged that it provides to Israel raw unfiltered information intercepts that include private details and messages of American citizens.[273]
American espionage against Israel
Despite intense intelligence cooperation, both countries have been heavily engaged in espionage operations against one another. The United States has mainly tried to penetrate Israel's political, military and intelligence circles and gather information on Israel's alleged nuclear and non-conventional capabilities, while Israel has also penetrated the U.S. government, and has engaged in industrial espionage in the United States in an attempt to boost its military and alleged nuclear capabilities.[274][275][276] In a most notable and publicized espionage case, Jonathan Pollard, a civilian analyst working for U.S. naval intelligence, was arrested in 1985 and charged with conveying highly classified documents to Israeli agents. He pleaded guilty to one count of conspiracy to deliver national defense information to a foreign government, and was sentenced to life imprisonment. Israel later granted him citizenship, and has periodically requested his release.
In 1996, two espionage scandals broke. It was revealed that the National Security Agency wiretapped the phone lines to Israel's embassy in Washington and broke the Israeli security code, exposing Israel's deepest policy secrets to the United States. The wiretapping was discovered following the widely publicized "Mega Scandal", when a phone call intercepted by the NSA became public. Due to Israel's expertise in computers and electronics and the sophistication of its electronic code system, it was widely believed that the NSA used an Israeli mole to obtain the security code. The resulting "Mega Scandal" was the allegation that Israeli intelligence had a highly placed mole within the U.S. government.[277]
On 10 November 2004, a U.S. submarine entered Israeli territorial waters eighteen kilometers off the coast of Haifa. The submarine's mission was never revealed. It was thought to have been trying to gather intelligence on the city's naval base and headquarters and other vital infrastructure, and was also suspected of intending to intercept Israeli naval electronic signals and test Israel's response to an intrusion. It also may have been trying to install sensors near Israeli naval headquarters and other vital installations. Minutes after it entered Israeli waters, the submarine was detected and tracked by the Israeli Navy. The submarine was initially identified as belonging to a NATO power, and later confirmed to be American. The Israeli General Staff refrained from ordering an attack on what was considered the asset of a friendly nation. After several hours, the submarine submerged and fled, presumably determining that it was under surveillance. The Israeli Navy then sent fast patrol craft, missile boats, and helicopters in pursuit. The submarine was not found, but military sources maintained that the submarine had failed to complete its mission.[278][279] According to Israeli officials, such spy missions were common, and Western spy submarines had been intercepted by Israel before.[280]
In December 2013, documents released by whistle-blower Edward Snowden revealed that in January 2009 the NSA and its British counterpart GCHQ had spied on an email address belonging to Israeli prime minister Ehud Olmert, and had monitored email traffic between then-Israeli defense minister Ehud Barak and his chief of staff, Yoni Koren.[281]
Israeli espionage against the United States
"The Israelis are pretty aggressive" when it comes to espionage, including against the United States. "They're all about protecting the security of the Israeli state and they do whatever they feel they have to achieve that objective," according to a former senior U.S. intelligence official.[282] In May 2014, a U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) document leaked by Edward Snowden and published by journalist Glenn Greenwald revealed the CIA was concerned that Israel had set up an extensive spying network in the United States. Defense secretaries from both countries denied the claim with Chuck Hagel saying he had no facts to substantiate the report, while Moshe Ya'alon said he was never allowed to spy on the United States while he was head of the Israeli intelligence services, "and as defense minister I don't allow spying on the United States whatsoever."[283]
After a careful study over a two-year period ending in September 2019, the United States intelligence community and FBI concluded that it "was pretty clear that the Israelis were responsible" for cellphone surveillance devices near the White House and other sensitive Washington, D.C.-area locations, according to several former senior U.S. officials.[who?][284][282] The Israeli agents placed Stingray phone trackers, which are miniature surveillance devices that act like ordinary cellphone towers, fooling cellphones in the area into providing their identity and location data and capturing the contents of telephone calls and other data. The devices were configured to gather information on the American president and his top aides (including Rudy Giuliani), an operation made easier by President Trump's failure to observe White House telecommunications security protocols. Publicly unknown is whether or to what extent Israel succeeded in gathering such information. In response, Israeli officials categorically strongly denied the allegation that Israel conducts espionage against the United States. President Trump stated he finds the story "hard to believe." However, U.S. officials with extensive intelligence experience derided the perfunctory Israeli denials.[282]
The U.S. journalists Dylan Howard, Melissa Cronin and James Robertson linked the Mossad to American sex offender Jeffrey Epstein in their book Epstein: Dead Men Tell No Tales. They relied for the most part on the former Israeli intelligence officer Ari Ben-Menashe.[285] According to him, Epstein's activities as a spy served to gather compromising material on powerful people in order to blackmail them.[286] Epstein's victim Virginia Giuffre also alleged Epstein to be an intelligence asset, linking on Twitter to a Reddit page, that alleged Epstein being a spy, running a blackmail operation.[287]
Visa Waiver Program
Israel applied to join the U.S. government's Visa Waiver Program in 2005. Under this program, citizens of selected countries can enter the United States for up to 90 days for tourism and business purposes without having to apply for an entry visa. The House of Representatives approved the bid, but the Senate rejected it. Israel failed to fulfill two basic requirements; not all citizens owning a biometric passport, and the entry visa rejection rate for Israelis exceeded 3%. In addition, the United States insisted that Palestinian Americans entering Israel not be subjected to any more security checks than other U.S. citizens.[288] In January 2013, a new bill was submitted to the House calling for Israel's inclusion, with its supporters saying Israel now meets the program's current criteria.[289] As of 2014, Israel regularly bars the entry of American citizens.[290]
Israeli judicial reform
The Biden administration objects to the Netanyahu government's plans for a "judicial reform", and has expressed as much on several occasions.[291][292]
See also
- Boycotts of Israel#United States
- Israel lobby in the United States
- Israel–Russia relations
- Israeli Americans
- Lavon Affair
- The Apollo Affair
- IMI Desert Eagle
- Iron Dome
- America–Israel Friendship League
- United States ambassador to Israel
- United States security assistance to the Palestinian National Authority
- International recognition of Israel
- United States support for Israel in the 2023 Israel–Hamas war
Notes
- ^ Sanders caucuses with the Democrats in the Senate, however is not formally a member of that party.
References
- ^ a b "U.S. Relations with Israel". United States Department of State. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ "Friends with Benefits: Why the U.S.-Israeli Alliance Is Good for America | The Washington Institute". www.washingtoninstitute.org. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ "American Israel Public Affairs Committee Political Action Committee". Federal Election Commission. Retrieved March 8, 2022.
- ^ Bennis, Phyllis (July 15, 2014). "Why Opposing the Israel Lobby Is No Longer Political Suicide". The Nation. Retrieved September 1, 2022.
- ^ Hussain, Murtaza (November 18, 2023). "Meet the Secret Donors Who Fund AIPAC's Israel Trips for Congress". The Intercept. Retrieved August 9, 2024.
- ^ a b c US Foreign Aid to Israel. Updated February 18, 2022
- ^ "Israel Gives Much More to the U.S. Economy Than You Imagined". The Tower. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Relations with Israel". State.gov. January 30, 2023. Retrieved April 23, 2023.
- ^ a b Mizroch, Amir. "The Shared Tech Roots Of Silicon Valley and Israel's Startup Nation". Forbes. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- ^ a b International Trade Administration (.gov) Israel - Information Communication Technology ICT
- ^ a b c d e f "An Expanded Agenda for U.S.-Israel Partnership: New Technologies, New Opportunities | The Washington Institute". www.washingtoninstitute.org. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- ^ Okhovat, Sahar. "The United Nations Security Council: Its Veto Power and Its Reform" (PDF). Sydney.edu.au. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "RUSI – Middle East Peace: The Principles behind the Process". RUSI. Archived from the original on October 23, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "What does US recognition of Jerusalem as Israel's capital mean?". The Guardian. December 6, 2017. Retrieved May 25, 2021.
- ^ Etzion, Eran. "Israeli-Russian Relations: Respect and Suspect | Middle East Institute". Mei.edu. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- ^ Mitchell, Lincoln (January 22, 2015). "If U.S. Support Weakens, Will Israel Turn to Russia?". Observer. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
- ^ a b c Israeli-United States Relations Archived 4 November 2002 at the Wayback Machine (Adapted from a report by Clyde R. Mark, Congressional Research Service. Updated 17 October 2002)
- ^ a b c "Top Secret American Military Installations in Israel". Jonathanpollard.org. January 28, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Helms, Jesse (January 11, 1995). "Jesse Helms: Setting the Record Straight". Middle East Quarterly (Interview). Vol. 2, no. 1. Interviewed by Daniel Pipes; Patrick Clawson. Middle East Forum. Retrieved 2018-06-01.
- ^ Josef Fraenkel, Patriot, Judge, and Zionist
- ^ Jeffrey S. Gurock, American Zionism: mission and politics, p. 144, citing Jacob De Haas, Louis D. Brandeis (New York: 1929) and Chaim Weizmann, Trial and Error (Philadelphia:1949). vol. I, p. 165
- ^ Walworth (1986) 473–83, esp. p. 481; Melvin I. Urofsky, American Zionism from Herzl to the Holocaust, (1995) ch. 6; Frank W. Brecher, Reluctant Ally: United States Foreign Policy toward the Jews from Wilson to Roosevelt. (1991) chapters 1–4.
- ^ Walter John Raymond, Dictionary of politics: selected American and foreign political and legal terms, p. 287
- ^ John Norton Moore, ed., The Arab Israeli Conflict III: Documents, American Society of International Law (Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1974), p. 107–8
- ^ Rubenberg, Cheryl (1986). Israel and the American National Interest: A Critical Examination. University of Illinois Press. p. 27. ISBN 0-252-06074-1.
- ^ American Jewish Year Book Vol. 45 (1943–1944) Pro-Palestine and Zionist Activities, pp. 206–214 Archived August 3, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Michael Oren, Power, Faith and Fantasy, Decision at Biltmore, pp. 442–445: Convening in the art deco dining halls of New York's Biltmore Hotel in May 1942, Zionist representatives approved an eight-point plan that, for the first time, explicitly called for the creation of a "Jewish Commonwealth integrated in the structure of the new democratic world". Gone were the proposals for an amorphous Jewish national home in Palestine, for carving out Jewish cantons and delineating autonomous regions with an overarching Arab state. Similarly, effaced was the long-standing Zionist assumption that Palestine's fate would be decided in London. Instead, the delegates agreed that the United States constituted the new Zionist "battleground" and that Washington would have the paramount say in the struggle for Jewish sovereignty. Henceforth the Zionist movement would strive for unqualified Jewish independence in Palestine, for a state with recognized borders, republican institutions, and a sovereign Army, to be attained in cooperation with America.
- ^ Rubenberg, p.27-28
- ^ Lenczowski, George (1990). American Presidents and the Middle East. Duke University Press. p. 6. ISBN 0-8223-0972-6.
- ^ "The Recognition of the State of Israel Online Research File". Truman Library. Archived from the original on February 8, 2019. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "A/RES/181(II) of 29 November 1947". United Nations. 1947. Archived from the original on May 24, 2012. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ Lenczowski, American Presidents and the Middle East, p. 28, cite, Harry S. Truman, Memoirs 2, p. 158. The facts were that not only were there pressure movements around the United Nations unlike anything that had been seen there before, but that the White House, too, was subjected to a constant barrage. I do not think I ever had as much pressure and propaganda aimed at the White House as I had in this instance. The persistence of a few of the extreme Zionist leaders—actuated by a political motive and engaging in political threats—disturbed and annoyed me.
- ^ a b "The United States and the Recognition of Israel: A Chronology". Trumanlibrary.org. Archived from the original on October 31, 2012. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel". GxMSDev.
- ^ "Eliahu Epstein to Harry S. Truman with attachments re: recognition of Israel". trumanlibrary.org. Retrieved July 11, 2022.
- ^ United states de facto Regnition of State of Israel: 14 May 1948: Retrieved 7 April 2012
- ^ Avi Shlaim, "The Protocol of Sèvres, 1956: Anatomy of a War Plot" published in International Affairs, 73:3 (1997), pp. 509–530
- ^ Herbert Parmet, JFK: The Presidency of John F. Kennedy (1983) pp 225–35.
- ^ Avnery, Uri (September 24, 2016). [zope.gush-shalom.org/home/en/channels/avnery/1474654260/ "The Saga of Sisyphus"]. Gush Shalom. Retrieved January 22, 2023.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ Shannon, Vaughn P. (2003). Balancing Act: US Foreign Policy and the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. p. 55. ISBN 0754635910.
- ^ Zachary K. Goldman, "Ties that bind: John F. Kennedy and the foundations of the American–Israeli alliance: The Cold War and Israel." Cold War History 9.1 (2009): 23–58, quoting Ben-Zvi on p 25.
- ^ a b Jeremy Salt, The Unmaking of the Middle East: A History of Western Disorder in Arab lands (2008). p 201–203
- ^ Gerhard & Millington 1981, p. 26
- ^ Crewdson, John (2 October 2007). "New revelations in attack on American spy ship". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 4 October 2007.
- ^ Ofer, Aderet (July 11, 2017). "'But sir, it's an American ship.' 'Never mind, hit her!' When Israel attacked USS Liberty". Haaretz.
- ^ "Ex-Navy Official: 1967 Israeli Attack on U.S. Ship Was Deliberate". Fox News Channel. Associated Press. 23 October 2003. Archived from the original on 15 April 2008. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ^ George Lenczowski, American Presidents and the Middle East, Duke University Press, 1990, p. 105–115
- ^ a b How much aid does the US give to Israel? USAFacts. Updated on October 12, 2023.
- ^ "Israel's Intelligence Contribution to US Security: The Cold War Years". Begin-Sadat Center for Strategic Studies. February 26, 2018.
- ^ "U.S. Foreign Policy and Israel's Qualitative Military Edge". Washington Institute for Near East Policy.
- ^ "The Obama Administration's Approach to U.S.-Israel Security Cooperation: Preserving Israel's Qualitative Military Edge". U.S. Department of State.
- ^ "Israel's Qualitative Military Edge: Legislative Background". Archived from the original on February 22, 2018.
- ^ "Ensuring Israel's Qualitative Military Edge". Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Cohen, Avner (May 3, 2019). "How a Standoff with the U.S. Almost Blew up Israel's Nuclear Program". Haaretz.
- ^ "The National Security Archive".
- ^ The Ceasefire/Standstill Proposal, 19 June 1970, updated from archive.org 2014/9/30
- ^ William B. Quandt, Peace Process, American Diplomacy and the Arab-Israeli Conflict since 1967, p. 194 and ff. Begin himself explained Gahal's resignation from the government, saying "As far as we are concerned, what do the words 'withdrawal from territories administered since 1967 by Israel' mean other than Judea and Samaria. Not all the territories; but by all opinion, most of them."
- ^ Shibley Telhami, The Camp David Accords: A Case of International Bargaining, Columbia International Affairs Online. Log-in required.
- ^ Rabin, Yitzhak (1996). The Rabin Memoirs. University of California Press. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-520-20766-0.
security versus sovereignty"... Israel would have to accept Egyptian sovereignty over all the Sinai, while Egypt, in turn, would have to accept Israeli military presence in certain [Sinai] strategic positions.
- ^ Kissinger, Henry (May 24, 2011). Years of Upheaval. Simon and Schuster. pp. 252–. ISBN 978-1-4516-3647-5.
"She (Golda Meir) would be prepared to have me (Kissinger) continue to explore in private with Hafiz Ismail (the Egyptian delegate) some general principles of an overall settlement" this hint is compatible with Rabin description of Golda readiness for recognizing Egyptian sovereignty in Sinai
- ^ P.R. Kumaraswamy (January 11, 2013). Revisiting the Yom Kippur War. Routledge. pp. 105–. ISBN 978-1-136-32888-6.
In February 1973, Kissinger held talks with Sadat's National Security Advisor, Hafez Ismail. ... memoirs that Kissinger told him that, on the basis of his conversations with Hafez Ismail, Egypt might be ready to start negotiating if Israel acknowledged Egyptian sovereignty over all of Sinai. Rabin consulted with Prime Minister Golda Meir and told Kissinger that Israel authorized him to explore this approach.
- ^ Richard Bordeaux Parker (2001). The October War: A Retrospective. University Press of Florida. pp. 64–. ISBN 978-0-8130-1853-9.
Dinits evidence
- ^ Spiegel, Steven L. (October 15, 1986). The Other Arab-Israeli Conflict: Making America's Middle East Policy, from Truman to Reagan. University of Chicago Press. pp. 237–. ISBN 978-0-226-76962-2.
based on Rabin
- ^ Cohen, Avner. "The Last Nuclear Moment" The New York Times, 6 October 2003.
- ^ Farr, Warner D. "The Third Temple's Holy of Holies: Israel's Nuclear Weapons". Counterproliferation Paper No. 2, USAF Counterproliferation Center, Air War College, September 1999.
- ^ Rabin, Yitzak (1996), The Rabin Memoirs, University of California Press, p. 256, ISBN 978-0-520-20766-0
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k John E. Lang, Israeli-United States Relationship (2006) pp 24–26.
- ^ a b Michael Oren, Power, Faith and Fantasy, p. 569
- ^ "New World Order". Al-bab.com. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ Scott Lasensky, "Underwriting Peace in the Middle East: U.S. Foreign Policy and the Limits of Economic Inducements" Archived 13 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Middle East Review of International Affairs: Volume 6, No. 1, March 2002
- ^ 260 General Assembly Resolution 46-86- Revocation of Resolution 3379- 16 December 1991– and statement by President Herzog, 16 Dec 1991 Vol. 11–12: 1988–1992 and statement by President Herzog Archived 3 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs web site.
- ^ Sharon warns U.S. not to 'appease' Arabs. CNN, 5 October 2001
- ^ U.S. official criticizes targeted killings. Chicago Tribune, 28 August 2001
- ^ "How Arafat Eluded Israel's Assassination Machine". January 23, 2018 – via New York Times Magazine.
- ^ U.S. to give Israel $9 billion in loan guarantees, $1 billion in military aid. The Marker, 20 March 2003
- ^ Elliott Abrams, Tested by Zion: The Bush Administration and the Arab-Israeli Conflict (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2013)', pp. 105ff.
- ^ "U.S.: UN Resolutions Must Condemn Palestinian Terror". Haaretz. July 27, 2002. Retrieved January 23, 2017.
- ^ "Archives.gov". Georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ "Defense Security Cooperation Agency news release" (PDF). Dsca.mil. July 14, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 27, 2009. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
Transmittal No. 06-40
- ^ "Israel to get U.S. 'bunker buster' bombs – report" Archived August 8, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, Reuters, 24 July 2006
- ^ "US probes Israel cluster bomb use". Archived from the original on August 29, 2006. Retrieved August 29, 2006.
- ^ "Headlines for July 17, 2006". Democracy Now!. Archived from the original on August 2, 2006.
- ^ "Headlines for July 19, 2006". Democracy Now!. July 19, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2006.
- ^ "Headlines for July 20, 2006". Democracy Now!. Archived from the original on August 2, 2006.
- ^ "Rome talks yield no plan to end Lebanon fighting". Reuters. July 26, 2006. Archived from the original on July 10, 2006.
- ^ Steele, Jonathan (September 25, 2008). "Israel asked US for green light to bomb nuclear sites in Iran". The Guardian. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ "Israeli bunker-busters cause Mideast alarm" UPI, 28 September 2011.
- ^ "U.S. vetoes U.N. resolution declaring Israeli settlements illegal" CNN, 18 February 2011
- ^ Rosenbaum, Greg (June 23, 2015). "Obama Has a Stronger Record on Israel Than You Might Have Been Led to Think". Haaretz.
- ^ "Congress Appropriates $235 Million For Israeli Iron Dome Procurement". Defense Daily. January 24, 2014.
- ^ a b "US-Israel row: Israeli views". BBC News. March 24, 2010.
- ^ "Clinton rebukes Israel over homes". BBC News. March 12, 2010.
- ^ a b "Reports: Netanyahu 'Humiliated' by Obama Snub". Fox News Channel. March 26, 2010.
- ^ Glick, Caroline (March 19, 2010). "Column One: Obama's war on Israel". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ Whittell, Giles (March 26, 2010). "Binyamin Netanyahu humiliated after Barack Obama dumped him for dinner". The Times. London. Archived from the original on August 5, 2010.
- ^ Wong, Curtis (July 16, 2010). "Netanyahu In 2001: 'America Is A Thing You Can Move Very Easily'". HuffPost.
- ^ Kessler, Glenn (July 16, 2010). "Netanyahu: 'America is a thing you can move very easily'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on February 23, 2011.
- ^ Gideon Levy, Tricky Bibi, Haaretz, 15 July 2010, archived 11 November 2010
- ^ "Israel Objects to Obama Remarks on Borders". Voice of America. May 19, 2011. Archived from the original on May 28, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Was Obama's speech too tough on Israel? Republican criticism mounts". The Christian Science Monitor. May 19, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Virginia Republicans twist Obama's statement on Israel's borders". politifact virginia. May 31, 2011. Retrieved September 1, 2012.
- ^ Cooper, Helene (May 19, 2011). "Turning Point For 2 Leaders Lacking Trust". The New York Times. p. A1. Retrieved April 3, 2012.
- ^ a b Kessler, Glenn (May 25, 2011). "Michele Bachmann twists Obama's words on Israel". The Washington Post. Retrieved September 1, 2012.
- ^ "Obama: No shortcut to peace in Middle East" Associated Press 21 September 2011
- ^ Haddadi, Anissa. "Is the Netanyahu Administration Responsible for Israel's Regional Isolation?" International Business Times, 4 October 2011.
- ^ Ravid, Barak. "U.S. to grant three-year extension of loan guarantees to Israel" Haaretz, 24 January 2012.
- ^ Shalev, Chemi (February 28, 2012). "U.S. policy aimed at 'buying time' with Iran, says senior official". Haaretz. Retrieved March 6, 2012.
- ^ "Israeli exports to U.S. top those to EU for first time since 2010". Haaretz. October 7, 2012.
- ^ Booth, William (November 24, 2013). "Israel's Netanyahu calls Iran deal 'historic mistake'". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ Tova Dvorin (November 24, 2013). "Bennett: Iran Deal Could Cause US Nuclear Attack". Arutz Sheva. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ "Israel's security chiefs endorse new Iran agreement". United Press International. November 26, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ "New Labor leader Herzog criticizes Netanyahu and government over Iran deal". The Jerusalem Post. November 25, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ Cohen, Gili (November 24, 2013). "Former army intel chief: Iran deal better than alternative – no deal". Haaretz. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen (September 30, 2024). "Why America is looking increasingly powerless as Israel's war expands". CNN.
- ^ Riechmann, Deb (April 2, 2014). "Power: US Opposes Palestinian Moves to Statehood". ABC News. Washington. Associated Press. Archived from the original on April 3, 2014. Retrieved April 2, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Marissa (August 14, 2014). "Israeli official confirms US nixed arms shipment; pols argue over who's to blame". The Times of Israel. Retrieved February 28, 2021.
- ^ Wilner, Michael (December 4, 2014). "Congress enshrines Israel in a new class of ally". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Horovitz, David (December 4, 2014). "US Congress passes Israel strategic partnership bill". The Times of Israel. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "US Congress passes Israel strategic partnership bill". Yahoo! News. Agence France-Presse. December 3, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Poll: Israelis appreciate America, but Obama – not so much". Haaretz. December 3, 2014. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ^ "Egypt: Trump convinced Sisi to withdraw UN resolution". Al Jazeera. December 23, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^ "Egypt delays UN motion on Israel as Trump intervenes". BBC News. December 23, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^ "Israeli settlements: UN Security Council calls for an end". BBC News. December 23, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^ Sanger, David E. (December 28, 2016). "Kerry Rebukes Israel, Calling Settlements a Threat to Peace". The New York Times. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ Barak, Ravid (December 26, 2016). "Netanyahu on UN Settlement Vote: Israel Will Not Turn the Other Cheek". Haaretz. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ "Israel-Palestinians: Netanyahu Condemns John Kerry Speech". BBC. December 29, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ "Israel Halts $6 million to UN to Protest UN Settlements Vote". Fox News Channel. Associated Press. January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ "House Overwhelmingly Votes to Condemn UN Resolution on Israel Settlements". Fox News Channel. January 5, 2017. Retrieved January 7, 2017.
- ^ Cortellessa, Eric (January 6, 2017). "US House Passes Motion Repudiating UN Resolution on Israel". The Times of Israel. Retrieved January 17, 2017.
- ^ "Report: Secret document affirms U.S.-Israel nuclear partnership". Haaretz. July 7, 2010. Retrieved December 19, 2014.
- ^ "Netanyahu Pledges Unrestricted Construction in East Jerusalem, Settlement Blocs". Haaretz. January 22, 2017. Retrieved January 23, 2017.
- ^ "Netanyahu Used Doctored Video of Abbas to Influence Trump's Policy, Woodward Reveals". Haaretz. September 12, 2020. Retrieved March 8, 2021.
- ^ Wootliff, Raoul (September 18, 2017). "US establishes first permanent military base in Israel". The Times of Israel. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ Landler, Mark (December 6, 2017). "Trump Recognizes Jerusalem as Israel's Capital". The New York Times. Washington. Retrieved December 6, 2017.
- ^ "Editorial: On the 70th anniversary of the establishment of Israel, its people would do well to reflect on the peaceful spirit of the agreement". The Independent. London, England. May 12, 2018. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- ^ Fulbright, Alexander (July 17, 2018). "In recording, Netanyahu boasts Israel convinced Trump to quit Iran nuclear deal". The Times of Israel. Retrieved February 28, 2021.
- ^ "Trump administration to reinstate all Iran sanctions". BBC News. November 3, 2018. Retrieved February 28, 2021.
- ^ Landler, Mark; Halbfinger, David M. (March 25, 2019). "Trump, With Netanyahu, Formally Recognizes Israel's Authority Over Golan Heights". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved March 25, 2019.
- ^ Wilner, Michael (February 28, 2019). "GOP lawmakers introduce bill recognizing Israeli sovereignty over Golan". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved August 1, 2024.
- ^ Singman, Brooke (August 14, 2020). "Trump announces 'Historic Peace Agreement' between Israel, UAE". Fox News Channel. Retrieved August 16, 2020.
- ^ "Morocco latest country to normalise ties with Israel in US-brokered deal". BBC News. December 10, 2020.
- ^ "White House confirms Biden will keep embassy in Jerusalem". Roll Call. February 9, 2021.
- ^ Ravid, Barak (March 10, 2021). "Israel pushes White House ceremony to seal Sudan normalization deal". Axios.
- ^ Knickmeyer, Ellen; Batrawy, Aya; Kellman, Laurie. "Biden administration laying groundwork for push to expand Abraham Accords". The Times of Israel.
- ^ Gosh Bobby (May 13, 2021). "Biden's Response to the Israeli Crisis Is Late and Lame". Bloomberg (Opinion). Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "Israel-Hamas Cease-Fire Holds Despite Jerusalem Clashes" The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- ^ Alemany, Jacqueline (May 17, 2021). "Power Up: Biden administration approves $735 million weapons sale to Israel, raising red flags for some House Democrats". The Washington Post. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- ^ a b Magid, Jacob (July 13, 2022). "Biden to back renewing US defense package for Israel". The Times of Israel. Retrieved July 19, 2022.
- ^ Algemeiner, The (July 13, 2022). "Biden Says He Would Use Force as 'Last Resort' to Keep Iran From Nuclear Weapons". Algemeiner.com.
- ^ "Biden Says Iranian Military Unit Will Remain on US Terrorist List". Bloomberg. July 13, 2022.
- ^ "India, Israel, UAE, US hold first 'I2U2' meeting". The Jerusalem Post. July 14, 2022.
- ^ Al Lawati, Abbas (March 24, 2023). "Why American Jews are distancing themselves from Netanyahu's government". CNN.
- ^ a b Bassist, Rina (March 22, 2023). "US summons Israeli ambassador as law restraining settlers rescinded". Al-Monitor.
- ^ ToI Staff (May 3, 2023). "Netanyahu said blocking Gallant from visiting US until he gets an invite". The Times of Israel.
- ^ Al Jazeera Staff (March 29, 2023). "'Friends': White House downplays Biden-Netanyahu public spat". Al Jazeera.
- ^ "Biden offers Israel support, faces criticism on Iran at home". Reuters. October 8, 2023.
- ^ Spetalnick, Matt; Mason, Jeff; Holland, Steve; Zengerle, Patricia (October 23, 2023). "'I am a Zionist': How Joe Biden's lifelong bond with Israel shapes war policy". Reuters. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "'I am a Zionist,' says Biden at Hanukkah event, promises continued military assistance to Israel". The Times of Israel. December 12, 2023. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "Biden lands in Israel, hugs Netanyahu and Herzog on tarmac". Reuters. October 18, 2023.
- ^ Shear, Michael D.; Demirjian, Karoun (October 20, 2023). "Biden Requests $105 Billion Aid Package for Israel, Ukraine and Other Crises". The New York Times.
- ^ Artsy, Avishay (December 1, 2023). "How Israel fractured the left and united the right". Vox.
- ^ Cook, Steven A. (May 30, 2024). "After the war in Gaza, America's relationship with Israel has to change. Here's how".
- ^ Jones, Jeffrey M (March 27, 2024). "Majority in U.S. Now Disapprove of Israeli Action in Gaza". Gallup Poll. Retrieved March 28, 2024.
- ^ "Biden and Netanyahu's deepening rift on public display". BBC News. March 12, 2024.
- ^ "US-Israel relations tested as gap between President Biden, Netanyahu widens - analysis". The Jerusalem Post. March 20, 2024.
- ^ Abutaleb, Yasmeen (February 8, 2024). "Biden says Israel's military conduct in Gaza has been 'over the top'". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 11, 2024.
- ^ Abutaleb, Yasmeen (February 8, 2024). "Biden says countries receiving U.S. weapons must adhere to international law". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 11, 2024.
- ^ Ravid, Barak. "U.S. wants Israeli written assurances on using U.S. weapons in Gaza by mid-March". Axios. Retrieved February 28, 2024.
- ^ "US pushes for UN to support temporary Gaza ceasefire, oppose Rafah assault". Reuters. February 20, 2024.
- ^ "UN Security Council resolution proposed by US 'significant'". Al Jazeera. Retrieved February 20, 2024.
- ^ "US VP Harris calls for 'immediate' Gaza truce in rare rebuke of Israel". Al Jazeera. Retrieved March 4, 2024.
- ^ a b "Biden praises Schumer's "good speech" criticizing Netanyahu". CBS News. March 15, 2024.
- ^ "'No choice': Schumer highlights American aid to Israel". Al Jazeera. Retrieved March 16, 2024.
- ^ "UN Security Council demands 'immediate ceasefire' in Gaza, ending months-long deadlock". UN News. United Nations. March 25, 2024.
- ^ "UN Security Council passes resolution calling for Gaza ceasefire". BBC News. March 26, 2024.
- ^ "Netanyahu's post-war plan for Gaza Strip draws cool US reception". The Times of Israel. February 24, 2024.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen (September 30, 2024). "Why America is looking increasingly powerless as Israel's war expands". CNN.
- ^ U.S. Embassy in Israel (.gov) Policy & History - U.S. Embassy in Israel
- ^ U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
- ^ a b c d e f g "Israel Gives Much More to the U.S. Economy Than You Imagined". The Tower. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- ^ a b US Census Bureau. "Trade in Goods with Israel". www.census.gov. Retrieved July 13, 2024.
- ^ a b c BRILLIANT, MYRON (November 23, 2019). "Deepening the US-Israel relationship through business". The Hill.
- ^ "Fact Sheet U.S. – Israel Economic Relationship". U.S. Embassy in Israel. Retrieved July 13, 2024.
- ^ a b 2023 Investment Climate Statements: Israel, United States Department of State https://www.state.gov/reports/2023-investment-climate-statements/israel/
- ^ "U.S. Relations with Israel". United States Department of State. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- ^ a b c Silicon Valley to Silicon Wadi California’s Economic Ties with Israel, Bay Area Council Economic Institute, https://www.bayareaeconomy.org/files/pdf/SiliconValleyToSiliconWadi.pdf Foundations of Innovation: Israel’s Technology Ecosystem
- ^ Catherine de Fontenay and Erran Carmel, Israel’s Silicon Wadi: The forces behind cluster formation Archived 14 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine, June 2002
- ^ "Israel Gives Much More to the U.S. Economy Than You Imagined". The Tower. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- ^ U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel. Congressional Research Service report. March 1, 2023. By Jeremy M. Sharp.
- ^ Forbes (29 July 2007)."Israeli PM announces 30 billion US dollar US defence aid". Retrieved 3 August 2007.
- ^ The New York Times, 17 August 2007 "US and Israel sign Military deal". Retrieved 17 August 2007.
- ^ a b "Foreign Military Financing Account Summary". state.gov.
- ^ "US Senator Rand Paul set to visit Israel". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013.
- ^ Pollak, Kenneth (2003). Unthinkable: Iran, the Bomb, and American Strategy. Simon and Schuster. p. 360. ISBN 1476733929.
- ^ "Lawrence Solomon: Israel can live without U.S. aid". Opinion.financialpost.com. Archived from the original on September 14, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Office of Management and Budget". White House. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ Lake, Eli (September 23, 2011). "Obama Sold Israel Bunker-Buster Bombs". The Daily Beast. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
- ^ Ramirez, Luis. "Israeli Purchase of Fighter Jets Seen as Litmus Test for Continued US Support" Archived 30 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine Voice of America, 17 August 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ^ "Israel's Offsets Soar; More Local Firms Earn a Share". Defense News. Archived from the original on February 20, 2013.
- ^ Jeremy M. Sharp, U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel, Congressional Research Service (11 April 2014).
- ^ "Israel Has Reached Childhood's End – It's Time to End U.S. Aid to Israel". HuffPost. November 10, 2013.
- ^ "US Lawmakers Call on Biden to End US Taxpayer Support of Israeli Human Rights Violations". www.commondreams.org. Retrieved April 16, 2023.
- ^ US House passes $14.5bn military aid package for Israel aljazeera.com Retrieved 4 November 2023
- ^ Green, David B. (January 2, 2015). "Settlers Throw Stones at U.S. Consulate Convoy in West Bank". Haaretz. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Williams, Dan (January 2, 2015). "American Diplomatic Convoy Stoned by Jewish Settlers on West Bank". Forward.com. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Beaumont, Peter. "Israeli settlers stone two cars belonging to US consulate staff". The Guardian. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Tait, Robert (January 2, 2015). "Israeli settlers in stone-throwing confrontation with US diplomats". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on January 12, 2022.
- ^ Horovitz, David (January 2, 2015). "US 'deeply concerned' by settler attack on consulate staff". The Times of Israel. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Israeli Settlers Threw Stones at U.S. Diplomats' Cars". Newsweek. January 2, 2015. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Eichner, Itamar (January 3, 2015). "US embassy: Diplomats did not pull guns on settlers". Ynetnews. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Israel Police Say Settlers Attack US Officials in West Bank". The New York Times. January 2, 2015. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Nearly 90 lawmakers call on Biden to sanction Israeli ultranationalist ministers". Axios.
- ^ a b "??". The Times. UK. December 20, 2006. Archived from the original on May 22, 2011. Retrieved February 26, 2007. (subscription required)
- ^ "Syrians and Israelis 'held talks'", BBC, 16 January 2007
- ^ "Syrian, Israeli backdoor talks now emerging", The Christian Science Monitor, 18 January 2007
- ^ "Why can't they just make peace?", The Economist, 18 January 2007
- ^ "U.S. takes harder line on talks between Jerusalem, Damascus". Archived from the original on March 6, 2007. Retrieved March 8, 2007.
- ^ a b "Aaron David Miller – Israel's Lawyer". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Urquhart, Conal (June 13, 2005). "US acts over Israeli arms sales to China". The Guardian. London.
- ^ a b Hussain, Murtaza (May 8, 2024). "They Used to Say Arabs Can't Have Democracy Because It'd Be Bad for Israel. Now the U.S. Can't Have It Either". The Intercept. Retrieved August 4, 2024.
- ^ a b Hamid, Shadi (May 9, 2024). "Opinion | How Israel and the United States suppress democracy in the Middle East". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved August 4, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Forced Israel to Freeze Venezuelan F-16 Contract: Ministry – 10/21/05 10:01". DefenseNews.com. Archived from the original on July 24, 2012. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Why the 1947 UN Partition Resolution Must Be Celebrated | The Washington Institute". www.washingtoninstitute.org. Retrieved July 18, 2024.
- ^ a b c "President Donald J. Trump's Proclamation on Jerusalem as the Capital of the State of Israel". White House. December 6, 2017. Archived from the original on December 6, 2017. Retrieved December 6, 2017.
- ^ Dershowitz, Alan M.; Lazaroff, Tovah (November 22, 2009). "Background: Gilo is not a settlement, it's part of Jerusalem". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "About the U.S. Consulate". Jerusalem.usconsulate.gov. Archived from the original on July 7, 2010. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ Newlin, Eliza. "Petraeus Throws His Weight into Middle East Debate". Security.nationaljournal.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "From the Horse's Mouth: Petraeus on Israel". Commentary Magazine. March 25, 2010. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ a b Bowen, Jeremy (May 9, 2010). "Analysis: Bleak climate for Mid-East talks". BBC News. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- ^ "Remarks by Vice President Mike Pence in Special Session of the Knesset". whitehouse.gov. Retrieved March 26, 2018 – via National Archives.
- ^ Pompeo, Mike (October 19, 2018). "On the Merging of U.S. Embassy Jerusalem and U.S. Consulate General Jerusalem". U.S. Consulate General in Jerusalem. Archived from the original on February 11, 2019. Retrieved October 21, 2018.
- ^ Wilner, Michael (October 18, 2018). "U.S. merges Jerusalem embassy and consulate". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved October 21, 2018.
- ^ Palladino, Robert (March 4, 2019). "Merger of U.S. Embassy Jerusalem and U.S. Consulate General Jerusalem". U.S. Embassy in Israel. Archived from the original on March 6, 2019. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
- ^ "US closes Jerusalem consulate, demoting Palestinian mission". The Times of Israel. Associated Press. March 4, 2019. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
- ^ Hansler, Jennifer (March 4, 2019). "US Consulate in Jerusalem will merge with embassy". CNN. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
- ^ Keinon, Herb; Lazaroff, Tovah (March 4, 2019). "US Consulate for Palestinians to be merged with Embassy Monday". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
- ^ Lis, Jonathan; Shpigel, Noa. "Israel's Knesset Approves Bill to Block U.S. Consulate for Palestinians in Jerusalem". Haaretz. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ "Country Ratings". Gallup.com. Gallup, Inc. February 21, 2007. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ "U.S. Image Suffers as Publics Around World Question Trump's Leadership". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. Pew Research Center. June 26, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ "PollingReport compilation". Pollingreport.com.
- ^ "Cbs News Poll: Fighting in the Middle East" (PDF). CBS News. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Thoughts on aid". Americans-world.org. March 21, 2002. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Israel, the Palestinians". Pollingreport.com. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ [1] Archived 30 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, N. Korea, China Viewed as World Hot Spots". Gallup, Inc. February 21, 2007. Retrieved June 8, 2011.
- ^ "Americans' Sympathies for Israel Match All-Time High". Gallup. March 15, 2013.
- ^ "Poll: American sympathy for Israel at record high". The Jerusalem Post. March 15, 2013. Archived from the original on March 17, 2013.
- ^ "2013 World Service Poll (BBC)" (PDF). Globalscan.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 10, 2015. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Global Unease With Major World Powers | Pew Global Attitudes Project". Pewglobal.org. June 27, 2007. Archived from the original on February 22, 2023. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ Zeveloff, Naomi (February 22, 2012). "Anti-Israel attitudes spreading at U.S. universities, report says". Haaretz. Retrieved February 22, 2012.
- ^ Shalev, Chemi (February 14, 2012). "The Israel Project: 'American Hispanics are the most hostile toward Israel'". Haaretz. Retrieved March 2, 2012.
- ^ Chomsky, Noam; Wainwright, Joel; Nir, Oded (2018). ""There Are Always Grounds for Seeking a World That Is More Free and More Just": An Interview with Noam Chomsky on Israel, Palestine, and Zionism". Rethinking Marxism. 30 (3): 363–364. doi:10.1080/08935696.2018.1525966. ISSN 0893-5696. S2CID 149553671.
- ^ Berger, Paul (March 8, 2012). "Pro-Israel campaign caught between backlash and success". Haaretz. Retrieved March 9, 2012.
- ^ Berger, Paul (March 8, 2012). "Campaign Succeeds in Stirring Charity Pot". Forward.com. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Horovitz, David (December 16, 2014). "Poll: Most Israelis believe US-Israel ties in crisis". The Times of Israel. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Poll finds Israelis appreciate US support, wary of Obama's policies". The Times of Israel. December 5, 2014.
- ^ Talev, Margaret (April 15, 2015). "Bloomberg Politics National Poll Finds Deep Partisan Split on Israel and Iran". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on April 16, 2015.
- ^ Telhami, Shibley (April 25, 2023). "Is Israel a democracy? Here's what Americans think". Brookings Institution. Retrieved April 26, 2023.
It is clear that public attitudes about Israel are shifting. The term "apartheid" appears to have become a common term among many Americans, especially Democrats, and even the BDS movement, which has faced considerable obstacles in the American mainstream, seems to have sizable support among Democrats who expressed their opinion. A recent Gallup poll found that, for the first time in their years of polling on Israeli-Palestinian issues, more Democrats sympathize with the Palestinians than with Israelis by a margin of 11 percentage points. And while about half of Republicans continue to say they want the United States to lean toward Israel, that support is diminishing among young Republicans — 32% in the current poll — and, as other research has shown, support for Israel is declining even among young evangelical Christians.
- ^ "Half of adults in new poll support Israel's action in Gaza, 45 percent disapprove". The Hill. November 30, 2023.
- ^ "Poll: Majority of Americans sympathize with Israel but growing number say military response in Gaza 'too much'". PBS. November 15, 2023.
- ^ "New poll of US voters finds overwhelming support for Israel over Hamas in Gaza war". The Times of Israel. January 24, 2024.
- ^ Americans divided over Israel response to Hamas attacks, AP-NORC poll shows
- ^ "Welcome to". Israeltrade.org. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "Israel: Second F-35 deal is in the cards." United Press International, 8 June 2012.
- ^ "Israel-Gaza: How much money does Israel get from the US?". BBC News. May 24, 2021. Retrieved April 5, 2022.
- ^ Magid, Jacob; staff, T. O. I.; JTA. "US House approves $1 billion for Israel's Iron Dome after months-long delay". www.timesofisrael.com. Retrieved April 5, 2022.
- ^ Top Secret American Military Installations in Israel – 28 January 2004 – Arutz Sheva
- ^ "If War Comes, Will US Open its Military Depots in Israel?". Archived from the original on December 13, 2014.
- ^ "Evolution of US-Israel Strategic Alliance". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ "Israel to install radar antennae near nuclear site". AFP. October 3, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2008.
- ^ "Trade secrets – Haaretz – Israel News". February 17, 2008. Archived from the original on February 17, 2008. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- ^ "U.S.-Israel Intelligence Collaboration – Jewish Virtual Library". jewishvirtuallibrary.org.
- ^ "Report: Israel receives intelligence from US containing private information on US citizens". The Jerusalem Post - JPost.com.
- ^ "U.S. spies on Israel nukes, govt: official history". Reuters. December 10, 2008.
- ^ Hamodia: "Israeli Cabinet Minister Spied for U.S." (23 June 2004)
- ^ Haaretz: "Believe Me, I Am A Spy – I Am Even Ready To Be Swapped With Jonathan Pollard" – 18 May 2011
- ^ Melman, Yossi (April 27, 2011). "U.S. spied on Israel's Washington embassy, claims ex-envoy". Haaretz. Retrieved May 27, 2011.
- ^ "WorldTribune.com: 'Advanced NATO' sub chased from Israeli waters". worldtribune.com.
- ^ "Report: Submarine spying off coast last year was American" Associated Press, 5 June 2005.
- ^ The Jerusalem Post – Mystery sub was spying for the US – 7 June 2005
- ^ "U.S., UK spies targeted Israeli PM, EU official: Snowden leaks". Reuters. December 20, 2013.
- ^ a b c Politico, 12 Sept.2019, "Israel Accused of Planting Mysterious Spy Devices Near the White House: The Likely Israeli Spying Efforts Were Uncovered during the Trump Presidency, Several Former Top U.S. Officials Said."
- ^ "Document reveals spying on US by Israel". Israel Herald. Archived from the original on May 29, 2014. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- ^ Israel accused of planting spying devices near White House The Guardian
- ^ "The disturbing reason Jeffrey Epstein's homes had a camera in every room". 7NEWS. December 9, 2019. Archived from the original on December 27, 2021. Retrieved April 13, 2024.
- ^ McKay, Hollie (June 17, 2020). "Jeffrey Epstein's alleged 'spy' ties under fresh scrutiny in new book". Fox News. Archived from the original on January 7, 2024. Retrieved April 13, 2024.
- ^ Correspondent, Jack Royston Chief Royal (October 5, 2023). "Prince Andrew's accuser shares Jeffrey Epstein spy theory". Newsweek. Archived from the original on January 7, 2024. Retrieved April 13, 2024.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Benhorin, Yitzhak (January 11, 2013). "US Congress to debate visa exemption for Israelis". Ynetnews. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ Benhorin, Yitzhak (January 15, 2013). "US lawmakers eye visa exemption by 2015". Ynetnews. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- ^ KLAPPER, BRADLEY; LEE, MATTHEW (April 25, 2014). "Israeli Push for Visa-Free Travel to US Faces Test". ABC News. Associated Press. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- ^ Pinkas, Alon (February 14, 2023). "On the 46th Day, the 46th President Had 46 Words for Israel". Haaretz. Retrieved February 14, 2023.
- ^ Friedman, Thomas L. (July 19, 2023). "Biden to Netanyahu: Please Stop Trying to Rush Through Your Judicial Overhaul. Build a Consensus First". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 22, 2023.
Bibliography
- "Israeli-United States Relations" Almanac of Policy Issues
- Ball, George W. and Douglas B. Ball. The Passionate Attachment: America's Involvement With Israel, 1947 to the Present. New York: W. W. Norton, 1992. (ISBN 0393-02933-6)
- Gerhard, William D.; Millington, Henry W. (1981). Attack on a SIGINT Collector, the USS Liberty (PDF). NSA History Report, U.S. Cryptologic History series (Report). National Security Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 30, 2012. partially declassified 1999, 2003.
- Rudolph, Laura C. "Israeli Americans." Gale Encyclopedia of Multicultural America, edited by Thomas Riggs, (3rd ed., vol. 2, Gale, 2014), pp. 493–503. online
Further reading
- Bass, Warren. Support Any Friend: Kennedy's Middle East and the Making of the US-Israel Alliance. (Oxford UP, 2003)
- Benson, Michael T. Harry S. Truman and the founding of Israel (Greenwood, 1997).
- Caspit, Ben. The Netanyahu Years (2017) excerpt
- Feis, Herbert. The birth of Israel: the tousled diplomatic bed (1969) online
- Friedman, Robert O. Israel and the United States: Six Decades of US-Israeli Relations (2012) Excerpt
- Gilboa, E. . "Obama in Israel: Fixing American-Israeli Relations". Israel Journal of Foreign Affairs, (2013) 7#2:19–28
- Goldberg, Joseph E. An Historical Encyclopedia of the Arab-Israeli Conflict (1996)
- Goldman, Zachary K. "Ties that bind: John F. Kennedy and the foundations of the American–Israeli alliance: The Cold War and Israel." Cold War History 9.1 (2009): 23–58.
- Hummel, Daniel G. Covenant Brothers: Evangelicals, Jews, and U.S.-Israeli Relations (U of Pennsylvania Press, 2019); online review.
- Judis, John B.: Genesis: Truman, American Jews, and the Origins of the Arab/Israeli Conflict. (Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 2014). ISBN 978-0-374-16109-5
- Keith Peter. U.S. Foreign Policy Discourse and the Israel Lobby: The Clinton Administration and the Israeli-Palestinian Peace Process (Springer, 2017).
- Klagsbrun, Francine. Lioness: Golda Meir and the Nation of Israel (Schocken, 2017) excerpt.
- Lasensky, Scott. "Dollarizing Peace: Nixon, Kissinger and the Creation of the US–Israeli Alliance." Israel Affairs 13.1 (2007): 164–186.
- Leep, Matthew Coen. "The Affective Production of Others: United States Policy towards the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict", Cooperation and Conflict (2010) 45#3: 331–352.
- Mearsheimer, John; Walt, Stephen. The Israel Lobby and U.S. Foreign Policy. (Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2007).
- Mitelpunkt, Shaul. Israel in the American Mind: The Cultural Politics of US-Israeli Relations, 1958–1988 (2018) Excerpt
- Pfeffer, Anshel. Bibi: The Turbulent Life and Times of Benjamin Netanyahu (2018).
- Rabinovich, Itamar. Yitzhak Rabin: Soldier, Leader, Statesman (Yale UP, 2017). excerpt
- Reich, Bernard. Securing the Covenant: United States-Israel Relations after the Cold War. (Greenwood, 1995).
- Roth, Ariel Ilan. "Reassurance: A Strategic Basis of U.S. Support for Israel", International Studies Perspectives 10:4 (2009): 378–394.
- Schoenbaum, David. The United States and the State of Israel (Oxford UP, 1993).
- Shlaim, Avi. "The Impact of U.S. Policy in the Middle East". Journal of Palestine Studies 17#2 (1988): 15–28.
- Snetsinger, John. Truman, the Jewish Vote, and the Creation of Israel (Hoover Institute Press, 1974).
- Spiegel, Steven L. The Other Arab– Israeli Conflict: Making America's Middle East Policy, From Truman to Reagan (U of Chicago Press, 1985).
External links
- Israel's Importance to the U.S. from the Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
- History of Israel – U.S. relations
- Israel and the United States: Friends, Partners, Allies
- Israeli–United States Relations Congressional Research Service
- Origins of the US-Israeli Strategic Partnership
- Israeli Embassy in Washington, D.C. page on US-Israel relations
- United States Embassy in Israel
- Israel: Background and Relations with the United States CRS Report for Congress
- Israeli–United States Relations Policy Almanac
- US-Israel Relations Archived June 18, 2018, at the Wayback Machine
- Coming Moment of Truth between Israel and the US Archived August 2, 2020, at the Wayback Machine by Gidi Grinstein Reut Institute Archived July 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- Vital Support: Aid to Israel and US National Security Interests[permanent dead link]
- A Crisis in U.S.-Israel Relations: Have We Been Here Before? Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs



