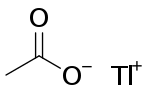
Thallous acetate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Thallium(I) Acetate
| |
| Other names
Thallium monoacetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.416 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1707 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| TlC2H3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 263.429 |
| soluble | |
| −69.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H330, H373, H411 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P284, P301+P310, P304+P340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
35 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 41.3 mg/kg (rat, oral)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin][1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin][1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
15 mg/m3 (as Tl)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Thallous acetate or thallium(I) acetate is a salt of thallium and acetate with the chemical formula TlCH3COO. It is used in microbiology as a selective growth medium.[3] It is poisonous.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0608". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Thallium (soluble compounds, as Tl)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Bulich, AA; Hartman, PA (1969). "Evaluation of thallium acetate-citrate medium for isolation of enterococci". Appl Microbiol. 18 (5): 944–5. doi:10.1128/AEM.18.5.944-945.1969. PMC 378124. PMID 5370465.
- ^ World Health Organization (2008). Anthrax in humans and animals. World Health Organization. pp. 139–. ISBN 978-92-4-154753-6. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
