Template:Transclude list item excerpts as random slideshow/testcases/Portal:Lithuania
| This is the template test cases page for the sandbox of Template:Transclude list item excerpts as random slideshow/testcases. Purge this page to update the examples. If there are many examples of a complicated template, later ones may break due to limits in MediaWiki; see the HTML comment "NewPP limit report" in the rendered page. You can also use Special:ExpandTemplates to examine the results of template uses. You can test how this page looks in the different skins and parsers with these links: |
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
Introduction



Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.88 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius.
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe. In 1386, the Grand Duchy entered into a de facto personal union with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The two realms were united into the bi-confederal Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, forming one of the largest and most prosperous states in Europe. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighbouring countries gradually dismantled it between 1772 and 1795, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuania's territory.
Towards the end of World War I, Lithuania declared Independence in 1918, founding the modern Republic of Lithuania. In World War II, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union, then by Nazi Germany, before being reoccupied by the Soviets in 1944. Lithuanian armed resistance to the Soviet occupation lasted until the early 1950s. On 11 March 1990, a year before the formal dissolution of the Soviet Union, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to break away when it proclaimed the restoration of its independence. (Full article...)
Selected pictures
-
Image 3Statutes of Lithuania were the central piece of Lithuanian law in 1529–1795. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 4Simple Words of Catechism by Martynas Mažvydas was the first Lithuanian book and was published in 1547. (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 5Traditional Lithuanian house from late 19th century (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 6Gryčia (traditional dwelling house, built in the 19th century) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 12Vilnius University, one of the oldest universities in the region. It was established by Stephen Báthory, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, in 1579. (from Lithuania)
-
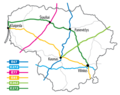
Image 13Major highways in Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 16The first Lithuanian printed book, Catechism of Martynas Mažvydas (1547, Königsberg) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 19Rock band Antis, which under firm censorship actively mocked the Soviet Union regime by using metaphors in their lyrics, during an anti-Sovietism, anti-communism concert in 1987 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 20Lithuania's name in writing (Litua, on line 7), 1009 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 22Lithuanian Army soldiers marching with their dress uniforms in Vilnius. An officer stands out with a sword. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 24Commemoration of the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania in the historical Seimas hall where it was originally signed in 1990. The ceremony is attended by the Lithuanian President, Prime Minister, Chairman of the Seimas and other high-ranking officials. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 25A ceremony of Lithuanian modern pagans. (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 29Le Château — Conte de fées (Lithuanian: Pilis — Pasaka) by Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis (1909) (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 34Lithuanian cemetery at All Souls night (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 36Guests of the 2023 Vilnius (NATO) summit in the Courtyard of the Presidential Palace in Vilnius (from Lithuania)
-
Image 38Real GDP per capita development of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 39The title page of Radivilias (1592, Vilnius). The poem celebrating commander Mikalojus Radvila Rudasis (1512–1584) and recounts the famous victory of Lithuanian Armed Forces over Moscow troops (1564). (from Lithuania)
-
Image 40Lithuanian counties by GDP per capita, 2022 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 43Stamp dedicated to Lithuania's presidency of the European Union. Post of Lithuania, 2013. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 44Trakai Island Castle, the former residence of the Grand Dukes. Trakai was the capital of the medieval state. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 47Lithuanian artist Jonas Mekas, regarded as godfather of American avant-garde cinema (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 51Lithuania's GDP per capita compared to rest of the world (2022) (from Lithuania)
-
Image 53The earliest known Lithuanian glosses (between 1520 and 1530) written in the margins of Johann Herolt book Liber Discipuli de eruditione Christifidelium. Words: teprÿdav[ſ]ʒÿ (let it strike), vbagÿſte (indigence). (from Lithuania)
-
Image 57Lithuania was a member of the United Nations Security Council. Its representatives are on the right side. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 61Panorama of Vilnius in 1600 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 62Baltic amber was once a valuable trade resource. It was transported from the region of modern-day Lithuania to the Roman Empire through the Amber Road. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 63Lithuanian basketball clubs Žalgiris and Šiauliai playing a match (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 64Physical map and geomorphological subdivision of Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 67Cepelinai, a potato-based dumpling dish characteristic of Lithuanian cuisine with meat, curd or mushrooms (from Lithuania)
-
Image 68Lithuania men's national basketball team is ranked eighth worldwide in FIBA Rankings. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 69The Great Courtyard of Vilnius University and the Church of St. Johns (from Culture of Lithuania)
-
Image 70Population density of Lithuania (from Lithuania)
-
Image 71Members of the Council of Lithuania after signing the Act of Independence of Lithuania in 1918 (from Lithuania)
-
Image 77The white stork is the national bird of Lithuania, which has the highest-density stork population in Europe. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 79Changes in the territory of Lithuania from the 13th to 15th century. At its peak, Lithuania was the largest state in Europe. (from Lithuania)
-
Image 84Cepelinai served with sour cream (from Culture of Lithuania)
Selected county
-
Image 1
Šiauliai County (Lithuanian: Šiaulių apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the north of the country, and its capital is Šiauliai. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Šiauliai County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Alytus County (Lithuanian: Alytaus apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is the southernmost county, and its capital is the city of Alytus. Its territory lies within the ethnographic region of Dzūkija. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Alytus County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
It borders the Vilnius County in the east, Marijampolė County and Kaunas County in the north, Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland in the west, and Grodno Region of Belarus in the south. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Marijampolė County (Lithuanian: Marijampolės apskritis) is one of the ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the southwest of the country and roughly corresponds to the historical region of Sudovia. Its capital and the largest town is Marijampolė. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Marijampolė County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
It borders the Tauragė County in the north, Kaunas County and Alytus County in the east, Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland in the south and Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia in the west. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Klaipėda County (Lithuanian: Klaipėdos apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania, bordering Tauragė County to the southeast, Telšiai County to the northeast, Kurzeme in Latvia to the north, and Kaliningrad Oblast in Russia to the south. To the west is the Baltic Sea. It lies in the west of the country and is the only county to have a coastline and not be landlocked. Its capital is Klaipėda. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Klaipėda County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Tauragė County (Lithuanian: Tauragės apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Tauragė. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Tauragė County remains as the territorial and statistical unit.
Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle and Panemunė Castle. (Full article...) -
Image 6
Utena County (Lithuanian: Utenos Apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is the country's most sparsely populated county. The capital and the largest city in the county is Utena, which is 95 km (59 mi) from Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished. Since that date, Utena County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Telšiai County (Lithuanian: Telšių apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the west of the country, and its capital is Telšiai. There are Lithuanians (98.7%), Latvians (0.1%), Russians (0.9%), and others (0.3%). On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Telšiai County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. It borders Latvia. (Full article...) -
Image 8Vilnius skyline
Vilnius County (Lithuanian: Vilniaus apskritis) is the largest of the 10 counties of Lithuania, located in the east of the country around the city Vilnius and is also known as Capital Region or Sostinės regionas by the Lithuanian statistics department and Eurostat. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Vilnius County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Panevėžys County (Lithuanian: Panevėžio apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is in the north-east of the country, and its capital is Panevėžys. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Panevėžys County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Kaunas County (Lithuanian: Kauno apskritis) is one of ten counties of Lithuania. It is in the centre of the country, and its capital is Kaunas. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished. (Full article...)
Selected municipality
-
Image 1

Radviliškis District Municipality (Lithuanian: Radviliškio rajono savivaldybė) is one of the seven municipalities of Šiauliai County (Šiaulių apskritis) in Lithuania. Radviliškis town has been its center since 1950.
Radviliškis district has 13 subdivisions or elderships (Seniūnija). (Full article...) -
Image 2Burbiškiai mound
Telšiai District Municipality (Lithuanian: Telšių rajono savivaldybė, Samogitian: Telšiū rajuona savivaldībė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania, containing the city of Telšiai. (Full article...) -
Image 3
-
Image 4

Marijampolė Municipality (Lithuanian: Marijampolės savivaldybė) is a municipality in Marijampolė County, south-western Lithuania. Its administrative seat and largest town is Marijampolė.
It borders Lazdijai District Municipality and Alytus District Municipality to the south-east, Prienai District Municipality to the east, Vilkaviškis District Municipality to the west, Kazlų Rūda Municipality to the north and Kalvarija Municipality to the south. (Full article...) -
Image 5
-
Image 6
-
Image 7

Klaipėda District Municipality (Lithuanian: Klaipėdos rajono savivaldybė) is a municipality in western Lithuania, east of the city of Klaipėda, by the Curonian Lagoon and the Baltic Sea. Its administrative centre is the town of Gargždai (unlike other Lithuanian municipalities, the name of this municipality does not correspond to its administrative centre). It covers an area of 1336 km² (2% of the total area of Lithuania). The municipality owns most of the Seaside Regional Park. It is home to the famous The Dutchman's Cap Hill, the highest cliff on the Lithuanian coast. (Full article...) -
Image 8
-
Image 9Landscape near Mikytai
Plungė District Municipality (Lithuanian: Plungės rajono savivaldybė, Samogitian: Plongės rajuona savivaldībė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 10
-
Image 11
-
Image 12
Tauragė District Municipality (Lithuanian: Tauragės rajono savivaldybė) is a municipality in Tauragė County, Lithuania
Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle and Panemunė Castle. (Full article...) -
Image 13
-
Image 14
Joniškis District Municipality (Joniškio rajono savivaldybė) is a territorial unit of Lithuania with a population of about 30,000. The administrative center of the municipality is the city of Joniškis. (Full article...) -
Image 15

Akmenė District Municipality (Lithuanian: Akmenės rajono savivaldybė) is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It lies in the Northwest of the country, with the administrative center in Naujoji Akmenė and borders Latvia in the north, Joniškis District in the east, Šiauliai District in the southeast, Telšiai District in the southwest, and Mažeikiai District in the west. The area of the municipality covers ca. 844 km2 and is the 43rd largest municipality by total area in the country. Its population shrank from some 30,300 (2001 census) to 18,500 (2021 census) which is around 39% in decline. (Full article...)
Selected World Heritage Site
-
Image 1The northernmost station of the Struve Geodetic Arc is located in Fuglenes, Norway.
The Struve Geodetic Arc is a chain of survey triangulations stretching from Hammerfest in Norway to the Black Sea, through ten countries and over 2,820 kilometres (1,750 mi), which yielded the first accurate measurement of a meridian arc.
The chain was established and used by the German-born Russian scientist Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve in the years 1816 to 1855 to establish the exact size and shape of the earth. At that time, the chain passed merely through three countries: Norway, Sweden and the Russian Empire. The Arc's first point is located in Tartu Observatory in Estonia, where Struve conducted much of his research. Measurement of the triangulation chain comprises 258 main triangles and 265 geodetic vertices. The northernmost point is located near Hammerfest in Norway and the southernmost point near the Black Sea in Ukraine. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Kaunas (/ˈkaʊnəs/; Lithuanian: [ˈkɐʊ̯ˑnˠɐs] ⓘ; previously known in English as Kovno /ˈkɒvnoʊ/) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county [pl] in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915.
During the interwar period, it served as the temporary capital of Lithuania, when Vilnius was seized and controlled by Poland between 1920 and 1939. During that period Kaunas was celebrated for its rich cultural and academic life, fashion, construction of countless Art Deco and Lithuanian National Revival architectural-style buildings as well as popular furniture, interior design of the time, and a widespread café culture. The city interwar architecture is regarded as among the finest examples of European Art Deco and has received the European Heritage Label. It contributed to Kaunas being designated as the first city in Central and Eastern Europe as a UNESCO City of Design, and also to becoming a World Heritage Site in 2023 as the only European city representing large scale urbanization during the interwar period and versatile modernism architecture. (Full article...) -
Image 3
The Old Town of Vilnius (Lithuanian: Vilniaus senamiestis), one of the largest surviving medieval old towns in Northern Europe, has an area of 3.59 square kilometres (887 acres). It encompasses 74 quarters, with 70 streets and lanes numbering 1487 buildings with a total floor area of 1,497,000 square meters. It was founded by the Lithuanian Grand Duke and King of Poland Jogaila in 1387 on the Magdeburg rights the oldest part of the Lithuanian capital of Vilnius, it had been developed over the course of many centuries, and has been shaped by the city's history and a constantly changing cultural influence. It is a place where some of Europe's greatest architectural styles—gothic, renaissance, baroque and neoclassical—stand side by side and complement each other. There are many Catholic, Lutheran and Orthodox churches, residential houses, cultural and architectural monuments, museums in the Old Town.
Pilies Street is the Old Town's main artery and the hub of cafe and street market life. The main street of Vilnius, Gediminas Avenue, is partially located in the Old Town. The central squares in the Old Town are the Cathedral Square and the Town Hall Square. (Full article...) -
Image 4The Valley of Death looking from the Parnidis Dune in Neringa Municipality, Lithuania in October 2022.
The Curonian (Courish) Spit (Lithuanian: Kuršių nerija; Russian: Ку́ршская коса́) is a 98-kilometre (61 mi) long, thin, curved sand-dune spit that separates the Curonian Lagoon from the Baltic Sea. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site shared by Lithuania and Russia. Its southern portion lies within Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, and its northern within southwestern Klaipėda County of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Kernavė was a medieval capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and today is a tourist attraction and an archeological site (population 238, 2021). It is located in the Širvintos district municipality located in southeast Lithuania. A Lithuanian state cultural reserve was established in Kernavė in 1989. In 2004 Kernavė Archaeological Site was included into UNESCO World Heritage list. (Full article...)
Selected history article
-
Image 1The history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648) covers a period in the history of Poland and Lithuania, before their joint state was subjected to devastating wars in the mid-17th century. The Union of Lublin of 1569 established the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a more closely unified federal state, replacing the previously existing personal union of the two countries. The Union was largely run by the Polish and increasingly Polonized Lithuanian and Ruthenian nobility, through the system of the central parliament and local assemblies, but from 1573 led by elected kings. The formal rule of the nobility, which was a much greater proportion of the population than in other European countries, constituted a sophisticated early democratic system, in contrast to the absolute monarchies prevalent at that time in the rest of Europe.[a]
The Polish–Lithuanian Union had become an influential player in Europe and a significant cultural entity. In the second half of the 16th and the first half of the 17th century, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a huge state in central-eastern Europe, with an area approaching one million square kilometers. (Full article...) -
Image 2
The rule of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Poland between 1386 and 1572 spans the Late Middle Ages and the Early Modern Period in European history. The Lithuanian Grand Duke Jogaila (Władysław II Jagiełło) founded the dynasty; his marriage to Queen Jadwiga of Poland in 1386 strengthened an ongoing Polish–Lithuanian union. The partnership brought vast territories controlled by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania into Poland's sphere of influence and proved beneficial for both the Polish and Lithuanian people, who coexisted and cooperated in one of the largest political entities in Europe for the next four centuries.
In the Baltic Sea region, Poland engaged in ongoing conflict with the Teutonic Knights. The struggles led to a major battle, the Battle of Grunwald of 1410, but there was also the milestone Peace of Thorn of 1466 under King Casimir IV Jagiellon; the treaty defined the basis of the future Duchy of Prussia. In the south, Poland confronted the Ottoman Empire and the Crimean Tatars, and in the east Poles helped Lithuania fight the Grand Duchy of Moscow. Poland's and Lithuania's territorial expansion included the far north region of Livonia. (Full article...) -
Image 3
The Lithuanian–Soviet War or Lithuanian–Bolshevik War (Lithuanian: karas su bolševikais) was fought between newly independent Lithuania and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic in the aftermath of World War I. It was part of the larger Soviet westward offensive of 1918–1919. The offensive followed the retreat of German troops and sought to establish Soviet republics in Ukraine, Belarus, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Poland and link up with the German Revolution. By the end of December 1918 Soviet forces reached Lithuanian borders. Largely unopposed, they occupied one town after another and by the end of January 1919 controlled about two thirds of the Lithuanian territory. In February, the Soviet advance was stopped by Lithuanian and German volunteers, who prevented the Soviets from capturing Kaunas, the temporary capital of Lithuania. From April 1919, the Lithuanian war went parallel with the Polish–Soviet War. Poland had territorial claims over Lithuania, especially the Vilnius Region; these tensions spilt over into the Polish–Lithuanian War.
British-Polish historian Norman Davies summarized the situation: "the German army was supporting the Lithuanian nationalists, the Soviets were supporting the Lithuanian communists and the Polish Army was fighting them all." In mid-May, the Lithuanian army, now commanded by General Silvestras Žukauskas, began an offensive against the Soviets in Northeastern Lithuania. By mid-June, the Lithuanians reached the Latvian border and cornered the Soviets among lakes and hills near Zarasai, where the Soviets held out until the end of August 1919. The Soviets and Lithuanians, separated by the Daugava River, maintained their fronts until the Battle of Daugavpils in January 1920. As early as September 1919, the Soviets offered to negotiate a peace treaty, but talks began only in May 1920. The Soviet–Lithuanian Peace Treaty was signed on July 12, 1920. Soviet Russia fully recognized independent Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Lithuania's name in writing, 1009
The first known record of the name of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuva) recorded in the Quedlinburg Chronicle (Latin: Annales Quedlinburgenses, written between 1008 and 1030) in a 9 March 1009 story of Saint Bruno . The Chronicle recorded in the form Litua (in the phrase "in confinio Rusciæ et Lituæ a paganis capite plexus"). Although it is clear the name originated from a Baltic language, scholars still debate the meaning of the word. (Full article...) -
Image 5
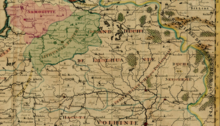
Lithuania proper (in green) and Samogitia (in red) within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in a map from 1712
Lithuania proper refers to a region that existed within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania where the Lithuanian language was spoken. The primary meaning is identical to the Duchy of Lithuania, a land around which the Grand Duchy of Lithuania evolved. The territory can be traced by Catholic Christian parishes established in pagan Baltic lands of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania subsequent to the Christianization of Lithuania in 1387. Lithuania proper (Lithuania Propria) was always distinguished from the Ruthenian lands since the Lithuanians differed from the Ruthenians in their language and faith (Paganism in the beginning and Catholicism since 1387). The term in Latin was widely used during the Middle Ages and can be found in numerous historical maps until World War I.
Lithuania proper is sometimes also called Lithuania Major, particularly in contrast with Lithuania Minor. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The Kingdom of Lithuania was an attempt to establish an independent constitutional Lithuanian monarchy in February 1918. It was created towards the end of World War I when Lithuanian-speaking lands were under military occupation by the German Empire. The state was officially dissolved in November 1918.
The Council of Lithuania declared Lithuania's independence on 16 February 1918, but the council was unable to form a government, police, or other state institutions due to the continued presence of German troops. The Germans presented various proposals to incorporate Lithuania into the German Empire, particularly Prussia. The Lithuanians resisted this idea and hoped to preserve their independence by creating a separate constitutional monarchy. (Full article...) -
Image 7

The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south.
The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. (Full article...) -
Image 8
The Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania or Act of 11 March (Lithuanian: Aktas dėl Lietuvos nepriklausomos valstybės atstatymo) was an independence declaration by Lithuania adopted on 11 March 1990, signed by all members of the Supreme Council of the Republic of Lithuania led by Sąjūdis. The act emphasized restoration and legal continuity of the interwar-period Lithuania, which was occupied by the Soviet Union and annexed in June 1940. In March 1990, it was the first of the 15 Soviet republics to declare independence, with the rest following to continue for 21 months, concluding with Kazakhstan's independence in 1991. These events (part of the broader process dubbed the "parade of sovereignties") led to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Yotvingia or Sudovia (Yotvingian: Sūdava, Lithuanian: Dainava, Polish: Jaćwież, German: Sudauen, Eastern Slavic: Яцьвезь (Ятвязь, Етвязь), Ятвягия) was a region where the Baltic tribe known as Yotvingians lived. It was located in the area of Sudovia and Dainava; south west from the upper Nemunas, between Marijampolė, Merkinė (Lithuania), Slonim, Kobryn (Belarus), Białystok, and Ełk (Poland).
Today this area corresponds mostly to the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, part of Lithuania and a part of Hrodna Province and Brest Province of Belarus. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Lithuanian Jews and a German Wehrmacht soldier during the Holocaust in Lithuania (June 24, 1941)
The military occupation of Lithuania by Nazi Germany lasted from the German invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941, to the end of the Battle of Memel on January 28, 1945. At first the Germans were welcomed as liberators from the repressive Soviet regime which had occupied Lithuania. In hopes of re-establishing independence or regaining some autonomy, Lithuanians organized a Provisional Government that lasted six weeks. (Full article...) -
Image 11
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties—the House of Mindaugas, the House of Gediminas, and the House of Jagiellon. Despite this, the one and only crowned king of Lithuania was King Mindaugas I. In two more instances, royal nobles were not crowned due to political circumstances, but held de jure recognition abroad —Vytautas the Great by Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, and Mindaugas II by Pope Benedict XV.
Others were seen as kings of Lithuania even though they had only considered it and never took further action to claim the throne, as in the case of Gediminas who was recognised as king of Lithuania by Pope John XXII. The hereditary monarchy in Lithuania was first established in the 13th century during the reign of Mindaugas I and officially re-established as a constitutional monarchy on 11 July 1918, only to be abandoned soon afterwards on 2 November 1918. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.88 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius.
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe. In 1386, the Grand Duchy entered into a de facto personal union with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The two realms were united into the bi-confederal Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, forming one of the largest and most prosperous states in Europe. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighbouring countries gradually dismantled it between 1772 and 1795, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuania's territory. (Full article...) -
Image 13The history of Lithuania between 1219 and 1295 concerns the establishment and early history of the first Lithuanian state, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The beginning of the 13th century marks the end of the prehistory of Lithuania. From this point on the history of Lithuania is recorded in chronicles, treaties, and other written documents. In 1219, 21 Lithuanian dukes signed a peace treaty with Galicia–Volhynia. This event is widely accepted as the first proof that the Baltic tribes were uniting and consolidating. Despite continuous warfare with two Christian orders, the Livonian Order and the Teutonic Knights, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was established and gained some control over the lands of Black Ruthenia, Polatsk, Minsk, and other territories east of modern-day Lithuania that had become weak and vulnerable after the collapse of Kievan Rus'.
The first ruler to hold the title of Grand Duke was Mindaugas. Traditionally he is considered the founder of the state, the one who united the Baltic tribes and established the Duchy. Some scholars, however, challenge this perception, arguing that an organized state existed before Mindaugas, possibly as early as 1183. After quelling an internal war with his nephews, Mindaugas was baptized in 1251, and was crowned as King of Lithuania in 1253. In 1261, he broke the peace with the Livonian Order, perhaps even renouncing Christianity. His assassination in 1263 by Treniota ended the early Christian kingdom in Lithuania. For another 120 years Lithuania would remain a pagan empire, fighting against the Teutonic and Livonian Orders during the Northern Crusades during their attempts to Christianize the land. (Full article...) -
Image 14

The Vilna Governorate was a province (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. In 1897, the governorate covered an area of 41,907.9 square kilometres (16,180.7 sq mi) and had a population of 1,591,207 inhabitants. The governorate was defined by the Minsk Governorate to the south, the Grodno Governorate to the southwest, the Suwałki Governorate to the west, the Kovno and Courland Governorates to the north, and the Vitebsk Governorate to the east. The capital was located in Vilna (Vilnius). The city also served as the capital of Vilna Governorate-General, which existed until 1912. The area roughly corresponded to the Vilnius Region, which was later occupied by Germany, Bolsheviks, and Poland. (Full article...) -
Image 15The Soviet Union (USSR) occupied most of the territory of the Baltic states in its 1944 Baltic Offensive during World War II. The Red Army regained control over the three Baltic capitals and encircled retreating Wehrmacht and Latvian forces in the Courland Pocket where they held out until the final German surrender at the end of the war. (Full article...)
Selected politics article
-
Image 1
The prime minister of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos ministras pirmininkas) is the head of government of Lithuania. The prime minister is appointed by the president with the assent of the Lithuanian parliament, the Seimas. The modern office of prime minister was established in 1990, when Lithuania declared its independence, although the official title was "Chairperson of the Council of Ministers" until 25 November 1992. (Full article...) -
Image 2The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties (Lithuanian: singular apskritis, plural apskritys), all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: singular savivaldybė, plural savivaldybės): 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities. Each municipality is then divided into elderates (Lithuanian: singular seniūnija, plural seniūnijos). This division was created in 1994 and slightly modified in 2000. (Full article...)
-
Image 3

Gitanas Nausėda (Lithuanian: [ɡɪˈtɐ.nɐs nɐˈu.sʲeː.dɐ]; born 19 May 1964) is a Lithuanian politician, economist, and banker who is serving as the ninth and incumbent president of Lithuania since 2019. Born in Klaipėda, Nausėda graduated from Vilnius University with an economics degree in 1987. He was director of monetary policy at the Bank of Lithuania from 1996 to 2000 and chief economist to the chairman of SEB bankas from 2008 to 2018. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Seniūnijos of Lithuania
A seniūnija (in English: eldership, elderate, ward, parish, or subdistrict) is the smallest administrative division of Lithuania. An eldership may comprise a very small region consisting of few villages, one single town, or a part of a big city. Elderships vary in size and population depending on their location and nature. A few elderships make up a municipality. Šilainiai, Dainava, Verkiai, Žirmūnai and Pašilaičiai are the most populous elderates, with population counts over 40,000, around twice the population of some entire municipalities. (Full article...) -
Image 5There have been fifteen referendums in Lithuania since it declared independence from the Soviet Union on 11 March 1990. Because of strict requirements, only four referendums have been successful. Older Lithuanian laws required that more than half of all registered voters (not half of voters who participate) would vote in support of a proposal for it to become a binding obligation to the government. In 2002, this requirement was lowered to one third of all registered voters. (Full article...)
-
Image 6This article lists political parties in Lithuania.
Lithuania has a multi-party system with numerous political parties, in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments. As of October 2024[update], there are 22 active political parties, one party undergoing formal registration, one inactive political party, and four political parties that are in the process of disestablishment registered with the Ministry of Justice. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Ingrida Šimonytė (Lithuanian: [ɪŋʲɡʲrʲɪˈdˠɐ ʃʲɪmˠoːˈnʲîːtʲeː]; born 15 November 1974) is a Lithuanian politician, public servant and economist who served as the 17th prime minister of Lithuania since 2020. She has been a Member of the Seimas for the Antakalnis constituency since 2016 and was Minister of Finance in the second Kubilius cabinet from 2009 until 2012. Šimonytė was a candidate in the 2019 and 2024 presidential election, but lost in the second round runoff to Gitanas Nausėda both times. She has been a member of Homeland Union since 2022, having previously been an independent politician. (Full article...) -
Image 8

The Seimas of the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Seimas), or simply the Seimas (/ˈseɪməs/ SAY-məs; Lithuanian: [ˈsɛɪˑmɐs]), is the unicameral legislative body of the Republic of Lithuania. The Seimas constitutes the legislative branch of government in Lithuania, enacting laws and amendments to the Constitution, passing the budget, confirming the Prime Minister and the Government and controlling their activities. (Full article...) -
Image 9

The Supreme Court of the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian: Lietuvos Respublikos Aukščiausiasis Teismas) is the only court of cassation in the Lithuania for reviewing effective judgements and rulings passed by the courts hearing criminal cases at the first and appeal instances as well as decisions and rulings in civil cases passed by the courts of appeals. It is the highest court of cassation, but it cannot interpret the constitution, since that is under the jurisdiction of the Constitutional Court of Lithuania. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Lithuanian municipalities and elderships map
Lithuania is divided into three levels of administrative divisions. The first-level division consists of 10 counties (Lithuanian: singular – apskritis, plural – apskritys). These are sub-divided into 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: plural – savivaldybės, singular – savivaldybė), which in turn are further sub-divided into over 500 smaller groups, known as elderships (Lithuanian: plural – seniūnijos, singular – seniūnija). (Full article...) -
Image 11
Election campaign poster in Vilnius
The 2014 European Parliament election in Lithuania was an election of the delegation from Lithuania to the European Parliament in 2014. It was part of the wider 2014 European election. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Parliamentary elections were held in Lithuania on 9 and 23 October 2016 to elect the 141 members of the Seimas. 71 were elected in single-member constituencies using the two-round system, and the remaining 70 in a single nationwide constituency using proportional representation. The first round was held on 9 October and the second round on 23 October. (Full article...) -
Image 13Taxes in Lithuania are levied by the central and the local governments. Most important revenue sources include the value added tax, personal income tax, excise tax and corporate income tax, which are all applied on the central level. In addition, social security contributions are collected in a social security fund, outside the national budget. Taxes in Lithuania are administered by the State Tax Inspectorate, the Customs Department and the State Social Insurance Fund Board. In 2019, the total government revenue in Lithuania was 30.3% of GDP. (Full article...)
-
Image 14In Lithuania, a public election committee (Lithuanian: visuomeninis rinkimų komitetas) is an organized group of voters outside of political parties which participates in local or European Parliament elections. (Full article...)
-
Image 15

Presidential elections were held in Lithuania on 11 May 2014, with a second round held on 25 May between the top two candidates from the first round. In the second round, incumbent President Dalia Grybauskaitė was re-elected with 58% of the vote. Second round took place alongside the 2014 European elections. (Full article...)
Selected biography
-
Image 1Mindaugas, as depicted in the chronicles of Alexander Guagnini (1611)
Mindaugas (German: Myndowen, Latin: Mindowe, Old East Slavic: Мендог, romanized: Mendog, Belarusian: Міндоўг, romanized: Mindowh, Polish: Mendog; c. 1203 – 12 September 1263) was the first known grand duke of Lithuania and the only crowned king of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or rise to power; he is mentioned in a 1219 treaty as an elder duke, and in 1236 as the leader of all the Lithuanians. The contemporary and modern sources discussing his ascent mention strategic marriages along with banishment or murder of his rivals. He extended his domain into regions southeast of Lithuania proper during the 1230s and 1240s. In 1250 or 1251, during the course of internal power struggles, he was baptised as a Roman Catholic; this action enabled him to establish an alliance with the Livonian Order, a long-standing antagonist of the Lithuanians. By 1245, Mindaugas was already being referred to as "the highest king" in certain documents. During the summer of 1253, he was crowned king, ruling between 300,000 and 400,000 subjects, and got nicknamed as Mindaugas the Sapient by the Livonians.
While Mindaugas's ten-year reign as king was marked by many state-building accomplishments, his conflicts with relatives and other dukes continued. The western part of Lithuania – Samogitia – strongly resisted the alliance's rule. His gains in the southeast were challenged by the Tatars. He broke peace with the Livonian Order in 1261, possibly renouncing Christianity, and was assassinated in 1263 by his nephew Treniota and another rival, Duke Daumantas of Pskov. His three immediate successors were assassinated as well. The disorder was not resolved until Traidenis gained the title of grand duke c. 1270. (Full article...) -
Image 2Epstein receiving the Edison Award for the Beatles at the Grand Gala du Disque 1965
Brian Samuel Epstein (/ˈɛpstaɪn/ EP-stine; 19 September 1934 – 27 August 1967) was an English music entrepreneur who managed the Beatles from 1961 until his death in 1967.
Epstein was born into a family of successful retailers in Liverpool, who put him in charge of their music shop, where he displayed a gift for talent-spotting. He first met the Beatles in 1961 at a lunchtime concert at Liverpool's Cavern Club. Although he had no experience of artist management, Epstein put them under contract and insisted that they abandon their scruffy image in favour of a new clean-cut style. He also attempted to get the Beatles a recording contract, eventually securing a deal with EMI's Parlophone label. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Jonas Vaitkus
Jonas Vaitkus (born 20 May 1944) is a Lithuanian theatre and film director, and academic. (Full article...) -
Image 4Rasa Polikevičiūtė during the introductions prior to one of the stages of the 2002 Women's Challenge stage race. She is wearing the Rainbow Jersey which signifies that she was the (then) current World Road Race Champion.
Rasa Polikevičiūtė (born September 25, 1970 in Panevėžys) is a Lithuanian cycle racer. One of her Lithuanian cycling contemporaries is her identical twin, Jolanta Polikevičiūtė.
She began cycling at age 13 under the influence of her childhood athletic coach and made her professional debut in 1990. In 1997, she won the Women's Challenge bicycle race and later went on to win the 2001 World Road Race Championships. (Full article...) -
Image 5
David Morris Lee (born January 20, 1931) is an American physicist who shared the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physics with Robert C. Richardson and Douglas Osheroff "for their discovery of superfluidity in helium-3." Lee is professor emeritus of physics at Cornell University and distinguished professor of physics at Texas A&M University. (Full article...) -
Image 6
-
Image 7

Henrikas Radauskas [ɣʲɛmrʲɪkaːs raːdaːʊskas] (23 April 1910 – 27 August 1970) was a Lithuanian poet and writer. Described as an "art alcoholic" by the contemporary Alfonsas Nyka-Niliūnas, Radauskas's works are marked by aestheticism, anti-lyricism, aesthetic distance, and poetic transformation of reality. He is described as "one of the most accomplished Baltic poets of the post-World War II years, and perhaps the greatest Lithuanian poet of the twentieth century". (Full article...) -
Image 8Deividas Česnauskis (born 30 June 1981) is a Lithuanian former professional footballer who played as a winger. He made 63 FIFA-official appearances for the Lithuanian national team scoring four goals. (Full article...)
-
Image 9

The house where Marija Pečkauskaitė lived in Židikai from 1915 to 1930
Šatrijos Ragana ("Witch of Šatrija") was the pen name of Marija Pečkauskaitė (Polish: Maria Pieczkowska; March 8, 1877 – July 24, 1930), a Lithuanian humanist and romantic writer and educator. Her most successful works are Sename dvare (In the Old Estate, 1922) and Irkos tragedija (Tragedy of Irka). (Full article...) -
Image 10
Balys Sruoga (2 February 1896 – 16 October 1947) was a Lithuanian poet, playwright, critic, and literary theorist.
He contributed to cultural journals from his early youth. His works were published by the liberal wing of the Lithuanian cultural movement, and also in various Lithuanian newspapers and other outlets (such as Aušrinė, Rygos naujienos etc.). In 1914, he began studying literature in Saint Petersburg, and later in Moscow, due to World War I and the Russian Revolution. In 1921, he enrolled in the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, where in 1924 he received his Ph.D for a doctoral thesis on the relations between Lithuanian and Slavic folk songs. Sruoga was also the first translator of Anna Akhmatova's poetry, which he likely completed between November 1916 and early 1917. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Charles Bronson (born Charles Dennis Buchinsky; November 3, 1921 – August 30, 2003) was an American actor. He was known for his roles in action films and his "granite features and brawny physique". Bronson was born into extreme poverty in Ehrenfeld, Pennsylvania, a coal mining town in the Allegheny Mountains. Bronson's father, a miner, died when Bronson was young. Bronson himself worked in the mines as well until joining the United States Army Air Forces in 1943 to fight in World War II. After his service, he joined a theatrical troupe and studied acting. During the 1950s, he played various supporting roles in motion pictures and television, including anthology drama TV series in which he would appear as the main character. Near the end of the decade, he had his first cinematic leading role in Machine-Gun Kelly (1958).
Bronson had sizeable co-starring roles in The Magnificent Seven (1960), The Great Escape (1963), This Property Is Condemned (1966), and The Dirty Dozen (1967). Bronson also performed in many major television shows, and was nominated for an Emmy Award for his supporting role in an episode of General Electric Theater. Actor Alain Delon (who was a fan of Bronson) hired him to co-star with him in the French film Adieu l'ami (1968). That year, he also played one of the leads in the Italian spaghetti Western, Once Upon a Time in the West (1968). Bronson continued playing leads in various action, Western, and war films made in Europe, including Rider on the Rain (1970), which won a Golden Globe Award for Best Foreign Language Film. During this time Bronson was the most popular American actor in Europe. (Full article...)
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



















































![Image 53The earliest known Lithuanian glosses (between 1520 and 1530) written in the margins of Johann Herolt book Liber Discipuli de eruditione Christifidelium. Words: teprÿdav[ſ]ʒÿ (let it strike), vbagÿſte (indigence). (from Lithuania)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f6/The_earliest_known_Lithuanian_glosses_%28~1520%E2%80%931530%29%2C_words_%28tepridau%C5%BEia%2C_ubagyst%C4%97%29.jpg/120px-The_earliest_known_Lithuanian_glosses_%28~1520%E2%80%931530%29%2C_words_%28tepridau%C5%BEia%2C_ubagyst%C4%97%29.jpg)
































































































