Second Ivorian Civil War
| Second Ivorian Civil War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Ivorian Civil Wars | |||||||
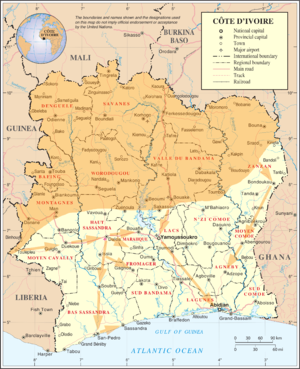 Map of the March 2011 Republican Forces (RFCI) offensive. Territory held by the RFCI prior to March 2011 is shown in orange. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
(Captured after war's end) |
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Unknown |
Unknown (New Forces) 10,000 (United Nations) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 44–61 security forces killed (before March)[5] |
50+ killed (RDR)[6] 2 killed (FNCI)[7] 2 killed[8][9] (UNOCI) (before March) | ||||||
| 3,000 killed overall[10] | |||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
The Second Ivorian Civil War[11][12] broke out in March 2011 when the crisis in Ivory Coast escalated into full-scale military conflict between forces loyal to Laurent Gbagbo, the President of Ivory Coast since 2000, and supporters of the internationally recognised president-elect Alassane Ouattara. After months of unsuccessful negotiations and sporadic violence between supporters of the two sides, the crisis entered a critical stage as Ouattara's forces seized control of most of the country with the help of the UN, with Gbagbo entrenched in Abidjan, the country's largest city. International organizations have reported numerous instances of human rights violations by both sides, in particular in the city of Duékoué where Ouattara's forces killed hundreds of people. Overall casualties of the war are estimated around 3000. The UN and French forces took military action, with the stated objective to protect their forces and civilians. France's forces arrested Gbagbo at his residence on 11 April 2011.[13]
Background
[edit]A civil war was fought in Ivory Coast between 2002 and 2004 between the incumbent President Laurent Gbagbo and the rebel Forces Nouvelles de Côte d'Ivoire (New Forces), representing Muslim northerners who felt that they were being discriminated against by the politically dominant and mostly Christian southerners.
In 2002 France sent its troops to Ivory Coast (Opération Licorne) as peacekeepers. In February 2004 the United Nations established the United Nations Operation in Côte d'Ivoire (UNOCI) "to facilitate the implementation by the Ivorian parties of the peace agreement signed by them in January 2003".[14] Most of the fighting ended by late 2004, with the country split between a rebel-held north and a government-held south. In March 2007 the two sides signed an agreement to hold fresh elections, though they ended up being delayed until 2010, five years after Gbagbo's term of office was supposed to have expired.[15]
After northern candidate Alassane Ouattara was declared the victor of the 2010 Ivorian presidential election by the country's Independent Electoral Commission (CEI), the President of the Constitutional Council – an ally of Gbagbo – declared the results to be invalid and that Gbagbo was the winner.[16] Both Gbagbo and Ouattara claimed victory and took the presidential oath of office.[17]
The international community, including the United Nations, the African Union, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), the European Union, the United States, and former colonial power France affirmed their support for Ouattara, who was "almost universally acknowledged to have defeated [Gbagbo] at the ballot box," and called for Gbagbo to step down.[18][19] On 18 December, Gbagbo ordered all UN peacekeepers to leave the country.[20] The UN refused and the UN Security Council extended the mandate of the UN Mission in Ivory Coast until 30 June 2011.[21] However, negotiations to resolve the dispute failed to achieve any satisfactory outcome. Hundreds of people were killed in escalating violence between pro-Gbagbo and pro-Ouattara partisans and at least a million people fled, mostly from Abidjan.[22]
Conflict
[edit]After the disputed election, sporadic outbreaks of violence took place, particularly in Abidjan, where supporters of Ouattara clashed repeatedly with government forces and militias. Gbagbo's forces were said to be responsible for a campaign of assassinations, beatings and abductions directed against Ouattara's supporters.[23]
The violence escalated through March 2011 with a number of incidents in Abidjan in which dozens of people were reported killed. In one of the deadliest single incidents, up to 30 people were killed on 17 March in a rocket attack on a pro-Ouattara suburb of Abidjan. The UN issued a statement saying that the shelling was "an act, perpetrated against civilians, [that] could constitute a crime against humanity."[24] 52 people were killed in further violence in Abidjan Between 21 and 26 March.[25]
Fighting also broke out in western Ivory Coast at the end of February 2011. On 25 February, the New Forces captured the towns of Zouan Hounien and Binhouye near the border with Liberia and took control of nearby Toulepleu on 7 March.[26] The town of Doké fell on 12 March as the New Forces pushed on towards Bloléquin,[27] which they took on 21 March after heavy fighting.[28]
On 28 March, the New Forces – now renamed the Republican Forces of Côte d'Ivoire (RFCI) – launched a full-scale offensive across the country. Ouattara issued a statement declaring: "All the peaceful routes to lead Laurent Gbagbo to admit his defeat have been exhausted." The towns of Duékoué and Daloa in the west of the country were captured by the RFCI, as were Bondoukou and Abengourou near the border with Ghana in the east.[29] On 30 March, Ivory Coast's political capital Yamoussoukro and the western town of Soubré were taken without resistance.[30] The port city of San Pédro, the world's largest cocoa exporting port, fell to the RFCI in the early hours of 31 March[31] as did the nearby coastal town of Sassandra.[32] On the same day Ivory Coast's borders with neighbouring countries were ordered to be sealed by Ouattara's forces.[33]
On 30 March United Nations Security Council Resolution 1975 was issued which, in particular, urged all Ivorian parties to respect the will of the people and the election of Alassane Ouattara as President of Ivory Coast, as recognised by ECOWAS, the African Union and the rest of the international community and reiterated that UNOCI could use "all necessary measures" in its mandate to protect civilians under imminent threat of attack.
The fighting was reported to have caused heavy damage in some contested towns, from which the inhabitants were said to have fled en masse.[34] Large numbers of people were said to have found dead after Ouattara's forces took control of the central Ivorian towns; in Duékoué alone, over 800 people were reported to have been killed, according to the International Committee of the Red Cross,[35] though responsibility for the massacres was unclear. Ouattara's government stated that numerous mass graves had been found in "Toulepleu, Bloléquin and Guiglo, whose authors are none other than the loyal forces, mercenaries and militias of Laurent Gbagbo."[36] However, the United Nations blamed the RFCI for many of the deaths.[37]
Battle of Abidjan
[edit]
In Abidjan, heavy fighting broke out on 31 March as pro-Ouattara forces advanced on the city from several directions. Residents reported seeing the RFCI forces entering the city in "a convoy of 2,000–3,000 people on foot and then dozens of cars without their headlights on."[38] Ouattara declared a three-day curfew in Abidjan from 2100 GMT to 0600 GMT.[39]
The United Nations peacekeepers took control of Abidjan's airport when Gbagbo's forces abandoned it, and Gbagbo's elite forces were reported to be surrounding the presidential residence. United Nations and French forces were also reported to be carrying out protective security operations in the city. The UN peacekeeping mission said its headquarters were fired on by Gbagbo's special forces on 31 March, and returned fire in an exchange lasting about three hours. UN convoys have also come under attack by Gbagbo loyalists four times since 31 March, with three peacekeepers injured in one of the attacks. The peacekeepers had exchanged fire with Gbagbo loyalists in several parts of the city.[40] Around 500 foreign nationals took refuge at the French base at Port-Bouët, near the airport.[41][42]
Ouattara appealed to Gbagbo's men to lay down their arms, promising that Gbagbo himself would come to no harm, and issued a statement: "There is still time to join your brothers. The country is calling you."[38] Many of them defected or gave up without a fight,[43] including the army chief of staff General Phillippe Mangou, who took refuge in the South African ambassador's house,[44] and the head of the military police, General Tiape Kassarate, who defected to Ouattara's side.[45] Despite belligerent language from Gbagbo's side, most of his forces appear to have decided not to fight – a decision attributed by some commentators to "the historically unwarrior-like nature of the Ivorian army" and the effect of sanctions on Gbagbo's ability to pay his forces.[46] Military sources said that an estimated 50,000 members of the gendarmerie and armed forces had deserted, with only some 2,000 Gbagbo loyalists remaining behind to fight.[41]
The fighting in Abidjan has been concentrated in two areas in the suburb of Cocody – around the state television building, which went off the air on the evening of 31 March, and around the residence of Laurent Gbagbo, where pro-Gbagbo Republican Guard members and armed students were said to be putting up strong resistance.[47] Gunfire and shelling was also reported around the presidential palace in the central Plateau district of the city.[38] Fighting also broke out in the Treichville district, where Gbagbo's Republican Guard was defending the city's main bridges, and around the gendarmerie base at Agban.[42]
On 2 April heavy fighting was around the Agban military base and the presidential palace.[48] State television station RTI appeared to be back under the control of Gbagbo supporters after being briefly taken off air.[49] Many residents of Abidjan reported that supplies of food were becoming limited, with the violence making it dangerous to leave buildings to buy more.[50]
Also on 2 April, UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon told the BBC that "[a]t this time, I strongly urge Mr Gbagbo to step down and transfer power to the legitimately elected president... Mr Ouattara."[48]
On 4 April, non-military United Nations personnel began to be evacuated from Abidjan and hundreds of additional French troops landed in the Abidjan airport.[51] UN and French helicopters also began firing on pro-Gbagbo military installations, a French military spokesman said the attacks were aimed at heavy artillery and armoured vehicles.[52] Eyewitnesses reported seeing two UN Mi-24P attack helicopters firing missiles at the Akouédo military camp in Abidjan.[53] UN helicopters were flown by Ukrainian Ground Forces crews seconded to the United Nations.[54] The attacks sparked protests by a Gbagbo spokesperson, who said that such actions were "illegal, illegitimate and unacceptable."[55] UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon defended the actions, however, saying that "the [UN] mission has taken this action in self-defence and to protect civilians."[55] He noted that Gbagbo's forces had fired on United Nations patrols and attacked the organization's headquarters in Abidjan "with heavy-caliber sniper fire as well as mortars and rocket-propelled grenades", wounding four peacekeepers.[52][55]
On 4 April General Phillippe Mangou left the South African ambassador's residence in Abidjan and rejoined the government forces. On Ouattara's TV station, Serges Alla, a journalist claimed: "Mangou was forced to leave the South African embassy because some of his relatives were made hostage by diehard supporters of Gbagbo, and Gbagbo militiamen were putting pressure on him, saying they would bomb his village if he doesn't show himself or doesn't return to the Gbagbo army."[56]
Early on 5 April 2011, Ouattara forces announced that they had captured the presidential palace.[57] The same day General Philippe Mangou, the military chief of Laurent Gbagbo, called for a ceasefire.[58]
Following calls for ceasefire by Gbagbo's military officials, it was reported that fighting has ceased in Abidjan.[59] Special UN representative Choi Young-jin stated that all Gbagbo's top generals had defected and that "the war is over".[59] Gbagbo had been negotiating a surrender;[60] French Foreign Minister Alain Juppe said that they were close to convincing Gbagbo to leave power.[61] The ECOWAS bloc promised a "safe and dignified exit" for Gbagbo and his family if he conceded the election, handing power over to Ouattara.[62] However, forces loyal to Ouattara moved to seize Gbagbo at his residence in Abidjan on 6 April 2011, after the negotiations failed.[63][64]
French forces were said to have destroyed several military vehicles belonging to troops loyal to Laurent Gbagbo during a helicopter-borne mission that rescued Japan's ambassador, Yoshifumi Okamura, during heavy fighting in Abidjan during the morning of 7 April.[65]
On 8 April pro-Ouattara forces continued to besiege Gbagbo in his residence. Ouattara said a blockade had been set up around the perimeter to make the district safe for residents. He said his forces would wait for Gbagbo to run out of food and water. However, Paris-based adviser Toussaint Alain to Gbagbo said that Gbagbo would not surrender.[66] Also on this day, Gbagbo forces using heavy weaponry such as rockets, grenade launchers and tanks were reported to have resumed fighting in Abidjan, taking control of the Plateau and Cocody areas of the city.[67]
On 9 April, pro-Gbagbo forces were reported to have fired on the Golf Hotel, where Ouattara was located.[68] The attackers reportedly used both sniper rifles and mortars; in response, UN peacekeepers fired on them.[68] Gbagbo's forces were reported to have pushed Ouattara's forces back, retaking control of the Plateau and Cocody districts of Abidjan.[69]
The following day, United Nations and French forces carried out further air strikes against Gbagbo's remaining heavy weapons, using Mi-24 and Aérospatiale Gazelle attack helicopters. The attack was reported to have caused heavy damage to the presidential palace.[69]
Arrest of Gbagbo
[edit]On 11 April, Ouattara's forces stormed Gbagbo's residence and arrested him. The final assault was assisted by French forces using helicopters and armoured vehicles, although the actual capture was made by Ouattara's troops. There have been persistent rumors that French special forces blew up a wall blocking a tunnel between the French Embassy and Gbagbo's residence in Abidjan; Ivorian forces loyal to Ouattara then rushed through the tunnel into the house and arrest him. Gbagbo, his wife, son and about 50 members of his entourage were captured unharmed and were taken to the Golf Hotel, Ouattara's headquarters, where they were placed under United Nations guard.[13][70][71]
Killing of civilians
[edit]Duékoué massacre
[edit]Unknown attackers wielding machetes and various guns were reported to have killed over 1,000 civilians in a neighbourhood of the town of Duékoué, which was largely controlled by forces fighting to install the internationally recognized president according to the Catholic charity Caritas. The U.N. mission in Ivory Coast said it has a team investigating the alleged mass killings in the west of the town.[72] The U.N. said forces of both Ouattara and Gbagbo were involved in the killings.[73] On the 4th Caritas repeated its claims that 800 to 1,000 had been killed in the Duékoué massacre. The nation's general descent into violence had frightened both the foreigners and Caritas aid workers.[74]
According to Guillaume N'Gefa, spokesman for the UN mission in Ivory Coast, 330 people had been killed in Duékoué as Ouattara's forces took over the town, More than 100 of them were killed by Gbagbo's troops. However, N'Gefa said the majority were executed by dozos, traditional hunters who support Ouattara.
N'Gefa said a UN team was still investigating and those figures were likely to rise. Earlier the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) said at least 800 died, while Caritas put the figure at more than 1,000. ICRC staff who visited Duékoué said the scale and brutality of the killings were shocking. Tens of thousands had fled Duékoué since 28 March.[36][48]
On 7 April Rupert Colville, spokesman for the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, said its team had found 15 new bodies, bringing the total number of known dead in a 28–29 March incident to 244. Victims mostly or all of Guere ethnicity, traditional Gbagbo supporters. Some seem to have been burnt alive and some corpses were thrown down a well.[66][75]
In addition to the issue of the presidency, the root cause of the massacre was believed to be over cocoa land and farming rights. The Guere are the traditional land-owners of the region; but migrant workers perform much of the manual labor on cocoa plantations. The two have a historic dispute over the rights to the farmland.[75][76][77]
Blolequin and Guiglo massacres
[edit]On 7 April Rupert Colville said that 40 bodies were found in Blolequin, where perpetrators were said to have been Liberian militias, who spared the Guere after separating them out from other groups. In Guiglo 60 bodies were found, including a number of West Africans.[66]
International reaction
[edit]- On 8 March, Leymah Gbowee issued a statement of support[78] for the peaceful protests of the Christian and Muslim women in the Ivory Coast and compared them to the women of Liberia.
- Nigerian Foreign Minister Henry Odein Ajumogobia accused the international community of "contradictions" by imposing a no-fly zone over Libya and focusing on the 2011 Libyan civil war, but failing to take action to protect civilians in the Ivory Coast.[79]
- On 23 March, at the ECOWAS Summit, Goodluck Jonathan, President of Nigeria urged the United Nations to pass a resolution to take decisive action, saying instability posed a threat to security in West Africa.[80]
- On 23 March, the "One Thousand Women March" was organized by peace activists in West Africa. They wore white T-shirts[81] and represented countries across West Africa including Ivory Coast, Ghana, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone and Togo. They issued a press release and presented a position statement to the ECOWAS Heads of State.[82]
- On 30 March, the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1975 was adopted unanimously, demanding that Laurent Gbagbo step down as president and allow internationally recognised President Alassane Ouattara to take power. The resolution imposed sanctions on Gbagbo and his close associates.[83] The resolution was sponsored by France and Nigeria.[84]
- Ivory Coast received more attention and obtained more consensus by the United Nations Security Council than any other country from 2009 to 2011.[85]
Criticism
[edit]- Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said that Russia intended to look into the legitimacy of the use of force by UN peacekeepers. The position of the Russian government was that any foreign interference would only lead to increasing violence.[86]
Refugees
[edit]
According to the United Nations, due to the continuing violence more than 100,000 people fled the country to neighbouring Liberia. At Old Pohan, a Liberian settlement next to the thickets that extend to the border, refugees greatly outnumbered the local population, and more were arriving all the time. President of Liberia Ellen Johnson Sirleaf said in an interview that "it’s a serious threat to the stability of Liberia and, I might say, to the stability of all neighboring countries". Seeking to move the Ivorians away from border settlements, the United Nations has opened a camp about 25 miles inside Liberia. Refugees are also starting to cross in significant numbers into Ghana.[87]
According to UK shadow international development minister Mark Lazarowicz, the UN aid programmes for Ivory Cost and Liberia are "grossly underfunded".[88]
Although many thousands of Ivorians remain in Liberia, convoys of Ivorian refugees – each convoy containing a few hundred people – have begun heading home, frequently finding their communities still in tatters from the conflict. Ivorian officials have blamed deadly attacks launched from Liberia that targeted Ivorian border towns in 2012 on former militia fighters that remain loyal to Gbagbo and now live in refugee camps in Liberia.[89]
In addition to refugees in Liberia, a significant number of displaced Ivorians stayed in camps throughout western Ivory Coast. The largest was in the Catholic Mission in Duékoué, where at one point church officials estimated 28,000 displaced were staying each night.[75] The displaced persons ultimately were relocated from the Catholic Mission to the Nahibly camp on the outskirts of Duékoué. The camp was burned down by attackers in July 2012, killing 7 and chasing about 5,000 people from their temporary homes.[90]
Mercenaries
[edit]General Gueu Michel, the commander of Ouattara's forces in western Ivory Coast, said that Liberian mercenaries were fighting on the side of Laurent Gbagbo. Liberian and United Nations officials said the general was correct to suspect Liberian mercenaries of crossing into Ivory Coast to help Gbagbo stay in power. Harrison S. Karnwea Sr., Liberia's interior minister said, however, that both sides were recruiting Liberian mercenaries.[87]
Impact on foreign nationals
[edit]By 2 April 1,400 French and other foreign nationals (900 of whom were Lebanese citizens) entered the French peacekeepers' camp close to the Abidjan Airport. The Lebanese president, U.N. officials and French commanders provided assistance to facilitate the departure of the Lebanese, French and African nationals who wish to leave the Ivory Coast.[91][92][93][94] The French army formally took over the running of Abidjan airport on the 4th in order to evacuate foreign citizens living in the Ivory Coast.[72][73][74] Evacuations took place on the 5th and 6th.[citation needed]
Fiscal effects
[edit]Ivory Coast's now defaulted $2,300,000,000 debt bond rose 1.2 points on the 6th to a new four-month high, a possible sign of increased investor confidence that Ouattara would take office and resume payments.[95]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ a b Themnér 2015, p. 342.
- ^ Nossiter, Adam (4 April 2011). "Strikes by U.N. and France Corner Leader of Ivory Coast". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ^ Рада направила в Кот-д’Ивуар 60 украинских миротворцев и три вертолёта. Комитет ВР и Томенко — против Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine // NEWSRU.UA от 4 февраля 2011 (in Russian)
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Former Liberian Rebel-' Benjamin Yeaten ' allegedly aiding War". Shout Africa. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2017.
- ^ [1][2][3][4][permanent dead link][5] Archived 27 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine Government fatalities
- ^ [6] Archived 10 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine[7] Archived 30 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine[8] Opposition fatalities
- ^ "Two rebel soldiers killed in Ivory Coast". AfricaNews. 16 December 2010. Archived from the original on 29 March 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ Une Suédoise de l'Onuci tuée par balle à Abidjan Archived 4 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine, , Le Point
- ^ "Côte d'Ivoire / Décès d'un casque bleu de l'ONUCI « Database of Press Releases related to Africa – APO-Source". Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ "First-ever video proof documenting murder of suspected Gbagbo militants | the Observers". Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ^ Nossiter, Adam (8 April 2011). "Civil war, Ivory Coast-style" (article). The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast" (article). BBC News. 9 April 2011. Archived from the original on 12 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b Lynch, Colum; William Branigin (12 April 2011). "Ivory Coast strongman arrested after French forces intervene". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 13 April 2011. Retrieved 11 April 2011.
- ^ United Nations Security Council Resolution 1528. S/RES/1528(2004) page 2. 27 February 2004. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ^ "Ivory Coast country profile". BBC News. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 31 January 2009. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast poll overturned: Gbagbo declared winner". BBC News. 3 December 2010. Archived from the original on 12 July 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Two presidents sworn in". SAPA. 5 December 2010. Archived from the original on 8 December 2010. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ David Smith (22 December 2010). "Ivory Coast: death squads on the rise as civil war looms". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 20 September 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- ^ Ivory Coast's Gbagbo defies world leaders, euronews.com, 4 December 2010, archived from the original on 2 October 2012, retrieved 1 April 2011
- ^ "BBC News Gbagbo orders peacekeepers to leave Ivory Coast". BBC News. 18 December 2010. Archived from the original on 23 December 2010. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- ^ "US eyes bigger UN force in Ivory Coast". The Washington Post. 22 December 2010. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Ouattara forces surround Gbagbo in Abidjan". BBC News. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 2 December 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ Smith, David (21 December 2010). "Death squads attacking Ivory Coast opposition, claims spokesman". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 20 September 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- ^ "Ivory Coast shelling in Abidjan 'a war crime' – UN". BBC News. 18 March 2011. Archived from the original on 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast's Ouattara 'rejects' African Union mediator". BBC News. 27 March 2011. Archived from the original on 27 March 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast Rebels Claim Capture of Third Town in West". Bloomberg News. 7 March 2011. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Ouattara forces make gains, seize west Ivorian town". Agence France-Presse. 12 March 2011. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Pro-Gbagbo youth answer call to join Ivorian army". Reuters. 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Key Ivory Coast towns fall as Gbagbo calls for ceasefire". Reuters. 29 March 2011. Archived from the original on 30 September 2012. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Pro-Ouattara forces reach Ivorian capital". Reuters. 30 March 2011. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "I. Coast cocoa town under pro-Ouattara forces". Agence France-Presse. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 30 September 2012. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Battle reaches Abidjan". Reuters. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast closes borders amid struggle over presidency". CNN. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast offensive weaves trail of devastation". Agence France-Presse. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 24 January 2013. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Fighting rages near presidential palace, residence in Ivory Coast as standoff may be near end". The Washington Post. Associated Press. 1 April 2011.[dead link]
- ^ a b "Gbagbo supporters accused of massacres in I.Coast". 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 24 January 2013. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Rival forces battle to control Abidjan". BBC News. 2 April 2011. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ a b c Blandy, Fran (1 April 2011). "Gbagbo's I. Coast rival tightens noose". StarAfrica. Archived from the original on 21 March 2012. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: 'Heavy fighting' near Gbagbo residence". BBC News. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 26 June 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ "Heavy fighting after Ouattara troops reach Abidjan". Reuters. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Rebels wonder; where did Gbagbo go?". SAPA. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Fighting spreads in Ivory Coast showdown". Reuters. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Drew Hinshaw (13 March 2011). "In Ivory Coast, Gbagbo's forces defect en masse: reports". Dakar, Senegal. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Smith, David (31 March 2011). "Ivory Coast president on brink as top general deserts". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 22 September 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast Rebels Fight for Gbagbo's Stronghold Abidjan". Bloomberg News. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Adam Nossiter (31 March 2011). "Ivory Coast Battle Nears Decisive Stage in Key City". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ^ "Ouattara forces say attack Gbagbo Abidjan residence". Reuters. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "Ivory Coast: Abidjan in grip of fierce fighting". BBC. 2 April 2011. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ Cocks, Tim (1 April 2011). "Pro-Gbagbo Ivorian television resumes broadcasting". Reuters. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- ^ Kouassi, Selay (3 April 2011). "Ivory Coast eyewitness: 'We need food, but the streets are full of bodies'". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 5 April 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Howden, Daniel (4 April 2011). "UN staff flee Abidjan amid warnings of 'bloodbath'". The Independent. UK. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ a b Adam Nossiter (4 April 2011). "UN and France Strike Leader's Forces in Ivory Coast". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- ^ "Battle rages in Ivory Coast, UN fires on Gbagbo bases". Reuters. 4 April 2011. Archived from the original on 6 April 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Laing, Aislinn (5 April 2011). "Ivory Coast: UN fire rockets at Laurent Gbagbo's palace". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 5 February 2018. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- ^ a b c "Ivory Coast: UN forces fire on pro-Gbagbo camp". BBC News. 4 April 2011. Archived from the original on 5 April 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Smith, David; Kouassi, Selay (4 April 2011). "Ivory Coast general rejoins Gbagbo forces, army says". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 5 March 2017. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Presidential residence 'taken' in Abidjan". BBC News. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ "Ivory Coast army chief Mangou calls for ceasefire". Reuters. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Obama: Ivory Coast's Gbagbo must stand down 'immediately'". USA Today. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Laurent Gbagbo 'negotiating surrender'". BBC. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Gbagbo 'Negotiating Surrender'". Sky News. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ^ "Obama: Gbagbo Must 'Stand Down' Immediately | News". Voice of America. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ "Source: Ouattara forces enter Gbagbo's Ivory Coast stronghold". CNN. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 9 November 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ^ (UKPA) – 2 days ago. "The Press Association: Gbagbo facing further air strikes". Archived from the original on 10 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ John, Mark (9 February 2009). "Ivory Coast's Ouattara seeks recovery despite standoff". Reuters. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "Ivory Coast: More than 100 bodies found, says UN". BBC. 8 April 2011. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ "Ivory Coast: Gbagbo forces regain ground in Abidjan". BBC News. 8 April 2011. Archived from the original on 10 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Ivory Coast: Gbagbo troops 'hit' Ouattara hotel HQ". BBC News. 9 April 2011. Archived from the original on 10 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b Laing, Aislinn (10 April 2011). "Ivory Coast: UN and French helicopter gunships attack Laurent Gbagbo residence". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- ^ "Ivory Coast's Laurent Gbagbo arrested". BBC News. 11 April 2011. Archived from the original on 25 June 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- ^ "Ivory Coast standoff ends with strongman's capture". Associated Press. 11 April 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Charity: More than 1,000 killed in Ivorian town
- ^ a b Andrew Harding (3 April 2011). "Ivory Coast: UN presses Ouattara over Duekoue massacre". BBC. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Pro-Ouattara forces launch palace assault – Africa". Al Jazeera. 5 April 2011. Archived from the original on 7 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b c DiCampo, Peter. "War's End in the West?". Ivory Coast: Elections Turn to War. Pulitzer Center. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ DiCampo, Peter. "An Uncertain Future". Ivory Coast: Elections Turn to War. Pulitzer Center. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ DiCampo, Peter. "Cocoa in the Shade of War". Ivory Coast: Cocoa, Justice, and the Road to Reconciliation. Pulitzer Center/Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on 26 November 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ "Statement on the Situation in Ivory Coast By Leymah Gbowee". Pray The Devil Back to Hell Blog. 8 March 2011. Archived from the original (statement) on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 10 March 2011.
- ^ Norman, Joshua (21 March 2011). "Nigeria: Ignoring Ivory Coast is hypocritical" (article). CBS News/World. Archived from the original on 28 July 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Nigeria urges firmer U.N. stance on Ivory Coast" (article). Reuters. 24 March 2011. Archived from the original on 31 May 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "ECOWAS Summit: West African women protest Ivorian situation". Afrique en ligne. 24 March 2011. Archived from the original (article) on 6 June 2012. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ "'Thousand Women Protest March' in Solidarity with the Women of Cote d'Ivoire". WIPSEN. 23 March 2011. Archived from the original (article) on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "Security Council demands end to violence in Côte d'Ivoire, imposing sanctions against former President and urging him to 'step aside'". United Nations. 30 March 2011. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ^ ""Gbagbo must go" is call as UN Council OKs Cote d'Ivoire resolution". Xinhua News Agency. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 3 April 2011. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ "Côte d'Ivoire: International response and origins of the conflict". United Explanations. 4 April 2011. Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Yelizaveta Isakova (5 April 2011). "Russia to inquire into Cote d'Ivoire crisis". The Voice of Russia. Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ a b Akam, Simon (31 March 2011). "Liberia Uneasily Linked to Ivory Coast Conflict". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 April 2011. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ "Labour urging Ivory Coast aid push as crisis worsens". BBC. 31 March 2011. Archived from the original on 1 April 2011. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ Merrill, Austin. "Ivory Coast: An Uncertain Return". Ivory Coast: Cocoa, Justice, and the Road to Reconciliation. Pulitzer Center/Warscapes. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ Merrill, Austin. "Once an Oasis of Calm in West Africa, Ivory Coast Can't Shake Its Recent, Bloody Past". Ivory Coast: Cocoa, Justice, and the Road to Reconciliation. Pulitzer Center/Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on 20 November 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ "1,400 foreigners flee Abidjan for French military base – Monsters and Critics". Archived from the original on 9 September 2012. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ "Hariri takes measures to facilitate the departure of Lebanese citizens from the Ivory Coast – Politics – iloubnan.info". Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ "French forces sheltering 1,400 foreigners in Ivory Coast < French news | Expatica France". Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ "Ajami: Setting up Flights between Beirut and Abidjan is Impossible – Naharnet Newsdesk".
- ^ Rao, Sujata (5 April 2011). "Ivory Coast dlr bond at new 4-mth high on Gbagbo exit hopes". Reuters. Archived from the original on 9 April 2011. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
Bibliography
[edit]- Themnér, Anders (2015). "Former Military Networks and the Micro-Politics of Violence and Statebuilding in Liberia". Comparative Politics. 47 (1). New York City: Graduate Center, CUNY: 334–353. doi:10.5129/001041515814709284.
Further reading
[edit]- Bah, Abu Bakarr (2010). "Democracy and civil war: Citizenship and peacemaking in Côte d'Ivoire". African Affairs. 109 (437): 597–615. doi:10.1093/afraf/adq046.
- Collier, Paul (2010). "Meltdown in Côte d'Ivoire". Wars, Guns, and Votes: Democracy in Dangerous Places. New York: Harper Perennial. pp. 155–168. ISBN 978-0-06-147964-9.
- Zounmenou, David (2011). "Côte d'Ivoire's post-electoral conflict: what is at stake?". African Security Review. 20 (1): 48–55. doi:10.1080/10246029.2011.561011. S2CID 144774578.
External links
[edit]- "Côte d'Ivoire: International response and origins of the conflict". United Explanations. 4 April 2011.
- Barbara Plett (7 April 2011). "Did UN forces take sides in Ivory Coast?". BBC.

