Rubidium carbonate
Appearance
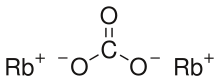
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rubidium carbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.666 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Rb2CO3 | |
| Molar mass | 230.945 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder, very hygroscopic |
| Melting point | 837 °C (1,539 °F; 1,110 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 900 °C (1,650 °F; 1,170 K) (decomposes) |
| Very soluble | |
| −75.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Lithium carbonate Sodium carbonate Potassium carbonate Caesium carbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rubidium carbonate, Rb2CO3, is a convenient compound of rubidium; it is stable, not particularly reactive, and readily soluble in water, and is the form in which rubidium is usually sold.
Preparation
[edit]This salt can be prepared by adding ammonium carbonate to rubidium hydroxide.[2]
Uses
[edit]It is used in some kinds of glass-making by enhancing stability and durability as well as reducing its conductivity. It is also used as a part of a catalyst for preparing short-chain alcohols from feed gas.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 23 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 809.
- ^ Canada Patents
