Portal:COVID-19
The COVID-19 portal
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Most scientists believe the SARS-CoV-2 virus entered into human populations through natural zoonosis, similar to the SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV outbreaks, and consistent with other pandemics in human history. Social and environmental factors including climate change, natural ecosystem destruction and wildlife trade increased the likelihood of such zoonotic spillover. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.

Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries, many of which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, use of face masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While drugs have been developed to inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is still symptomatic, managing the disease through supportive care, isolation, and experimental measures.
The WHO ended the PHEIC for COVID-19 on 5 May 2023. The disease has continued to circulate, but as of 2024, experts were uncertain as to whether it was still a pandemic. Pandemics and their ends are not well-defined, and whether or not one has ended differs according to the definition used. As of 10 November 2024, COVID-19 has caused 7,073,453[1] confirmed deaths. The COVID-19 pandemic ranks as the fifth-deadliest pandemic or epidemic in history. (Full article)About the virus

SARS‑CoV‑2 belongs to the broad family of viruses known as coronaviruses. It is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) virus, with a single linear RNA segment. Coronaviruses infect humans, other mammals, including livestock and companion animals, and avian species. Human coronaviruses are capable of causing illnesses ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS, fatality rate ~34%). SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh known coronavirus to infect people, after 229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1, MERS-CoV, and the original SARS-CoV.
Like the SARS-related coronavirus implicated in the 2003 SARS outbreak, SARS‑CoV‑2 is a member of the subgenus Sarbecovirus (beta-CoV lineage B). Coronaviruses undergo frequent recombination. The mechanism of recombination in unsegmented RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 is generally by copy-choice replication, in which gene material switches from one RNA template molecule to another during replication. The SARS-CoV-2 RNA sequence is approximately 30,000 bases in length, relatively long for a coronavirus—which in turn carry the largest genomes among all RNA families. Its genome consists nearly entirely of protein-coding sequences, a trait shared with other coronaviruses. (Full article)
Disease progress
As of 10 November 2024, 776,753,553 cases of COVID-19 have been reported, resulting in 7,073,453 reported deaths.[1]
| Location | Cases | Deaths | |
|---|---|---|---|
| World[a] | 776,753,553 | 7,073,453 | |
| European Union[b] | 186,262,640 | 1,265,282 | |
| United States | 103,436,829 | 1,206,141 | |
| China[c] | 99,381,078 | 122,367 | |
| India | 45,044,196 | 533,653 | |
| France | 39,024,965 | 168,091 | |
| Germany | 38,437,756 | 174,979 | |
| Brazil | 37,511,921 | 702,116 | |
| South Korea | 34,571,873 | 35,934 | |
| Japan | 33,803,572 | 74,694 | |
| Italy | 26,826,486 | 197,542 | |
| United Kingdom | 25,010,212 | 232,112 | |
| Russia | 24,572,846 | 403,557 | |
| Turkey | 17,004,729 | 101,419 | |
| Spain | 13,980,340 | 121,852 | |
| Australia | 11,861,161 | 25,236 | |
| Vietnam | 11,624,000 | 43,206 | |
| Argentina | 10,106,404 | 130,697 | |
| Taiwan | 9,970,937 | 17,672 | |
| Netherlands | 8,644,647 | 22,986 | |
| Iran | 7,627,863 | 146,837 | |
| Mexico | 7,622,283 | 334,783 | |
| Indonesia | 6,829,704 | 162,059 | |
| Poland | 6,758,426 | 120,897 | |
| Colombia | 6,394,361 | 142,727 | |
| Austria | 6,082,860 | 22,534 | |
| Greece | 5,727,906 | 39,639 | |
| Portugal | 5,669,567 | 29,027 | |
| Ukraine | 5,541,305 | 109,923 | |
| Chile | 5,403,559 | 64,482 | |
| Malaysia | 5,318,418 | 37,351 | |
| Belgium | 4,889,242 | 34,339 | |
| Israel | 4,841,558 | 12,707 | |
| Canada | 4,819,055 | 55,282 | |
| Czech Republic | 4,811,887 | 43,687 | |
| Thailand | 4,803,632 | 34,734 | |
| Peru | 4,526,977 | 220,975 | |
| Switzerland | 4,468,044 | 14,170 | |
| Philippines | 4,173,631 | 66,864 | |
| South Africa | 4,072,813 | 102,595 | |
| Romania | 3,566,594 | 68,899 | |
| Denmark | 3,442,484 | 9,919 | |
| Singapore | 3,006,155 | 2,024 | |
| Hong Kong | 2,876,106 | 13,466 | |
| Sweden | 2,765,204 | 28,006 | |
| New Zealand | 2,652,096 | 4,442 | |
| Serbia | 2,583,470 | 18,057 | |
| Iraq | 2,465,545 | 25,375 | |
| Hungary | 2,236,219 | 49,092 | |
| Bangladesh | 2,051,463 | 29,499 | |
| Slovakia | 1,883,895 | 21,249 | |
| Georgia | 1,864,383 | 17,151 | |
| Republic of Ireland | 1,750,138 | 9,900 | |
| Jordan | 1,746,997 | 14,122 | |
| Pakistan | 1,580,631 | 30,656 | |
| Norway | 1,524,523 | 5,732 | |
| Kazakhstan | 1,504,370 | 19,072 | |
| Finland | 1,499,712 | 11,466 | |
| Lithuania | 1,400,088 | 9,848 | |
| Slovenia | 1,359,884 | 9,914 | |
| Croatia | 1,348,642 | 18,775 | |
| Bulgaria | 1,337,733 | 38,751 | |
| Morocco | 1,279,115 | 16,305 | |
| Puerto Rico | 1,252,713 | 5,938 | |
| Guatemala | 1,250,392 | 20,203 | |
| Lebanon | 1,239,904 | 10,947 | |
| Costa Rica | 1,235,724 | 9,374 | |
| Bolivia | 1,212,149 | 22,387 | |
| Tunisia | 1,153,361 | 29,423 | |
| Cuba | 1,113,662 | 8,530 | |
| Ecuador | 1,078,795 | 36,055 | |
| United Arab Emirates | 1,067,030 | 2,349 | |
| Panama | 1,044,987 | 8,756 | |
| Uruguay | 1,041,682 | 7,686 | |
| Mongolia | 1,011,489 | 2,136 | |
| Nepal | 1,003,450 | 12,031 | |
| Belarus | 994,038 | 7,118 | |
| Latvia | 977,765 | 7,475 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 841,469 | 9,646 | |
| Azerbaijan | 836,474 | 10,353 | |
| Paraguay | 735,759 | 19,880 | |
| Cyprus | 708,580 | 1,492 | |
| Palestine | 703,228 | 5,708 | |
| Bahrain | 696,614 | 1,536 | |
| Sri Lanka | 672,809 | 16,907 | |
| Kuwait | 667,290 | 2,570 | |
| Dominican Republic | 661,103 | 4,384 | |
| Moldova | 650,609 | 12,281 | |
| Myanmar | 643,215 | 19,494 | |
| Estonia | 612,467 | 2,998 | |
| Venezuela | 552,695 | 5,856 | |
| Egypt | 516,023 | 24,830 | |
| Qatar | 514,524 | 690 | |
| Libya | 507,269 | 6,437 | |
| Ethiopia | 501,239 | 7,574 | |
| Réunion | 494,595 | 921 | |
| Honduras | 472,909 | 11,114 | |
| Armenia | 453,016 | 8,778 | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 403,960 | 16,402 | |
| Oman | 399,449 | 4,628 | |
| Luxembourg | 396,017 | 1,000 | |
| North Macedonia | 352,043 | 9,990 | |
| Zambia | 349,892 | 4,078 | |
| Brunei | 349,279 | 181 | |
| Kenya | 344,109 | 5,689 | |
| Albania | 337,195 | 3,608 | |
| Botswana | 330,696 | 2,801 | |
| Mauritius | 329,121 | 1,074 | |
| Kosovo | 274,279 | 3,212 | |
| Algeria | 272,173 | 6,881 | |
| Nigeria | 267,189 | 3,155 | |
| Zimbabwe | 266,396 | 5,740 | |
| Montenegro | 251,280 | 2,654 | |
| Afghanistan | 235,214 | 7,998 | |
| Mozambique | 233,845 | 2,252 | |
| Martinique | 230,354 | 1,104 | |
| Laos | 219,060 | 671 | |
| Iceland | 210,675 | 186 | |
| Guadeloupe | 203,235 | 1,021 | |
| El Salvador | 201,960 | 4,230 | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 191,496 | 4,390 | |
| Maldives | 186,694 | 316 | |
| Uzbekistan | 175,081 | 1,016 | |
| Namibia | 172,556 | 4,110 | |
| Ghana | 172,210 | 1,462 | |
| Uganda | 172,159 | 3,632 | |
| Jamaica | 157,326 | 3,618 | |
| Cambodia | 139,325 | 3,056 | |
| Rwanda | 133,266 | 1,468 | |
| Cameroon | 125,279 | 1,974 | |
| Malta | 123,136 | 925 | |
| Barbados | 108,835 | 593 | |
| Angola | 107,482 | 1,937 | |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 100,976 | 1,474 | |
| French Guiana | 98,041 | 413 | |
| Senegal | 89,312 | 1,972 | |
| Malawi | 89,168 | 2,686 | |
| Kyrgyzstan | 88,953 | 1,024 | |
| Ivory Coast | 88,448 | 835 | |
| Suriname | 82,503 | 1,406 | |
| New Caledonia | 80,203 | 314 | |
| French Polynesia | 79,451 | 650 | |
| Eswatini | 75,356 | 1,427 | |
| Guyana | 74,491 | 1,302 | |
| Belize | 71,430 | 688 | |
| Fiji | 69,047 | 885 | |
| Madagascar | 68,575 | 1,428 | |
| Jersey | 66,391 | 161 | |
| Cabo Verde | 64,474 | 417 | |
| Sudan | 63,993 | 5,046 | |
| Mauritania | 63,876 | 997 | |
| Bhutan | 62,697 | 21 | |
| Syria | 57,423 | 3,163 | |
| Burundi | 54,569 | 15 | |
| Guam | 52,287 | 419 | |
| Seychelles | 51,892 | 172 | |
| Gabon | 49,056 | 307 | |
| Andorra | 48,015 | 159 | |
| Papua New Guinea | 46,864 | 670 | |
| Curaçao | 45,883 | 305 | |
| Aruba | 44,224 | 292 | |
| Tanzania | 43,263 | 846 | |
| Mayotte | 42,027 | 187 | |
| Togo | 39,533 | 290 | |
| Bahamas | 39,127 | 849 | |
| Guinea | 38,582 | 468 | |
| Isle of Man | 38,008 | 116 | |
| Lesotho | 36,138 | 709 | |
| Guernsey | 35,326 | 67 | |
| Faroe Islands | 34,658 | 28 | |
| Haiti | 34,556 | 860 | |
| Mali | 33,171 | 743 | |
| Federated States of Micronesia | 31,765 | 65 | |
| Cayman Islands | 31,472 | 37 | |
| Saint Lucia | 30,288 | 410 | |
| Benin | 28,036 | 163 | |
| Somalia | 27,334 | 1,361 | |
| Solomon Islands | 25,954 | 199 | |
| United States Virgin Islands | 25,389 | 132 | |
| San Marino | 25,292 | 126 | |
| Republic of the Congo | 25,234 | 389 | |
| Timor-Leste | 23,460 | 138 | |
| Burkina Faso | 22,146 | 400 | |
| Liechtenstein | 21,605 | 89 | |
| Gibraltar | 20,550 | 113 | |
| Grenada | 19,693 | 238 | |
| Bermuda | 18,860 | 165 | |
| South Sudan | 18,847 | 147 | |
| Tajikistan | 17,786 | 125 | |
| Monaco | 17,181 | 67 | |
| Equatorial Guinea | 17,130 | 183 | |
| Samoa | 17,057 | 31 | |
| Tonga | 16,992 | 13 | |
| Marshall Islands | 16,297 | 17 | |
| Nicaragua | 16,194 | 245 | |
| Dominica | 16,047 | 74 | |
| Djibouti | 15,690 | 189 | |
| Central African Republic | 15,443 | 113 | |
| Northern Mariana Islands | 14,985 | 41 | |
| Gambia | 12,627 | 372 | |
| Collectivity of Saint Martin | 12,324 | 46 | |
| Vanuatu | 12,019 | 14 | |
| Greenland | 11,971 | 21 | |
| Yemen | 11,945 | 2,159 | |
| Caribbean Netherlands | 11,922 | 41 | |
| Sint Maarten | 11,051 | 92 | |
| Eritrea | 10,189 | 103 | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 9,674 | 124 | |
| Guinea-Bissau | 9,614 | 177 | |
| Niger | 9,528 | 315 | |
| Comoros | 9,109 | 160 | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 9,106 | 146 | |
| American Samoa | 8,359 | 34 | |
| Liberia | 8,090 | 294 | |
| Sierra Leone | 7,985 | 126 | |
| Chad | 7,702 | 194 | |
| British Virgin Islands | 7,628 | 64 | |
| Cook Islands | 7,375 | 2 | |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | 6,824 | 40 | |
| Sao Tome and Principe | 6,771 | 80 | |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 6,607 | 46 | |
| Palau | 6,372 | 10 | |
| Saint Barthélemy | 5,507 | 5 | |
| Nauru | 5,393 | 1 | |
| Kiribati | 5,085 | 24 | |
| Anguilla | 3,904 | 12 | |
| Wallis and Futuna | 3,760 | 9 | |
| Macau | 3,514 | 121 | |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | 3,426 | 2 | |
| Tuvalu | 2,943 | 1 | |
| Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha | 2,166 | 0 | |
| Falkland Islands | 1,923 | 0 | |
| Montserrat | 1,403 | 8 | |
| Niue | 1,092 | 0 | |
| Tokelau | 80 | 0 | |
| Vatican City | 26 | 0 | |
| Pitcairn Islands | 4 | 0 | |
| Turkmenistan | 0 | 0 | |
| North Korea | 0 | 0 | |
| |||
About the symptoms

The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable depending on the type of variant contracted, ranging from mild symptoms to a potentially fatal illness. Common symptoms include coughing, fever, loss of smell (anosmia) and taste (ageusia), with less common ones including headaches, nasal congestion and runny nose, muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, eye irritation, and toes swelling or turning purple, and in moderate to severe cases, breathing difficulties. People with the COVID-19 infection may have different symptoms, and their symptoms may change over time. (Full article)
About the spread
COVID-19 is mainly transmitted when people breathe in air contaminated by droplets/aerosols and small airborne particles containing the virus. Infected people exhale those particles as they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing. Transmission is more likely the closer people are. However, infection can occur over longer distances, particularly indoors.
Infectious particles range in size from aerosols that remain suspended in the air for long periods of time to larger droplets that remain airborne briefly or fall to the ground. Additionally, COVID-19 research has redefined the traditional understanding of how respiratory viruses are transmitted. The largest droplets of respiratory fluid do not travel far, but can be inhaled or land on mucous membranes on the eyes, nose, or mouth to infect. Aerosols are highest in concentration when people are in close proximity, which leads to easier viral transmission when people are physically close, but airborne transmission can occur at longer distances, mainly in locations that are poorly ventilated; in those conditions small particles can remain suspended in the air for minutes to hours. (Full article)
Containment measures

Videos
-
Animation describing the structure of a coronavirus
-
Video about what SARS-CoV-2 does to the human body
-
Video about the transmission of coronaviruses
Recent news
- 23 October 2024 – Demographics of Germany, German economic crisis
- The Ifo Institute for Economic Research reports that Germany experienced a 13% birth rate decline nationally and up to a 17.5% birth rate decline in eastern Germany between 2021 and 2023, with the institute attributing the decline to several reasons including the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russo-Ukrainian war, and high inflation. (DW)
- 6 September 2024 –
- The Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs announces the end of its international adoption program after suspending the program during the COVID-19 pandemic. (Al Jazeera)
Did you know?
- ... that Potamophylax coronavirus's range has been described as a battlefield between scientists and hydropower plant management?
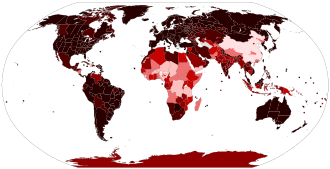
Data maps
-
Total confirmed cases by reporting area3,000 + per 100,000 inhabitants1,000–3,00 per 100,000 inhabitants300–1,000 per 100,000 inhabitants100–300 per 100,000 inhabitants30–100 per 100,000 inhabitants0–30 per 100,000 inhabitantsNone or no data
-
Total confirmed deaths by country100+ per 100,000 inhabitants18–100 per 100,000 inhabitants3.3–18 per 100,000 inhabitants0.6–3.3 per 100,000 inhabitants0.1–0.6 per 100,000 inhabitants<0.1 per 100,000 inhabitantsNone or no data
Economic impact
The COVID-19 pandemic caused far-reaching economic consequences including the COVID-19 recession, the second largest global recession in recent history, decreased business in the services sector during the COVID-19 lockdowns, the 2020 stock market crash (which included the largest single-week stock market decline since the financial crisis of 2007–2008), the impact of COVID-19 on financial markets, the 2021–2023 global supply chain crisis, the 2021–2023 inflation surge, shortages related to the COVID-19 pandemic including the 2020–present global chip shortage, panic buying, and price gouging. The pandemic led to governments providing an unprecedented amount of stimulus, and was also a factor in the 2021–2022 global energy crisis and 2022–2023 food crises.
Amidst the recovery and containment, the world economic system was characterized as experiencing significant, broad uncertainty. Economic forecasts and consensus among macroeconomics experts show significant disagreement on the overall extent, long-term effects and projected recovery. A large general increase in prices was attributed to the pandemic. In part, the record-high energy prices were driven by a global surge in demand as the world quit the economic recession caused by COVID-19, particularly due to strong energy demand in Asia. (Full article)
Workplace
Hazard controls for COVID-19 in workplaces are the application of occupational safety and health methodologies for hazard controls to the prevention of COVID-19. Multiple layers of controls are recommended, including measures such as remote work and flextime, personal protective equipment (PPE) and face coverings, social distancing, and enhanced cleaning programs. Recently, engineering controls have been emphasized, particularly stressing the importance of HVAC systems meeting a minimum of 5 air changes per hour with ventilation or MERV-13 filters, as well as the installation of UVGI systems in public areas. (Full article)
Misinformation
False information, including intentional disinformation and conspiracy theories, about the scale of the COVID-19 pandemic and the origin, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of the disease has been spread through social media, text messaging, and mass media. False information has been propagated by celebrities, politicians, and other prominent public figures. Many countries have passed laws against "fake news", and thousands of people have been arrested for spreading COVID-19 misinformation. The spread of COVID-19 misinformation by governments has also been significant. (Full article)
Testing
COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that cases COVID-19 and is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The two main types of tests detect either the presence of the virus or antibodies produced in response to infection. Molecular tests for viral presence through its molecular components are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests (serology immunoassays) instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate. (Full article)
Vaccine research
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
The COVID‑19 vaccines are widely credited for their role in reducing the spread of COVID‑19 and reducing the severity and death caused by COVID‑19. According to a June 2022 study, COVID‑19 vaccines prevented an additional 14.4 to 19.8 million deaths in 185 countries and territories from 8 December 2020 to 8 December 2021. Many countries implemented phased distribution plans that prioritized those at highest risk of complications, such as the elderly, and those at high risk of exposure and transmission, such as healthcare workers. (Full article)Drug research
Long COVID
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial period of COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after the initial COVID-19 infection, but other agencies define it as starting at four weeks after the initial infection.
The causes of long COVID are not yet fully understood. Hypotheses include lasting damage to organs and blood vessels, problems with blood clotting, neurological dysfunction, persistent virus or a reactivation of latent viruses and autoimmunity. Diagnosis of long COVID is based on (suspected or confirmed) COVID-19 infection or symptoms—and by excluding alternative diagnoses. (Full article)Images
-
Scanning electron microscope image of SARS-CoV-2 (centre, yellow)
-
This image reveals ultra-structural morphology exhibited by the virus
-
SARS-CoV-2 structure
Topics
Get involved!

Get involved by joining WikiProject COVID-19. We discuss collaborations and all manner of issues on our talk page. As of 14 November 2024, there are 2,478 articles within the project's scope. A full list is available here.
Categories
Related portals
References
- ^ a b c Mathieu, Edouard; Ritchie, Hannah; Rodés-Guirao, Lucas; Appel, Cameron; Giattino, Charlie; Hasell, Joe; Macdonald, Bobbie; Dattani, Saloni; Beltekian, Diana; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban; Roser, Max (2020–2024). "Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19)". Our World in Data. Retrieved 2024-11-10.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus