Portal:Guatemala
The Guatemala portal
Republic of Guatemala República de Guatemala (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
Motto:
| |
| Anthem: Himno Nacional de Guatemala (English: "National Anthem of Guatemala") | |
| ISO 3166 code | GT |
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically bordered to the south by the Pacific Ocean and to the northeast by the Gulf of Honduras.
The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica; in the 16th century, most of this was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence from Spain and Mexico in 1821. From 1823 to 1841, it was part of the Federal Republic of Central America.
For the latter half of the 19th century, Guatemala suffered instability and civil strife. From the early 20th century, it was ruled by a series of dictators backed by the United States. In 1944, authoritarian leader Jorge Ubico was overthrown by a pro-democratic military coup, initiating a decade-long revolution that led to social and economic reforms. In 1954, a US-backed military coup ended the revolution and installed a dictatorship.
From 1960 to 1996, Guatemala endured a bloody civil war fought between the US-backed government and leftist rebels, including genocidal massacres of the Maya population perpetrated by the Guatemalan military. The United Nations negotiated a peace accord, resulting in economic growth and successive democratic elections.
Guatemala's abundance of biologically significant and unique ecosystems includes many endemic species and contributes to Mesoamerica's designation as a biodiversity hotspot.
Although rich in export goods, around a quarter of the population (4.6 million) face food insecurity. Other extant major issues include poverty, crime, corruption, drug trafficking, and civil instability.
With an estimated population of around 17.6 million,0 Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America, the 4th most populous country in North America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. Its capital and largest city, Guatemala City, is the most populous city in Central America. (Full article...)
Selected article -
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries.
Pedro de Alvarado arrived in Guatemala from the newly conquered Mexico in early 1524, commanding a mixed force of Spanish conquistadors and native allies, mostly from Tlaxcala and Cholula. Geographic features across Guatemala now bear Nahuatl placenames owing to the influence of these Mexican allies, who translated for the Spanish. The Kaqchikel Maya initially allied themselves with the Spanish, but soon rebelled against excessive demands for tribute and did not finally surrender until 1530. In the meantime the other major highland Maya kingdoms had each been defeated in turn by the Spanish and allied warriors from Mexico and already subjugated Maya kingdoms in Guatemala. The Itza Maya and other lowland groups in the Petén Basin were first contacted by Hernán Cortés in 1525, but remained independent and hostile to the encroaching Spanish until 1697, when a concerted Spanish assault led by Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi finally defeated the last independent Maya kingdom. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that the Adelaide L. T. Douglas House, built for a New York City socialite, housed the United States Olympic Committee before being sold to Guatemala?
- ... that the Central American government voted for annexation to the First Mexican Empire after a request from Regent Agustín de Iturbide?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
Iximcheʼ (/iʃimˈtʃeʔ/) (or Iximché using Spanish orthography) is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its abandonment in 1524. The architecture of the site included a number of pyramid-temples, palaces and two Mesoamerican ballcourts. Excavators uncovered the poorly preserved remains of painted murals on some of the buildings and ample evidence of human sacrifice. The ruins of Iximche were declared a Guatemalan National Monument in the 1960s. The site has a small museum displaying a number of pieces found there, including sculptures and ceramics. It is open daily.
For many years the Kaqchikel served as loyal allies of the Kʼicheʼ Maya. The growing power of the Kaqchikel within the alliance eventually caused such friction that the Kaqchikel were forced to flee the Kʼicheʼ capital and founded the city of Iximche. The Kaqchikel established their new capital upon an easily defensible ridge almost surrounded by deep ravines. Iximche developed quickly as a city and within 50 years of its foundation it had reached its maximum extent. The rulers of Iximche were four principal lords drawn from the four main clans of the Kaqchikel, although it was the lords of the Sotzʼil and Xahil clans who held the real power. (Full article...)
Selected image -
More did you know -
- El Mirador was by far the most populated city in Pre-Columbian America and contains the second largest pyramid in the world by volume.
Pinguicula moranensis /pɪŋˈɡwɪkjʊlə ˌmɒrəˈnɛnsɪs/ is a perennial rosette-forming insectivorous herb in the flowering plant family Lentibulariaceae. It is native to El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico. A species of butterwort, it forms summer rosettes of flat, succulent leaves up to 10 centimeters (4 in) long, which are covered in mucilaginous (sticky) glands that attract, trap, and digest arthropod prey. Nutrients derived from the prey are used to supplement the nutrient-poor substrate that the plant grows in. In the winter the plant forms a non-carnivorous rosette of small, fleshy leaves that conserves energy while food and moisture supplies are low. Single pink, purple, or violet flowers appear twice a year on upright stalks up to 25 centimeters long.
The species was first collected by Humboldt and Bonpland on the outskirts of Mina de Morán in the Sierra de Pachuca of the modern-day Mexican state of Hidalgo on their Latin American expedition of 1799–1804. Based on these collections, Carl Sigismund Kunth described this species in Nova Genera et Species Plantarum in 1817. The extremely variable species has been redefined at least twice since, while several new species have been segregated from it based on various geographical or morphological distinctions, although the legitimacy of some of these is still debated. P. moranensis remains the most common and most widely distributed member of the Section Orcheosanthus. It has long been cultivated for its carnivorous nature and attractive flowers, and is one of the most common butterworts in cultivation. (Full article...)
List of Featured articles
|
|---|
General images -
The following are images from various Guatemala-related articles on Wikipedia.
Topics
Departments
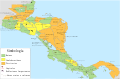
Guatemala is divided into 22 departments (departamentos) and sub-divided into about 332 municipalities (municipios).
The departments include:

Related portals
Things you can do

Here are some things you can do for WikiProject Guatemala:
- Create requested articles:
- El Viejo Palmar -- Village south of Quetzaltenango, hit by a volcanic eruption
- Expand "stub" and "start" articles:
- Assess the importance of articles:
Recognized content
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Guatemala}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
Good articles
- 5to Piso
- 2010 Guatemala City sinkhole
- Adentro
- Gómez de Alvarado
- El Amor (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Francisco Javier Arana
- Jacobo Árbenz
- Ricardo Arjona
- La Blanca, Peten
- Bartolomé de las Casas
- Central America under Mexican rule
- Como Duele (Ricardo Arjona song)
- El Chal
- Fuiste Tú
- Guatemala at the 2016 Summer Paralympics
- Guatemalan Revolution
- Haʼ Kʼin Xook
- Independiente (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Itzam Kʼan Ahk II
- Iximche
- Kʼinich Yat Ahk II
- Kʼinich Yoʼnal Ahk I
- Manche Chʼol
- Marta (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Mi Novia Se Me Está Poniendo Vieja
- Mixco Viejo
- Motul de San José
- Mundo Perdido, Tikal
- North Acropolis, Tikal
- Poquita Ropa
- Puente (song)
- Quién Dijo Ayer
- Quién (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Battle of Roatán
- Simplemente Lo Mejor
- Spanish American wars of independence
- Spanish conquest of Yucatán
- Spanish conquest of the Maya
- Te Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Tikal
- Trópico (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Vida (Ricardo Arjona song)
- White-lipped peccary
- Yoʼnal Ahk III
- Zaculeu
Featured pictures
-
Cinnamon hummingbird (Amazilia rutila) in flight Los Tarrales
-
Emerald swift (Sceloporus malachiticus) Finca El Pilar
-
Ocellated turkey (Meleagris ocellata) male Peten
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Guatemala news
The current date and time in Guatemala is Thursday, November 21, 2024, 04:44.
News media:
- The Guatemala Times
- La Prensa Libre (in Spanish)
- Wikinews Guatemala portal