Liangzi Lake
| Liangzi Lake | |
|---|---|
| Location | Liangzihu District (Ezhou) and Jiangxia District (Wuhan), Hubei |
| Coordinates | 30°14′25″N 114°31′13″E / 30.2404°N 114.5204°E |
| Lake type | Fresh water lake |
| Catchment area | 3,265 km2 (1,261 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | China |
| Max. length | 31.7 km (20 mi) |
| Max. width | 12.3 km (8 mi) |
| Surface area | 370.0 square kilometres (142.9 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 4.16 m (14 ft) |
| Max. depth | 6.2 m (20 ft) |
| Water volume | 1,265×106 m3 (44.7×109 cu ft) |
| Surface elevation | 20 m (66 ft) |
Liangzi Lake (Chinese: 梁子湖), originally Fan Lake (Chinese: 樊湖),[1] is a freshwater lake in the southeast of Hubei Province, divided between the Liangzihu Scenic Spot Office of Jiangxia District, Wuhan and the Liangzihu District of Ezhou City (both areas named after the lake). This rural area south of Wuhan, situated in the south bank of the middle reaches of Yangtze River. The lake is 370 km 2, with a drainage area of 3265 km 2, an elevation of 20 m, length 31.7 km and mean width 9.6 km (max 12.3 m).[2] The shoreline of lake is highly indented.
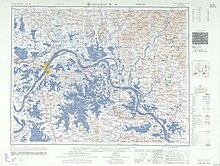
Liangzi Lake appears to have two outlets. On the northers side of the lake, a small river or canal flows from Liangzi into Tangxun Lake, an urban lake on the south side of Wuhan, which eventually drains into the Yangtze. On the eastern side of the lake, another river flows from Liangzi Lake toward Ezhou, where it enters the Yangtze as well.[citation needed]
On January 1, 2018, Ezhou officially implemented a new law called "Liangzihu District Marine Life Protection Zone Absolute Fishing Ban Work Implementation Plan" (《梁子湖区水生生物保护区全面禁捕工作实施方案》).[3] The lake is rich in fish and it is the origin of Wuchang Bream.[citation needed]
Analysis of core samples extracted from the bottom of the lake allows scientists to measure the presence of metals such as copper, lead, nickel and zinc in the environment over the last several thousand ages; they provide evidence for the existence of mining and metal smelting in the region as early as 1500 BC, during the time of the State of Chu.[4] (The Huangshi/Daye region east of the lake continues to be a mining and metallurgical center to this day.)
"Sister Lakes" partnership has been established between Liangzi Lake and Lake Pepin in Minnesota.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ 大梁子湖水系生态修复系列报道:人水和谐 长远之道 (in Simplified Chinese). Ezhou News. 23 August 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
梁子湖,原名樊湖,由梁子湖、鸭儿湖、保安湖、三山湖等湖泊组成,分别与武汉、咸宁、大冶等市(县)交界。至今,鄂州人仍通称梁子湖周围地区为樊湖地区,称梁子湖水系为樊湖水系。
- ^ Sumin, Wang; Hongshen, Dou (1998). Lakes in China. Beijing: Science Press. p. 193. ISBN 7-03-006706-1.
- ^ 梁子湖鄂州水域开始禁捕 1100户渔民上岸安置转产 (in Simplified Chinese). 湖北省人民政府台湾事务办公室 华夏经纬网版权所有. 2 January 2018. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
1月1日,鄂州市《梁子湖区水生生物保护区全面禁捕工作实施方案》正式实施,(...)
- ^ Jia, Hepeng (2008-06-23), Lake sediments reveal 7000 years of history
- ^ Sister Lakes: Pepin in Minnesota and Liangzi in China