Traditional Korean medicine
| This article is part of a series on |
| Alternative medicine |
|---|
 |

Traditional Korean medicine[n 1] (known in North Korea as Koryo medicine) refers to the forms of traditional medicine practiced in Korea.
History
[edit]
Korean medicine traditions originated in ancient and prehistoric times and can be traced back as far as 3000 BCE when stone and bone needles were found in North Hamgyong Province, in present-day North Korea.[2][3] In Gojoseon, where the founding myth of Korea is recorded, there is a story of a tiger and a bear who wanted to reincarnate in human form and who ate wormwood and garlic. In Jewang Ungi (제왕운기), which was written around the time of Samguk Yusa, wormwood and garlic are described as 'edible medicine', showing that, even in times when incantatory medicine was the mainstream, medicinal herbs were given as curatives in Korea. Medicinal herbs at this time were used as remedial treatment such as easing the pain or tending injury, along with knowing what foods were good for health. In the period of the Three Kingdoms, traditional Korean medicine was mainly influenced by other traditional medicines such as ancient Chinese medicine. There was important trade with foreign countries during the period of the Three Kingdoms.[4] “In particular, medical knowledge from China and India supplemented the foundation of traditional medicine that had been handed down from the Old Joseon period."[4] In Korea, this has “spurred further developments."[4]
Medicine flourished in the period of the Joseon. For example, the first training system of nurses was instituted under King Taejong (1400–1418), while under the reign of King Sejong the Great (1418–1450) measures were adopted to promote the development of a variety of Korean medicinal ingredients.[5] These efforts were systematized and published in the Hyangyak Jipseongbang (향약집성방, 1433), which was completed and included 703 Korean native medicines, providing an impetus to break away from dependence on Chinese medicine.[6] The medical encyclopaedia named Classified Collection of Medical Prescriptions (醫方類聚, 의방유취), which included many classics from traditional chinese medicine, written by Kim Ye-mong (金禮蒙, 김예몽) and other Korean official doctors from 1443 to 1445, was regarded as one of the greatest medical texts of the 15th century.[6] It included more than 50,000 prescriptions and incorporated 153 different Korean and Chinese texts,[6] including the Concise Prescriptions of Royal Doctors (御醫撮要方, 어의촬요방) which was written by Choi Chong-jun (崔宗峻, 최종준) in 1226. Classified Collection of Medical Prescriptions has very important research value, because it keeps the contents of many ancient Korean and Chinese medical books that had been lost for a long time.[7]

After this, many books on medical specialties were published. There are three physicians from the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1910) who are generally credited with further development of traditional Korean medicine—Heo Jun, Saam, and Yi Je-ma. After the Japanese invasion in 1592, Dongeui Bogam (동의보감) was written by Heo Jun, the first of the major physicians. This work further integrated the Korean and Chinese medicine of its time and was influential to Chinese, Japanese and Vietnamese medicine. In the late period of Joseon, Yi Je-ma's “unique system of constitutional medicine” illustrates the “nature of” the medicine that has been traditionally developed in Korea by example.[4] Medical treatments were based upon yin and yang principles “and the five elements."[4] A warm treatment would treat a person who is a yin.[4] On the other hand, a cold treatment would treat a person who is a yang.[4]
The next major influence to traditional Korean medicine is related to Sasang typology (사상의학). Yi Je-ma and his book, The Principal of Life Preservation in Oriental Medicine (東醫壽世保元, 동의수세보원) systematically theorized with the influence of Korean Confucianism and his clinical experiences in Korea. Yi Je-ma said that even if patients suffer the same illness, patients need to use different herbal applications to treat the same illness due to the pathophysiologies of individuals. He stresses that the health of human body had a close relationship with the state of mind. He believed that the human mind and body were not separate and they closely reflected each other, and the aspect of mind needed to be considered when examining the causes of disease. Thus, not only food and natural environment but also emotional changes in humans can be another major reason for illness. He believed that medical diagnosis and treatment should be based on person's typology rather than on symptoms alone and each person should be given different prescriptions depending on the constitution of the individual.[8] Sasang typology (사상의학) focuses on the individual patients based on different reactions to disease and herbs. Treat illness by the treatment of the root cause through proper diagnosis. Key to this diagnosis is to first determine the internal organs or pathophysiology of each patient.[9]
The next recognized individual is Saam, a priest-physician who is believed to have lived during the 16th century. Although there is much unknown about Saam, including his real name and date of birth, it is recorded that he studied under the famous monk Samyang. He developed a system of acupuncture that employs the five element theory.
In the late Joseon dynasty, positivism was widespread. Clinical evidence was used more commonly as the basis for studying disease and developing cures. Scholars who had turned away from politics devoted themselves to treating diseases and, in consequence, new schools of traditional medicine were established. Simple books on medicine for the common people were published.
Yi Je-ma classified human beings into four main types, based on the emotion that dominated their personality and developed treatments for each type:
- Tae-Yang (태양, 太陽) or "greater yang"
- So-Yang (소양, 小陽) or "lesser yang"
- Tae-Eum (태음, 太陰) or "greater yin"
- So-Eum (소음, 小陰) or "lesser yin"
The Japanese took control of Korea, which made the Korean traditional medicine fall on difficult times.[4] Colonial rule of the Japanese started since 1910.[4] The continuance of developing Korean medicine was suspended for 40 years due to the Japanese rule.[4] Academic research of this medicine was suspended as well.[4] The suppression lasted until 1945, when Korea was freed from the Japanese rule.[4] In 1951, the enactment of the National Medical Treatment Law established an organized framework for skillful practitioners who use the medicine that has been traditionally developed to treat patients.[4] Koreans and their government supported this medicine.[4] In 1970s, Korean traditional medicine including acupuncture was generally acknowledged by healthcare clinics because of its value.[4]
Originally, Korean traditional medicine was called “medicine of symptoms."[10] “Principles of traditional medicine call for an assessment of eight symptoms."[10] These symptoms are categorized “into four pairs: cold/hot, deficiency/sufficiency, large/small, and yin/yang."[10] Korean traditional medicine is ineffective when used alone in some situations.[10] The medicine from the West can be used with Korean medicine, which is more effective.[10] In Korea, this widespread practice occurs for a long time.[10] Currently, Korean Traditional Medicine is under challenges to undergo scientific examinations such as clinical trials to counter growing distrust.[11] The meme '한무당'(Hanmudang), a neologism that relates Korean Traditional Medicine to shamanism has become too prevalent among young generations that there the association of Korean Traditional Medicine Protectionists had to take measures to stop the meme from auto-completing in internet searches.[12]
In general, the history of Korean medicine can be divided into five periods. The first period, up to about the 12th century, was one of the alleged dark ages of Korean medicine, with TKM based primarily on folk tradition and some foreign (mostly Chinese) elements. In the second period, the 13th to 15th centuries, Hyangyak medicine, which emphasized the use of domestic herbs, emerged. Hyangyak medicine is a type of TKM that prescribed only Hyangyak.[13] This local focus was crucial during times of war, when access to foreign medicinal supplies was limited.The third period, the 15th to early 17th centuries, was marked by the creation of the great medical texts such as Hyangyak Jipseongbang, which combined indigenous and foreign knowledge to form a complete system of Korean medicine.
In the 17th to 19th centuries, TKM became more independent with the publication of the Principles and Practice of Eastern Medicine (東醫寶鑑, 동의보감, Dongui Bogam) in 1613, a seminal text that solidified TKM as distinct from TCM. The fifth period, roughly the 20th and 21st centuries, required a great deal of adjustment to TKM to modern medical research, yet retained TKM. This period is the time of Korea trying to incorporate KM into the national health care system and at the same time dealing with modernization and globalization.
To sum up, the growth of Korean Medicine reveals how traditional wisdom can evolve when faced with external factors or contemporary demands. Synthesis of TKM with modern science traces TKM’s evolution from folk herbal medicine to integration with scientific research, albeit with a cultural dilemma of retaining the past while modernizing. Such progression provides insights into the durability and applicability of traditional systems in the contemporary world.
Methods
[edit]
The most common applications of Korean traditional medicine are acupuncture, herbal medicine, and moxibustion.[10] They describe a combination of natural and medical sciences research.[10] In Korea, adherents of the medicine that has been traditionally developed advise that acupuncture comes first.[10] Moxibustion comes second and herbal medicine comes third.[10] Depending on physical state and particular condition of the individual, these practices can be prescribed in separate ways.[10]
Herbal medicine
[edit]Herbalism is the study and practice of using plant material for the purpose of food, medicine, or health. They may be flowers, plants, shrubs, trees, moss, lichen, fern, algae, seaweed or fungus. The plant may be used in its entirety or with only specific parts.
Herbal medicines may be presented in many forms including fresh, dried, whole, or chopped. Herbs may be prepared as infusions when an herb is soaked in a liquid or decocted—simmered in water over low heat for a certain period. Some examples of infusion are chamomile or peppermint, using flowers, leaves and powdered herbs. Decocting examples may be rose hips, cinnamon bark, and licorice root consisting of fruits, seeds, barks, and roots. Fresh and dried herbs can be tinctured where herbs are kept in alcohol or contained in a vinegar extract. They can be preserved as syrups such as glycerites in vegetable glycerin or put in honey known as miels.
Non-oral herbal uses consist of creams, baths, oils, ointments, gels, distilled waters, washes, poultices, compresses, snuffs, steams, inhaled smoke and aromatics volatile oils.
Many herbalists consider the patient's direct involvement to be critical. These methods are delivered differently depending on the herbal traditions of each area. Nature is not necessarily safe; special attention should be used when grading quality, deciding a dosage, realizing possible effects, and any interactions with herbal medications.[14]
An example of herbal medicine is the use of medicinal mushrooms as a food and as a tea. A notable mushroom used in traditional Korean medicine is Phellinus linteus, also known as Song-gen.
Another example of herbal medicine is cheongsimhwan (Korean: 청심환, lit. 'clear-mind pill'), a pill formulated with thirty odd herbs and other medicinal ingredients, including calculus bovis, ginseng, musk, and Chinese yam root.[15]
Acupuncture
[edit]Acupuncture is used to withdraw blood or stimulate certain points on humans and animals by inserting them on specific pressure points of the body. Traditional acupuncture involves the belief that a "life force" (qi) circulates within the body in lines called meridians.[16] Scientific investigation has not found any histological or physiological evidence for traditional Chinese concepts such as qi, meridians, and acupuncture points,[n 2][21] and many modern practitioners no longer support the existence of life force energy (qi) flowing through meridians, which was a major part of early belief systems.[22][23][24] Pressure points can be stimulated through a mixture of methods ranging from the insertion and withdrawal of very small needles to the use of heat, known as moxibustion. Pressure points can also be stimulated by laser, massage, and electrical means.[25]: 234 Constitutional acupuncture, medicinal acupuncture, Sa-am acupuncture, and single-needle acupuncture are unique methods of acupuncture.[10]
Moxibustion
[edit]Moxibustion is a technique in which heat is applied to the body with a stick or a cone of burning mugwort. The tool is placed over the affected area without burning the skin. The cone or stick can also be placed over a pressure point to stimulate and strengthen the blood.[26]
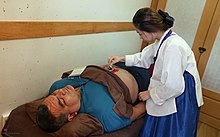
A Cochrane Review found moderate certainty evidence for the use of moxibustion plus usual care for reducing the chance of breech presentation of babies but uncertainty about the need for ECV.[27] Moxibustion has also been studied for the treatment of pain,[28] cancer,[29] stroke,[30] ulcerative colitis,[31] constipation,[32] and hypertension.[33] Systematic reviews of moxibustion show that there is a need for further research about these other therapeutic applications to reduce risk of publication bias.[34]
Education
[edit]Graduate School of Korean Medicine
[edit]The South Korean government established a national school of traditional Korean medicine to establish its national treasure on a solid basis after the closing of the first modern educational facility (Dong-Je medical school) one hundred years ago by the Japanese invasion.
In 2008, the School of Korean Medicine was established inside Pusan National University with the 50 undergraduate students on the Yangsan medical campus. The new affiliated Korean Medical Hospital and Research Center for Clinical Studies are under construction.
Compared with common private traditional medicine undergraduate schools (6 years), this is a special graduate school (4+4).
General Hospital of Koryo Medicine
[edit]Koryo medicine is a form of traditional medicine used in North Korea and promoted by the North Korean government, providing half of the reported healthcare in the country.[35] It is largely practised in the General Hospital of Koryo Medicine, Pyongyang.[36] Examples of Koryo medicine sold commercially are Kumdang-2 and Royal Blood-Fresh, sold by the Pugang Pharmaceutic Company, both of which are popular with Chinese tourists to North Korea.[37]
Influence of Western medicine
[edit]According to Han (1997), Christian missionaries introduced Western medicine to Korea in the late 19th century. It was the time when there was an increased exposure to Western influences and imperialist pressures in Korea, which led to a rapid adoption of Western medical practices. During the Japanese colonial period, the suppression of Hanbang reinforced its decline, and it was treated as secondary and behind Western medicine. However, the late 20th century witnessed a revival of Hanbang, and there was a growing nationalistic sentiment and affluence at that period. [38]
Criticism
[edit]The primary criticism of the integration of Western medicine into Korean society is its impact on accessibility because the benefits of medical development were mostly available to urban and wealthier parts of the population. This inequality was intensified by the commercialisation of healthcare, where both Western and traditional medicines were marketed aggressively, often prioritising profit over patient care. Furthermore, the overshadowing of traditional practices by Western medicine led to the marginalisation of Korean identity and culture. Despite this criticism, there have been undeniable advancements in public health, including better disease control and medical technologies that have significantly improved the quality of life. Additionally, the establishment of medical schools and training programs has professionalised and standardised healthcare, thus elevating the overall health condition of the nation.
See also
[edit]- Dongui Bogam
- Ginseng
- Kampo
- Korean philosophy
- Korean traditional pharmacist
- Kyung-ok-ko
- List of forms of alternative medicine
- List of topics characterized as pseudoscience
- Pharmacognosy
- Sasang typology
- Traditional Chinese medicine
- Traditional Vietnamese medicine
- Yakchim
Notes
[edit]- ^ 한의학; 韓醫學; Hanuihak; or 향약; 鄕藥; Hyangyak
- ^ Singh & Ernst (2008) stated, "Scientists are still unable to find a shred of evidence to support the existence of meridians or Ch'i",[17] "The traditional principles of acupuncture are deeply flawed, as there is no evidence at all to demonstrate the existence of Ch'i or meridians"[18] and "As yin and yang, acupuncture points and meridians are not a reality, but merely the product of an ancient Chinese philosophy".[19][20]
References
[edit]- ^ "A Korean acupuncturist inserting a needle into the leg of a male patient". Wellcome Collection. Retrieved 2024-05-26.
- ^ "Acupuncture Stimulated Healing". Archived from the original on 2015-04-09.
- ^ Dr. DiLeva, Rose. "The Evolution of Acupuncture in Veterinary Medicine" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 7, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Shin Joon-shik. (2008). Introduction to Korea’s Traditional Medicine. Koreana, 22(1), 8–13.
- ^ Korean Medicine: A Holistic Way to Health and Healing By Seoul Selection
- ^ a b c Selin, Helaine (2013-11-11). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 506. ISBN 9789401714167. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- ^ "The Influence of Chinese Clothing | Oriental Style". Archived from the original on 2011-10-08. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- ^ Archaeology of Psychotherapy in Korea: A Study of Korean Therapeutic Work ... By Haeyoung Jeong
- ^ "ChaeLab - Sasang Typology". Archived from the original on 2010-11-15. Retrieved 2010-09-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Ko Changham. (2008). Three Popular Applications of Korea’s Traditional Medicine. Koreana, 22(1), 14–23.
- ^ 김, 준호 (2020-07-16). "의사단체 "한방첩약은 비과학적, 안전·효과 불신"". 메디칼트리뷴 (in Korean). Retrieved 2023-04-27.
- ^ "네이버, 카카오 등에서 '한무당' 자동완성 검색어 사라진다". 한의신문 (in Korean). Retrieved 2023-04-27.
- ^ Kang, Y. (2011). The characteristics of Korean medicine based on time classification. China Perspectives, 2011(3), 33-41.
- ^ Micozzi, Marc S., and Lisa Meserole (2000). Marc S. Micozzi and C. Everett Koop (ed.). Herbal Medicine: Fundamentals of Complementary and Integrative Medicine. St. Louis: Saunders El Sevier.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Cheongsimhwan" 청심환. Korean-English Learners' Dictionary. National Institute of Korean Language. Archived from the original on 10 January 2017. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ^ "Acupuncture". NHSChoices. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 72
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 107
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 387
- ^ Singh; Ernst (2008). Trick or Treatment?. Bantam. ISBN 9780593061299. OCLC 190777228.
- ^ Ahn, Andrew C.; Colbert, Agatha P.; Anderson, Belinda J.; Martinsen, ØRjan G.; Hammerschlag, Richard; Cina, Steve; Wayne, Peter M.; Langevin, Helene M. (2008). "Electrical properties of acupuncture points and meridians: A systematic review" (PDF). Bioelectromagnetics. 29 (4): 245–256. doi:10.1002/bem.20403. PMID 18240287. S2CID 7001749.
- ^ de las Peñas, César Fernández; Arendt-Nielsen, Lars; Gerwin, Robert D (2010). Tension-type and cervicogenic headache: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Jones & Bartlett Learning. pp. 251–254. ISBN 9780763752835.
- ^ Mann, F (2000). Reinventing Acupuncture: A New Concept of Ancient Medicine. Elsevier. ISBN 0750648570.
- ^ Ulett, GA (2002). "Acupuncture". In Shermer, M (ed.). The Skeptic: Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience. ABC-CLIO. p. 283291. ISBN 1576076539.
- ^ Pizzorno, Joseph E. Jr. and Pamela Snider (2000). Marc S. Micozzi and C. Everett Koop (ed.). Naturopathic Medicine: Fundamentals of Complementary and Integrative Medicine. St. Louis: Saunders El Sevier.
- ^ Kim, Y.-S. (2005). "Korean Oriental Medicine in Stroke Care". Complementary Health Practice Review. 10 (2): 105–117. doi:10.1177/1533210105279482.
- ^ Coyle, Meaghan E.; Smith, Caroline; Peat, Brian (2023-05-09). "Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (5): CD003928. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003928.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 10167788. PMID 37158339.
- ^ Lee, Myeong Soo; Choi, Tae-Young; Kang, Jung Won; Lee, Beom-Joon; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Moxibustion for Treating Pain: A Systematic Review". The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 38 (5): 829–38. doi:10.1142/S0192415X10008275. PMID 20821815.
- ^ Lee, Myeong Soo; Choi, Tae-Young; Park, Ji-Eun; Lee, Song-Shil; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Moxibustion for cancer care: A systematic review and meta-analysis". BMC Cancer. 10: 130. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-130. PMC 2873382. PMID 20374659.
- ^ Lee, M. S.; Shin, B.-C.; Kim, J.-I.; Han, C.-h.; Ernst, E. (2010). "Moxibustion for Stroke Rehabilitation: Systematic Review". Stroke. 41 (4): 817–20. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.566851. PMID 20150551.
- ^ Lee, Dong-Hyo; Kim, Jong-In; Lee, Myeong Soo; Choi, Tae-Young; Choi, Sun-Mi; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Moxibustion for ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis". BMC Gastroenterology. 10: 36. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-10-36. PMC 2864201. PMID 20374658.
- ^ Lee, Myeong Soo; Choi, Tae-Young; Park, Ji-Eun; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Effects of moxibustion for constipation treatment: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Chinese Medicine. 5: 28. doi:10.1186/1749-8546-5-28. PMC 2922210. PMID 20687948.
- ^ Kim, Jong-In; Choi, Jun-Yong; Lee, Hyangsook; Lee, Myeong Soo; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Moxibustion for hypertension: A systematic review". BMC Cardiovascular Disorders. 10: 33. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-10-33. PMC 2912786. PMID 20602794.
- ^ Lee, Myeong Soo; Kang, Jung Won; Ernst, Edzard (2010). "Does moxibustion work? An overview of systematic reviews". BMC Research Notes. 3: 284. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-3-284. PMC 2987875. PMID 21054851.
- ^ Canaway, Rachel (1 October 2017). "Integration of traditional and 'modern' medicine: Reflections on a visit to DPR Korea". European Journal of Integrative Medicine. 15: 32–38. doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2017.08.005. ISSN 1876-3820.
- ^ Choe Thae Sop (2001). "Koryo system of medicine in DPR Korea". Traditional medicine in Asia (PDF). World Health Organization. pp. 69–74. ISBN 9789290222248. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 31, 2020.
- ^ Talmadge, Eric (27 August 2018). "Ostrich skin, Neo-Viagra and cancer cures: A shopping guide to North Korea". National Post. Associated Press. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ Han, Gil Soo. “The Rise of Western Medicine and Revival of Traditional Medicine in Korea: A Brief History.” Deleted Journal 21, no. 1 (January 1, 1997): 96–121. https://doi.org/10.1353/ks.1997.0000.




