Interleukin-7 receptor
| Interleukin-7 receptor-α | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | IL7R | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | CD127 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 3575 | ||||||
| HGNC | 6024 | ||||||
| OMIM | 146661 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_002185 | ||||||
| UniProt | P16871 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 5 p13 | ||||||
| |||||||
| interleukin 2 receptor, gamma | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | IL2RG | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | SCIDX1, IMD4, CD132 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 3561 | ||||||
| HGNC | 6010 | ||||||
| OMIM | 308380 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_000206 | ||||||
| UniProt | P31785 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. X q13 | ||||||
| |||||||
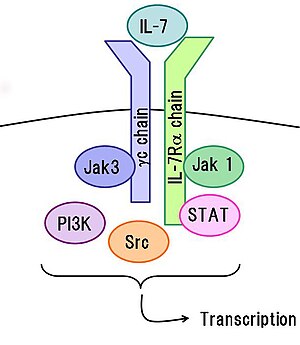
The interleukin-7 receptor is a protein found on the surface of cells. It is made up of two different smaller protein chains - i.e. it is a heterodimer, and consists of two subunits, interleukin-7 receptor-α (CD127) and common-γ chain receptor (CD132).[2][3] The common-γ chain receptors is shared with various cytokines, including interleukin-2, -4, -9, and -15.[4] Interleukin-7 receptor is expressed on various cell types, including naive and memory T cells and many others.
Function
[edit]Interleukin-7 receptor has been shown to play a critical role in the development of immune cells called lymphocytes - specifically in a process known as V(D)J recombination[citation needed]. This protein is also found to control the accessibility of a region of the genome that contains the T-cell receptor gamma gene, by STAT5 and histone acetylation [citation needed]. Knockout studies in mice suggest that blocking apoptosis is an essential function of this protein during differentiation and activation of T lymphocytes. Functional defects in this protein may be associated with the pathogenesis of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).[5]
Diseases
[edit]Several diseases are associated with Interleukin-7 receptor including T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia,[6] multiple sclerosis,[7] rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.[8]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ PDB: 2B5IWang X, Rickert M, Garcia KC (November 2005). "Structure of the quaternary complex of interleukin-2 with its alpha, beta, and gammac receptors". Science. 310 (5751): 1159–63. Bibcode:2005Sci...310.1159W. doi:10.1126/science.1117893. PMID 16293754. S2CID 85394260.
- ^ Noguchi M, Nakamura Y, Russell SM, Ziegler SF, Tsang M, Cao X, Leonard WJ (December 1993). "Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-7 receptor". Science. 262 (5141): 1877–80. Bibcode:1993Sci...262.1877N. doi:10.1126/science.8266077. PMID 8266077.
- ^ Kroemer RT, Richards WG (December 1996). "Homology modeling study of the human interleukin-7 receptor complex". Protein Eng. 9 (12): 1135–42. doi:10.1093/protein/9.12.1135. PMID 9010926.
- ^ "IL2 family". Guide to Pharmacology. IUPHAR/BPS. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: IL7R interleukin 7 receptor".
- ^ Zenatti PP, Ribeiro D, Li W, Zuurbier L, Silva MC, Paganin M, Tritapoe J, Hixon JA, Silveira AB, Cardoso BA, Sarmento LM, Correia N, Toribio ML, Kobarg J, Horstmann M, Pieters R, Brandalise SR, Ferrando AA, Meijerink JP, Durum SK, Yunes JA, Barata JT (October 2011). "Oncogenic IL7R gain-of-function mutations in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia". Nat. Genet. 43 (10): 932–9. doi:10.1038/ng.924. PMC 7424552. PMID 21892159.
- ^ Gregory SG, Schmidt S, Seth P, Oksenberg JR, Hart J, Prokop A, Caillier SJ, Ban M, Goris A, Barcellos LF, Lincoln R, McCauley JL, Sawcer SJ, Compston DA, Dubois B, Hauser SL, Garcia-Blanco MA, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (September 2007). "Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis". Nat. Genet. 39 (9): 1083–91. doi:10.1038/ng2103. PMID 17660817. S2CID 16426835.
- ^ O'Doherty C, Alloza I, Rooney M, Vandenbroeck K (November 2009). "IL7RA polymorphisms and chronic inflammatory arthropathies". Tissue Antigens. 74 (5): 429–31. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2009.01342.x. PMID 19744146.
External links
[edit]- IL7R+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
