Glybuzole
 Skeletal structure of glybuzole | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Desaglybuzole, Gludiase [1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.620 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15N3O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 297.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.344 [2] g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 163[1] °C (325 °F) |
| |
Glybuzole is a hypoglycaemic medicine, mainly used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. It is an oral antidiabetic drug (OAD), when administered in the right dose it will help bring the blood glycose level down by stimulating the insulin production. Similar medicines are glimepiride, glipizide, glibenclamide, gliclazide, and gliquidone.
Structure
[edit]The molecular formula of glybuzole is C12H15N3O2S2. It is also known as desaglybuzole or gludiase. The systematic name is N-(5-tert-butyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide.[1] It consists of a benzene ring connected to sulfonamide. The nitrogen-atom of the sulfonamide is bound to a thiadiazole. In this thiadiazole two nitrogen-atoms and one sulfur-atom are present. The thiadiazole is bound to a tert-butyl group.
Mechanism of action
[edit]Glybuzole has an anti-hyperglycaemic activity. Glybuzole is a sulfonylurea and can therefore lower the blood glucose levels.[1] Sulfonylureas can bind to receptors at β-pancreatic cells which are specific for sulfonylurea binding. When a sulfonylurea binds to its receptor, the ATP-dependent channels for K+ ions will be blocked. Therefore, the flow of K+ ions into the β-pancreatic cell will stop and the cell membrane becomes depolarized. As a result, calcium ions will flow into the cell and that will then cause the contraction of actomyosin filaments which are responsible for the exocytosis of insulin. Finally, the increased secretion of insulin can then lead to a decrease in the blood glucose level.[3]
Function
[edit]Glybuzole is a hypoglycaemic medicine that is primarily used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. Glybuzole and other sulfonylureas cannot be used to treat diabetes type 1, because they are ineffective if insulin production is inhibited, in such cases as diabetes type 1 and post-pancreatectomy.[4]
Side effects
[edit]The main side effects of glybuzole and other sulfonylureas are induction of hypoglycaemia, weight gain, abdominal upset, headache, and hypersensitivity reactions. Hypoglycaemia is mainly caused by excesses in insulin production due to doses that are too high, or due to the eating habits of the patient.[5]
Contraindications
[edit]It should not be taken if the patient has a hypersensitivity for sulfonylureas.
Interactions
[edit]There are some drugs that prolong the effects of drugs such as glybuzole and thereby increase the possibility of hypoglycaemia, these drugs include allopurinol, sulfonamides, acetylsalicylic acid and derivatives and fibrates.[6][7]
Toxicity
[edit]Glybuzole is a drug with low toxicity, it causes no irritation. Sometimes it results in dyspnoea, or shortness of breath, and it could result in hypoglycaemia.[8]
In case of pregnancy, there are more severe toxic effects as tested in rats. At a dose of 2100 mg/kg, there were cases of fetal death, developmental abnormalities in the central nervous system, the eye and ear, and craniofacial abnormalities (including face and nose) 7 to 13 days after conception. At a lower dose (1050 mg/kg) it resulted in fetotoxicity (no death, but e.g. stunted fetus), and developmental abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system.[9]
For several rodent species the lethal dose has been investigated for several exposure routes, this is displayed in table 1.[9]
Table 1: LD50 doses for several organisms and exposure routes.[9]
| Organism | Exposure route | Reported dose (=normalized dose) |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse | intraperitoneal | 235 mg/kg |
| Mouse | intravenous | 193 mg/kg |
| Mouse | oral | 550 mg/kg[8] |
| Mouse | subcutaneous | 248 mg/kg |
| Rabbit | intraperitoneal | 300 mg/kg |
| Rabbit | intravenous | 118 mg/kg |
| Rabbit | oral | 967 mg/kg |
| Rat | intraperitoneal | 249 mg/kg |
| Rat | oral | 500 mg/kg |
| Rat | subcutaneous | 310 mg/kg |
Synthesis
[edit]A general way to synthesize sulfonamides is to perform a substitution reaction with an amine, a pyridine and a sulfonyl chloride (Figure 1).[10]
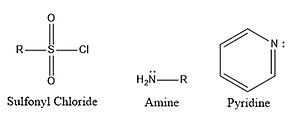
Figure 1: General structures of the reactants required to synthesize a sulfonamide
This method of synthesizing a sulfonamide is often used for the synthesis of glybuzole.
Glybuzole can be synthesized using benzenesulfonyl chloride, 2-amino-5-tert-butyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole and pyridine.[11] The reaction that will proceed is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2) (Figure 2). The nitrogen atom from the amino-group of 2-amino-5-tert-butyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole will attack the sulfur atom of benzene-sulfonyl chloride, leading to a chloride ion being removed from the benzenesulfonyl chloride. The intermediate which is now formed still has a positive charge. This positive charge is removed due to the uptake of a hydrogen atom by pyridine and the final product of interest, glybuzole, is produced.
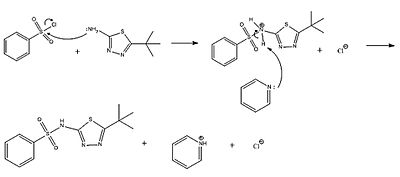
Figure 2: Reaction mechanism of the bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in the synthesis of glybuzole from benzenesulfonyl chloride and 2-amino-5-tert-butyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole, using pyridine.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f "Glybuzole". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. February 25, 2017. Retrieved February 25, 2017.
- ^ "Compound:N-(5-tert-butyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide". www.chemsrc.com. 1996. Retrieved March 2, 2017.
- ^ Sola D, Rossi L, Schianca GP, Maffioli P, Bigliocca M, Mella R, et al. (August 2015). "Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice". Archives of Medical Science. 11 (4): 840–848. doi:10.5114/aoms.2015.53304. PMC 4548036. PMID 26322096.
- ^ Seino S (August 2012). "Cell signalling in insulin secretion: the molecular targets of ATP, cAMP and sulfonylurea". Diabetologia. 55 (8): 2096–2108. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2562-9. PMID 22555472. S2CID 7146975.
- ^ Diaßeta® (glyburide) Tablets USP - 1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg (PDF) (Technical report). Sanofi-Aventis. 2009.
- ^ Haberfeld H. Austria-Codex. Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 3-85200-196-X.
- ^ Dinnendahl VM, Fricke U. Arzneistoff-Profile. Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ^ a b Oyo, Yakuri Kenkyukai (1969). "unknown". Pharmocometrics. 3: 131.
- ^ a b c Yamaguchi DI, Kogushi U (1969). "unknown". Yamaguchi Medicine. 18: 21.
- ^ De Boer J, Backer HJ (1954). "p-TOLYLSULFONYLMETHYLNITROSAMIDE". Organic Syntheses. 34: 96. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0096.
- ^ "Glybuzole". www.thieme.com. Thieme. Retrieved February 23, 2017.
