Craniofacial surgery
Craniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty that deals with congenital and acquired deformities of the head, skull, face, neck, jaws and associated structures. Although craniofacial treatment often involves manipulation of bone, craniofacial surgery is not tissue-specific; craniofacial surgeons deal with bone, skin, nerve, muscle, teeth, and other related anatomy.[1][2]
Defects typically treated by craniofacial surgeons include craniosynostosis (isolated and syndromic), rare craniofacial clefts, acute and chronic sequelae of facial fractures, cleft lip and palate, micrognathia, Treacher Collins Syndrome, Apert's Syndrome, Crouzon's Syndrome, Craniofacial microsomia, microtia and other congenital ear anomalies, and many others. Training in craniofacial surgery requires completion of a Craniofacial surgery fellowship. Such fellowships are available to individuals who have completed residency in oral and maxillofacial surgery, plastic and reconstructive surgery, or ear, nose, and throat surgery. Those who have completed residency in oral and maxillofacial surgery may be either single degree or dual-degree surgeons with no differences. There is no specific board for craniofacial surgery. In the US, cleft and craniofacial centers are found in many major academic centers.
Craniosynostosis
[edit]
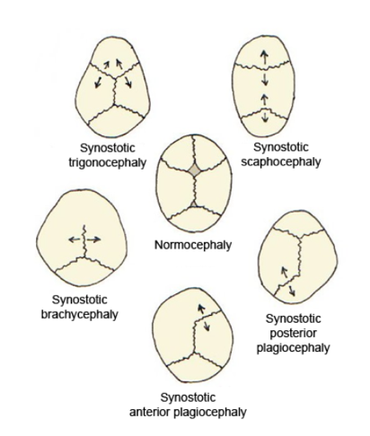
The bones of the human skull are joined by cranial sutures (see figure 1). The anterior fontanelle is where the metopic, sagittal and coronal sutures meet. Normally the sutures gradually fuse within the first few years after birth. In infants where one or more of the sutures fuses too early the growth of the skull is restricted, resulting in compensation mechanisms which cause irregular growth patterns. Growth in the skull is perpendicular to the sutures. When a suture fuses too early, the growth perpendicular to that suture will be restricted, and the bone growth near the other sutures will be stimulated, causing an abnormal head shape. The expanding brain is the main stimulus for the rapid growth of the skull in the first years of life. Inhibited growth potential of the skull can restrict the volume, needed by the brain. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure.[3]
Craniosynostosis is called simple when one suture is involved, and complex when two or more sutures are involved. It can occur as part of a syndrome or as an isolated defect (nonsyndromic).[4]
Scaphocephaly
[edit]In scaphocephaly, the sagittal suture is prematurely fused. The sagittal suture runs from the front to the back of the head. The shape of this deformity is a long narrow head, formed like a boat (Greek skaphe, "light boat or skiff"). The compensatory head-growth forward at the coronal suture gives a prominent forehead, frontal bossing and a prominent back of the head, called coning.[5] The incidence of scaphocephaly is 2.8 per 10,000 births in the Netherlands; therefore, it is the most common form of craniosynostosis.[6][7]
Trigonocephaly
[edit]In trigonocephaly, the metopic suture is prematurely fused. The metopic suture is situated in the medial line of the forehead. Premature fusion of this suture causes the forehead to become pointed, giving the head a triangular shape when viewed from above (Greek trigono, "triangle"). The incidence of trigonocephaly is 1 - 1.9 per 10,000 births in the Netherlands.[6]
Plagiocephaly
[edit]In plagiocephaly, one of the coronal sutures is prematurely fused. The coronal sutures run over the top of the head, just in front of the ears. The shape of this deformity is an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side of the head) as you can see in figure 2. The incidence is 1 in 10,000 births.[6][8]
Brachycephaly
[edit]In brachycephaly, both of the coronal sutures are prematurely fused. The shape of this deformity is a wide and high head. The incidence at birth is 1/20,000.[9]
Team
[edit]Craniofacial surgery and follow-up care are usually conducted by a multidisclinary team of doctors, surgeons, nurses, and various therapists.[10] As of 2016, there is a new multidisciplinary care team of Neuroplastic Surgeons working with Neurosurgeons to prevent and/or correct neurosurgical-related deformities and to maximize outcomes in adult patients.
Surgical procedures
[edit]

In cases where the forehead is involved (trigonocephaly and plagiocephaly), a technique called fronto-supraorbital advancement is used to correct the shape of the head. The procedure is performed at a young age in order to provide the brain with enough space to grow and prevent further abnormal growth of the skull. Fronto-orbital advancement literally means moving the front of the skull including the eye sockets forward. A section of the skull, ranging from the coronal sutures to the eye sockets is cut loose in order to correct the shape of the skull. The incision is cut in a zigzag shape from ear to ear so that the hair will cover the scar and make it less visible. The incision is made to the bone only, leaving the underlying meninges intact. The top half of the eye sockets is cut loose. Once the eye socket section has been cut loose, a vertical incision is made in the midline, and the whole section of the eye socket is bent outwards in order to correct the pointed shape of the forehead. Because the section is now too wide, a wedge needs to be cut on either side to allow the section to fit into the skull. Figure 4 shows the sections that are loosened and adjusted, and Figure 3 shows the location of the vertical incision (arrow A) and the two wedges (arrow B).[citation needed]
In scaphocephaly, the sagittal suture is prematurely fused, preventing the skull from growing perpendicular to the suture. Thus, the head becomes very narrow and long. If a scaphocephaly is diagnosed within 4 to 5 months after birth, it can be corrected with a relatively simple procedure whereby the sagittal suture is surgically reopened. Once the suture has been opened the bone segments will be able to grow again, and the head can regain its normal shape. This operation is only performed on patients younger than five months old with a scaphocephaly. This is due to the fact that the bone segments only have the ability to adapt so severely when the operation is performed at this young age. A scaphocephaly that is diagnosed and treated later in life requires a more extensive secondary operation than one that is treated before five months.[citation needed]
A major focus in craniosynostosis reconstruction is maintaining normalized aesthetics of temporal region, and avoiding temporal hollowing. Despite using overcorrection methods, autologous fat transfer, and bone grafts to prevent temporal hollowing, up to 50% of patients still experience post-operative depression in the temporal fossa.
Cranioplasty, or skull reconstruction, is the main concentration of a new field for adult neurosurgical patients known as Neuroplastic Surgery. There are now several centers around the world, including the United States and Israel. The first center of Neuroplastic Surgery was started at Johns Hopkins by Dr. Chad Gordon and the Department of Neurosurgery, which is where this new craniofacial subspecialty was born (c. 2016).[11]
Complications in craniofacial surgery
[edit]Some of the surgical complications in craniofacial surgery may include Death, Shock, Haemorrhage, visual loss, Intracranial collection of air/fluid, Epileptic seizures, Unexpected respiratory complications, etc.[12]
See also
[edit]- Plastic surgery
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery
- Orthognathic Surgery
- Scalp reconstruction
- Zygoma reduction plasty
- Neuroplastic Surgery
- Craniofacial Fellowship
References
[edit]- ^ "Craniofacial Surgery - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2021-09-20.
- ^ "Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery | ScienceDirect.com by Elsevier". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2021-09-20.
- ^ JJ van der Vlugt, JJ van der Meulen and HE Creemers, et al., The risk of psychopathology in children with craniosynostosis, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, December 2009, pp 2054-2060
- ^ Haidar Kabbani; Talkad S. Raghuveer (2004-06-15). "Craniosynostosis". American Family Physician. 69 (12): 2863–2870. PMID 15222651.
- ^ Persing, John A. (2008-04-01). "MOC-PS(SM) CME Article: Management Considerations in the Treatment of Craniosynostosis". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 121 (Supplement): 1–11. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000305929.40363.bf. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 18379381.
- ^ a b c CF Kweldam, JJ van der Vlugt and JJNM van der Meulen, The incidence of craniosynostosis in the Netherlands 1997 – 2007, Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery
- ^ BL Hutchison, Alistair W Stewart and Edwin A Mitchell, Characteristics, head shape measurements and developmental delay in 287 consecutive infants attending a plagiocephaly clinic, Acta Paediatrica98, September 2009, pp 1494–1499
- ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Isolated plagiocephaly".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Isolated brachycephaly".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Buchanan, EP; Xue, Y; Xue, AS; Olshinka, A; Lam, S (2017). "Multidisciplinary care of craniosynostosis". Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare. 10: 263–270. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S100248. PMC 5505551. PMID 28740400.
- ^ Neuroplastic Surgery. Gordon CR, Huang J, Brem H. Neuroplastic Surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2018 Jan;29(1):4-5. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004063. PMID 29077688
- ^ Poole, M. D. (November 1988). "Complications in craniofacial surgery". British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 41 (6): 608–613. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90168-3. ISSN 0007-1226. PMID 3207961.
Further reading
[edit]- Parens, E., Ed. (2006). Surgically Shaping Children : Technology, Ethics, and the Pursuit of Normality. Baltimore, Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-8305-9.
- "Faltenkorrektur" (in German).
