Gas Exporting Countries Forum
Gas Exporting Countries Forum (GECF) | |
|---|---|
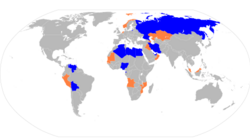 Members (blue) and observers (orange) of the Gas-Exporting Countries Forum. | |
| Headquarters | Doha, Qatar |
| Official language | English |
| Type | Trade forum |
| Members[1] | 11 states 8 observers |
| Leaders | |
• Secretary General | Mohammad Hamel |
| Establishment | Tehran, Iran |
• Forum | May 20, 2001 |
• Statute | December 23, 2008 |
| Area | |
• Total | 26,965,287.87 km2 (10,411,355.85 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 599,861,442 |
• Density | 22.2/km2 (57.5/sq mi) |
Website www | |



The Gas Exporting Countries Forum (GECF) is an intergovernmental organization currently comprising 19 Member Countries of the world's leading natural gas producers: Algeria, Bolivia, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Iran, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Russia, Trinidad and Tobago, and Venezuela are members and Angola, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Mozambique, Malaysia, Norway, Peru and the United Arab Emirates are observers. GECF members together control over 71% of the world's natural proven gas reserves, 44% of its marketed production, 53% of the pipeline, and 57% of the liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports across the globe.[2] It is headquartered in Doha, Qatar.
History
[edit]The idea of creating a forum as an official organization was first discussed at the meeting in 2001 in Tehran, but it was legally instituted after the idea was supported by Russia. Vladimir Putin, on a visit to Qatar, one of the largest gas-producing countries, reached an agreement with the Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani to coordinate activities in the gas sector.[3]
Until 2007, the GECF was a platform for the exchange of experience in the gas sector, which did not have a permanent leadership, budget and headquarters. But within the framework of this platform, high-level meetings were regularly held. At the 6th Ministerial Meeting of the GECF in Doha, it was decided to create a working group under the leadership of the Ministry of Industry and Energy of Russia to coordinate actions to form a full-fledged organization. This step was perceived as the inevitability of creating a gas analogue of OPEC. As a result, the agreement on the establishment of the organization with the preservation of the name of the Gas Exporting Countries Forum was signed a year later on December 23, 2008 at the 7th Ministerial Meeting in Moscow.
Since 2008, the Forum has had three governing tools: the Ministerial Meeting (held once a year), the Executive Board Meeting and the Secretariat.
On December 9, 2009 the Secretary General of the GECF was elected vice-president of "Stroytransgaz" Leonid Bokhanovskiy,[4] whose candidacy was put forward for a vote by Russia. November 13, 2011, Leonid Bokhanovskiy was re-elected as Secretary General of the Forum.
On November 15, 2011, a declaration was adopted at the first GECF summit in Doha.[5] It confirmed the importance of natural gas for the world economy, determined the course for deepening the coordination of exporting countries and the need to establish fair gas prices and the principle of balanced distribution of risks for gas producers and consumers.
In November 2013, the Iranian diplomat Seyed Mohammad Hossein Adeli, was elected Secretary General of the GECF[6] and in November 2015 he was re-elected for a second term.
At the third summit in 2015, the GECF presented a forecast for the development of the gas market until 2050. According to GECF analysts, the key to the successful development of the global gas industry is the growth of the economy and population. Analysts have determined that by 2050 the population will grow by 2.2 billion people and reach 9.8 billion. The main trend for the gas industry: energy will become more affordable, and this will provide almost 30% of additional demand. However, in 2020, analysts announced that due to the minimum oil price and the consequences of the pandemic, this forecast could be revised. According to GECF experts, the Asia-Pacific region, North America and the Middle East will become the regions-drivers of demand. The growth of future demand will be 39%, 24% and 13%, respectively. Demand in Europe will grow until 2030, and then there will be a gradual decline. This gas market forecast until 2050 is updated annually.[7]
In January 2018, Yuri Sentyurin became the 3rd General Secretary of the GECF.[8] In 2019 the members of the GECF countries joined Angola and Malaysia in 2020. Also, prospective members participating Mozambique, Tanzania, Senegal, Mauritania, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
In 2021, GECF sent an official submission to the United Nations in the wake of the Glasgow climate talks where GECF complained that gas exporters were a victim of "cancel culture."[9]
Gas OPEC
[edit]Since the establishment of the GECF in 2001 there has always been speculation that some of the world's largest producers of natural gas, in particular Russia and Iran, intend to create a gas cartel equivalent to OPEC which would set quotas and prices. The idea of a gas OPEC was first floated by Russian President Vladimir Putin and backed by Kazakh President Nursultan Nazarbaev in 2002. In May 2006 Gazprom deputy chairman Alexander Medvedev threatened that Russia would create "an alliance of gas suppliers that will be more influential than OPEC" if Russia did not get its way in energy negotiations with Europe.[10] Iranian officials have explicitly expressed strong support for a gas cartel and held official talks with Russia.[11] Cartel speculation was again raised when the ministers met on 9 April 2007.[12] The 6th Ministerial Meeting of the GECF established an expert group, chaired by Russia, to study how to strengthen the GECF. According to the Algerian Energy and Mines Minister Chakib Khelil, this mean that in the long term the GECF will move toward becoming a gas OPEC.[12] On 11 December 2009, Russia's Energy Minister Sergey Shmatko stated: "Today we can speak about gas OPEC as a fully fledged international organization. By a unanimous decision a Russian national was elected its secretary general. This is to show that member countries expect Russia to use its political weight to promote it."[citation needed]
Creation of the Gas OPEC was one of the topics of the first GECF summit. However, some GECF's members are concerned over the gas exports to be politicized.[13] GECF generally refrains from coordinating production rates.[14][15]
According to GECF General Secretary Yuri Sentyurin, the issue of creating the creation of a "gas OPEC " is regularly raised at ministerial meetings. But unlike the oil market, there is no single market and pricing on the gas market. In addition, the forum was originally conceived as a discussion platform, therefore, without changing the Charter, it is premature to talk about practical instruments by analogy with OPEC.[16]
Organisational structure
[edit]The highest body of the GECF is a ministerial meeting. In between of ministerial meetings, the work is organized through the Secretariat, headquartered in Doha, Qatar. The 2009 chairman of the GECF was Abdullah bin Hamad Al Attiyah and the vice chairman was Chakib Khelil.[17][18] The Secretary-General is Mohammad Hamel.
Secretaries-General
[edit]| Name | Country | Service Period |
|---|---|---|
| Leonid Bokhanovskiy | 9 December 2009 – 1 January 2014 (2 Terms) | |
| Mohammad Hossein Adeli | 1 January 2014 – 12 January 2018 (2 Terms) | |
| Yury Sentyurin | 12 January 2018 – 31 December 2022 (2 Terms) | |
| Mohammad Hamel | 1 January 2022 – present |
Ministerial Meetings
[edit]This meeting of senior government officials in the energy sector is the supreme authority of the Forum. The GECF has had ministerial meetings since 2001:[19]
| Location | Year | |
|---|---|---|
| Tehran, Iran | 2001 | |
| Algiers, Algeria | 2002 | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2003 | |
| Cairo, Egypt | 2004 | |
| Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago | 2005 | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2007 | |
| Moscow, Russia | 2008 | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2009 (June) | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2009 (December) | |
| Oran, Algeria | 2010 (April) | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2010 (December) | |
| Cairo, Egypt | 2011 (June) | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2011 (November) | |
| Malabo, Equatorial Guinea | 2012 | |
| Tehran, Iran[20] | 2013 | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2014 | |
| Tehran, Iran[21] | 2015 | |
| Doha, Qatar | 2016 | |
| Moscow, Russia | 2017 | |
| Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago | 2018 | |
| Moscow, Russia | 2019 | |
| Algiers, Algeria (via videoconference) | 2020 | |
Heads of State and Government Summits
[edit]The Gas Summit is a meeting of Heads of State and Government of countries Members of the Gas Exporting Countries Forum.
| Meeting | Country | Year |
|---|---|---|
| I | 15 November 2011 | |
| II | 1 July 2013[23] | |
| III | 23 November 2015 | |
| IV | 24 November 2017[24] | |
| V | 29 November 2019[25] | |
| VI | 18 November 2021 | |
| VII | 02 March 2024[26] |
Holding the GECF's summit was decided at the 10th ministerial meeting in Oran in 2010.
The first GECF's summit was held in Doha on 15 November 2011, under patronage of Emir Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa al-Thani, following the thirteenth ministerial meeting held at the same place on 13 November 2011.[27] Two main issues which were discussed at the summit, were natural gas prices and a common approach to the natural gas market.[28] It was agreed on the summit that the price of gas used to generate electricity is too low and the gap between prices for gas and crude oil need to be narrowed. The linking of gas prices to the oil price was considered. However, the GECF will not set output limits for its members.[29] The final communique issued was the Doha Declaration, which read that GECF members "recognized the importance of long-term gas contracts to achieve a balanced risk sharing mechanism between producers and consumers" and "acknowledge the need to reach a fair price for natural gas based on gas to oil/oil products prices indexation with the objective of an oil and gas price convergence ..."[30][31] Russian president Dmitry Medvedev made a statement calling the summit "an important event, which marked a new stage in the development of the global energy sector and the gas sector in particular."[32]
The 2nd Gas Summit was held in Moscow on July 1, 2013. The key outcomes of the 2nd GECF Summit were reflected in the Moscow Declaration: "Natural gas: the answer to the 21st century sustainable development challenges."[33] The final communique stresses the importance of the fundamental principles of long-term contracts that guarantee the safety of investments for producers and preservation of prices for consumers.[34]
The 3rd GECF Summit was held 23 November 2015 in Tehran. The main topics were the transfer of expertise of members countries and pricing mechanism for natural gas.[35][36] The participants also called for cooperation in ensuring the security of natural gas supplies to world markets.
The 4th GECF Summit convened in Santa Cruz, Bolivia on November 24, 2017. The outcome of the Summit was the Declaration of Santa Cruz de la Sierra.[37] Basic principles: promoting gas as a reliable, secure, clean source of energy. Attracting investment to the global natural gas market. Fair price for natural gas considering its energy efficiency and environmental benefits.
As the outcome of the 5th Gas Exporting Countries Forum in Malabo The Declaration of Malabo was published. It stressed the importance of the role of natural gas for African countries. The GECF members have specified the terms of contracts between producers and consumers. To ensure that the pricing associated with oil indexation serves the benefit of the member countries to ensure the implementation of their projects.[38]
The Sixth Gas Summit of Heads of State and Government of GECF Member Countries will convey in Doha, Qatar on 18 November 2021.
Membership
[edit]The members are Algeria, Bolivia, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Iran, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Russia, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela and Angola, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Norway, Peru and the United Arab Emirates are observers. Other countries like Turkmenistan,[citation needed] Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Yemen have participated at different meetings.[17][39][40][41] Yemen is interested to become members of the organisation.[42]
Any gas exporting country can become a member, the full membership will be granted by the approval of at least three quarters of all members at the ministerial meeting.[39] Also, to become an observer, a country can apply to the Secretariat. Such a resolution is adopted by a majority of three quarters of the members at the ministerial meeting. Observer members may attend ministerial plenary meetings and participate without the right to vote.
| Country | Region | Signed GECF statute |
|---|---|---|
| North Africa | 2008 | |
| South America | 2008 | |
| North Africa | 2008 | |
| Central Africa | 2008 | |
| Southern Asia | 2008 | |
| North Africa | 2008 | |
| West Africa | 2008 | |
| West Asia | 2008 | |
| Eurasia | 2008 | |
| South America | 2008 | |
| West Asia | 2012[43] | |
| South America | 2008 |
| Country | Region | Signed GECF statute |
|---|---|---|
| Central Africa | 2018[44] | |
| Central Asia | 2018 | |
| MENA | 2009 | |
| Eastern Africa | [45] | |
| Asia-Pacific | ||
| Europe | ||
| South America | 2008 | |
| MENA |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ GECF Members & Observers Archived 2015-11-08 at the Wayback Machine GECF
- ^ "Restored GCC unity to bring stability to energy markets: GECF". Gulf-Times (in Arabic). 2021-01-13. Retrieved 2021-03-04.
- ^ "Alexey Miller and Emir of Qatar Hamad bin Khalifa Al-Thani discuss world energy market development trends". www.gazprom.com. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ "Gas group elects Russia's Bokhanovsky as sec-gen". Reuters. 2009-12-09. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ Laura El-Katiri; Anouk Honoré. "The Gas Exporting Countries' Forum: Global or Regional Cartelization?" (PDF). In Jonathan P Stern (ed.). The Pricing of Internationally Traded Gas – via The Oxford Institute for Energy Studies.
- ^ "FarsNews Agency Secretary-General: GECF Should Bring Other Gas Exporters to Circle". www.farsnews.ir. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ "GECF Global Gas Outlook 2050". GECF. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ "Award Detail - Al-Attiyah Foundation". www.abhafoundation.org. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ "Top Gas Exporters Say They're Victims of 'Cancel Culture'". Gizmodo. 17 November 2021. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ Roman Kupchinsky (2006-08-14). "Russia: Algeria Deal Revives Talk Of Gas Cartel". RFE/RL. Archived from the original on 2008-12-12. Retrieved 2008-12-23.
- ^ "Russia, Iran in talks to create natural gas organization". CNN. 2007-02-02. Archived from the original on 2008-05-09. Retrieved 2008-12-23.
- ^ a b Barbara Lewis, Simon Webb (2007-04-09). "Gas club seeks more clout, but not yet an OPEC". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2008-02-15. Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- ^ Fedoruk, Vladimir (2011-11-14). "A gas OPEC to dominate GECF summit in Doha, Russia not present". Voice of Russia. Archived from the original on 2011-11-16. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Feature: Unfettered global natural gas market a sign of the times | Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide". www.hellenicshippingnews.com. 6 April 2020. Archived from the original on 9 April 2020.
There is no history of coordinated action on production and the closest thing to a "Gas OPEC" — the Gas Exporting Countries Forum (GECF) — has repeatedly ruled out joint intervention in the market
- ^ "Feature: Unfettered global natural gas market a sign of the times | S&P Global Platts". www.spglobal.com. 2 April 2020. Archived from the original on 12 April 2020.
- ^ "OPEC : OPEC, GECF hold first high-level meeting". www.opec.org. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ^ a b Kevin Baxter (2009-07-02). "Qatar energy chief says UAE to join gas forum". ArabianOilandGas.com. ITP Business Publishing Ltd. Archived from the original on 2009-07-25. Retrieved 2009-07-02.
- ^ Ayesha Daya, Robert Tuttle (2009-06-30). "Gas Producers Count on Oil-Linked Contracts in Qatar". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 2012-04-08. Retrieved 2009-07-02.
- ^ "Ministerial Meetings of the Gas Exporting Countries Forum". Archived from the original on 2017-11-07. Retrieved 2017-11-04.
- ^ "Iran's Oil Minister Appointed GECF Head". Mees. 21 August 2013. Archived from the original on 13 September 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ^ "17th Ministerial Meeting". Archived from the original on 2017-11-16. Retrieved 2017-11-15.
- ^ "Russia ready to host 2nd GECF summit". Voice of Russia. TASS. 2011-11-15. Archived from the original on 2011-11-16. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "GECF". Archived from the original on 2017-11-16. Retrieved 2017-11-15.
- ^ "Fourth GECF Gas Summit". Archived from the original on 2017-08-15. Retrieved 2017-08-15.
- ^ "5th Gas Summit of Heads of State and Government of the GECF Member Countries". Retrieved 2021-03-04.
- ^ "7th GECF Summit in Algiers". Retrieved 2024-03-02.
- ^ "GECF gas summit focuses on stable supplies, markets". Gulf Times. 2011-11-15. Archived from the original on 2011-11-15. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- ^ Wrede, Insa (2011-11-17). "Global 'gas cartel' is a long way off, experts say". Deutsche Welle. Archived from the original on 2011-11-18. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Gas Exporters Seek 'High' Prices as They Cooperate on Supply, Projects". Bloomberg. 2011-11-15. Archived from the original on 2011-11-17. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ John, Pratap (2011-11-16). "Doha summit urges fair price for gas". Gulf Times. Archived from the original on 2011-11-16. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "First Summit of Gas Exporting Countries Forum Concludes in Doha". MENAFN. 2011-11-16. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Medvedev welcomes 1st GESF summit in Doha". Voice of Russia. TASS. 2011-11-15. Archived from the original on 2013-04-17. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "GECF Moscow Declaration" (PDF).
- ^ "Putin Pushes Russian Agenda at Global Gas Summit | Voice of America - English". www.voanews.com. Retrieved 2021-03-09.
- ^ "Third GECF Gas Summit". GECF. Retrieved 2021-04-15.
- ^ "Tehran to host 3rd GECF summit in 2015". IRNA English. 2014-12-30. Retrieved 2021-04-15.
- ^ "The Declaration of Santa Cruz de la Sierra" (PDF).
- ^ Nongrum, Nonalynka. "GECF summit launches Declaration of Malabo". Oil Review Africa (in Polish). Retrieved 2021-03-08.
- ^ a b "World gas producers approve charter for Doha-based forum". Xinhua. 2008-12-24. Archived from the original on 2009-01-10. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ^ "Putin says 'cheap gas era' ending". BBC. 2008-12-23. Archived from the original on 2008-12-23. Retrieved 2008-12-23.
- ^ "Russia Says Gas Forum Will Not Be OPEC-Like Cartel". RFE/RL. 2008-12-23. Archived from the original on 2009-01-14. Retrieved 2008-12-23.
- ^ Ahmed Rouaba (2010-04-19). "Yemen in Talks to Join Gas Exporting Countries Forum". Bloomberg. Retrieved 2010-04-22.
- ^ "UAE joins Gas Exporting Countries Forum - Energy, Industries, GCC, Energy, Energy - ArabianBusiness.com". Archived from the original on 2017-11-16. Retrieved 2017-11-15.
- ^ "Angola Joins GECF". Energycapitalpower.com. 2018-11-15. Retrieved 2022-05-07.
- ^ "Mozambique - Republic of Mozambique".
Bibliography
[edit]- Hallouche, Hadi (June 2006). The Gas Exporting Countries Forum: Is it really a Gas OPEC in the Making? (PDF). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. ISBN 978-1-901795-50-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-27. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- Socor, Vladimir (2008). "A Russian-led "OPEC for Gas"? Design, Implications, Countermeasures" (PDF). Lithuanian Foreign Policy Review (20). Foreign Policy Research Center. ISSN 1392-5504. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-27. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- Flynn, Chris; Dyer, Erin (2008). "The Creation of a Gas Cartel v The Commoditisation of Gas" (PDF). The International Comparative Legal Guide to: Gas Regulation 2008. Global Legal Group. pp. 1–3. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
External links
[edit]- 2001 establishments in Iran
- Energy economics
- Energy policy
- Gas Exporting Countries Forum
- International energy organizations
- International trade organizations
- Intergovernmental organizations
- Intergovernmental commodity organizations
- Natural gas organizations
- Organizations established in 2001
- Organisations based in Doha


