Galepsus (Thrace)
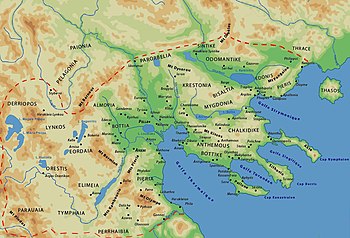

Galepsus or Galepsos (Ancient Greek: Γαληψός) was a Greek city located in the region of Edonis in ancient Thrace and later in Macedon.[1] It was located east of Phagres and about 17 km from Amphipolis.[1] It belonged to the Delian League and it was founded as a colony of Thasos.[2] After the conquest of Amphipolis it was occupied by Brasidas in 424 BCE,[3] but recovered by Cleon in the ensuing year.[4] Perseus of Macedon, fleeing the Romans who had defeated him at Pydna, sailed the mouth of the Strymon, and towards Galepsus, staying there before moving on to Samothrace.[5]
It was named after Galepsos who was a descendant of Thasos and of Telephe.
The site of Galepsus is near the modern Kariani.[6][7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Benjamin H. Isaac, The Greek Settlements in Thrace Until the Macedonian Conquest, p.63
- ^ Hatzfeld, Jean. History of Ancient Greece (trans. by Andre Aymard, 1968, W.W. Norton & Co., New York), p. 34-35.
- ^ Thucydides. History of the Peloponnesian War. Vol. 4.107.
- ^ Thucydides. History of the Peloponnesian War. Vol. 5.6.
- ^ Livy. Ab urbe condita Libri [History of Rome]. Vol. 44.45.
- ^ Richard Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World. Princeton University Press. p. 51, and directory notes accompanying. ISBN 978-0-691-03169-9.
- ^ Lund University. Digital Atlas of the Roman Empire.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Galepsus". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Galepsus". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
40°45′00″N 23°59′04″E / 40.749931°N 23.984506°E
