Edonis (region)
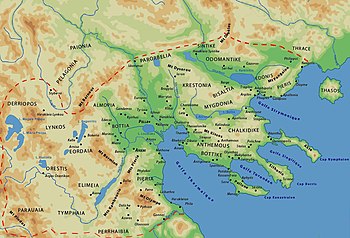
Edonis or Edonida (Ancient Greek: Ἠδωνίς, Ἠδωνίδα), also transliterated as Edonia, was an ancient region of Thrace which later became a district of Macedon. Its name is derived from the ancient Thracian inhabitants of the region, the Edonians.[1] Later, the Greeks settled in the region, drove out the Edonians and built several colonies, including Amphipolis and Eion.[2] It was bordered by Odomantice in the north, Bisaltia in the west, and the Aegean Sea in the south, and was separated from Thrace proper by the river Nestos in the east.
Geography and history
[edit]Edonis stretched from the lake Cercinitis (today Achinos) and the mouth of the Strymon river in the west, to Nestos river in the east (natural border between the regions of Macedonia and Thrace).
The region was predominantly settled by the tribe of Edoni. Later, the Greeks settled in the region, drove out the Edonians and built several colonies, including Amphipolis and Eion.[3] Within its limits was Pangaion, whose mines were being exploited by Philip II after his conquest and the annexation of the region to the kingdom of Macedon. After the Roman conquest, Via Egnatia was passing through Edonis and with the establishment of Philippi as a Roman colony (42 BC) most of Edonis became part of its territory (territorium).[4]
Pieris
[edit]Thucydides testified that at the foot of Pangaion settled Pierians, who had been expelled from their homeland, Pieria, when the Macedonians conquered it. There they built the namesake town Edonian Methoni in contrast to Pierian Methoni and they named the nearby land "Pieris".[5]
Towns
[edit]Edonis and especially mount Pangaio was one of the oldest worship places of the gods Apollo, Dionysus and Orpheus. The most important towns of Edonis, apart from Methoni, were also:[6][7]
|
See also
[edit]- Resident Evil 6, A fictional Republic of Edonia can be visited in this game.
References
[edit]- ^ D. C. Samsaris, Historical Geography of Eastern Macedonia during the Antiquity (in Greek), Thessaloniki 1976 (Society for Macedonian Studies), p. 95–97. Archived 2017-04-24 at the Wayback Machine ISBN 960-7265-16-5.
- ^ The Peloponnesian War (The Landmark Thucydides edition, Robt. B. Strassler, editor), Touchstone, New York, 1998, sec. 1.100 and 4.107, and maps 1.99 and 4.106
- ^ The Peloponnesian War (The Landmark Thucydides edition, Robt. B. Strassler, editor), Touchstone, New York, 1998, sec. 1.100 and 4.107, and maps 1.99 and 4.106
- ^ [1] Archived 2017-04-24 at the Wayback Machine D. C. Samsaris, Historical Geography of Eastern Macedonia during the Antiquity (in Greek), Thessaloniki 1976 (Society for Macedonian Studies), p. 87-88 ISBN 960-7265-16-5.
- ^ Thucydides, Book II, 99
- ^ [2] Archived 2017-04-24 at the Wayback Machine D. C. Samsaris, Historical Geography of Eastern Macedonia during the Antiquity (in Greek), Thessaloniki 1976 (Society for Macedonian Studies), p. 135-170 ISBN 960-7265-16-5.
- ^ Benjamin H. Isaac, The Greek Settlements in Thrace Until the Macedonian Conquest, p. 4-69
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Edonis at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Edonis at Wikimedia Commons
