Flag of Gagauzia
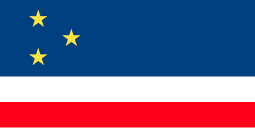 | |
| Other names | Gagauz Yerin bayraa, Sky Flag |
|---|---|
| Use | State flag |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | October 31, 1995 |
 | |
| Use | Civil flag |
 | |
| Use | Ethnic flag |
The flag of Gagauzia (Gagauz: Gagauz Yerin bayraa, Romanian: Steagul Găgăuziei, Russian: Флаг Гагаузии) has served as an official symbol of the Gagauz Territorial Unit since 1995, and is recognized as a regional symbol by Moldova. Popularly known as the "Sky Flag", it is a triband of blue-white-red, with a wider blue stripe, charged with three yellow stars arranged in triangular pattern. The overall symbolism is debated, but the stars may represent the three Gagauz municipalities within Moldova. The tricolor is reminiscent of the Russian flag, which is also popular in Gagauzia; the issue has created friction between Gagauz and Moldovan politicians.
Before their mass migration into Bessarabia and the Budjak, Gagauz people were associated with several polities—including the Despotate of Dobruja—which, according to Gagauz tradition, had a rooster flag. The emergence of Gagauz nationalism dates back to the 1860s, when the Gagauz and the Bessarabian Bulgarians rejected both Tsarist autocracy and Romanian nationalism. A Gagauz quasi-state, the "Comrat Republic", was formed during the Russian Revolution of 1905, but its leaders only used the generic red flag, publicizing their loyalty toward the All-Russian Peasant Union. Separate symbols for the Gagauz and their territory are comparatively new, first emerging as marks of the resistance to Russification in the Soviet Union. Several ethnic and semi-official flags were recorded for Gagauz separatists during the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, generally featuring the grey wolf (Turkish: bozkurt).
The self-proclaimed Gagauz Republic adopted wolf symbolism in various forms; the device was featured on its official flag, which reportedly existed in only one copy. Despite their initial popularity, grey-wolf flags were tainted by controversy, being read as references to Pan-Turkism and the eponymous far-right group. They fell out of use in 2000–2010, but reemerged as popular in the following decade. In 2017, Governor Irina Vlah proposed the introduction of a flag bearing the wolf's head in red as a "historical flag" with official status. If adopted, this resolution would not replace the "Sky Flag".
Symbolism
[edit]The current "national flag" of Gagauzia has "a blue field bearing a narrow white and red horizontal stripes on the bottom and three yellow stars on the upper hoist."[1] Reportedly, the three stars stand for "the past, present and future",[2] or, alternatively, for the three constituent municipalities of Gagauzia: Comrat (Komrat), Ceadîr-Lunga (Çadır-Lunga), and Vulcănești (Valkaneş).[3] Writer Ștefan Curoglu was an early proponent of a triband arrangement, which was to attest the ancestry of Gagauz people. In this interpretation, each color represents an ancestral contributor to Gagauz ethnogenesis: the Pechenegs, the Kipchaks, and the Oghuz Turks.[4]
The triband replaced earlier designs with a grey wolf (bozkurt) or wolf's head. These were notably in use under the self-proclaimed Gagauz Republic of Governor Stepan Topal (served 1990–1995). According to reports of the time, the imagery recalls "a myth of the Gagauz people's founding", when "a wolf led [the Gagauz] to freedom."[2] Writing in 1990, Curoglu linked the wolf's head with another tradition, that of "nine mourners", or "nine wolves", guarding the Gagauz nation, or with the folkloric depiction of the pole star as a wolf.[4] Other readings describe the bozkurt as a Pan-Turkic symbol, namely as "the legendary grey wolf that led the Turks across the mountains onto the steppes."[5] Journalist Àlex Bustos quotes Gagauz tourism expert Vera Garciu, who links that symbolism with "pagan aspects [that] are still used in our culture. [...] We have festivities that we dedicate to wolves: we simultaneously fear and respect them."[6] Researcher Anatol Măcriș claims that the ancient Gagauz flag had "a wolf on a green field", and proposes that it may derive from the Dacian Draco.[7]
History
[edit]Emergence of Gagauz nationalism
[edit]The Gagauz report their origins as linked to the high-medieval Despotate of Dobruja, and see themselves as a Turkic or Turkified Christian people which resisted the spread of Islam. Folk tradition describes the Despotate as a Turkish "Uzi Eyalet", co-founded by the Seljuk ruler Kaykaus II and the Alevi mystic Sarı Saltık.[8] Such records claim that the state switched to a Christian Kipchak dynasty, whose most notable exponent was Dobrotitsa, and whose main symbol was a "red flag with a white rooster at its center."[9] The Despotate was conquered by the Ottoman Empire, but the main branches of the Gagauz stayed behind in the Dobrujan and Ludogorian areas of Rumelia. According to Gagauz sources, in the 18th century they established a republic centered on, and named, the town of Vister; it also comprised some 100 Dobrujan villages.[10] Some Ludogorian Gagauzes moved to Moldavia in the 1780s, settling in its eastern regions—later known as Bessarabia. These colonists established villages in the Leova area, but were angered by the heavy taxes imposed on them, and resettled to the south, in the Ottoman-held Budjak (Silistra Eyalet).[11]
Chased out of Dobruja during the Russo-Turkish War of 1806, many Gagauzes were accepted by the Russian Empire, which now occupied Bessarabia and the Budjak, regrouped as the Bessarabia Governorate. Their colonization helped "fill the gap that occurred with the forced exile of the Tatars who had formerly lived in this region."[12] Part of the Budjak was returned to Moldavia in 1856, together with its Gagauz, but re-annexed by Russia with the 1878 Berlin Treaty.[13] During the first decades of their presence, they were officially designated as "Bulgarians/Greeks of the Turkish tongue", or as "baptized Turks";[14] opinion gravitated toward them being an "ethnographic group among the Bulgarians".[15] Into the 1860s, they remained closely aligned and confounded with the Bessarabian Bulgarians. In 1842–1844, inspired by the Minkov family of Bolgrad, the two groups bonded in rebelling against the Russian administration, who had formed a habit of using the colonists as cheap labor.[16] Like the Bulgarians, the Gagauz opted for incorporation with the United Principalities, but were disappointed to discover that Moldavian and Romanian laws would not prolong their regional autonomy; in 1861, Bulgarians and Gagauz staged a rebellion against conscription into the Romanian Land Forces, and thereafter organized waves of emigration into Russia.[17]

Gagauzia first expressed aspirations of becoming an independent nation in the wake of the 1905 Revolution: a small "Comrat Republic", or Gagauz Khalki, survived for some days in January 1906.[18] It formed a government, with Andrey Galatsan serving as the "Comrat President" (Komrat Cumhurbaşkanı),[19] and "took a decision to abolish all taxes on its territory".[20] Although cited as a precedent and "the world's first Turkish Republic"[21] by later nationalists, this polity was mainly concerned with land reform, rather than ethnic self-determination.[22] The episode also brought Gagauz settlements under the influence of left-wing political parties, including most of all the Esers and the All-Russian Peasant Union (of which Galatsan himself was a member), but also an anarchist club established by Ferdinand Bragalia.[23] Revolutionary pamphlets referred to the red flag as a central symbol, and carried the Esers' Russian-language slogan: Въ борьбѣ обрѣтешь ты право свое ("Through struggle you will attain your rights").[24]
A second statehood was established following the February Revolution of 1917, with hopes of joining the Moldavian Democratic Republic (RDM) as an autonomous unit. The community was allocated two seats in the RDM legislature, Sfatul Țării,[25] wherein Krste Misirkov, an immigrant from Macedonia, described himself as "elected by the Bulgarians and the Gagauz".[26] Invaded by the Ukrainian People's Republic and the Odessa Soviet Republic, the Gagauz polity sought protection from the Kingdom of Romania, and eventually supported the union of Bessarabia with Romania.[27] This decision was fought against by Tighina's "Bulgarian-and-Gagauz committee", which sought to achieve union with the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic.[28] In 1921–1924, a Gagauz guerilla force, established by the Bessarabian Communist Party, engaged the Romanian Gendarmes in skirmishes, culminating as a Gagauz participation in the larger Tatarbunary Uprising.[29]
Turkic symbols
[edit]During the interwar, in Greater Romania, Gagauz nationalism was centered on the localized version of Romanian Orthodoxy, in combination with the tenets of Turkish nationalism, and even Kemalism. The synthesis was effected by the priest and propagandist Mihail Ciachir.[30] Anti-communism and conservatism were introduced into this mix as a result of the Soviet anti-religious campaign: "This threat from communism was another crucial factor in the development of Gagauz religiosity and formed a significant component of [Ciachir's] 'national message'".[31] The Christian ingredient, meanwhile, reduced compatibility with Kemalist Turkey, which barred the Gagauz from obtaining citizenship—while at the same time extending its definition of "Turkishness" to include Muslim Slavs (Bosniaks and Pomaks).[32] The Turkish Ambassador in Romania, Hamdullah Suphi Tanrıöver, supported Ciachir's efforts by assigning scholarships to the Gagauz, and connecting them culturally to the Turks of Romania; he then considered a plan for resettling some Gagauz in Marmara Region.[33] Tanriover was also able to obtain from the Romanian government that schools around Comrat provide basic education in Turkish.[21] Future Gagauzia developed into a multicultural region under the early stages of Romanian rule,[34] with segments of the community aligning themselves more closely with Romanian nationalism, rather than Kemalism. In 1937, a multi-ethnic section of the far-right National Christian Party in Comrat, headed by the Gagauz Dumitru Topciu, was only flying the flag of Romania.[35]
Gagauz-inhabited regions were separated during the 1940–1941 Soviet occupation of Bessarabia: "The border between Moldova and Ukraine, delineated in 1940, arbitrarily crossed the compact area of Bulgarian–Gagauz settlement."[36] The Gagauz had resisted measures to bring about their Romanianization or expulsion, but were also exposed to Russification during the first and second Soviet occupations. As a result of the latter, the Gagauz population dwindled, suffering through the great famine of 1946, and also through a wave of punitive deportations, primarily into the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic and Gorno-Altai.[37] Russification was intensified following the consolidation of a Moldavian SSR within the Soviet Union, although some linguistic concessions were made in the 1950s and '60s.[38] The Soviet administration, meanwhile, tolerated discourses which linked the Gagauz with the Pechenegs and Oghuz Turks of Central Asia, "not only because they link [the Gagauzes'] ancestry with regions within the Soviet Union, but also because they present their Christianisation as a relatively insignificant, obscure and late historical event."[39] Turkologist Astrid Menz observed that more and more Gagauz intellectuals "emphasized their 'Turkic' identity by means of [...] reconstructed history and an increased use of 'Turkic' motifs, especially from the great heroic past in the fine arts."[40]
The first attested nationalist flags of the Gagauz Moldovan people emerged during the Perestroika years, before the fall of the Moldavian SSR. The emancipation movement used "a light blue field bearing a centered yellow disk charged with a black wolf's head",[1] reportedly designed by Petru (Pötr) Vlah, who first flew it on October 29, 1989.[21] This was also reported as a black wolf's head in profile, on a golden circle with outer white ring, all on a field of light blue.[4] Another variant of the flag, which was notably painted as a mural in Comrat, is "blue with white borders and has a white medallion in the middle showing the Bozkurt".[5] This was originally a military flag, designed in 1990 by the same Petru Vlah. In his version, the wolf's head, colored grey, was shown in profile, facing the mast; the bordure was a sewn pattern.[41] The ethnic flag had numerous other reported variants. A triangular pennon, of uncertain coloring, had the wolf's head, cabossed, on a plain circle, with no outer ring. This version was reported as in use by Stepan Topal's government in August 1990, and flown alongside the Soviet flag during the separatist uprising.[4] In parallel protests for the establishment of Comrat State University, Gagauz activists allegedly used a light-blue field defaced with a red wolf's head on a white disk, with a yellow motif running vertical near the mast.[42][43]


On August 11, 1990, a Gagauz Republic was formed, seceding from the Moldavian SSR and seeking to unite with the Gagauz in Ukraine. During the subsequent clashes in the enclave of Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Romanian volunteers reported that the Gagauz had "their own flag, with the head of a jackal".[44] Although the new state of Moldova had lost any control over the Gagauz region by 1992, the nationalist movement became divided between a minority which pressed for Gagauzia to join the Russian Federation and a majority which looked forward to autonomy within Moldova.[45] The latter vision was supported by scholar Mariya Maruneviç, who argued that the Republic was meant "not as a separation from Moldova as a whole, but as a guarantee of maintaining national equality in areas densely populated by the Gagauz."[46] As reported by historian Frederick Quinn, by 1993 the Topal government—which had embraced full separatism—was using a new version of the Gagauz flag, its "only extant copy" displayed in Topal's own office. It showed the full-bodied wolf in black, facing the mast and standing on a mound, all within a golden-and-red circle. This was superimposed over a triband closely resembling the current flag, but with a narrower white stripe, and with the three stars aligned vertically.[47]
Under the "Special Status"
[edit]In December 1994, Gagauzia and Moldova agreed on a "Special Status" for the former, which became the first autonomous ethnic enclave to achieve recognition in all of post-communist Eastern Europe.[48] This led to the adoption of a revised flag, in its current form, with the nickname "Sky Flag".[49] It was favored over the wolf symbols, which were resented by moderate Gagauz, in particular those who feel a religious solidarity with the Pontic Greeks; the grey wolf was also seen as associated with the far-right of Pan-Turkism, as embodied by the Idealist Hearths.[50] Menz noted in 2007 that Gagauz villagers "were nostalgic about Soviet times", and also that they displayed some measure of Turkophobia—"because all the Turks they had ever seen were businessmen while they were farmers." She found Turkophilia to be mostly an upper-class phenomenon, with the other social groups "more or less unaffected by a search for an independent Gagauz identity."[51] Moreover, according to literary historian Attila Jorma: "Moldovan Gagauzes are afraid to be Turkish, since reference to Turkishness could give Moldovan Romanians a reason to point out that they have a 'mother country', to which one should move."[52]
After 2000, the wolf's head symbol has been quietly taken out of public displays.[53] In 2010 the new Gagauz triband was taken to the top of Mount Elbrus by Anna Zanet, daughter of the nationalist poet-journalist Todur Zanet.[49][54] This flag also created controversy; its usage remains central to the disputes between Romanian nationalism and those Gagauz who fear a potential unification with Romania. Also in 2010, Governor Mihail Formuzal announced that he and his cabinet opposed the decree by Moldovan President Mihai Ghimpu, which ordered the flying of state symbols at half-mast on June 28—that is, for the commemoration of Soviet annexation. Formuzal referred in particular to the lowering of the "Sky Flag", which "can only be done by order of the Governor. I will not issue such an order."[55] Instead, June 28 was celebrated in Gagauzia as a "day of liberation from Romanian fascist occupation".[55]

After a unionist rally in May 2012, the Gagauz mayor of Comrat, Nicolai Dudoglo, threatened that his city would only hoist the Gagauz symbols, and remove Moldovan flags.[56] In 2014, in the context of the pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine on Moldova's borders, there was some concern about similar events unfolding in Moldova. In Moldova's Parliament, Gheorghe Duca moved to ban the Gagauz flag as resembling the flag of Crimea, but his motion was met with opposition from the Party of Communists.[57] Also during that interval, a group of pro-Russian Gagauz in Comrat flew the flag of Russia.[58] Public institutions in Gagauzia still displayed the flag of Europe, honoring Moldova's pro-enlargement policy, but the employees' mood was reported as sour on this issue.[59]
At her swearing-in ceremony the following year, Governor Irina Vlah made a show of kissing the Gagauz flag, and thereafter gave unofficial equal status to the Moldovan and Russian flags.[60] Vlah created additional controversy by wearing a scarf of blue-red-white, colors which are shared by Gagauzia and Russia. Moldovan voices saw this as evidence that Vlah was "set[ting] herself up as a promoter of Russian interests."[61] Russia Day 2016 was openly celebrated in Comrat with Governor Vlah's approval. As Radio Free Europe reports, it saw the Gagauz waving a "flurry of Russian Federation flags".[62] By March of the following year, the European flag had been reportedly removed from the gubernatorial residence in Comrat.[63] In May 2022, at the height of the Russian invasion in Ukraine, Vlah allowed the Ribbon of Saint George, which had been outlawed in Moldova, to be flown on Gagauz territory.[64]
During August 2017, Governor Vlah announced an initiative to reinstate the "historical flag" of Gagauzia as an official symbol, to be flown on state buildings alongside the "Sky Flag". Speaking at the time, she identified the former as a flag appearing at public rallies in 1990–1994, and argued that the proposal "has been for long discussed in our society."[43] Illustrations and videos published alongside such reports showed a return to the red wolf's head on a white disk, over a field of light blue.[42][43] According to a report on Realitatea TV, Vlah was inspired by a separatist group, Gagauz Halkı, which resumed its activities in March 2017.[42] In September, Ana Sözü newspaper reported that there were political disagreements which made it improbable that the commission for a new flag would ever be functional.[41] The "Sky Flag" was still being used as a rallying symbol for Gagauz supporters of Moldova's Prosecutor General, Alexandru Stoianoglo. Shortly after Stoianoglo's arrest in October 2021, these groups blocked a road between Chișinău and Giurgiulești, by stretching a Gagauz flag across it.[65]
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b Minahan, p. 630
- ^ a b Quinn, p. 24
- ^ Bulut, p. 62
- ^ a b c d "Nové vlajky. Gagauzsko", in Vexilologie. Zpravodaj Vexilologického Klubu při okd Praha, Issue 81, 1991, pp. 1602–1603
- ^ a b Smith Albion, p. 6
- ^ Àlex Bustos, Gagauzia: Turkic, Orthodox Crossroads between Moldova, Russia and Turkey, Nationalia (CIEMEN), January 12, 2022
- ^ Măcriș, p. 58
- ^ Karanfil, pp. 61–62. See also Menz, p. 127
- ^ Karanfil, p. 61
- ^ Karanfil, pp. 62–63
- ^ Karanfil, p. 63
- ^ Menz, p. 125
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 47–53, 58–83; Karanfil, pp. 62–63; Măcriș, pp. 5–74, 96–99, 117–119, 149–195; Menz, p. 126; Minahan, pp. 631–632. See also Jorma, pp. 143–145
- ^ Duminică (2017), pp. 13–14
- ^ Skrukwa, p. 293
- ^ Duminică (2017), pp. 19–20
- ^ Sever Mircea Catalan, "Principiul integrității teritoriale în politica românească în vremea lui Alexandru Ioan Cuza", in Revista Istorică, Vol. 3, Issues 7–8, July–August 1992, pp. 762–765. See also Kapaló, pp. 51–52; Menz, p. 126
- ^ Bulgar, pp. 304–305; Bulut, p. 63; Kapaló, p. 54; Karanfil, pp. 63–64; Minahan, p. 632; Romanova, pp. 201–201; Tufar et al., passim
- ^ Karanfil, pp. 63–64
- ^ Bulgar, p. 304
- ^ a b c Karanfil, p. 64
- ^ Kapaló, p. 54. See also Basciani, pp. 61–62
- ^ Bulgar, p. 302. See also Tufar et al., passim
- ^ Tufar et al., pp. 27, 48, 49
- ^ Basciani, p. 89
- ^ Vlado Treneski, Deyan Tanchovski, Erlin Ago, Ivan Nikolov, Iliya Stoyanovski, Metodiy Ivanov, Rumen Srebranov, Spas Tashev, White Book about the Language Dispute Between Bulgaria and the Republic of North Macedonia, pp. 46–47. Sofia & Toronto: Orbel, 2021. ISBN 978-954-496-149-7
- ^ Minahan, pp. 632–633
- ^ Gheorghe Brătianu, Basarabia. Drepturi naționale și istorice, p. 56. Bucharest: Editura Semne, 1995. OCLC 38112407
- ^ Romanova, pp. 201–202. See also Kapaló, p. 55
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 56–115. See also Bulut, p. 62; Menz, p. 129
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 55–56
- ^ Fuat Dündar, Challenges of Examining the Ottoman/Turkish Immigration Policies, ZMO Working Papers, No. 28, 2021, pp. 3, 7, 10–14; Kemal Kirişci, "Migration and Turkey: the Dynamics of State, Society and Politics", in Reşat Kasaba (ed.), The Cambridge History of Turkey, Volume 4, pp. 178–180, 195–196. Cambridge etc.: Cambridge University Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-521-62096-3
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 100–101
- ^ Măcriș, pp. 60–84
- ^ Ivan Duminică, "Бессарабские болгары и гагаузы во взглядах румынского писателя и политика Георге А. Куза", in Ivan Duminică, Kalcho Kalchev, Gheorghe Gonța, Nadejda Cara, Maria Paslar, Sergiy Strashnyuk, Yekaterina Chelak (eds.), България метрополия и диаспора. Сборник по случай 65-годишнината на д.и.н. Николай Червенков, p. 311. Chișinău: Academy of Sciences of Moldova & Gregory Tsamblak State University, 2013. ISBN 978-9975-9577-2-4
- ^ Skrukwa, p. 171
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 75, 178; Karanfil, p. 64
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 53–83; Karanfil, p. 64; Menz, p. 126; Minahan, pp. 633–634. See also Măcriș, pp. 84–85, 87–89, 106–107, 120–141; Romanova, pp. 204–205
- ^ Kapaló, p. 62
- ^ Menz, p. 127
- ^ a b "İş komisiyasız da belli! Gagauz Respublikamızın hem Milli Bayraamızın işi bitti!", in Ana Sözü, September 29, 2017, p. 1
- ^ a b c (in Romanian) Drapelul mișcării separatiste din anii '90 din Găgăuzia va fi oficializat. Irina Vlah: Sub acest simbol s-au desfășurat primele mitinguri, Realitatea TV, August 23, 2017
- ^ a b c (in Romanian) Iurii Botnarenco, "Drapelul așa-numitei Republici Găgăuzia va fi oficializat la Comrat", in Adevărul Moldova, August 19, 2017
- ^ Ion D. Goia, "Vom lupta pînă la capăt", in Flacăra, Issue 46, November 1990, p. 14
- ^ Minahan, p. 634. See also Kapaló, pp. 76–78; Smith Albion, pp. 7–10
- ^ Romanova, pp. 206–207
- ^ Quinn, pp. 24, 160
- ^ Minahan, p. 634–635. See also Măcriș, pp. 85–87, 106–107; Smith Albion, pp. 6–10
- ^ a b Ülkü Çelik Şavk, "Todur (Fedor) Zanet Gagauzluk ve Gagauzlara Adanmış Bir Hayat", in Tehlikedeki Diller Dergisi, Winter 2013, p. 134
- ^ Kapaló, pp. 80–81
- ^ Menz, pp. 126–128
- ^ Jorma, p. 76
- ^ Kapaló, p. 81
- ^ (in Romanian) Monitor Media, "Ziarul găgăuz Ana Sözü a ajuns pe Elbrus", in Moldova Azi, August 9, 2010
- ^ a b (in Romanian) "Comrat: 'Ziua eliberării de sub ocupația fasciștilor români'", in Timpul de Dimineață, June 29, 2010
- ^ (in Romanian) Vitalie Călugăreanu, Moldova. Tendințele unioniste de la Chișinău au agitat Rusia, Deutsche Welle, May 14, 2012
- ^ (in Romanian) "Deputații vor discuta mâine situația Ucrainei în spatele ușilor închise", in Timpul de Dimineață, March 20, 2014
- ^ Paul Goble, Commentaries: A Russian Flag Over Gagauzia, Jamestown Foundation, April 4, 2014
- ^ (in French) Victoria Puiu, "Moldavie. Les Gagaouzes se sentent trop éloignés de la culture européenne", in Courrier International, May 20, 2014
- ^ Kit Gillet, A Tiny Region in Moldova Holds the Key to Understanding Eastern Ukraine's Future, Business Insider, May 25, 2015
- ^ Igor Botan, Real and Imagined Dangers in the Elections in Gagauzia, E-democracy.md (Association for Participatory Democracy ADEPT), March 16, 2015
- ^ (in Romanian) Tatiana Ețco, Cum a fost sărbătorită Ziua Rusiei la Comrat (mai mult) și la Chișinău (mai puțin), Radio Free Europe, June 13, 2016
- ^ (in Romanian) Svetlana Corobceanu, "O zi 'fără politică' în Găgăuzia", in Jurnal de Chișinău, March 17, 2017
- ^ (in Romanian) Irina Vlah a semnat legea ce prevede utilizarea panglicii negru-oranj pe teritoriul autonomiei găgăuze, Teleradio-Moldova, May 3, 2022
- ^ (in Romanian) După protestul de la Comrat, mai mulți automobiliști au blocat circulația: Drapelul a fost întins pe toată porțiunea de drum de la intrarea în regiune, Unimedia, October 10, 2021
References
[edit]- Alberto Basciani, La difficile unione. La Bessarabia e la Grande Romania, 1918–1940. Rome: Aracne Editore, 2007. ISBN 978-88-548-1248-2
- Stepan Bulgar, "Комратское восстание и роль интеллигенции в революционных событиях 1905–1906 гг", in Știință, Educație, Cultură, Vol. III, 2022, pp. 301–306.
- Remzi Bulut, "The Economic and Political Structure of Gagauzian Turks", in Journal of Institute of Social Sciences (Mehmet Akif Ersoy University), Vol. 3, Issue 6, Autumn 2016, pp. 60–71.
- Ivan Duminică, Coloniile bulgarilor în Basarabia (1774–1856). Chișinău: Academy of Sciences of Moldova & Moldovan Society of Bulgarists, 2017. ISBN 978-9975-139-27-4
- Attila Jorma, Bulgarianturkkilainen romaani 1960-luvulla (Annales Universitatis Turkuensis, Scripta lingua Fennica edita, Ser. C, Tom. 276). Turku: University of Turku, 2008. ISBN 978-951-29-3755-4
- James Alexander Kapaló, Text, Context and Performance: Gagauz Folk Religion in Discourse and Practice. Leiden & Boston: Brill Publishers, 2011. ISBN 978-90-04-19799-2
- Güllü Karanfil, "Gagauzlar ve devletleşme", in Știință, Educație, Cultură, Vol. II, 2021, pp. 61–65.
- Anatol Măcriș, Găgăuzii. Bucharest: Editura Paco, 2008.
- Astrid Menz, "The Gagauz between Christianity and Turkishness", in Filiz Kıral, Barbara Pusch, Claus Schönig, Arus Yumul (eds.), Cultural Changes in the Turkic World, pp. 123–130. Würzburg: Ergon-Verlag, 2007.
- James Minahan, Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations. Ethnic and National Groups around the World, Volume II D–K. Westport & London: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2002. ISBN 0-313-32110-8
- Frederick Quinn, Democracy at Dawn: Notes from Poland and Points East. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 1998. ISBN 0-89096-786-5
- Svetlana Romanova, "Провинциализм как один из факторов сохранения самобытности гагаузов", in V. P. Stepanova, Svetlana Gubanenkova (eds.), Провинциализм: сохранение самобытности или самоизоляционизм?, pp. 199–211. Oryol & Chișinău: Oryol State University, 2018. ISBN 978-5-9929-0623-3
- Grzegorz Skrukwa, O Czarnomorską Ukrainę. Procesy narodowotwórcze w regionie nadczarnomorskim do 1921 roku w ukraińskiej perspektywie historycznej (Uniwersytet im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu, Seria Historia Nr 229). Poznań: Wydawnictwo Naukowe UAM, 2016. ISBN 978-83-232-3081-6
- Adam Smith Albion, Travels in Romania, Moldova and Gagauzia, Institute of Current World Affairs Letters, ASA-7 1995, Europe/Russia (May 10, 1995).
- Nikolai Kharlampiyevich Tufar, Nikolai Nikolaevich Tufar, Zardyhan Kinayatuly, Очерки истории гагаузов. Комратская Республика 1906 год. Огузское государство IX–X в.в. Comrat: M. V. Maruneviç Center for Scientific Research, 2015. ISBN 978-9975-3075-2-9
