Portal:Ecology
| |
|
|
Ecology
|
|
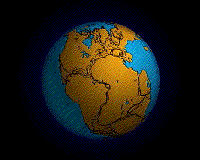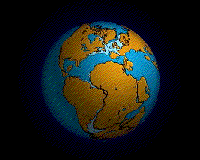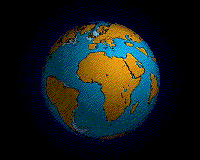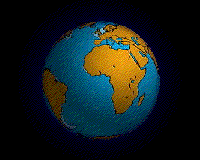
Ecology (from Ancient Greek οἶκος (oîkos) 'house' and -λογία (-logía) 'study of') is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries, mining, tourism), urban planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). The word ecology (German: Ökologie) was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel. The science of ecology as we know it today began with a group of American botanists in the 1890s. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection are cornerstones of modern ecological theory. Ecosystems are dynamically interacting systems of organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living (abiotic) components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, nutrient cycling, and niche construction, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. Ecosystems have biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and abiotic components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and provide ecosystem services like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber, and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection, and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value. (Full article...) Selected article - Intertidal ecology is the study of intertidal ecosystems, where organisms live between the low and high tide lines. At low tide, the intertidal is exposed whereas at high tide, the intertidal is underwater. Intertidal ecologists therefore study the interactions between intertidal organisms and their environment, as well as between different species of intertidal organisms within a particular intertidal community. The most important environmental and species interactions may vary based on the type of intertidal community being studied, the broadest of classifications being based on substrates—rocky shore and soft bottom communities. Organisms living in this zone have a highly variable and often hostile environment, and have evolved various adaptations to cope with and even exploit these conditions. One easily visible feature of intertidal communities is vertical zonation, where the community is divided into distinct vertical bands of specific species going up the shore. Species ability to cope with abiotic factors associated with emersion stress, such as desiccation determines their upper limits, while biotic interactions e.g.competition with other species sets their lower limits. (Full article...) Selected image -An animation of the Earth's hypothesized Pangaea separation. Pangaea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration.
General imagesThe following are images from various ecology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related WikiProjectsThings you can do
Entries here consist of Good and Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.
 In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (endoparasitism), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to paralysing the host and living outside it (ectoparasitism). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. (Full article...) Selected biography -Paul Bigelow Sears (December 17, 1891 – April 30, 1990) was an American ecologist and writer. (Full article...) Did you know (auto-generated)
Selected quote -
Ecology news
Additional News Highlights
Selected publication -Environmental Research Letters is an open-access electronic-only peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in all aspects of environmental science. Numerical modelling or simulation, as well as theoretical and experimental approaches to environmental science form the core content. Approaches from a range of physical and natural sciences, economics, and political, sociological and legal studies are also present. Related portalsMore did you know -Related articlesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Web resources
Discover Wikipedia using portals |