Dromaeosauroides
| Dromaeosauroides Temporal range: Early Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Cast of the holotype tooth (DK 315), Natural History Museum, London | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Dromaeosauridae |
| Clade: | †Eudromaeosauria |
| Subfamily: | †Dromaeosaurinae |
| Genus: | †Dromaeosauroides Christiansen & Bonde, 2003 |
| Type species | |
| †Dromaeosauroides bornholmensis Christiansen & Bonde, 2003
| |
Dromaeosauroides is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of what is now Denmark and possibly also England. It was discovered in the Jydegaard Formation in the Robbedale valley, on the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea. This is the only likely place for dinosaur remains to be discovered on Danish territory, since the Mesozoic deposits exposed in the rest of the country are marine. Dromaeosauroides is the first known dinosaur from Denmark, and the only one which has been scientifically named. It is one of the oldest known dromaeosaurs in the world, and the first known uncontested dromaeosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Europe.
It is known from two teeth, the first of which was found in 2000 and the second in 2008. Based on the first tooth (the holotype), the genus and species Dromaeosauroides bornholmensis was named in 2003. The genus name means "Dromaeosaurus-like", due to the similarity to the teeth of that genus, and the species name means "from Bornholm". After this discovery, remains and tracks of more dinosaurs were found in various geological formations on Bornholm. Coprolites containing fish remains found in the Jydegaard Formation may belong to Dromaeosauroides. Some teeth from the United Kingdom that have been assigned to the genus Nuthetes may also belong to this animal.
The holotype tooth is 21.7 millimetres (0.85 in) long, and the second tooth is 15 millimetres (0.59 in). They are curved and finely serrated. In life, Dromaeosauroides would have been 2 to 3 metres (7 to 10 ft) in length, and weighed about 40 kilograms (88 lb). As a dromaeosaur it would have been feathered, and had a large sickle claw on its feet like its relatives Dromaeosaurus and Deinonychus. It lived in a coastal lagoon environment with sauropods, as evidenced by a possible titanosaur tooth.
Discovery and naming
[edit]Few dinosaur remains have been found in Scandinavia. The mainland of western Denmark is an unlikely region to find dinosaur remains, since the Mesozoic sediments there are marine Maastrichtian chalk. Fossils of non-dinosaurian marine animals, including mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, have been found in these deposits.[1] Mesozoic deposits in Scania, Sweden, are much richer in fossils, including those of dinosaurs. The Danish island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea was part of the same land mass as Scania (the Scandinavian-Russian continent), and has a similar geology. The southwestern part of the island is the only place in Denmark which has yielded dinosaur remains.[2]

During the 1990s, the Fossil Project (disbanded in 2005) was formed by a group of unemployed people who received funding from Denmark and the EEC to maintain geological sites on Bornholm.[2] One of these, "Carl Nielsen's sandpit" in the Robbedale valley (not to be confused with the Robbedale Formation, where no vertebrate remains have been found), is part of the Jydegaard Formation. This formation is 140 million years old, dating to the Late Berriasian (or Ryazanian) stage of the Early Cretaceous period. The Fossil Project sifted sand at these sites in cooperation with the NaturBornholm interpretation centre, which exhibited the fossils discovered. In September 2000, Danish palaeontologists Per Christiansen and Niels Bonde taught a field course at the site, "The Hunt for Danish Dinosaurs". During the course, geology student Eliza Jarl Estrup found a theropod tooth, the first dinosaur discovered on Danish territory, and the find was recorded by a local television station.[1][3]
The tooth was presented at the 45th annual meeting of the Palaeontological Association in 2001, and identified as a dromaeosaur.[4] In 2003 the tooth (MGUH 27218/DK 315) was made the holotype specimen of Dromaeosauroides bornholmensis—named and described by Christiansen and Bonde. The genus name combines Dromaeosaurus with the Greek -ides ("in the form of"), referring to the resemblance between the teeth of the two genera. The specific name refers to Bornholm.[5] The name Dromaeosaurus itself has been translated as "swift" or "running reptile".[6][7] Bonde and Christiansen had expected the first Danish dinosaur remains to be teeth of herbivorous dinosaurs such as hypsilophodonts or Iguanodon, and were surprised to find a dromaeosaur tooth instead, since these are rare in Early Cretaceous formations; herbivores would have been more abundant than carnivores.[1][8] Because the dromaeosaur seems to have been large, they expected that resilient bones, such as claws, might be found in the future. The palaeontologists did not expect bones of larger dinosaurs to be discovered in the formation (since these would most likely have been found when the sand was commercially exploited), but hoped the remains of a Mesozoic mammal would be found.[1] The holotype tooth has been illustrated in several books and research articles. It was certified "Danekræ" ("Danish creature", according to a 1990 Danish museum law securing important fossils) when its scientific importance was evaluated by the Geological Museum in Copenhagen.[1][2]

In late summer 2008, ranger Jens Kofoed found a second dromaeosaurid tooth.[9] This specimen (DK 559) was found in the same location, and later assigned to D. bornholmensis as well.[2] Kofoed explained that the finds were surprising because people had been unsuccessfully searching for dinosaur remains in Denmark for years, and it was like finding a "needle in a haystack".[10] In a press release, the second dromaeosaur tooth was also certified Danekræ by the Natural History Museum of Denmark, which compared the animal to the raptors in the film Jurassic Park, noting that the animals, unlike the film's raptors, would have been feathered.[9]
Since the discovery of Dromaeosauroides, evidence of more dinosaurs has been found in various geological formationsF on Bornholm, such as additional teeth and footprints from various groups.[2][11][12][13][14][15] In 2012, Jesper Milàn and colleagues described two coprolites (fossilised faeces) containing fish scales and bones. They were found in the Jydegaard Formation, the first such fossils found in Danish continental Mesozoic deposits. Although the producer of these faeces cannot be identified with certainty, marine turtles and dromaeosaurids such as Dromaeosauroides are the most likely candidates.[16]
Description
[edit]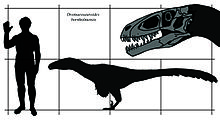
Fossil theropod teeth are typically identified according to features including size, proportion, curvature of the crown and the morphology and number of denticles (serrations). The holotype of D. bornholmensis is a tooth crown 21.7 millimetres (0.85 in) long, 9.7 millimetres (0.38 in) from front to back and 6.6 millimetres (0.26 in) wide at the base. The front part of the tooth was worn, indicating that it was shed when the animal was alive. It was further affected by taphonomic wear; the base of the tooth is irregular, so it may have been slightly longer in life.[1] The curvature and length of the holotype tooth and the length of its hindmost cutting edge (carina) indicates it was in the front of the jaw.[8]
The tooth is recurved with a backward bend, and is oval in cross-section. Its front and back cutting edges are finely serrated, extending two-thirds down each edge.[8] There are six denticles per millimeter (0.04 in), and each denticle is square and chiseled. The overall form of the tooth, its width and shape in cross-section and its curvature resemble those in the maxilla (upper jawbone) and mandible of the species Dromaeosaurus albertensis from North America. Blood grooves are indistinct or absent, also similar to Dromaeosaurus, and differing from members of the Velociraptorinae subfamily. Dromaeosauroides differs from Dromaeosaurus in that the cutting edge at the front side is further from the middle of the tooth. Although the tooth is larger and the denticles similar, each denticle was smaller than those of Dromaeosaurus, which had only 13–20 denticles per 5 millimetres (0.20 in), instead of Dromaeosauroides' 30.[1] The second known tooth is smaller—15 millimetres (0.59 in)—with the same features as the holotype.[2]
The holotype tooth is roughly 25 percent larger than equivalent Dromaeosaurus teeth, from which a body length of 3 metres (120 in) or more was estimated for Dromaeosauroides; it may have been as long as 3 to 4 metres (9.8 to 13.1 ft).[1][8] In an interview, Christiansen estimated its skull to be 35 centimetres (14 in) long and the animal's weight 40 kilograms (88 lb); a Bengal tiger of the same length would weigh 150 to 180 kilograms (330 to 400 lb) by comparison.[17] As a dromaeosaur, Dromaeosauroides would have had a large sickle claw on its highly mobile second toe, like its relatives Dromaeosaurus, Velociraptor and Deinonychus. That group is closely related to birds, and the NaturBornholm interpretive centre houses a roughly life-sized sculpture of Dromaeosauroides covered in feathers. Later Chinese finds of well-preserved feathered dromaeosaurs indicate that the sculpture should have more and longer feathers to be accurate. Although some smaller dromaeosaurs may have been able to fly, flight was unlikely for an animal the size of Dromaeosauroides.[8]
Classification
[edit]
Several features of the tooth are only known from members of the family Dromaeosauridae of theropod dinosaurs.[8] Dromaeosauroides was classified as a member of the Dromaeosaurinae subfamily within the Dromaeosauridae, due to its similarity to Dromaeosaurus. Despite the resemblance, Dromaeosauroides is not considered part of that genus. It is unlikely that a genus would survive for 60 million years; Dromaeosauroides lived during the Early Cretaceous, and Dromaeosaurus during the Late Cretaceous. The differences between their denticles also indicate they should be kept separate.[1]
According to Bonde, Dromaeosauroides is one of the oldest known dromaeosaurs in the world; older remains, for the most part, have only tentatively been assigned to Dromaeosauridae. Dromaeosauroides was the first definite dromaeosaurid known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe, depending on the identity of Nuthetes from the Middle Purbeck formation of the United Kingdom (which may slightly predate the Jydegaard Formation). It is uncertain whether the juvenile holotype specimen of Nuthetes has dromaeosaurid characteristics.[1] Large specimens assigned to Nuthetes appear to belong to true dromaeosaurs, and may belong to Dromaeosauroides rather than Nuthetes. These specimens measure 15 to 18 millimetres (0.59 to 0.71 in).[2]
Dromaeosauroides was considered an indeterminate dromaeosaur by Johan Lindgren and colleagues in 2008.[11] Bonde responded that since the teeth differ from those of other dromaeosaurs from the Early Cretaceous (and later members of the group, including Dromaeosaurus), it should be considered valid. He also said that these scientists had provided incorrect information about the location, strata and age of the specimen, and that the circumstances of its naming were no different from those of other tooth-based taxa.[2] Oliver W. M. Rauhut and colleagues cautioned in 2010 that theropod teeth from the Late Jurassic/Early Cretaceous similar to those of dromaeosaurids may instead have belonged to the small tyrannosauroid Proceratosaurus or related taxa.[18] Nicholas R. Longrich and colleagues stated in 2021 that Dromaeosauroides may have been an early eudromaeosaur.[19]
Palaeoenvironment
[edit]
Only a corner of the Jydegaard Formation is exposed today; the remainder is overgrown. Jydegaard is part of the Nyker Group, which includes three formations (Rabekke, Robbedale, and Jydegaard) ranging from the Berriasian to the Valanginian ages of the Early Cretaceous. Jydegaard consists of sediments deposited in a fresh-to-brackish lagoon facing a coastal strip. In addition to Dromaeosauroides and a possible titanosaur, remains of hybodont sharks, fish such as Lepidotes and Pleuropholis, turtles, lizards, the crocodile Pholidosaurus and thin bone fragments from birds or pterosaurs have been found in the deposit.[1] The bivalve Neomiodon is found in abundance in the sediments below (the Neomiodon Bed), indicating mass mortality, perhaps due to dinoflagellate toxins.[20]
The fish and bivalves were found in clay which was probably a lagoon, and the dinosaurs and lizards in sand which probably was land, perhaps a beach; turtles and crocodiles were found in both. Freshwater snails were found in clay that may have been shallow, drying lakes behind a sandy barrier between lagoon and sea, in a setting perhaps similar to the Florida Keys or the southwestern coast of Jutland.[2] Dinosaurs may have fed there, based on the remains of plants and small land animals, and theropods may have hunted along the shore.[1] Bornholm and Scania appear to be the only places were remains of the Scandinavian-Russian fauna of the Early Cretaceous can be found. Further investigations there may show whether this fauna has European or Asian affinities.[2]
Based on possible dromaeosaur coprolites from the Jydegaard Formation, which contained scales of the fish Lepidotes, Milàn and colleagues speculated that some dromaeosaurids were able to catch fish with the enlarged sickle claw on the second digit of the foot, similar to the "spear fishing" that has been proposed for the theropod Baryonyx and its enlarged thumb claw. The larger of the two coprolites has evidence of coprophagous organisms.[16]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Bonde, N.; Christiansen, P. (2003). "New dinosaurs from Denmark". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 2 (1): 13–26. Bibcode:2003CRPal...2...13B. doi:10.1016/S1631-0683(03)00009-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Bonde, N. (2012). "Danish Dinosaurs: A Review". In Godefroit, P. (ed.). Bernissart Dinosaurs. Indiana University Press. pp. 435–449. ISBN 9780253005700.
- ^ Estrup, E. J. (2007). "Jurassic Park Denmark" (PDF). Scient. 4 (in Danish). 1: 12–14.[dead link]
- ^ Bonde, N. (2001). "A Berriasian "Wealden fauna" from Bornholm, Denmark". Palaeontological Association 45th Annual Meeting. 4.
- ^ Christiansen P. & Bonde N. (2003). "The first dinosaur from Denmark". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen. 227 (2): 287–299. doi:10.1127/njgpa/227/2003/287.
- ^ Holtz, T. R. Jr. (2012). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages. New York: Random House. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-375-82419-7.
- ^ Norman, D. B. (1985). "Dromaeosaurids". The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs: An Original and Compelling Insight into Life in the Dinosaur Kingdom. New York: Crescent Books. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-517-46890-6.
- ^ a b c d e f Bonde, N.; Andersen, S.; Hals, N.; Jakobsen, S.T. (2008). Danekræ – Danmarks bedste fossiler (in Danish). Gyldendal. pp. 28–32. ISBN 9788702049855.
- ^ a b "Sensationelt dinosaurfund på Bornholm" (in Danish). Jyllands-Posten. 2009. Archived from the original on 2013-06-16.
- ^ Barslev, K. (2008). "Tand fra dinosaur fundet på Bornholm" (in Danish). Kristeligt Dagblad. Archived from the original on 2012-08-30.
- ^ a b Lindgren, J.; Currie, P. J.; Rees, J.; Siverson, M.; Lindström, S.; Alwmark, C. (2008). "Theropod dinosaur teeth from the lowermost Cretaceous Rabekke Formation on Bornholm, Denmark". Geobios. 41 (2): 253–262. Bibcode:2008Geobi..41..253L. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2007.05.001.
- ^ Surlyk, F.; Milàn, J.; Noe-Nygaard, N. (2008). "Dinosaur tracks and possible lungfish aestivation burrows in a shallow coastal lake; lowermost Cretaceous, Bornholm, Denmark" (PDF). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 267 (3–4): 292–304. Bibcode:2008PPP...267..292S. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.07.004.
- ^ Milàn, J. (2011). "New theropod, thyreophoran, and small sauropod tracks from the Middle Jurassic Bagå Formation, Bornholm, Denmark" (PDF). Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark. 59: 51–59. doi:10.37570/bgsd-2011-59-06. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-06-16. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
- ^ Clemmensen, L. B.; Milàn, J.; Pedersen, G. K.; Johannesen, A. B.; Larsen, C. (2014). "Dinosaur tracks in Lower Jurassic coastal plain sediments (Sose Bugt Member, Rønne Formation) on Bornholm, Denmark". Lethaia. 47 (4): 485–493. Bibcode:2014Letha..47..485C. doi:10.1111/let.12073.
- ^ Milàn, Jesper; Mateus, Octávio (2023). "A turiasaurian (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) tooth from the Pliensbachian Hasle Formation of Bornholm, Denmark, shows an Early Jurassic origin of the Turiasauria". Diversity. 16 (1): 12. doi:10.3390/d16010012. hdl:10362/172148.
- ^ a b Milàn, J.; Rasmussen, B. W.; Bonde, N. (2012). "Coprolites with prey remains and traces from coprophagous organisms from the Lower Cretaceous (Late Berriasian) Jydegaard Formation of Bornholm, Denmark" (PDF). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. Bulletin. 57: 235–240. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-09-23. Retrieved 2013-09-21.
- ^ Ejsing, J. (2003). "Fortidsmonstre ser dagens lys" (in Danish). Berlingske. Archived from the original on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2013-04-26.
- ^ Rauhut, Oliver W. M.; Milner, Angela C.; Moore-Fay, Scott (2010). "Cranial osteology and phylogenetic position of the theropod dinosaur Proceratosaurus bradleyi (Woodward, 1910) from the Middle Jurassic of England". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 158 (1): 155–195. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00591.x.
- ^ Longrich, Nicholas R.; Martill, David M.; Jacobs, Megan L. (2022). "A new dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Wessex Formation (Lower Cretaceous, Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, and implications for European palaeobiogeography". Cretaceous Research. 134: 105123. Bibcode:2022CrRes.13405123L. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2021.105123. S2CID 245324247.
- ^ Bonde, N. (2004). "An early Cretaceous (Ryazanian) fauna of "Purbeck-Wealden type" at Robbedale, Bornholm, Denmark". In Arratia, G.; Tintori, A. (eds.). Mesozoic Fishes 3 – Systematics, Paleoenvironments and Biodiversity. Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. pp. 507–528. ISBN 9783899370539.


