Bushveld Igneous Complex
It has been suggested that Draft:Bushveld Igneous Complex be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since November 2024. |

The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion[1][2] within the Earth's crust.[3] It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately two billion years old[4] and is divided into four limbs: northern, eastern, southern and western. It comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments.[5] The site was first publicised around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff who found the native South African tribes residing in and around the area.[6]
Located in South Africa, the BIC contains some of the richest ore deposits on Earth.[7][8][9] It contains the world's largest reserves of platinum-group metals (PGMs) and platinum group elements (PGEs) — platinum, palladium, osmium, iridium, rhodium and ruthenium — along with vast quantities of iron, tin, chromium, titanium and vanadium. These are used in, but not limited to, jewellery, automobiles and electronics. Gabbro or norite is also quarried from parts of the complex and rendered into dimension stone. There have been more than 20 mine operations.[10] There have been studies of potential uranium deposits.[11] The complex is well known for its chromitite reef deposits, particularly the Merensky reef and the UG2 reef. It represents about 75 percent of the world's platinum and about 50 percent of the world's palladium resources. In this respect, the Bushveld complex is unique and one of the most economically significant mineral deposit complexes in the world.[12]
Geology
[edit]


Origin and formation
[edit]The Bushveld Igneous Complex covers a pear-shaped area in the central Transvaal. It is divided into an eastern and western lobe, with a further northern extension.
All three sections of the system were formed around the same time—about 2 billion years ago—and are remarkably similar. Vast quantities of molten rock from Earth's mantle were brought to the surface through long vertical cracks in Earth's crust—huge arcuate differentiated lopolithic intrusions—creating the geological intrusion known as the Bushveld Igneous Complex.
These intrusions are thought to predate the nearby Vredefort impact to the south, by some 30 million years.[13] The effects of these injections of molten rock over time, combined with the crystallisation of different minerals at different temperatures, resulted in the formation of a structure rather like a layered cake consisting of distinct rock strata, including three PGM-bearing layers, referred to as reefs. Large portions of the central area are covered by younger rocks.
The extrusions were emplaced over an early diabasic sill, outcrops of which are visible on the southeastern side of the Complex. These are typically greenish in colour and composed of clinopyroxene, altered to hornblende and plagioclase, and are regarded as the earliest phase of the Complex.
The Complex includes layered mafic intrusions (the Rustenburg Layered Suite) and a felsic phase. The complex has its geographic centre located north of Pretoria in South Africa at about 25° S and 29° E. It covers over 66,000 km2 (25,000 sq mi), an area the size of Ireland.
The complex varies in thickness, in places reaching 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) thick. Lithologies vary from largely ultramafic peridotite, chromitite, harzburgite, and bronzitite in the lower sections to mafic norite, anorthosite, and gabbro toward the top, and the mafic Rustenburg Layered Suite is followed by a felsic phase (the Lebowa Granite Suite).
The orebodies within the complex include the UG2 (Upper Group 2) reef containing up to 43.5% chromite, and the platinum-bearing horizons Merensky Reef and Platreef. The Merensky Reef varies from 30 to 90 cm in thickness. It is a norite with extensive chromitite and sulfide layers or zones containing the ore.
The Reef contains an average of 10 ppm platinum group metals in pyrrhotite, pentlandite, and pyrite as well as in rare platinum group minerals and alloys. The Merensky and UG2 reefs contain approximately 90% of the world's known PGM reserves. About 80% of the platinum and 20% of the palladium mined each year are produced from these horizons.
Proposed mechanisms of formation
[edit]The formation mechanisms of the chromitite seams in the Bushveld Igneous Complex are highly debated: numerous mechanisms have been proposed. The following is a non-exhaustive list of chromitite formations process.
- Changes in chemical and physical properties causes the magma to become concentrated in chromite. When this happens the liquidus becomes free from any other phases. Therefore, chromite is the only mineral to crystallize in the melt thus, accumulating in monomineralic layers on the floor of the magma chamber.[14]
- Increase in total pressure of the system, oxygen fugacity and alpha-silica.[14]
- One of the most accepted mechanisms were proposed by Irvine: it is suggested the chromitites may have formed when a chemically primitive magma intruded into an existing chamber to mix with a differentiated magma.[14][15]
- Gravity and size controlled settling and separation of chromite (concurring with olivine and OPX) grains within crystal-rich slurries[14]
- The mixing of resident magma and granitic melts derived from fusible country rocks[15]
- Mixing of ultramafic magma of layered intrusions, with magma parental to anorthosites[15]
- Deformation of the magma chamber, nucleation, ascent and expansion of gas bubbles or the emplacement of a new pulse of magma increasing total pressure conditions.[15]
- An increase in oxygen fugacity of the magma within the chamber possibly through the release of gas pressure, differential diffusion of hydrogen, or loss of gasses by diffusion.[15]
- Absorption of water by the magma[15]
There has been a proposal of the origins of at least three different processes used to model the PGE mineralization in the area:
- Collection by the sulphide liquids, due to the PGE's affinity toward a sulphide melt[16]
- Directly crystallised from a silicate magma,[16] and then collected by oxide minerals[17][18]
- Concentration by hydrothermal and or hydromagmatic fluids[16]
Structures
[edit]Layers
[edit]
The Bushveld Igneous Complex is a layered mafic intrusion (LMI) with well-defined ore bodies of stratiform chromitite layers concentrated with the so-called Critical Zone; these are referred to as reefs. The three main reef deposits are the Merensky reef, UG2 Reef, and the Platreef. These reefs are mostly continuous to discontinuous chromite layers with amounts of PGE mineralization. The surface rocks are exposed as separate lobes or limbs (the main ones being eastern, western and northern limbs) spans an area of approximately 66,000 km2. This large igneous province comprises the three main igneous suites the Lebowa Granite Suite (large A-type granitic intrusions), Rustenburg Layered Suite (c. 8 km-thick layered mafic-ultramafic cumulate sequence), and the Rashoop Granophyre Suite (granophyric rocks).[20] These are exposed as layered sequences of sheet like intrusions that are commonly subdivided as five main zones (from bottom to surface): Marginal, Lower, Critical, Main, and Upper Zones. These can be seen in sequence within the mentioned lobes. As for the center area, it is dominated by granites and other related rocks.
A large metamorphic contact aureole is observed within the northern limb, the Potgietersrus area.[21]
The Vredefort impact structure is predated by the BIC intrusion and has been shown to be likely unrelated to the BIC's mineralization.[22]
The Merensky Reef can be subdivided into five layers (from bottom to top):[16]
- Mottled Anorthosite (Mer-Ano): light coloured footwall (base of the overlying chromite layers) anorthosite with dark-coloured bands of pyroxene oikocrysts. This layer has a much higher ratio in Pd/Pt minerals (~20:2) and contains Fe-poor sulphides such as chalcopyrite, pentlandite, pyrrhotite with minor amounts of galena and sphalerite.
- Lower Chromitite (Mer-ChL): dark coloured layer of subhedral to anhedral chromite with varying grain sizes from 0.5 to 2 mm in diameter, enclosed by plagioclase (some observed relicts within poikilitic feldspar with comparable sizes to the anorthosite base layer) and orthopyroxene oikocrysts. This layer is terminated by a sharp footwall contact. In terms of mineralization, in contains minor amounts (c. 0.7%) of granular pentlandite, chalcopyrite, pyrrhotite and pyrite. The PGE mineralization is dominated by Pt-sulphides and other Pt-minerals with minor amounts of Pd-minerals resulting in a high Pt/Pd ratio (c. 106:4).
- Upper Chromitite (Mer-ChU): somewhat similar to the Lower Chromitite layer, but the chromite grains are finer (0.2 to·4 mm) and more densely packed. It is again Pt-mineral dominant with respect to Pd with minor amounts of Cu-Ni-rich sulphides (chalcopyrite, pentlandite and minor pyrrhotite).
- Merensky Pegmatite (Mer-Peg): a green-brown layer of coarse-grained to pegmatitic melanorite that is about 2.4 to 2.8 cm thick. It contains blebby patches of intercumulus plagioclase with meso- to adcumulate pyroxenite with some orthopyroxene grains reaching sizes of up to 5 cm. Chromite grains are next to absent with minor amounts near the upper chromitite contact. Sulphide mineralization is again less than c. 0.7% of the minerals and is dominated by Fe-rich sulphides (more pyrrhotite with respect to pentlandite and chalcopyrite). There are lesser amounts of PGMs compared to the chromitites.
- Merensky Melanorite (Mer-Nor): Somewhat similar to the previous layer, but is a finer (medium-grained) orthocumulate melanorite with an account 1.6% of disseminated and intergranular to granular Fe-dominant sulphide mineralization (pyrrhotite with some pentlandite and chalcopyrite). It is more chalcopyrite-rich, but occurs as smaller (< 1.5 mm) grains than those found within the pegmatite. There is intercumulus quartz, rare earth element-bearing minerals and albite–anorthite–orthoclase symplectites.
The UG2 Pyroxenite (Reef): The host rock of the UG2 chomitites is dominated by granular orthopyroxene, interstitial plagioclase and clinopyroxene with minor variable amounts accessory minerals such as phlogopite. The UG2 chromitites are underlain by pyroxenite footwall that is distinct from hanging wall pyroxenite. Chromite subhedral to subrounded (less than 0.5 mm in size) grains are a minor (c. 4%) but constant phase that is embedded with orthopyroxene (and other interstitial phases such as mentioned) throughout this footwall pyroxenite. Large oikocrysts are visible within the outcrops and on mine walls.[14]
The Platreef: this reef structure is divided into three sections:[16]
- The Lower Reef is composed of norites and feldspathic pyroxenites that have been recrystallized and overprinted. This layer has abundant country-rock xenoliths particularly near the base of the layer.
- The Central or Middle Reef is composed of igneous peridotite and recrystallized "vari-textured" mafic rocks with metasedimentary xenoliths.
- The Upper Reef is composed primarily of plagioclase-pyroxenite and norite that gradually changed to norite and gabbronorite toward the Main Zone (see units) contact. There are xenoliths but these are relatively scarce brecciated chromitite within the feldspathic pyroxenite near the top of the reef.
Faults and Shear Structures of The Bushveld Igneous Complex
[edit]The BIC contains several shear zones, some are within known faults, the most important of which are the Jagersfontein Shear Zone (JSZ), the Klerksdorp Shear Zone (KSZ), the Potgietersrus Shear Zone (PSZ), the Thabazimbi-Murchison Lineament (TML), the Brits Shear Zone (BSZ), the Olifants River Shear Zone (ORSZ) and the Steelpoort Shear Zone (SSZ).
These shear structures control several factors and have major geological implications within the Bushveld Igneous Complex, including structural, mineralogical, tectonic, metamorphic and economic. Some structural controls include the direction and flow of magma and intrusions, structural traps for mineralization and the structural evolution of the complex. Mineralization controls the Platinum Group Elements (PGEs) and Platinum Group Metals (PGMs), chromium, copper, nickel, gold and vanadium concentrates, reef formation and orientation, and affect the type of mineralization, for example magmatic and hydrothermal deposits.[23][24] Tectonic controls and effects can be seen or indicated by stratigraphic and crustal thickening and thinning, record of tectonic activity by type of structure such as collision and rifting, and influence on the evolution of the BIC. Metamorphic controls are localised metamorphism and alteration in shear zones, they affect mineral formation and stability, and they may show evidence of pressure-temperature-time (P-T-T) paths.[25] Economic controls include, mineral deposits, they help to guide mining and exploration and with resource and reserve estimation and extraction.
Eastern Lobe
[edit]The eastern lobe of the Bushveld Complex comprises three distinct zones, each of which is separated from the others by structural boundaries. The southern and central zones are separated by the Steelpoort Fault. The eastern lobe is further subdivided by the presence of the Stofpoort and Wonderkop Faults, which serve to differentiate the northeast from the central zone. The Stofpoort Fault is situated in close proximity to the Olifants River. The western zone is separated from the remainder of the region by two anticlines, namely the Katloof and Phosiri.[26]
The Merensky Reef has been displaced by 2 km to the south in the vicinity of Zebediela, as a consequence of the Madika Fault. The Madika Fault is sub-parallel to the Wonderkop Fault, which is located in the Bojanala Platinum District Municipality in the vicinity of the town of Wonderkop. The critical zone of the Rustenburg Layered Suite is displaced 500 m to the south by the Makweng Fault.[26]
The Sekhukhune Fault trends in a north-south direction and has a throw of up to 2 km to the west. The Sekhukhune Fault is situated to the east of the Fortdraai Anticline. The Laersdrift Fault is located to the NW of the eastern Bushveld Complex.[27]
Western Lobe
[edit]The Pilanesberg Complex is situated in the western lobe of the Bushveld Complex. The southern part of the Pilanesberg Complex exhibits NW–SE isopach lines that trend parallel to the Rustenburg Fault, which dips in the same direction towards the center of the Western Bushveld Complex.[27]
Southern Lobe
[edit]The Brits Graben is situated in the eastern region, in close proximity to Hartebeespoort. This Graben is delimited by a series of parallel faults, among which the most prominent is the Brits Fault, which trends NW–SE and intersects the Rustenburg Layered Suite, the Transvaal Supergroup and the Pretoria Group.[27] The BSZ is NW–SE trending and is located within the Brits Fault.
Northern Lobe
[edit]The NE–SW trending Ysterberg–Planknek Fault (YPF) is situated within the northern lobe of the Bushveld Complex. An additional ENE–WSW trending fault is situated within the northern lobe and is designated the Grasvally Fault.[27]
The boundary between the northern and southern lobes is defined by the Melinda Fault, which dips to the west and is situated within the Pietersburg terrane. The Melinda Fault extends in an eastern direction along the Palala Shear Zone (PSZ). This Fault and the PSZ are collectively designated as the Palala-Zoetfontein Lineament.[28]
The TML represents the boundary between the southern portion of the Northern Limb and the remainder of the Bushveld. It demarcates the boundary between the Pietersburg terrane and the central portion of the Kaapvaal Craton.[28] In general, the TML is a large EW trending shear zone that forms a boundary between the Bushveld Complex and the Limpopo Belt and is 20 and 30 km wide. The JSZ is located within the TML, it trends NE–SW and is between 10 and 15 km wide. The KSZ runs parallel to the JSZ, trends NS and can be up to 10 km thick in places, while the PSZ is located in the northern part of the BIC, trends EW and can be 5–10 km wide.
Two distinct fault orientations have been identified within the Pietersburg terrane: a NE–SW orientation and an ENE–WSW orientation. The most conspicuous faults with these orientations are the YPF and the Zebediela Faults.[28]
Mineralization within Shear Zones
[edit]Different mineral occurrences are more strongly associated in the BIC[25] in specific shear zones. PGEs are generally associated with the Jagersfontein, Klerksdorp and Potgietersrus shear zones and the Thabazimbi-Murchison lineament, chromium with the Rustenburg Layered Suites (RLS) critical zone and the TML, and gold with the Jagersfontein and Klerksdorp shear zones. Vanadium deposits are associated with the vanadium-rich magnetite deposits of the Bushveld, such as the TML, some of which may be associated with shear zones, and copper and nickel deposits, which often occur together in the same deposit, are associated with mafic and ultramafic intrusions and shear zones, such as the JSZ.
Units
[edit]
The general mineral assemblage of the chromitite seams in the Bushveld Complex consists of olivine + chromite, chromite +/- bronzite + plagioclase, chromite + plagioclase, and chromite + clinopyroxene.[29]
The BIC's layered sequence is commonly divided into five different zones:
- Upper Zone : This is the uppermost component of the Rustenburg Layered Suite (RLS). This zone is a thick gabbroic succession and is laterally dominant in iron-rich cumulates that host one of the world's largest titanium-magnetite resources.[30] The general rock assemblage is Gabbro + Olivine diorite + Anorthorsite. The upper zone is approximately 1,000-2,700 m thick and is composed of gabbro and anorthosite which overlays more differentiated rocks such as diorite progressively. The Upper Zone composes of 24 major layers of massive magnetite up to roughly 6 m thick. The contact between the Main and Upper Zones is commonly defined via the first occurrence of cumulus magnetite. On the other hand, some workers place the boundary on a notable pyroxenite layer characterized by reversals in stratigraphic trends of Sr isotopic ratios and iron enrichment that is located hundreds of meters under the first occurrence of cumulus magnetite.[20]
- Main Zone : This is composed of a succession of gabbronorites with bands of pyroxenite and anorthosite.[30] The Main Zone is roughly 1,600–3,500 m thick. There is a uniform sequence of cumulates consisting of norite and gabbronorite. The anorthosite layers make up roughly 5 percent of the lithology. Moreover, pyroxenite is scarce, and magnesian olivine and chromium spinel are not present in this zone.[20]
- Critical Zone : Approximately 930-1500m thick, delimited as its section because it contains several chromitite seams/layers, this is where the chromitite layers are concentrated: composed of Lower Group chromites (LG) LG1-LG7, LG6 (subdivided as LG6A, LG6B), Middle Group chromites (found between lcz and ucz, t boundary) (MG) MG1 to MG4, and Uper Group chromites (UG) UG1 and UG2 for a total of 13 chromite[20] seams recognized in the Critical zone. Zone subdivided as Upper and Lower critical subzones. As many as 25 individual chromite layers have been identified in the critical zone alone[29] with 14 being identified as major chromitite seams subdivided into four different type: Type I-LCZ base cycles, Type II-UCZ base cycles, Type III-thin intermediate layer within cyclens, Type IV-stringers associated to OPX pegmatoids.[29]
- Upper Critical Zone: Approximately 450-1000m thick, defined as Anorthosite layer found between two chromite layers, MG2 and MG3 chromitites, with repetitive or cyclic layers of (the cyclic origin is disputed whether it is multiple injections of new magma[31][32] or if it is by basal settling of a crystal mush transported by slurry flow[33]), chromites overlain by harzburgite (not always present), then pyroxenite, norite and finally anorthosite.
- Lower Critical Zone: It is an olivine-rich ultramafic cumulates that is approximately 500 m thick, composed entirely of ultramafic cumulates,[20] dominated by pyroxenite with some presence of cumulus plagioclase in some rock layers. The LGs (LG1-LG7) hosted by this feldspathic pyroxenite contains LG6 is the thickest and most economic chromitite seam in Bushveld with a general rock assemblage of Pyroxenite, Harzburgite, Dunite[29]
- Lower Zone: The general rock assemblage is Pyroxenite + Harzburgite + Dunite. The Lower Zone is roughly 900–1,600 m in thickness and is composed of layered olivine-saturated and orthopyroxene-saturated cumulates. The chromitite layers in this zone are only known from the northern and western parts of the complex.[20]
- Marginal Zone: (not always present) is a section that is up to 250 m thick, composed of massive, fine to medium-grained norite and gabbronorite[20] with varying amounts of accessory minerals such as quartz, hornblende, clinopyroxene, and biotite. This is a clear indication of metasediments contaminating the magma.[34]
Industry
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2019) |
Mining
[edit]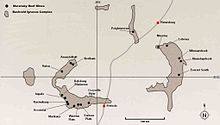
The area has many different ore deposits, but mostly with a focus on PGEs (primarily platinum and palladium), vanadium, iron (generally from magnetite), chromium, uranium, tin, ...[7] There are multiple major mining companies that are heavily involved within this area, particularly AngloAmerican, African Rainbow Minerals, Impala Platinum, Northam Platinum Ltd., Lonmin plc, and more recently Bushveld Minerals. It has been reported that more than 20 billion metric tons of PGE ore rock has been indicated in South Africa by the different exploration and mining companies of which contains about 38.1 kilotons of platinum metal in mineral reserves and resources in the Bushveld. The sum of PGEs and Gold resources and reserves equates to a total of about 72 kilotons from the Bushveld Complex alone.[20] Most are underground mines (such as Longhole Stoping, Drift-and-Fill mining, etc.[34]), fewer are open pit like the large Mogalakwena mine.[35]
Environmental and health issues
[edit]Mining feasibility studies have identified impacts on surface water, groundwater, wetlands, flora, fauna and related social issues. Additionally, these impacts include increased drainage of salts, sediments thought channels and streams near the mine sites. There has been an increased fleeting dust generation contaminating air and water, surface water runoff is leading to a decrease in water recharge for downstream users, possibly the loss of certain vulnerable flora and fauna species, soil compaction and land erosion; the contamination and quality deterioration of the surface and ground water is driven by seepage from waste rock dumps, stockpiles, gas spills, etc. The mining activities that make large use of water could potentially lead to dewatering of local aquifers. Moreover, construction activity impacts such as removal of natural land and noise from machinery and vehicles may disrupt the surrounding ecosystems.[34]
Depending on the beneficiation and concentration methods, there are different impacts plausible such acid runoff from leaching and metal slimes.[36] Hexavalent chromium from mine wastes has been shown to be highly toxic.[29]
A study has shown that up to 5% of the world total production of PGEs is lost and emitted as dust entering the global biogeochemical cycle.[9] Nearby towns have shown elevated levels of platinum within the soil, atmosphere and vegetation. Since some of the food production activities are located near these areas, the primary concern is that the local population (several towns and cities, including Rustenburg with more than 500,000 inhabitants[37]) will ultimately be exposed to the contaminants either by skin contact, dietary intake or inhalation.[38] PGEs such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium have been shown to bioaccumulate under the form of PGE-Chloride in the liver, kidneys, bones and lungs. The intake is generally through metallic or oxide dust that is inhaled or is absorbed through the skin causing contact dermatitis, on the long term causing sensitization and can eventually to lead to cancers.[39] A study from January 2013, has shown an increasing trend of the development of silicosis caused by silica dust and asbestos fibers related to workers mining in the Bushveld igneous complex.[40] Similarly, another study has found high concentrations of microscopic (<63 μm) PGE airborne dust particles near the mining areas. These have been found to be transported surface runoff and atmospherically, then further concentrated into soils and rivers such as the Hex River which flows directly into Rustenburg, the most populated municipality of North West Province of South Africa.[8]
A study from Maboeta et al. in 2006, has revealed through chemical analysis that the soil from a tailings disposal facility had higher levels of C, N, NH4 and K in comparison to the other general sampling sites. The difference was attributed to rehabilitation regimes being implemented reducing the abundance of these microbial and bacterial nutrients.[41]
Mining operations in general consume much energy and water, producing much waste rock, trailings and greenhouse gases. A study has shown that PGM mining has a significant impact on the global environment. The environmental costs for platinum mines are only slightly higher in energy, somewhat lower in water and moderately higher in greenhouse gas emissions when compared to gold mining.[42]
Social issues
[edit]South Africa's economy is heavily tied to its mining industry and has been greatly affected by low metal prices. Mining companies have had to cut costs by lowering production, closing mines, selling off projects, and reducing the work force. Miners are quite often on strike asking to get the minimum salary, and mines continue to fail safety standards and face labour unrest.[citation needed] A research study in 2016 by eunomix showed that Rustenburg, one of the fastest-growing cities in South Africa, has an "abnormally high concentration of young men who are separated from their families due to the migrant labour system". The population is facing a lack of education, high crime levels, and health problems within the workforce. Additionally, they are facing high poverty levels, government deficits, and are still heavily dependent on the platinum mining industry which is "responsible for more than 65% of local GDP and 50% of all direct jobs" (over 70,000 jobs). The accommodations and housing are lacking and have seen little to no effort from the mining companies to improve them. Between 2013 and 2016, the platinum companies contributed more than ZAR 370 million into the city; funding local infrastructure, water supply and treatment centres, sporting programmes, tourism, public road expansions, sewage treatment plants, cultural activities. The primary concern is the combination of high poverty rates and social injustice.[43]
Operations
[edit]There have been much more than 30 individual mine operations mostly mining for PGEs, some chrome, tin, and others (of which most are underground, few are open cut). These are shown below as a non-exhaustive list:
- Western Lobe: Rustenburg, Impala, Bafokeng Rasimone,[44] Union,[45][46] Amandelbult[47] (composed of Tumela and Dishaba[48]), Northam, Hartebeestpoort, Styldrift, Elandsfontein,[49] Crocodile River,[50] Thaba, Vametco Mine, Pandora,[51] Lonmin, Marikana.[52] Kroondal,[53][54] Rooiberg Tin mine, Leeuwpoort,[55] Pilanesberg,[56] 2008 Prospects: Frishgewaagd Ledig, Leeuwkop[57]
- Eastern Lobe: Lebowa/Bokoni, Twickenham, Marula,[56] Modikwa, Smokey Hills,[56] Two Rivers,[56] Mototolo, Everest,[56] Limpopo and Mogalakwena (Potgietersrus),[58] Maandagshoek, Middelpunt Hill, Blue Ridge,[56] 2008 Prospects: Ga-Phasha,[59] Kennedy's Vale, Sheba's Ridge and Booysendal[60]
Reserves
[edit]The three largest ore bodies are the Merensky Reef, the UG2 Chromitite Reef and the Platreef:[20]
- The Merensky Reef is a predominantly sulfide-rich pyroxenite layer mined on both the eastern and western limbs of the Bushveld Complex not only supplies most of the world's PGEs but also notable amounts of copper, nickel, cobalt and gold as byproducts.[56]
- The UG2 Chromitite Reef, known as the UG2 Reef Upper Group 2, is a chromite-rich layer that lacks sulfide minerals. As a whole, it is possibly one of the largest resources in terms of platinum group elements, larger than the overlying Merensky Reef. and is also mined on both the eastern and western limbs.[56]
- The Platreef is the world's third largest PGE deposit (after UG2 and Merensky reefs). The ore body is composed of three "broadly mineralised horizons rather than a distinct reef".[56]
| Ore body | Ore (Mt) | Platinum (t) | Palladium (t) | Rhodium (t) | Ruthenium (t) | Iridium (t) | Gold (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merensky Reef | 4200 | 13000 | 6100 | 800 | 250 | 51 | 1200 |
| UG2 Chromitite | 7300 | 20000 | 13000 | 3700 | 940 | 230 | 420 |
| Platreef | 5200 | 4500 | 5400 | 300 | N/A | N/A | 590 |
| Miscellaneous | 850 | 590 | 610 | 58 | N/A | N/A | 58 |
| Total | 17550 | 38090 | 25110 | 4858 | 1190 | 281 | 2268 |
* Table modified from USGS, 2010.[20]
Most of the identified mineral inventory is from the three described reefs, most of it is located within the eastern limb but most of the reserves are found within the western limb.[20]
Economy
[edit]The chrome deposits of the Bushveld forms the majority in terms of the proportion of all the known chrome reserves of the world. This area is very strategic as it is easy and cheap for mining; this is because their continuity in thick seams over scores of miles of strike and their persistence in depth, which has all been proved via deep drilling. Just like the chrome seams, Bushveld's titano-magnetite seams of the Main Zone illustrates similar continuity and persistence though, have not been extracted to date. Contained within the titano-magnetite ore is a persistent fractional percentage of vanadium. Reserves of the titanium and vanadium in these iron ores could potentially be very large. With that being said, it is evident that the ores existing in Bushveld occupy an important place in the world of mineral resources.[61]
Although other major platinum deposits have been found in places like the Sudbury Basin or Norilsk (Russia), the Bushveld Complex still remains as one of the prime sources of PGE ore. There have been many strikes for unfair pay and working conditions, illegal miners (so-called "zama-zamas"), gun-fire conflicts, political swindles and legal fights.[62] The prime use of platinum is for auto-catalytic converters (in cars) and jewellery.[63]
The total net demand of PGE in 2012 was 197.4 metric tons according to a Johnson Matthey 2013 estimate. The demand of platinum has somewhat steadily been increasing, driven by the more intensive use per capita with developing area and urbanization,[20] the demand reached an all-time high in 2005 of 208.3 metric tons.[63] From 1975 to 2013, the autocatalytic and jewellery industry dominated the market with more than 70% of the gross demand. Jewellery was barely ahead of autocatalysts prior to 2002 with brute gross demand values being somewhat similar or higher. From 2002 to 2003, the gross demand significantly decreased in jewellery (87.7 to 78.1 tons), but has largely increased in autocatalysts (80.6 to 101.7 tons) and has since then almost consistently dominated the market (with 2009[64] being the one exception linked to weak car sales).[65] In 2016, the platinum market continued to be in deficit for the 5th consecutive year, just barely reaching a demand 200,000 oz. In 2017, the two still dominate the market gross demand by far.[66] That being said, the global platinum demand is still expected to increase in subsequent years to 2017.[20]
The price of platinum is quite volatile in comparison to gold, but both have greatly increased over the last century.[64] Despite platinum being far much rarer than gold,[67] 2014 was the last year platinum was valued at a higher price than gold (2018).[64] This coincides with the 2014 South African platinum strike.
Platinum is more likely to be affected by social, environmental, political and economic issues where as gold not as much. This is because platinum has large mineral resources already identified and is not expected to be depleted for many decades (potentially up to year 2040). Furthermore, platinum is geographically restricted to the three by far the most significant resources, namely the BIC, the great dyke (Zimbabwe) and Noril'sk-Talnakh in Russia. An important detail to note is that palladium has been and is considered as the alternative to platinum.[20] Recently (2017), the supply-demand gap has greatly decreased.[66] Looking at political and social issues, there have been quite a few platinum mining-related strikes since before the 21st century: Impala strike,[68] 1986 Gencor strike,[69] 2004 Impala[70] and Anglo Plats strikes,[71] 2007 South Africa miners' strike, 2012 Marikana killings, Lonmin 2013 strike,[72] and 2014 South African platinum strike.
See also
[edit]- Cumulate rocks
- Hans Merensky
- Platinum group metals
- Stillwater igneous complex
- Ultramafic to mafic layered intrusions
- Waterberg Biosphere
References
[edit]- ^ Pirajno, Franco (2012-12-06). Hydrothermal Mineral Deposits: Principles and Fundamental Concepts for the Exploration Geologist. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783642756719.
- ^ Roberts, Benjamin W.; Thornton, Christopher P. (2014-01-07). Archaeometallurgy in Global Perspective: Methods and Syntheses. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9781461490173.
- ^ Eriksson, P. G.; Hattingh, P. J.; Altermann, W. (1995-04-01). "An overview of the geology of the Transvaal Sequence and Bushveld Complex, South Africa". Mineralium Deposita. 30 (2): 98–111. Bibcode:1995MinDe..30...98E. doi:10.1007/BF00189339. ISSN 0026-4598. S2CID 129388907.
- ^ Hustrulid, W. A.; Hustrulid, William A.; Bullock, Richard C. (2001). Underground Mining Methods: Engineering Fundamentals and International Case Studies. SME. p. 157. ISBN 978-0-87335-193-5.
- ^ Chamber of Mines. "Platinum". Chamber of Mines South Africa. Archived from the original on 24 February 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- ^ G.A.F. Molengraaff Geology of the Transvaal (1904), Edinburgh & Johannesburg (translation from ~1902 original), pp 42–57.
- ^ a b Klemm, D. D.; Snethlage, R.; Dehm, R. M.; Henckel, J.; Schmidt-Thomé, R. (1982). "The Formation of Chromite and Titanomagnetite Deposits within the Bushveld Igneous Complex". Ore Genesis. Special Publication of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. pp. 351–370. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-68344-2_35. ISBN 9783642683466.
- ^ a b Almécija, Clara; Cobelo-García, Antonio; Wepener, Victor; Prego, Ricardo (2017-05-01). "Platinum group elements in stream sediments of mining zones: The Hex River (Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa)". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 129: 934–943. Bibcode:2017JAfES.129..934A. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.02.002. hdl:10261/192883. ISSN 1464-343X.
- ^ a b Rauch, Sebastien; Fatoki, Olalekan S. (2015). "Impact of Platinum Group Element Emissions from Mining and Production Activities". Platinum Metals in the Environment. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. pp. 19–29. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-44559-4_2. ISBN 9783662445587. S2CID 73528299.
- ^ Oancea, Dan (September 2008). "Platinum in South Africa" (PDF). MINING.com.
- ^ Andreoli; et al. (June 1987). "THE URANIUM POTENTIAL OF THE BUSHVELD IGNEOUS COMPLEX: A CRITICAL REAPPRAISAL" (PDF). Progress Report No. 4 – via ATOMIC ENERGY CORPORATION OF SOUTH AFRICA LIMITED.
- ^ R. P. Schouwstra and E. D. Kinloch (2000). "A Short Geological Review of the Bushveld Complex" (PDF). Platinum Metals Review. 44 (1): 33–39. doi:10.1595/003214000X4413339. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-03-16. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ Kamo, S.L; Reimold, W.U; Krogh, T.E; Colliston, W.P (1996), "A 2.023 Ga age for the Vredefort impact event and a first report of shock metamorphosed zircons in pseudotachylitic breccias and Granophyre", Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 144 (3–4): 369, Bibcode:1996E&PSL.144..369K, doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(96)00180-X
- ^ a b c d e Mondal, Sisir K.; Mathez, Edmond A. (2007-03-01). "Origin of the UG2 chromitite layer, Bushveld Complex". Journal of Petrology. 48 (3): 495–510. Bibcode:2007JPet...48..495M. doi:10.1093/petrology/egl069. ISSN 0022-3530.
- ^ a b c d e f Latypov, Rais; Chistyakova, Sofya; Mukherjee, Ria (2017-10-01). "A Novel Hypothesis for Origin of Massive Chromitites in the Bushveld Igneous Complex". Journal of Petrology. 58 (10): 1899–1940. Bibcode:2017JPet...58.1899L. doi:10.1093/petrology/egx077. ISSN 0022-3530.
- ^ a b c d e Hutchinson, D.; Foster, J.; Prichard, H.; Gilbert, S. (2015-01-01). "Concentration of Particulate Platinum-Group Minerals during Magma Emplacement; a Case Study from the Merensky Reef, Bushveld Complex". Journal of Petrology. 56 (1): 113–159. Bibcode:2015JPet...56..113H. doi:10.1093/petrology/egu073. ISSN 0022-3530.
- ^ Finnigan, Craig; Brenan, James; Mungall, James; McDonough, W (2008). "Experiments and Models Bearing on the Role of Chromite as a Collector of Platinum Group Minerals by Local Reduction". Journal of Petrology. 49 (9): 1647–1665. Bibcode:2008JPet...49.1647F. doi:10.1093/petrology/egn041.
- ^ Anenburg, Michael; Mavrogenes, John (2016). "Experimental observations on noble metal nanonuggets and Fe-Ti oxides, and the transport of platinum group elements in silicate melts". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 192: 258–278. Bibcode:2016GeCoA.192..258A. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2016.08.010.
- ^ Hill, M.; Barker, F.; Hunter, D.; Knight, R. (1996). "Geochemical characteristics and origin of the Lebowa Granite Suite, Bushveld Complex". International Geology Review. 38 (3): 195. Bibcode:1996IGRv...38..195H. doi:10.1080/00206819709465331. Retrieved 3 July 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Michael L. Zientek; J. Douglas Causey; Heather L. Parks; Robert J. Miller (May 1, 2014). "USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2013–5090–Q: Platinum-Group Elements in Southern Africa—Mineral Inventory and an Assessment of Undiscovered Mineral Resources". pubs.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ Nell, J. (1985-07-01). "The Bushveld metamorphic aureole in the Potgietersrus area; evidence for a two-stage metamorphic event". Economic Geology. 80 (4): 1129–1152. Bibcode:1985EcGeo..80.1129N. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.80.4.1129. ISSN 0361-0128.
- ^ MARTINI, J. E. J. (1992-07-01). "The metamorphic history of the Vredefort dome at approximately 2 Ga as revealed by coesite-stishovite-bearing pseudotachylites". Journal of Metamorphic Geology. 10 (4): 517–527. Bibcode:1992JMetG..10..517M. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.1992.tb00102.x. ISSN 1525-1314.
- ^ Micklethwaite, Steven; Sheldon, Heather A.; Baker, Timothy (2010). "Active fault and shear processes and their implications for mineral deposit formation and discovery". Journal of Structural Geology. 32 (2): 151–165. Bibcode:2010JSG....32..151M. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2009.10.009. ISSN 0191-8141.
- ^ Klemd, Reiner; Beinlich, Andreas; Kern, Matti; Junge, Malte; Martin, Laure; Regelous, Marcel; Schouwstra, Robert (2020-06-25). "Magmatic PGE Sulphide Mineralization in Clinopyroxenite from the Platreef, Bushveld Complex, South Africa". Minerals. 10 (6): 570. Bibcode:2020Mine...10..570K. doi:10.3390/min10060570. ISSN 2075-163X.
- ^ a b "PorterGeo Database - Ore Deposit Description". portergeo.com.au. Retrieved 2024-10-10.
- ^ a b Lea, S.D. (1996). "The geology of the Upper Critical Zone, northeastern Bushveld Complex". South African Journal of Geology. 99 (3): 263–283.
- ^ a b c d Bamisaiye, O.A.; Eriksson, P.G.; Van Rooy, J.L.; Brynard, H.M.; Foya, S.; Billay, A.Y.; Nxumalo, V. (2017). "Subsurface mapping of Rustenburg Layered Suite (RLS), Bushveld Complex, South Africa: Inferred structural features using borehole data and spatial analysis". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 132: 139–167. Bibcode:2017JAfES.132..139B. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.05.003. hdl:2263/61117. ISSN 1464-343X.
- ^ a b c Brits, J. A. N.; Grobler, D. F.; Crossingham, A.; Blenkinsop, T. G.; Maier, W. D. (2024). "Structural context of the Flatreef in the Northern Limb of the Bushveld Complex". Mineralium Deposita. Bibcode:2024MinDe.tmp...67B. doi:10.1007/s00126-024-01289-w. ISSN 1432-1866.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bibcode (link) - ^ a b c d e Schulte, Ruth F.; Taylor, Ryan D.; Piatak, Nadine M.; II, Robert R. Seal (2012). "Stratiform chromite deposit model: Chapter E in Mineral deposit models for resource assessment". Scientific Investigations Report: 148. Bibcode:2012usgs.rept...94S. doi:10.3133/sir20105070E. ISSN 2328-0328.
- ^ a b Scoon, R. N.; Mitchell, A. A. (2012-12-01). "The Upper Zone of the Bushveld Complex at Roossenekal, South Africa: Geochemical Stratigraphy and Evidence of Multiple Episodes of Magma Replenishment". South African Journal of Geology. 115 (4): 515–534. Bibcode:2012SAJG..115..515S. doi:10.2113/gssajg.115.4.515. ISSN 1012-0750.
- ^ Eales, H.V.; Marsh, J.S.; Mitchell, Andrew; De Klerk, William; Kruger, F; Field, M (1986-01-01). "Some geochemical constraints upon models for the crystallization of the upper critical zone-main zone interval, northwestern Bushveld complex". Mineralogical Magazine. 50 (358): 567–582. Bibcode:1986MinM...50..567E. doi:10.1180/minmag.1986.050.358.03. S2CID 56419196.
- ^ Mitchell, Andrew A.; Eales, Hugh V.; Krueger, F. Johan (1998-08-01). "Magma replenishment, and the significance of poikilitic textures, in the Lower Main Zone of the western Bushveld Complex, South Africa". Mineralogical Magazine. 62 (4): 435–450. Bibcode:1998MinM...62..435M. doi:10.1180/002646198547783. ISSN 1471-8022. S2CID 128969014.
- ^ Mungall, James E.; Naldrett, Anthony J. (2008-08-01). "Ore Deposits of the Platinum-Group Elements". Elements. 4 (4): 253. Bibcode:2008Eleme...4..253M. doi:10.2113/GSELEMENTS.4.4.253. ISSN 1811-5209.
- ^ a b c "Platreef 2017 Feasibility Study" (PDF). Ivanhoe Mines LTD. 4 September 2017.
- ^ "ANNUAL FACILITY VISIT 28 February 2002" (PDF). angloamericanplatinum.com.
- ^ Wesseldijk, Q.I; Reuter, M.A; Bradshaw, D.J; Harris, P.J (1999-10-01). "The flotation behaviour of chromite with respect to the beneficiation of UG2 ore". Minerals Engineering. 12 (10): 1177–1184. Bibcode:1999MiEng..12.1177W. doi:10.1016/S0892-6875(99)00104-1. ISSN 0892-6875.
- ^ "Rustenburg Local Municipality – Population Size". Statistics South Africa. 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- ^ Rauch, Sebastien; Fatoki, Olalekan S. (2013-01-01). "Anthropogenic Platinum Enrichment in the Vicinity of Mines in the Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa". Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. 224 (1): 1395. Bibcode:2013WASP..224.1395R. doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1395-y. ISSN 0049-6979. S2CID 97231760.
- ^ Gebel, T. (2000). "Toxicology of platinum, palladium, rhodium, and their compounds". Anthropogenic Platinum-Group Element Emissions. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. pp. 245–255. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-59678-0_25. ISBN 9783642640803.
- ^ Nelson, Gill (2013-01-24). "Occupational respiratory diseases in the South African mining industry". Global Health Action. 6: 19520. doi:10.3402/gha.v6i0.19520. PMC 3562871. PMID 23374703.
- ^ Maboeta, M. S.; Claassens, S.; Rensburg, L. van; Rensburg, P. J. Jansen van (2006-09-01). "The Effects of Platinum Mining on the Environment from a Soil Microbial Perspective". Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. 175 (1–4): 149–161. Bibcode:2006WASP..175..149M. doi:10.1007/s11270-006-9122-1. ISSN 0049-6979. S2CID 84659048.
- ^ Glaister, Bonnie J; Mudd, Gavin M (2010-04-01). "The environmental costs of platinum–PGM mining and sustainability: Is the glass half-full or half-empty?". Minerals Engineering. 23 (5): 438–450. Bibcode:2010MiEng..23..438G. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2009.12.007. ISSN 0892-6875.
- ^ "The impact of platinum mining in Rustenburg A high – level analysis" (PDF). Eunomix Research. 14 March 2016.
- ^ "Bafokeng Rasimone Platinum Mine". www.srk.co.za. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ "Anglo American Platinum to complete sale of Union Mine and MASA Chrome". www.angloamericanplatinum.com. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ "Anglo American Platinum > Our Business > Rustenburg Section (Khomanani Mine, Bathopele Mine, Siphumelele Mine, Thembelani Mine, Khuseleka Mine)". 2013-05-27. Archived from the original on 2013-05-27. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "Anglo American Platinum disposes of mineral resources within the Amandelbult mining right". www.angloamericanplatinum.com. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ "Platinum Group Metals". www.angloamerican.com. Retrieved 2018-03-30.
- ^ "AIA: 17 PROPOSED DRILLING SITES FOR THE PROPOSED PROSPECTING OF PHOSPHATE ON PORTION 4 AND 2 OF THE FARM ELANDSFONTYN 349 NEAR HOPEFIELD, WESTERN CAPE | SAHRA". www.sahra.org.za. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "CROCODILE RIVER MINE, South Africa, Independent Technical Report" (PDF). RSG Global. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2018-04-11.
- ^ Haren. "Pandora – Lonmin". www.lonmin.com. Archived from the original on 2018-04-12. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ Stephan. "Marikana – Lonmin". www.lonmin.com. Archived from the original on 2018-04-12. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "Joint venture agreement Anglo/Kroondal Joint Venture signed". angloamericanplatinum.com.
- ^ "Social and Labour Plan: Rustenburg Section PSA" (PDF). Anglo American Platinum.
- ^ Leube, A.; Stumpfl, E. F. (1963-06-01). "The Rooiberg and Leeuwpoort tin mines, Transvaal, South Africa". Economic Geology. 58 (4): 527–557. Bibcode:1963EcGeo..58..527L. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.58.4.527. ISSN 0361-0128.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Cawthorn, R. Grant (2010). "The Platinum Group Element Deposits of the Bushveld Complex in South Africa" (PDF). Platinum Metals Review. 54 (4): 205–215. doi:10.1595/147106710X520222.
- ^ "Leeuwkop Platinum Mine | SAHRA". www.sahra.org.za. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "Anglo American Platinum > Our Business > Rustenburg Section (Khomanani Mine, Bathopele Mine, Siphumelele Mine, Thembelani Mine, Khuseleka Mine)". 2013-05-27. Archived from the original on 2013-05-27. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "Anooraq-Anglo Platinum – Ga-Phasha PGM Project Update". www.angloamericanplatinum.com. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ "Booysendal". www.northam.co.za. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ Cousins, M.Sc., C. A. (1959). "The Bushveld Igneous Complex. The Geology of South Africas Platinum Resources". Technology Review. 3 (94). Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- ^ "South African mining is in crisis". The Economist. 2017-07-08. Retrieved 2018-03-01.
- ^ a b "Market data tables". www.platinum.matthey.com. Retrieved 2018-04-06.
- ^ a b c "databank.worldbank.org".
- ^ Jollie, David (2010). "Platinum 2010" (PDF). Platinum – Johnson Matthey.
- ^ a b "pgm_market_report_may_2017.pdf" (PDF). Johnson Matthey.
- ^ "USGS Minerals Information: Mineral Commodity Summaries". minerals.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
- ^ Los Angeles Times 1986
- ^ Cowell, Alan (7 January 1986). "20,000 Striking South African Miners Are Dismissed". The New York Times.
- ^ "South African platinum industry halted by two major strikes, 2004 | libcom.org". libcom.org. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- ^ "World Business Briefing | Africa: South Africa: Strike at Platinum Mine". The New York Times. October 2004.
- ^ "Lonmin's South African platinum strike enters second day". Reuters. 15 May 2013.
Sources
[edit]- Guilbert, John M.; Park, Charles F. Jr. (1986). The Geology of Ore Deposits. New York: Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-1456-9.
- Richardson, Stephen H.; Shirey, Steven B. (2008). "Continental mantle signature of Bushveld magmas and coeval diamonds". Nature. 453 (7197): 910–913. Bibcode:2008Natur.453..910R. doi:10.1038/nature07073. PMID 18548068. S2CID 4393778.
- Viljoen, M. J.; Schürmann, L. W. (1998). "Platinum-group metals". In Wilson, M. G. C.; Anhaeusser, C. R. (eds.). Council for Geoscience Handbook 16, Mineral Resources of South Africa. Pretoria: Council for Geoscience. ISBN 978-1-875061-52-5.
External links
[edit]- USGS: Platinum-Group Elements in Southern Africa—Mineral Inventory and an Assessment of Undiscovered Mineral Resources
- USGS: Stratiform Chromite Deposit Model
- Concentration of Particulate Platinum-Group Minerals during Magma Emplacement; a Case Study from the Merensky Reef, Bushveld Complex
- Origin of the UG2 chromitite layer, Bushveld Complex
- A Novel Hypothesis for Origin of Massive Chromitites in the Bushveld Igneous Complex
- Bushveld Igneous Complex by Judith A. Kinnaird (PDF 39 pages) – retrieved 2009-05-22
- Photos of Bushveld Igneous Complex (Rustenburg Layered Suite) – field exposures (University of Cape Town) retrieved 2018-03-23
- Bushveld Igneous Complex (Rustenburg Layered Suite) photomicrographs of thin sections (University of Cape Town) retrieved 2018-03-23
